-
window c++异常处理与设计原理
前言
本文需要基础
SEH知识,如果不熟悉可以参阅作者其他文章:SEH 学习笔记链接我们知道C++有异常语法如下所示:
#include#include class MyClass {}; int main(int argc, char* arg) { try { printf(" try %d\r\n", argc); switch (argc) { case 1: { throw 1; break; } case 2: { throw MyClass(); break; } default: break; } } catch (int i) { printf("catch (int i) %d\r\n", i); } catch (MyClass i) { printf("catch (MyClass i)\r\n"); } printf("xxxxxx\r\n"); try { printf(" try22 %d\r\n", argc); switch (argc) { case 1: { throw 1; break; } case 2: { throw MyClass(); break; } default: break; } } catch (int i) { printf("catch222 (int i) %d\r\n", i); } catch (MyClass i) { printf("catch2222 (MyClass i)\r\n"); } printf("program end \r\n"); return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
在windows中其实现本质采用SEH来完成的。
如果一上来全盘脱出汇编实现很难理解其本质思想,我们先自己设计实现在看VC编译器作者汇编实现更容易理解。我们自定义实现c++异常的步骤:
- 在进入main函数的插入SEH处理器这样我们可以捕获这个函数的全部异常。
- 在编译扫描代码时我们可以记录一个表,给每个try记录一个条目并赋值编号,再触发异常的时候根据id找到条目进行下一步catch分发

那么我们在代码中如何知道是try表中的id项处理呢?
我们可以编译插入局部变量 我们先取名为
curtryID,当执行try函数体时赋值为对应try表ID,当发生异常时我们查看当前curtryID取出对应try表的某个条目,如果ID没有对应的证明当前代码行没有try包裹。

现在我们知道了哪些代码被try包裹但是我们无法感知异常发生时应该被try的哪个catch处理,因此我们需要在try表的每个条目下额外增加一个catch表

(3) 构建
catch表,当异常发生时判断类型,在catch表中获取对应类型进行寻找处理函数(利用RTTI)。上面的逻辑我们绘制一个流程图来表示如下:

源码层查看try表
首先打开相关调试符号关联

相关Demo:
class MyClass { }; int main(int argc, char* arg) { try { printf("try catch\r\n"); //...略 throw 3; } catch (int i) { printf("catch (int i)\r\n"); } catch (MyClass i) { printf("catch (MyClass i)\r\n"); } return 0; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
按照上节讲述代码应该会覆盖异常处理链条(fs:[0])

上面的代码可以简化用如下图所示

我们在跳转到0AC67E0h地址处:

我们首先在最后一行下一个断点00AC67FB jmp ___CxxFrameHandler3 (0AC137Fh)
单步步入最终到微软一个导入函数中。注意这里eax传入了一个地址,这个地址是一个对象地址,存储就是我们上文讨论的各种try表。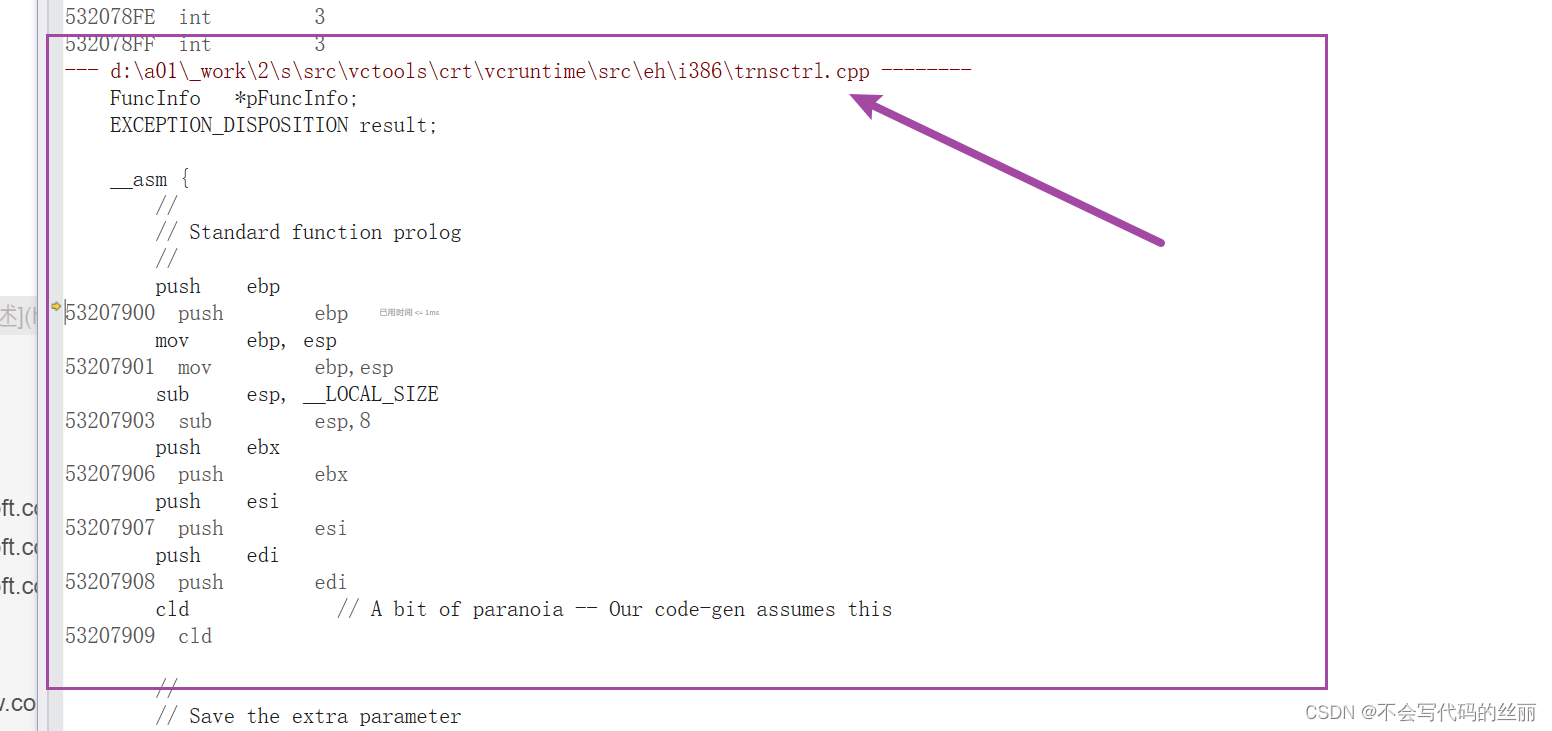
我们在VS安装目录下可以打开这个文件继续进行源码调试
"C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Visual Studio\2019\Community\VC\Tools\MSVC\14.29.30133\crt\src\i386\trnsctrl.cpp"
查看上面的代码你就会明白
FuncInfo就是我们传入的数据结构,我们先不讨论这个结构的具体细节,我们假设里面有表就行。
我们继续跟进函数

继续跟进相关函数

继续查看FindHandler



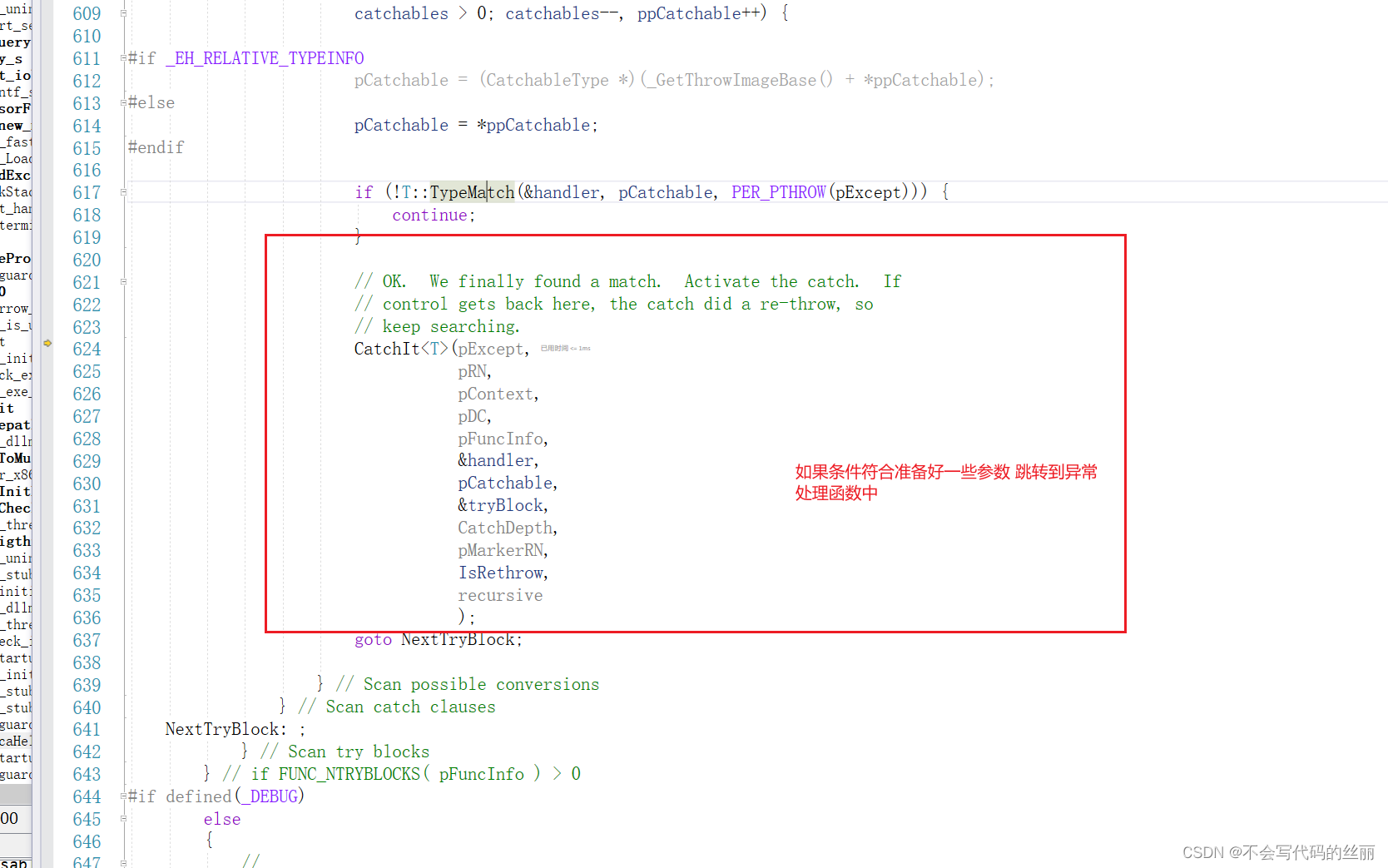

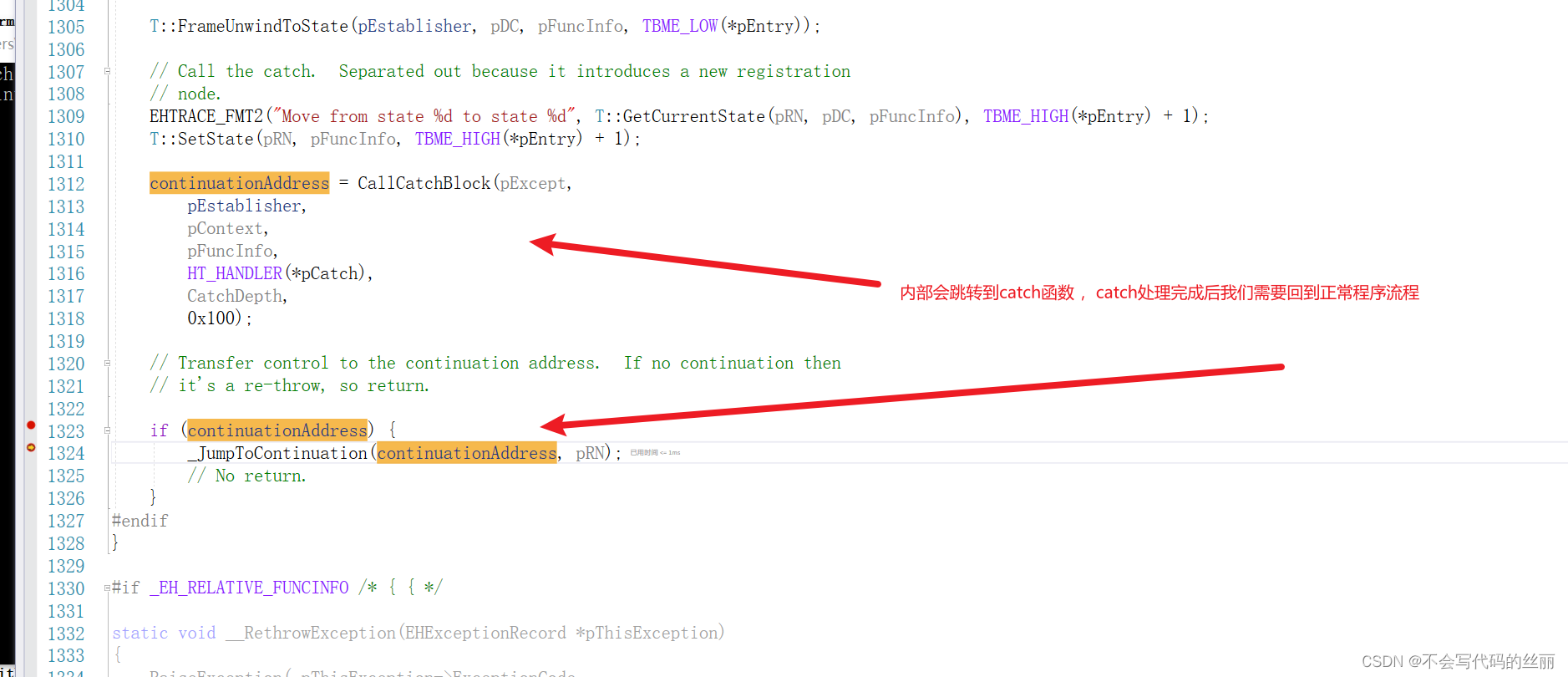


查看了相关流程后我们直接详细的查看FuncInfo对应的数据结构,我们只需要关心
TryBlockMapEntry* pTryBlockMap;即可/* * The magicNumber here is incremented with every compiler change that does not * break backwards compatibility. If for some reason backward compatibility * should be broken, then we will add new handler. What this means is that * current handler functions can assume that the structure layout that they * know about will remain the same and so even if magicNumber > my_magicNumber, * the handler can assume that what all it needs is there. The magicNumber will * be revised every time new data is added at the end of this structure. */ typedef const struct _s_FuncInfo { unsigned int magicNumber:29; // Identifies version of compiler unsigned int bbtFlags:3; // flags that may be set by BBT processing __ehstate_t maxState; // Highest state number plus one (thus // number of entries in unwind map) #if _EH_RELATIVE_FUNCINFO int dispUnwindMap; // Image relative offset of the unwind map unsigned int nTryBlocks; // Number of 'try' blocks in this function int dispTryBlockMap; // Image relative offset of the handler map unsigned int nIPMapEntries; // # entries in the IP-to-state map. NYI (reserved) int dispIPtoStateMap; // Image relative offset of the IP to state map int dispUwindHelp; // Displacement of unwind helpers from base int dispESTypeList; // Image relative list of types for exception specifications #else UnwindMapEntry* pUnwindMap; // Where the unwind map is unsigned int nTryBlocks; // Number of 'try' blocks in this function TryBlockMapEntry* pTryBlockMap; // Where the handler map is unsigned int nIPMapEntries; // # entries in the IP-to-state map. NYI (reserved) void* pIPtoStateMap; // An IP to state map. NYI (reserved). ESTypeList* pESTypeList; // List of types for exception specifications #endif int EHFlags; // Flags for some features. } FuncInfo;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
TryBlockMapEntry* pTryBlockMap;是我们所有try表,可参阅如下代码,我们知道try表往往会嵌套一个catch表其内部表示就是HandlerType* pHandlerArray// // HandlerMapEntry - associates a handler list (sequence of catches) with a // range of eh-states. // typedef const struct _s_TryBlockMapEntry { __ehstate_t tryLow; // Lowest state index of try __ehstate_t tryHigh; // Highest state index of try __ehstate_t catchHigh; // Highest state index of any associated catch int nCatches; // Number of entries in array #if _EH_RELATIVE_FUNCINFO int dispHandlerArray; // Image relative offset of list of handlers for this try #else HandlerType* pHandlerArray; // List of handlers for this try #endif } TryBlockMapEntry;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
我们最后看catch项存储的信息至少有两个一个是异常处理类型
TypeDescriptor* pTyp还有一个异常处理地址void * addressOfHandler;// // HandlerType - description of a single 'catch' // typedef const struct _s_HandlerType { unsigned int adjectives; // Handler Type adjectives (bitfield) #if _EH_RELATIVE_FUNCINFO int dispType; // Image relative offset of the corresponding type descriptor int dispCatchObj; // Displacement of catch object from base int dispOfHandler; // Image relative offset of 'catch' code #if defined(_WIN64) || defined(_CHPE_X86_ARM64_EH_) int dispFrame; // displacement of address of function frame wrt establisher frame #endif #else // _EH_RELATIVE_FUNCINFO TypeDescriptor* pType; // Pointer to the corresponding type descriptor ptrdiff_t dispCatchObj; // Displacement of catch object from base void * addressOfHandler; // Address of 'catch' code #endif // _EH_RELATIVE_FUNCINFO } HandlerType;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
java异常表的对比
java异常可能就简单很多了 我们查看如下代码
package org.example; public class Main { static void studyExceptionTable(){ try { System.out.printf("try"); throw new Exception(); }catch (IllegalAccessException exception){ System.out.printf("IllegalAccessException"); }catch (IllegalArgumentException e){ System.out.printf("IllegalArgumentException"); }catch (Exception e){ System.out.printf("Exception"); } } public static void main(String[] args) { } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20

由于java是依赖JVM进行跨平台因此相关数据结构需要较为通用的结构,所以异常表非常简单易懂,异常处理后直接拼接goto回到正常程序流程。参考链接
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/cpp/cppcx/wrl/raiseexception-function?view=msvc-170
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/win32/debug/getexceptioninformation
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/win32/api/winnt/ns-winnt-exception_recordhttps://stackoverflow.com/questions/39113168/c-rtti-in-a-windows-64-bit-vectoredexceptionhandler-ms-visual-studio-2015
-
相关阅读:
.NET 6学习笔记(1)——通过FileStream实现不同进程对单一文件的同时读写
CentOS服务器利用docker搭建中间件命令集合
Linux ubuntu 服务器部署详细教程
Kepler.gl笔记:地图交互
【ubuntu】中文输入法设置
Spring Event 观察者模式, 业务解耦神器
推荐接口压测报告
Spring自动加载数据几种方式执行顺序
聊聊MySQL中的死锁
【华为OD:C++机试】Day-1
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qfanmingyiq/article/details/126453995
