-
SpringBoot WEB开发
目录
3.Thymeleaf标准表达式语法(Thymeleaf Standard Expression syntax)。
⚪核心!!!自动装配
springboot到底帮我们配置了什么?我们能不能进行修改?能不能扩展?
- xxxxAutoConfiguration..向容器中自动配置组件
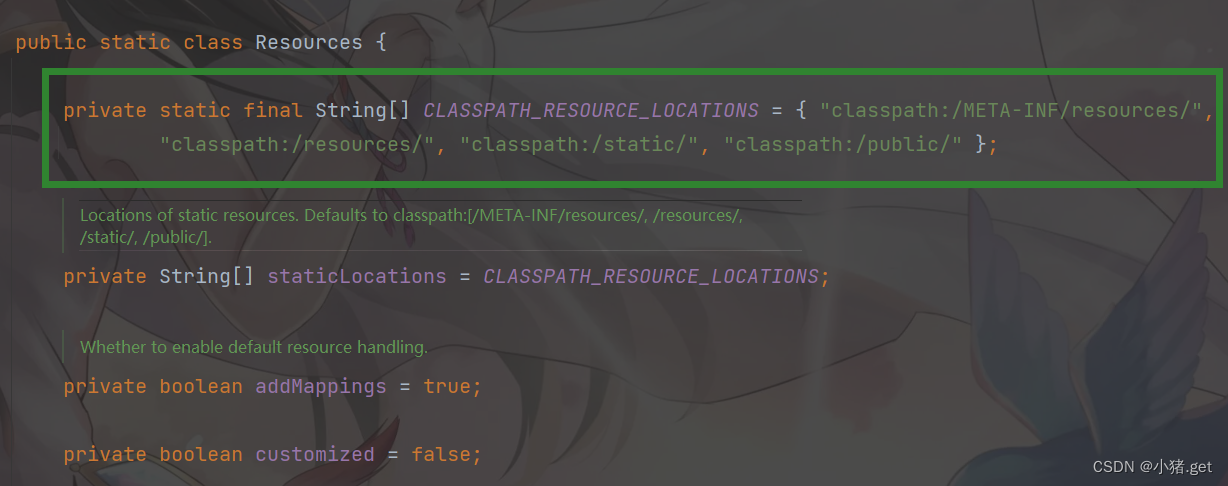
- xxxxProperties:自动配置类,装配配置文件中自定义的一些内容
一、实现web开发要解决的问题?
- 静态资源的导入
- 首页(index.html)
- jsp,模板引擎Thymeleaf
- 装配和扩展SpringMVC
- CRUD
- 拦截器
- 国际化(中英文切换)
⚪WebMvc的自动配置类
WebMvcAutoConfiguration- @Override
- public void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
- if (!this.resourceProperties.isAddMappings()) {
- logger.debug("Default resource handling disabled");
- return;
- }
- addResourceHandler(registry, "/webjars/**", "classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/");
- addResourceHandler(registry, this.mvcProperties.getStaticPathPattern(), (registration) -> {
- registration.addResourceLocations(this.resourceProperties.getStaticLocations());
- if (this.servletContext != null) {
- ServletContextResource resource = new ServletContextResource(this.servletContext, SERVLET_LOCATION);
- registration.addResourceLocations(resource);
- }
- });
- }
- private void addResourceHandler(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry, String pattern, String... locations) {
- addResourceHandler(registry, pattern, (registration) -> registration.addResourceLocations(locations));
- }
- private void addResourceHandler(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry, String pattern, Consumer
customizer) { - if (registry.hasMappingForPattern(pattern)) {
- return;
- }
- ResourceHandlerRegistration registration = registry.addResourceHandler(pattern);
- customizer.accept(registration);
- registration.setCachePeriod(getSeconds(this.resourceProperties.getCache().getPeriod()));
- registration.setCacheControl(this.resourceProperties.getCache().getCachecontrol().toHttpCacheControl());
- registration.setUseLastModified(this.resourceProperties.getCache().isUseLastModified());
- customizeResourceHandlerRegistration(registration);
- }
二、导入静态资源
1.通过Maven导入
什么是webjars?
WebJars是被打包成JAR文件 (Java Archive)形式的客户端web资源库(例如:jQuery、Bootstrap等)。即WebJars是库,是各种web资源库,打包成jar文件形式。
webjars官网:WebJars - Documentation
具体参考:SpringBoot之使用WebJars - 简书 (jianshu.com)

复制并添加到pom.xml中

启动项目,在地址栏输入jquery文件路径localhost:8080/webjars/github-com-jquery-jquery/3.6.0/jquery.js

2. publi、static、/**、resources

🔥可以被识别到的目录
测试

结果:

3.优先级

resource > static > public
三、首页
⭐WelcomePageHandlerMapping
- /**
- * An {@link AbstractUrlHandlerMapping} for an application's welcome page. Supports both
- * static and templated files. If both a static and templated index page are available,
- * the static page is preferred.
- *
- * @author Andy Wilkinson
- * @author Bruce Brouwer
- */
- final class WelcomePageHandlerMapping extends AbstractUrlHandlerMapping {
- private static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(WelcomePageHandlerMapping.class);
- private static final List
MEDIA_TYPES_ALL = Collections.singletonList(MediaType.ALL); - WelcomePageHandlerMapping(TemplateAvailabilityProviders templateAvailabilityProviders,
- ApplicationContext applicationContext, Resource welcomePage, String staticPathPattern) {
- if (welcomePage != null && "/**".equals(staticPathPattern)) {
- logger.info("Adding welcome page: " + welcomePage);
- setRootViewName("forward:index.html");
- }
- else if (welcomeTemplateExists(templateAvailabilityProviders, applicationContext)) {
- logger.info("Adding welcome page template: index");
- setRootViewName("index");
- }
- }
- private boolean welcomeTemplateExists(TemplateAvailabilityProviders templateAvailabilityProviders,
- ApplicationContext applicationContext) {
- return templateAvailabilityProviders.getProvider("index", applicationContext) != null;
- }
- private void setRootViewName(String viewName) {
- ParameterizableViewController controller = new ParameterizableViewController();
- controller.setViewName(viewName);
- setRootHandler(controller);
- setOrder(2);
- }
- @Override
- public Object getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
- for (MediaType mediaType : getAcceptedMediaTypes(request)) {
- if (mediaType.includes(MediaType.TEXT_HTML)) {
- return super.getHandlerInternal(request);
- }
- }
- return null;
- }
- private List
getAcceptedMediaTypes(HttpServletRequest request) { - String acceptHeader = request.getHeader(HttpHeaders.ACCEPT);
- if (StringUtils.hasText(acceptHeader)) {
- return MediaType.parseMediaTypes(acceptHeader);
- }
- return MEDIA_TYPES_ALL;
- }
- }
测试:


注意:在templates目录下的所有页面,只能通过controller来跳转
四、Thymeleaf模板引擎
1.什么是模板引擎?
模板引擎(用于Web开发)是为了使用户界面与业务数据(内容)分离而产生的,它可以生成特定格式的文档,用于网站的模板引擎就会生成一个标准的HTML文档。
前端交给我们的页面,是html页面。如果是我们以前开发,我们需要把他们转成jsp页面
jsp好处就是当我们查出一些数据转发到JSP页面以后,我们可以用jsp轻松实现数据的显示,及交互等。
jsp支持非常强大的功能,包括能写Java代码,但是SpringBoot项目是以jar的方式,不是war,且使用了Tomcat,因此默认是不支持jsp的。
SpringBoot推荐使用模板引擎:
其实jsp就是一个模板引擎,还有用的比较多的freemarker,包括SpringBoot给我们推荐的Thymeleaf,模板引擎有非常多,但再多的模板引擎,他们的思想都是一样的,如图:

2.模板引擎的作用
模板引擎的作用就是我们来写一个页面模板,比如有值的,动态的,表达式。
而这些值是我们在后台封装一些数据。然后把这个模板和这个数据交给模板引擎,模板引擎按照数据把表达式解析、填充到我们指定的位置,然后把这个数据最终生成一个我们想要的内容给我们写出去。
Thymeleaf旨在提供⼀个优雅的、⾼度可维护的创建模板的⽅式。 为了实现这⼀⽬标,Thymeleaf建⽴在⾃然模板的概念上,将其逻辑注⼊到模板⽂件中,不会影响模板设计原型。 这改善了设计的沟通,弥合了设计和开发团队之间的差距。 做到了页面和展示的分离。
3.引入thymeleaf依赖
http://13. Build Systems (spring.io)

spring-boot/pom.xml at v2.1.6.RELEASE · spring-projects/spring-boot · GitHub

- <dependency>
- <groupId>org.thymeleafgroupId>
- <artifactId>thymeleaf-spring5artifactId>
- dependency>
- <dependency>
- <groupId>org.thymeleaf.extrasgroupId>
- <artifactId>thymeleaf-extras-java8timeartifactId>
- dependency>
确认成功导入

ThymeleafProperties 源码
- @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.thymeleaf")
- public class ThymeleafProperties {
- private static final Charset DEFAULT_ENCODING = StandardCharsets.UTF_8; //默认编码
- public static final String DEFAULT_PREFIX = "classpath:/templates/"; //前缀
- public static final String DEFAULT_SUFFIX = ".html"; //后缀必须以.html结尾
- /**
- * Whether to check that the template exists before rendering it.
- */
- private boolean checkTemplate = true;
- /**
- * Whether to check that the templates location exists.
- */
- private boolean checkTemplateLocation = true;
- /**
- * Prefix that gets prepended to view names when building a URL.
- */
- private String prefix = DEFAULT_PREFIX;
- /**
- * Suffix that gets appended to view names when building a URL.
- */
- private String suffix = DEFAULT_SUFFIX;
- /**
- * Template mode to be applied to templates. See also Thymeleaf's TemplateMode enum.
- */
- private String mode = "HTML";
- /**
- * Template files encoding.
- */
- private Charset encoding = DEFAULT_ENCODING;
- /**
- * Whether to enable template caching.
- */
- private boolean cache = true;
- /**
- * Order of the template resolver in the chain. By default, the template resolver is
- * first in the chain. Order start at 1 and should only be set if you have defined
- * additional "TemplateResolver" beans.
- */
- private Integer templateResolverOrder;
- /**
- * Comma-separated list of view names (patterns allowed) that can be resolved.
- */
- private String[] viewNames;
- /**
- * Comma-separated list of view names (patterns allowed) that should be excluded from
- * resolution.
- */
- private String[] excludedViewNames;
- /**
- * Enable the SpringEL compiler in SpringEL expressions.
- */
- private boolean enableSpringElCompiler;
- /**
- * Whether hidden form inputs acting as markers for checkboxes should be rendered
- * before the checkbox element itself.
- */
- private boolean renderHiddenMarkersBeforeCheckboxes = false;
- /**
- * Whether to enable Thymeleaf view resolution for Web frameworks.
- */
- private boolean enabled = true;
- private final Servlet servlet = new Servlet();
- private final Reactive reactive = new Reactive();
- public boolean isEnabled() {
- return this.enabled;
- }
- public void setEnabled(boolean enabled) {
- this.enabled = enabled;
- }
- public boolean isCheckTemplate() {
- return this.checkTemplate;
- }
- public void setCheckTemplate(boolean checkTemplate) {
- this.checkTemplate = checkTemplate;
- }
- public boolean isCheckTemplateLocation() {
- return this.checkTemplateLocation;
- }
- public void setCheckTemplateLocation(boolean checkTemplateLocation) {
- this.checkTemplateLocation = checkTemplateLocation;
- }
- public String getPrefix() {
- return this.prefix;
- }
- public void setPrefix(String prefix) {
- this.prefix = prefix;
- }
- public String getSuffix() {
- return this.suffix;
- }
- public void setSuffix(String suffix) {
- this.suffix = suffix;
- }
- public String getMode() {
- return this.mode;
- }
- public void setMode(String mode) {
- this.mode = mode;
- }
- public Charset getEncoding() {
- return this.encoding;
- }
- public void setEncoding(Charset encoding) {
- this.encoding = encoding;
- }
- public boolean isCache() {
- return this.cache;
- }
- public void setCache(boolean cache) {
- this.cache = cache;
- }
- public Integer getTemplateResolverOrder() {
- return this.templateResolverOrder;
- }
- public void setTemplateResolverOrder(Integer templateResolverOrder) {
- this.templateResolverOrder = templateResolverOrder;
- }
- public String[] getExcludedViewNames() {
- return this.excludedViewNames;
- }
- public void setExcludedViewNames(String[] excludedViewNames) {
- this.excludedViewNames = excludedViewNames;
- }
- public String[] getViewNames() {
- return this.viewNames;
- }
- public void setViewNames(String[] viewNames) {
- this.viewNames = viewNames;
- }
- public boolean isEnableSpringElCompiler() {
- return this.enableSpringElCompiler;
- }
- public void setEnableSpringElCompiler(boolean enableSpringElCompiler) {
- this.enableSpringElCompiler = enableSpringElCompiler;
- }
- public boolean isRenderHiddenMarkersBeforeCheckboxes() {
- return this.renderHiddenMarkersBeforeCheckboxes;
- }
- public void setRenderHiddenMarkersBeforeCheckboxes(boolean renderHiddenMarkersBeforeCheckboxes) {
- this.renderHiddenMarkersBeforeCheckboxes = renderHiddenMarkersBeforeCheckboxes;
- }
- public Reactive getReactive() {
- return this.reactive;
- }
- public Servlet getServlet() {
- return this.servlet;
- }
- public static class Servlet {
- /**
- * Content-Type value written to HTTP responses.
- */
- private MimeType contentType = MimeType.valueOf("text/html");
- /**
- * Whether Thymeleaf should start writing partial output as soon as possible or
- * buffer until template processing is finished.
- */
- private boolean producePartialOutputWhileProcessing = true;
- public MimeType getContentType() {
- return this.contentType;
- }
- public void setContentType(MimeType contentType) {
- this.contentType = contentType;
- }
- public boolean isProducePartialOutputWhileProcessing() {
- return this.producePartialOutputWhileProcessing;
- }
- public void setProducePartialOutputWhileProcessing(boolean producePartialOutputWhileProcessing) {
- this.producePartialOutputWhileProcessing = producePartialOutputWhileProcessing;
- }
- }
- public static class Reactive {
- /**
- * Maximum size of data buffers used for writing to the response. Templates will
- * execute in CHUNKED mode by default if this is set.
- */
- private DataSize maxChunkSize = DataSize.ofBytes(0);
- /**
- * Media types supported by the view technology.
- */
- private List
mediaTypes; - /**
- * Comma-separated list of view names (patterns allowed) that should be executed
- * in FULL mode even if a max chunk size is set.
- */
- private String[] fullModeViewNames;
- /**
- * Comma-separated list of view names (patterns allowed) that should be the only
- * ones executed in CHUNKED mode when a max chunk size is set.
- */
- private String[] chunkedModeViewNames;
- public List
getMediaTypes() { - return this.mediaTypes;
- }
- public void setMediaTypes(List
mediaTypes) { - this.mediaTypes = mediaTypes;
- }
- public DataSize getMaxChunkSize() {
- return this.maxChunkSize;
- }
- public void setMaxChunkSize(DataSize maxChunkSize) {
- this.maxChunkSize = maxChunkSize;
- }
- public String[] getFullModeViewNames() {
- return this.fullModeViewNames;
- }
- public void setFullModeViewNames(String[] fullModeViewNames) {
- this.fullModeViewNames = fullModeViewNames;
- }
- public String[] getChunkedModeViewNames() {
- return this.chunkedModeViewNames;
- }
- public void setChunkedModeViewNames(String[] chunkedModeViewNames) {
- this.chunkedModeViewNames = chunkedModeViewNames;
- }
- }
- }
3.使用
导入对应的依赖,将html放在templates目录下即可

- //在templates目录下的所有页面,只能通过controller来跳转
- //需要模板引擎的支持:thymeleaf
- @Controller
- public class IndexController {
- @RequestMapping("/test")
- public String index(){
- return "test";
- }
- }
运行结果

五、Thymeleaf语法
1.thymeleaf 中文文档
关于我们 · Using Thymeleaf 译文 (gitbooks.io)
2.thymeleaf 属性优先级

3.Thymeleaf标准表达式语法(Thymeleaf Standard Expression syntax)。
我们已经见过了两种用这种语法表达的合理的属性值:消息和变量表达式:
- <p th:utext="#{home.welcome}">Welcome to our grocery store!p>
- <p>Today is: <span th:text="${today}">25 August 2022span>p>
但是表达式的种类远不止这些,而且关于我们已知的这两种还有一些更有趣的细节需要了解。首先,让我们快速的看一下标准表达式的功能。
- 简单表达式 Simple Expressions:
- 变量表达式 Variable Expressions:
${...} - 选中变量表达式 Selection Variable Expressions:
*{...} - 消息表达式 Message Expressions:
#{...} - 连接URL表达式 Link URL Expressions:
@{...} - 片段表达式 Fragment Expressions:
~{...}
- 变量表达式 Variable Expressions:
- 常量 Literals
- 文本常量 Text literals:
'one text','Another one!',… - 数字常量 Number literals:
0,34,3.0,12.3,… - 布尔常量 Boolean literals:
true,false - 空常量 Null literal:
null - 常符号 Literal tokens:
one,sometext,main,…
- 文本常量 Text literals:
- 文本操作 Text operations:
- 字符串连接 String concatenation:
+ - 常量替换 Literal substitutions:
|The name is ${name}|
- 字符串连接 String concatenation:
- 算数操作 Arithmetic operations:
- Binary operators:
+,-,*,/,% - Minus sign (unary operator):
-
- Binary operators:
- 布尔操作 Boolean operations:
- 布尔操作符 Binary operators:
and,or - 布尔否定 一元操作符Boolean negation (unary operator):
!,not
- 布尔操作符 Binary operators:
- 比较和相等 Comparisons and equality:
- 比较符 Comparators:
>,<,>=,<=(gt,lt,ge,le) - 相等符 Equality operators:
==,!=(eq,ne)
- 比较符 Comparators:
- 条件操作符 Conditional operators:
- If-then:
(if) ? (then) - If-then-else:
(if) ? (then) : (else) - 默认值 Default:
(value) ?: (defaultvalue)
- If-then:
- 特殊符号 Special tokens:
- 无操作符 No-Operation:
_
- 无操作符 No-Operation:
这些功能可以自由的组合和嵌套:
'User is of type ' + (${user.isAdmin()} ? 'Administrator' : (${user.type} ?: 'Unknown')) -
相关阅读:
BPMN2.0协议简介
nginx安装和使用
JVM性能优化案例:优化垃圾回收器的年轻代和老年代占比
计算机毕业设计微信小程序校园辩论管理平台
.Net依赖注入神器Scrutor(上)
LeetCode 1161.最大层内元素和:层序遍历
【Redis学习笔记】第二章 Redis数据类型
JAVA计算机毕业设计员工婚恋交友平台Mybatis+源码+数据库+lw文档+系统+调试部署
Bi-Modal Progressive Mask Attention for Fine-Grained Recognition
JavaScript常见面试题(二)
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_52982868/article/details/126498988
