-
数据结构——树
数据结构——树

想要查询一个数组
需要遍历数组,时间复杂度为O(n)
如何降低时间复杂度呢?
我们知道有序数组可以使用折半查找法,其时间复杂度为O(logn),但是一个数组变成有序数组最低也需要O(nlogn),这样并不能降低时间复杂度。
简化数组查询的时间复杂度——这就是树的产生的背景
树(有序二叉树)——时间复杂度是O(logn)

把数组{5,3,7,2,4,6,8}按如图的形式存储,这就是树
树的基本概念
树按孩子划分一般分为二叉树和多叉树

叶子节点:没有孩子的节点
节点的权:即value值
二叉树
每个节点最多有两个子节点
二叉树的种类
- 完全二叉树:数据从上到下,再从左到右进行排列,度为1的节点只能有一个

- 满二叉树:叶子节点都在一层上,且最后一层节点数位2 ^ n-1(最后一层是满的)。满二叉树一定是完全二叉树,发过来不一定

- 有序二叉树
- 平衡二叉树
- 红黑树
- 哈夫曼树
二叉树的遍历
-
深度优先遍历(根据父节点输出的顺序区分)
-
- 先序遍历:先输出父节点,再输出左节点,再输出右节点
- 中序遍历:先输出左节点,再输出父节点,再输出右节点
- 后序遍历:先输出左节点,再输出右节点,再输出父节点
看父节点的输出顺序就能看出是哪一种遍历方式,父节点在第一位,可能是先序或者中序(看树的结构),父节点在最后一位,可能是后序或者中序,父节点在中间,只能是中序遍历

//先序遍历(根左右) public void beforeOrder(TreeNode node){ if (node == null){ return; } System.out.println("" + node.getValue()+ ""); beforeOrder(node.getLeftTreeNode()); beforeOrder(node.getRightTreeNode()); } //中序遍历(左根右) public void inOrder(TreeNode node){ if (node == null){ return; } inOrder(node.getLeftTreeNode()); System.out.println("" + node.getValue()+ ""); inOrder(node.getRightTreeNode()); } //后序遍历(左右根) public void afterOrder(TreeNode node){ if (node == null){ return; } afterOrder(node.getLeftTreeNode()); afterOrder(node.getRightTreeNode()); System.out.println("" + node.getValue()+ ""); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
-
中序遍历非递归版本
-
//中序遍历(非递归版本) public ArrayList<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) { TreeNode cur = root; Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<TreeNode>(); ArrayList<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<Integer>(20); while (cur != null || !stack.isEmpty()) { // 相当于一个开关 if (cur != null) { stack.push(cur); cur = cur.getLeftTreeNode(); } else { cur = stack.pop(); ans.add(cur.getValue()); if (cur.getRightTreeNode() == null) { cur = null; } else { cur = cur.getRightTreeNode(); stack.push(cur); cur = cur.getLeftTreeNode(); } } } return ans; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
-
广度优先遍历(层次遍历)
利用辅助队列(先进先出)实现广度优先遍历——>队列的底层一定是一个链表(数组存在空间不够的情况,避免空间不足)
当结点从队列中pop出来打印的时候,把结点的左子树和右子树根结点push进入队列,这样能够保证同一个深度的结点在队列中连续排布

我们要一层一层的遍历?那么如何在输出5后,去获取其左右孩子,并循环?————我们可以借助队列,队列先入根节点(然后判断是否有左右孩子),有的话把左右孩子存入队列(先进先出),把根节点给弹出(循环整个过程)
//广度优先遍历(层次遍历) public void levelOrder(){ LinkedList<TreeNode> queue= new LinkedList<>(); queue.add(root); while (!queue.isEmpty()){ root = queue.pop(); if (root.getLeftTreeNode() != null){ queue.add(root.getLeftTreeNode()); } if ( root.getRightTreeNode() != null){ queue.add(root.getRightTreeNode()); } System.out.print(root.getValue() + " "); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
package com.qcby.datastructure.tree; public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { BinaryTree binaryTree =new BinaryTree(); binaryTree.insert(5); binaryTree.insert(7); binaryTree.insert(4); binaryTree.insert(2); binaryTree.insert(0); binaryTree.insert(3); binaryTree.levelOrder(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15

二叉树的查找
public TreeNode select(int value){ LinkedList<TreeNode> queue= new LinkedList<>(); queue.add(root); while (root.getValue() != value && !queue.isEmpty()){ root = queue.pop(); if (root.getLeftTreeNode() != null){ queue.add(root.getLeftTreeNode()); } if ( root.getRightTreeNode() != null){ queue.add(root.getRightTreeNode()); } } return root; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
有序二叉树的构建
传统方法
package com.qcby.datastructure.tree; import javafx.scene.transform.Rotate; public class BinaryTree { public TreeNote root;//代表了一整个树,而不是根节点 public void insert(Integer value){ //创建一个节点 TreeNote newNode = new TreeNote(value); if (root==null){ root=newNode; return; } //定义游标来遍历二叉树 TreeNote currentNote = root; //定义一个游标来记录currentNode的前一个地址 TreeNote preNode = null; while (true) { preNode = currentNote; //判断currentNode指向的值和value进行对比 if (newNode.getValue() > currentNote.getValue()) { //游标需要往右走 currentNote = currentNote.getRightTreeNode(); //右子树为空 if (currentNote == null) { preNode.setRightTreeNode(newNode); return; } } else { //游标需要往左走 currentNote = currentNote.getLeftTreeNote(); //左子树为空 if (currentNote == null) { preNode.setLeftTreeNote(newNode); return; } } } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
递归方法
先找递归表达式
再找递归出口
//采用递归的方式,来插入数据(有序二叉树) public void insertDiGui(TreeNode node, Integer value){ //新建节点 TreeNode newNode = new TreeNode(value); if (root ==null){ root = newNode; return; } if (node.getValue() > value){ //递归出口。插入去完成的时候 if (node.getLeftTreeNode() == null){ node.setLeftTreeNote(newNode); return; } insertDiGui(node.getLeftTreeNode(), value); }else { if (node.getRightTreeNode() == null){ node.setRightTreeNode(newNode); return; } insertDiGui(node.getRightTreeNode(), value); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
测试
public static void main(String[] args) { TreeNode node =new TreeNode(5); binaryTree.insertDiGui(node,7); binaryTree.insertDiGui(node,4); binaryTree.insertDiGui(node,2); System.out.println(node); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
有序二叉树的删除
跳过要删除的节点(没有对象指向该节点),jvm回收机制就会回收该节点的内存空间

删除节点后,保证还是有序二叉树
删除叶子节点

删除节点只有一个子树

删除节点有两个子树

/** *递归查找节点 * @param node * @param value * @return */ public TreeNode searchTargetNode(TreeNode node,int value){ //判断不是空树 if (root == null) { return null; } if (value == node.getValue()){ return node; }else if (value <node.getValue()){ if (node.getLeftTreeNode()==null){ return null; } return searchTargetNode(node.getLeftTreeNode(),value); }else { if (node.getRightTreeNode()==null){ return null; } return searchTargetNode(node.getRightTreeNode(),value); } } //查询节点的父节点 public TreeNode searchParentNode(TreeNode node,int value){ //判断不是空树 if (root == null) { return null; } //判断当前节点是不是我们删除节点的父节点 if((node.getLeftTreeNode() !=null && node.getRightTreeNode().getValue()== value) || (node.getRightTreeNode() !=null && node.getRightTreeNode().getValue() ==value)){ return node; }else { if(node.getLeftTreeNode() !=null && value<node.getValue()){ return searchParentNode(node.getLeftTreeNode(),value); }else if(node.getRightTreeNode() !=null && value>node.getValue()){ return searchParentNode(node.getRightTreeNode(),value); }else { return null; } } } /** * 找打右子树的最小值 * @param node * @return */ public int deleteRightMin(TreeNode node){ //定义指针 TreeNode target = node; while (target.getLeftTreeNode() !=null){ target = target.getLeftTreeNode(); } deleteNode(root,target.getValue()); return target.getValue(); } //删除节点(删除后还是有序二叉树) public void deleteNode(TreeNode node,int value){ if (node == null){ System.out.println("这是一个空树"); return; } //找到要删除的节点 TreeNode targetNode = searchTargetNode(node, value); //判断有没有这个节点 if (targetNode ==null){ System.out.println("没有这个节点"); return; } //表示该树只有一个节点 if (node.getLeftTreeNode() == null && node.getRightTreeNode() == null){ root = null; return; } //找到这个节点的父节点 TreeNode parentNode = searchParentNode(node, value); //这是一个叶子节点 if (targetNode.getLeftTreeNode() == null && targetNode.getRightTreeNode() == null){ //确认targetNode是parentNode的左子树还是右子树 if (parentNode.getLeftTreeNode() !=null && parentNode.getLeftTreeNode().getValue() == value){ parentNode.setLeftTreeNote(null); }else if (targetNode.getRightTreeNode() !=null && parentNode.getRightTreeNode().getValue() ==value){ parentNode.setRightTreeNode(null); } } //目标节点左右子树都不空,表示有两个子树的节点 else if (targetNode.getLeftTreeNode() !=null && targetNode.getRightTreeNode() != null){ //找到右子树的最小值 int minValue = deleteRightMin(targetNode.getRightTreeNode()); targetNode.setValue(minValue); } //只有一个子树的情况 else { //判断 targetNode是有左子树还是有右子树 if(targetNode.getLeftTreeNode() !=null){ //有左子树 //判断targetNode 是parentNode的左子树还是右子树 if(parentNode.getLeftTreeNode().getValue() == value){ //targetNode 是parentNode的左子树 parentNode.setLeftTreeNote(targetNode.getLeftTreeNode()); }else { //targetNode 是parentNode的右子树 parentNode.setRightTreeNode(targetNode.getLeftTreeNode()); } }else {//有右子树 //判断targetNode 是parentNode的左子树还是右子树 if(parentNode.getLeftTreeNode().getValue() == value){ //targetNode 是parentNode的左子树 parentNode.setLeftTreeNote(targetNode.getRightTreeNode()); }else { //targetNode 是parentNode的右子树 parentNode.setRightTreeNode(targetNode.getRightTreeNode()); } } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
平衡二叉树
平衡二叉树的背景

传统数组的查询是依靠遍历(时间复杂度为O(n)),有序数组的查询的时间复杂度是(O(logn))——折半查找法。但是无序数据变成有序数组的最小时间复杂度为O(nlogn)。
有人提出了哈希算法来减少时间复杂度,
**哈希算法:**通过一个公式计算出的值作为索引把值存入哈希表中,理想情况下(没有哈希碰撞)的情况下,用哈希算法的查询时间复杂度为O(1)。
哈希碰撞:两个或多个值通过哈希算法得到同一个值——哈希碰撞
如何解决哈希碰撞的问题:————拉链法
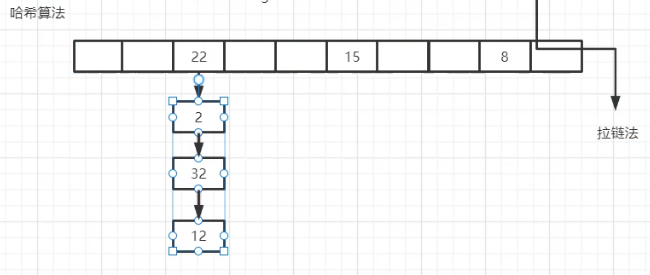
使用链表来存放哈希碰撞的数据
拉链法的弊端———随着碰撞的数据越来越多,拉链法在链表上的查询的时间复杂度为o(n)
如何降低链表的查询时间复杂度?
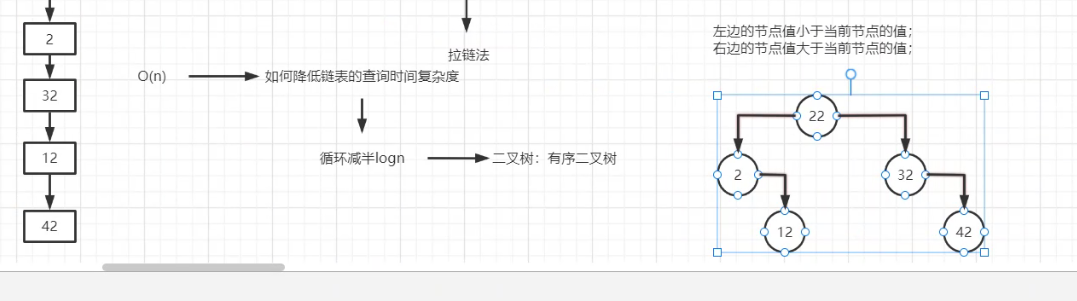
通过引进树的概念(把链表构建成有序二叉树)
有序二叉树理论上的查询的时间复杂度为O(logn)
那么有序二叉树存在的问题呢?试想一个极端情况,如下图,这个有序二叉树查询的时间复杂度为O(n)

理论上有序二叉树查询的时间复杂度是一个logn级别的,实际上是在logn到n之间(不稳定)
如何解决有序二叉树不稳定的问题?
引入平衡二叉树
平衡二叉树的概念
1.平衡二叉树是一个有序二叉树(左边的节点值小于当前节点值小于右边节点值)
2.左右两颗子树的高度差的绝对值小于等于1

平衡二叉树的旋转
在插入新的节点后,可能会导致平衡二叉树不再”平衡“,我们通过旋转来使二叉树重新达到平衡
每次跳转只走两步来判断是什么型
LL型旋转
先找新插入的节点(造成不平衡的节点)
找到不平衡节点(离造成不平衡节点最近的)
- 将A节点的左孩子提升为新的跟节点
- 将跟节点A变为新跟节点的右子树
- 剩余各个子树按大小关系排列

举例1

举例2
造成不平衡的节点1
不平衡节点 4

RR型旋转
先找新插入的节点(造成不平衡的节点)
找到不平衡节点(离造成不平衡节点最近的)
- 将A节点的右子树B升为子树的根节点点
- 节点A降为B的左子树
- 其与子树按大小关系进行排列

举例

LR型旋转
先找新插入的节点(造成不平衡的节点)
找到不平衡节点(离造成不平衡节点最近的)

例子
不平衡点:5
造成不平衡的点:3

RL型旋转
先找新插入的节点(造成不平衡的节点)
找到不平衡节点(离造成不平衡节点最近的)

例子

红黑树(最优二叉树)
二三四树
二三四树查找的实际时间复杂度会小于平衡二叉树(O(logn))
二三四树所有叶子节点保存着相同的深度

二三四树转换红黑树

2节点的只能变成一个黑节点
3节点变成一个黑节点连接着一个子红节点
4节点变成一个黑色节点连接着两个子红节点
红黑树也是一个有序二叉树
红黑树的特点
由2-3-4树过渡而来
-
每个节点不是黑色就是红色
-
根节点永远都是黑色——转换的时候是黑色在上
-
红黑树有叶子节点,每个叶子节点都是null
-

-
如果一个节点是红色的,那么他的子节点一定是黑色的(由二三四树转换红黑树可知,红色节点是二三四树的结束,而黑色节点是开始)
-
从根节点到任意一个叶子节点上的黑色节点的数目相同(二三四树所有叶子节点保存着相同的深度)
-
在红黑树上没有一条路径比其他路径长过2倍
-
假设极端情况,红黑树路径最长的就是红黑相间的,但是红黑树任意路径的黑色节点数目相同,最长路径红色节点最多=黑色节点的数量,所以在红黑树上没有一条路径比其他路径长过2倍
多叉树
B树
一个节点上可以分出多个(2个以上)的分支
B树是多叉树(有序),如2-3-4树就是B树(3阶b树,最多三个分支)
一个节点最多能有多少分支(就是几阶b树)——B树中所有结点的孩子结点个数的最大值即为阶吧
m阶b树,每个节点上最多存储m-1个值,如4阶b树每个节点上最多存储3个值

B树的存储格式是以key—value形式存储的,按key值排序

导线中传递是电压而不是电流(电压的变化小,稳定)
一个导线一次只能传递一个电压信号,为了解决这个问题,把多个导线并联形成总线,可以一个时刻传递多个电压信号,总线的根数表示了是几位的操作系统
B+树
数据库底层数据结构采用B+树
B+树非叶子节点仅具有索引功能,非叶子节点上只能存储key值,不能存储value值
B+树非叶子节点上存储数据越多,树的高度越低
B+树的叶子节点会构成一个有序链表,有利于区间查询

对于一个查询语句
select * from user where id = ?- 1
key:主键id
value:数据
哈夫曼树和哈夫曼编码
哈夫曼树和哈夫曼编码的背景
如:I LOVE YOU如何变成二进制信息就行存储呢?
是通过编码格式表(以ASCII码为例)
ASCII码是针对于英文的编码格式,一个字符占8bit
I LOVE YOU有10个字符(中间两个空格)
采用定长编码的方式,那么就需要80个bit
定长编码:无论数据多大,都存储为固定大小,小的话则前补,大的话就裁剪
定长编码:能够方便的进行截取数据
数据压缩
网络并不稳定,把数据进行压缩,提高数据的传输速度
如何进行数据压缩
把定长的编码变成变长的编码,就可以减少空间
如何设计一个变长的编码规则
我们可以把字符的出现次数做一个统计,字符出现次数越多,编码后占用的bit越少,这样就可以有效进行数据压缩(把出现次数多的字符,减少了占用的bit)
如下图,空格和o出现的最多,编码后他们代表0和1 u只出现了一次,编码后代表的是110

采用变长编码可以有效的数据压缩,但是对应的在数据解析(解压、翻译)对的时候,无码正确识别编码,数据的翻译会出现歧义
如何在采用变长编码进行数据压缩的同时,也确保数据翻译的正确性呢?————哈夫曼编码————哈夫曼树
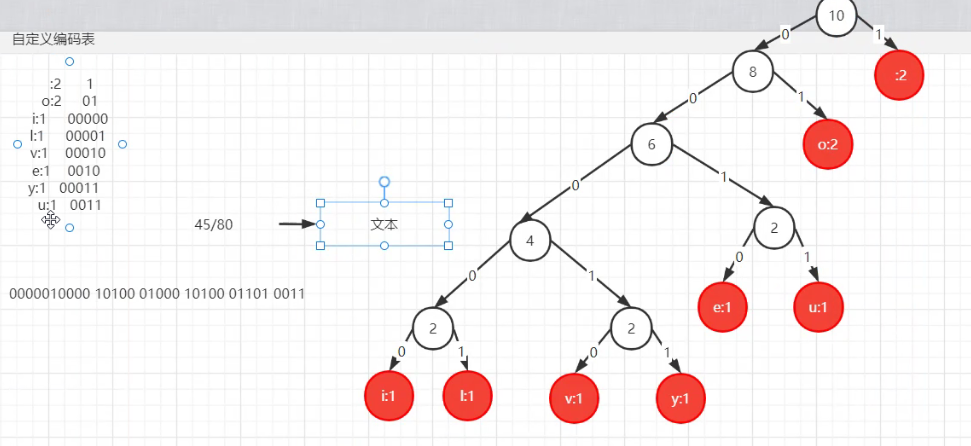
可以看出哈夫曼编码的前缀是不重复的,哈夫曼编码的平均压缩效率在60%左右,但是不会出现翻译歧义的现象发生。
哈夫曼树
基本概念
路径和路径长度:根节点到该节点中间的路径数量,如根节点到13的路径长度为2
节点的权:节点的value值(一般为数出现的次数)
带权路径长度:路径长度 * 节点的权

树的带权路径长度(WPL):每条路径上带权路径长度之和
树的带权路径长度(WPL)最小的就是哈夫曼树
哈夫曼树所有节点的权全在叶子节点上
哈夫曼树不唯一,但是一定是最小的WPL
构建哈夫曼树
给定一个数组
1.从小到大进行排序

2.把数组的数放入一个集合,取出集合中最小的数(一个或者两个),构成的新节点也进入集合,但是不是实际的节点。哈夫曼树所有节点的权全在叶子节点上.
3.重复第二步,直到所有节点构成一个树

-
相关阅读:
Latex工具(texlive+texstudio)的详细安装及基本使用
优化用户体验:直播带货系统源码的界面设计与互动功能
售后服务管理系统(Java+Web+J2EE+MySQL)
node 第十八天 中间件express-session实现会话密钥
Hbuilder打包成APP流程,以及遇到的坑
【html5期末大作业】基于HTML+CSS+JavaScript管理系统页面模板
acwing算法基础之基础算法--高精度除法算法
C语言进阶第七课-----------自定义类型的讲解(结构体枚举联合)
Rb(redis blaster),一个为 redis 实现 non-replicated 分片的 python 库
c++11~c++20 -06-字节对齐alignof、alignas
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_61820867/article/details/126548376
