-
react学习笔记
创建
- 创建: npx create-react-app 项目名
- 打开项目:cd 项目名
- 启动项目:npm start
- 暴露配置项:npm run eject
JSX语法
JSX是⼀种JavaScript的语法扩展,其格式⽐较像模版语⾔,但事实上完全是在JavaScript内部实现的。JSX可以很好地描述UI,能够有效提⾼开发效率,体验JSX基本使用
// 表达式 {}的使用 const name = 'react' const jsx = <div>hello, {name}</div>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
函数
const obj = { firstName:'harry', lastName: 'potter' } function formatName(name){ return name.firstName + "" + name.lastName } const jsx = <div>{formatName(obj)}</div>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
对象
// jsx是js对象,也是合法表达式 const greet = <div>good</div>; const jsx = <div>{greet}</div>- 1
- 2
- 3
条件语句
const show = true const greet = <div>good</div> const jsx = ( <div> {/* 条件语句 */} {show ? greet : '登录'} {show && greet } </div> )- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
数组
const a = [0,1,2,3] const jsx = ( <div> <ul> {/* diff时候,⾸先⽐较type,然后是key,所以同级同类型元素,key值必须得 唯⼀ */} {a.map(item => (<li key={item}>{item}</li>))} </ul> </div> )- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
属性的使用
import logo from './logo.svg' const jsx = ( <div> {/* 属性:静态值⽤双引号,动态值⽤花括号;class、for等要特殊处理。 */} <img src={logo} style={{width:100}} className="img" /> <div> )- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
模块化
import style from './index.css' <img className={style.logo} />- 1
- 2
组件
组件形式:
class组件和function组件class 组件
拥有状态和生命周期,继承于Compontent,实现render方法import React, {Compontent} from 'react' export default class ClassCompontent extends React.Compontent { constructor(props){ super(props); // 使⽤state属性维护状态,在构造函数中初始化状态 this.state = {data: new Date()} } compontentDidMount(){ this.timer = setInterval(() => { // 使⽤setState⽅法更新状态 this.setState({data: new Date()}) },1000) } compontentwillUnmount() { clearInterval(this.timer) } compontentDidUpdate() { console.log('compontentDidUpdate') } render() { return <div>{this.state.date.toLocaleTimeString()}</div> } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
function 组件
无状态,仅关注内容展示,返回渲染结果即可import React, {useState, useEffect} from 'react' export function FunctionComponent(props) { const [date, setDate] = useState(new Date) useEffect(() => { // 副作用 const timer = setInterval(() => { setDate(new Date()) }, 1000) return () => clearInterval(timer) //组件卸载的时候执⾏ },[]) return ( <div>{date.toLocaleTimeString()}</div> ) }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
提示:可以把 useEffect Hook 看做componentDidMount , componentDidUpdate 和 componentWillUnmount 这三个函数的组合setState
setState(partialState,callback)
- partialState:object | function 用于产生与当前state合并的子集
- callback:function state更新后被调用
1. 不要直接修改State,应该用setState 2. State的更新可能是异步的 如果要获取到最新状态值有以下⽅式: 1. 在回调中获取状态值 ```javascript changeVal = v => { this.setState({counter:this.state.counter + v},() => { console.log("counter", this.state.counter) }) } ``` 2. 使用定时器 setTimeout(() =>{this.setCounter},0) 3. 原生事件中修改 compontentDidMount() { doucument.body.addEventListener('click',this.changeVal, false) } ```总结: setState只有在合成事件和⽣命周期函数中是异步的,在原⽣事件和setTimeout中都是同步的,这⾥的异步其实是批量更新。 ```- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
State的更新会被合并
changeval = v => { this.setState({ counter: this.state.counter + v }) } setCounter =() => { this.changeval(1) this.changeval(2) }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
生命周期

- compontentWillMount
- compontentReceiveProps
- compontentWillUpdate
两个新生命周期 - static getDerivedStateFromProps
- getSnapshotBeforeUpdate
如果不想⼿动给将要废弃的⽣命周期添加 UNSAFE_ 前缀,可以⽤下⾯的命令。
npx react-codemod rename-unsafe-lifecycles <path>- 1
getDerivedStateFromProps
static getDerivedStateFromProps(props,state)
会在调⽤ render ⽅法之前调⽤,并且在初始挂载及后续更新时都会被
调⽤。它应返回⼀个对象来更新 state,如果返回 null 则不更新任何内容。UNSAFE_componentWillReceiveProps 形成对⽐,后者仅在⽗组件重新渲染时触发,⽽不是在内部 调⽤ setState 时``` ```getSnapshotBeforeUpdate``` getSnapshotBeforeUpdate(prevProps,prevState) 在render之后,在componentDidUpdate之前。 ```getSnapshotBeforeUpdate() 在最近⼀次渲染输出(提交到 DOM 节点)之前调⽤。它使得组件能 在发⽣更改之前从 DOM 中捕获⼀些信息(例如,滚动位置)。此⽣命周期的任何返回值将作为参数传递给 componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState, snapshot) 。``` ```javascript import React, {Compontent} from 'react' import PropTypes from 'prop-types' /* V17可能会废弃的三个⽣命周期函数⽤getDerivedStateFromProps替代,⽬前使⽤的话加上 UNSAFE_: - componentWillMount - componentWillReceiveProps - componentWillUpdate */ export default class LifeCyclePage extends Compontent { static defaultProps = { masg: 'omg' } static propsTypes = { mag: PropTypes.string.isRequired } constructor(props) { super(props) this.state = { count: 0 } } static getDerivedStateFromProps(props,state){ // getDerivedStateFromProps 会在调⽤ render ⽅法之前调⽤, // getDerivedStateFromProps 会在调⽤ render ⽅法之前调⽤, //它应返回⼀个对象来更新 state,如果返回 null 则不更新任何内容。 const {count} = state return count < 5 ? null : {count: 0} } //在render之后,在componentDidUpdate之前。 getSnapshotBeforeUpdate(prevProps, prevState, snapshot) { const { count } = prevProps return null } compontentDidMount() { console.log("componentDidMount", this.state.count) } componentwillUnmount() { console.log("componentwillUnmount") } componentDidUpdate() { console.log("componentDidUpdate", this.state.count); } shouldComponentUpdae(nextProps,nextState){ const { count } = nextProps return count !== 3 } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
组件复合
不具名
// Layout页面 import React, {Component} from 'react' import TopBar from '../components/TopBar' import BottomBar from '../components/BottomBar' export default class Layout extends Component { componentDidMount() { const { title = '商城' } = this.props document.title = title } render() { const { children, showTopBar, showBottomBar} = this.props return ( <div> {showTopBar && <TopBar />} {children.content} <button onClick={children.ntnClick}>buttom</button> {showBottomBar && <BottomBar />} </div> ) } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
// UserPage import React, {Component} from 'react' import Layout from './Layout' export default class UserPage extends Component { render() { return ( <Layout showTopBar={true} showBottomBar = {true} title="用户中心"> <div> <h3>userpage</h3> </div> </Layout> ) } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
具名
传个对象进去
import React, {Component} from 'react' import Layout from './Layout' export default class HomePage extends Component { render() { return ( <div> <Layout showTopBar={false} showBottomBar={true} tilte="首页"> {{ content:( <div><h3>homePage</h3></div> ), txt: '文本', btnClick: () => { console.log('btnClick') } }} </Layout> </div> ) } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
复合组件—card
import React, {Component} from 'react' function Card(props){ return <div xu="card">{props.children}</div> } function Formbutton(props) { return <div className="Formbutton"> <button onClick={props.children.defaultBtns.searchClick}>默认查询</button> <button onClick={props.children.defaultBtns.resetClick}>默认重置</button> { props.children.btns.map((item,index) => { return <button key={'btn' + index} onClick={item.onClick}>{item.title}<button> }) } </div> } export default class CompositionPage extends Component { render() { return ( <div> <Card>我是内容</Card> <Card>我是内容2</Card> <Formbutton> {{ defaultButton: { searchClick: () => console.log('查询'), resetClick: () => console.log('重置') }, btns: [ {title: '查询', onClick: () => console.log('查询')}, {title:'重置', onClick: () => console.log('重置')} ] }} </Formbutton> </div> ) } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
redux
Redux 是负责组织 state 的⼯具
应用场景:- 你有着相当⼤量的、随时间变化的数据;
- 你的 state 需要有⼀个单⼀可靠数据来源;
- 你觉得把所有 state 放在最顶层组件中已经⽆法满⾜需要了。
- 某个组件的状态需要共享。

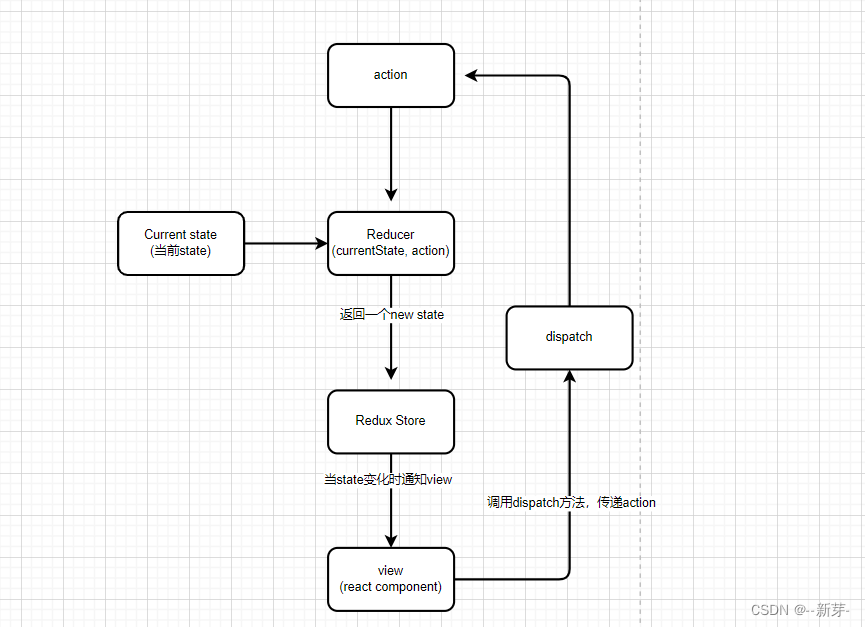
安装
npm install redux --save累加器
- 创建store
import {createStore} from 'redux' const counterReducer = (state = 0, action) => { switch(action.type){ case 'ADD': return state + 1 case 'MINUS': return state - 1 default: return state } } const store = createStore(counterReducer) export default store- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
创建 reduxPage
import React, {Component} from 'react' import store from '../store/ReduxStore' export default class ReduxPage extends Component { componentDidMount() { store.subscribe(() => { this.forceUpdate() }) } add = () => { store.dispatch({type: 'ADD'}) } minus = () => { store.dispatch({type:'MINUS'}) } render() { return ( <div>{store.getState()}<div> <button onClick={this.add}>add</button> <button onClick={this.minus}>minus</button> ) } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
注意:如果点击按钮不能更新,因为没有订阅(subscribe)状态变更
可以在src/index.js的render⾥订阅状态变更import store from './store/ReduxStore' const render = () => { ReactDom.render( <App/>, document.querySelector('#root') ) } render() store.subscribe(render)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- createStore 创建store
- reducer 获取状态值
- getState 获取状态值
- dispatch 提交更新
- subscribe更新订阅
react-redux
安装
npm install react-redux --save使用
提供了两个api
- Provider为后代组件提供store
- connect为组件提供数据和变更方法
全局提供store, index.js
import React from 'react' import ReactDom from 'react-dom' import App from './App' import store from 'store' import {Provider} from 'react-redux' ReactDom.render( <Provider store={store}> <App/> </Provider>, document.querySelector('#root') )- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
获取数据状态
import { connect } from 'react-redux' class ReactRedux extends Component { render() { const {num,add,minus} = this.props return (<div>{num}<button onClick={add}>add</button><button onClick={minus}>minus</button></div>) } } const mapStateToProps = state => { return { num: state } } const mapDispatchToProps = { add: () => { return {type: 'add'} }, minus: () => { return {type: 'minus'} } } export default connect( mapStateToProps, //状态映射 mapStateToProps mapDispatchToProps, //状态映射 mapStateToProps )(ReactRedux)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
connect中的参数:state映射和事件映射react-router
安装
npm install --save react-router-dom
基本使用定向-Redirect都以组件形式存在``` ```javascript import React, {Component} from 'react' import {BrowserRouter as Router,Route, Link} from 'react-router-dom' export default class RouterPage extends Component { render() {} }首页 ⽤户中⼼ {/* 根路由要添加exact,实现精确匹配 */} children} //render={() =>render} />- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
Route渲染的三种方式
Route渲染优先级:children>component>render。这三种⽅式互斥,只能⽤⼀种children:func
有时候,不管location是否匹配,都需要渲染⼀些内容,这时候可以⽤children。
除了不管location是否匹配都会被渲染之外,其它⼯作⽅法与render完全⼀样。render:func
但是当⽤render的时候,你调⽤的只是个函数。
只在当location匹配的时候渲染。component: component
只在当location匹配的时候渲染。
404页面
设定⼀个没有path的路由在路由列表最后⾯,表示⼀定匹配
{/* 添加Switch表示仅匹配⼀个*/} <Switch> {/* 根路由要添加exact,实现精确匹配 */} <Route exact path="/" component={HomePage} /> <Route path="user" component={userpage}> <Route component={EmptyPage}> </Switch>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
PureComponent 性能优化
shouldComponentUpdate后的Componentimport React, {Component, PureComponent} from 'react' export default class PureComponent extends PureComponent { constructor(props){ super(props) this.state = { counter: 0, } } setCounter = () => { this.setState({ counter: 100 }) } render() { const {counter} = this.state return ( <div> <div onClick={this.setCounter}>counter:{counter}</div> </div> ) } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
浅比较
缺点是必须要⽤class形式,⽽且要注意是浅比较
与Component比较
React.PureComponent 与 React.Component 很相似。两者的区别在于 React.Component 并未实 现 shouldComponentUpdate() ,⽽ React.PureComponent 中以浅层对⽐ prop 和 state 的⽅式来 实现了该函数 如果赋予 React 组件相同的 props 和 state, render() 函数会渲染相同的内容,那么在某些情况下使 ⽤ React.PureComponent 可提⾼性能。- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
React.PureComponent 中的 shouldComponentUpdate() 仅作对象的浅层⽐较。如果对象中 包含复杂的数据结构,则有可能因为⽆法检查深层的差别,产⽣错误的⽐对结果。仅在你的 props 和 state 较为简单时,才使⽤ React.PureComponent ,或者在深层数据结构发⽣变化时 调⽤ forceUpdate() 来确保组件被正确地更新。你也可以考虑使⽤ immutable 对象加速嵌套数据的⽐较. 此外, React.PureComponent 中的 shouldComponentUpdate() 将跳过所有⼦组件树的 prop 更新。因此,请确保所有⼦组件也都是“纯”的组件。- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
Hook
Hook 是⼀个特殊的函数,它可以让你“钩⼊” React 的特性。例如, useState 是允许 你在 React 函数组件中添加 state 的 Hook。 如果你在编写***函数组件***并意识到需要向其添加⼀些 state,以前的做法是必须 将其它转化为 class。现在你可以在现有的函数组件中使⽤ Hook- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
import React, {useState} from 'react' export default function HookPage(props){ // 声明⼀个叫 “count” 的 state 变量,初始化为0 const [count, setCount] = useState(0) return (<div> {count} <button onClick={() => setCount(count + 1)}>add</button> </div>) }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
Effect Hook
可以让你在函数组件中执⾏副作⽤操作
数据获取,设置订阅以及⼿动更改 React 组件中的 DOM 都属于副作⽤。import React, {useState,useEffect} from 'react' export default function HookPage { const [count, setCount] = useState(0) // 与 componentDidMount 和 componentDidUpdate相似 useEffect(() => { // 更新title document.title = count },[]) return (<div> {count} <button onClick={() => setCount(count + 1)}>add</button> </div>) }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
在函数组件主体内(这⾥指在 React 渲染阶段)改变 DOM、添加订阅、设置定时器、记录⽇志以及执⾏其他包含副作⽤的操作都是不被允许的,因为这可能会产⽣莫名其妙的 bug 并破坏 UI 的⼀致性。 使⽤ useEffect 完成副作⽤操作。赋值给 useEffect 的函数会在组件渲染到屏幕之后执⾏。你可以 把 effect 看作从 React 的纯函数式世界通往命令式世界的逃⽣通道。默认情况下,effect 将在每轮渲染结束后执⾏,但你可以选择让它 在只有某些值改变的时候 才执⾏。- 1
- 2
- 3
effect 的条件执⾏
默认情况下,effect 会在每轮组件渲染完成后执⾏。这样的话,⼀旦 effect 的依赖发⽣变化,它就会被重新创建。 然⽽,在某些场景下这么做可能会矫枉过正。⽐如,在上⼀章节的订阅示例中,我们不需要在每次组件更新时都创建新的订阅,⽽是仅需要在 source props 改变时重新创建。 要实现这⼀点,可以给 useEffect 传递第⼆个参数,它是 effect 所依赖的值数组。- 1
- 2
- 3
import React, {useState,useEffect} from 'react' export default function HookPage(props) { const [count, setCount] = useState(0) const [date,setDate] = useState(new Date()) useEffect(() => { document.tilte = count },[count]) useEffect(() => { const Timer = setInterval(() => { setDate(new Date()) },1000) },[]) return ( <div> {count} <button onClick={() => setCount(count + 1)}>add</button> {date.toLocaleTimeString()} </div> ) }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
只有当 useEffect第⼆个参数数组⾥的数值 改变后才会重新创建订阅。清除effect
通常,组件卸载时需要清除 effect 创建的诸如订阅或计时器 ID 等资源。要实现这⼀点, useEffect 函数需返回⼀个清除函数,以防⽌内存泄漏,清除函数会在组件卸载前执⾏。- 1
- 2
useEffect(() => { const timer = setInterval(() => { setDate(new Date()); }, 1000); return () => clearInterval(timer); }, [])- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
自定义Hook与Hook的使用规则
自定义Hook
有时候我们会想要在组件之间重⽤⼀些状态逻辑。⽬前为⽌,有两种主流⽅案来解决这个问题:⾼阶组件和 render props。⾃定义 Hook 可以让你在不增加组件的情况下达到同样的⽬的。- 1
⾃定义 Hook 是⼀个函数,其名称以 “use” 开头,函数内部可以调⽤其他的 Hook。import React, {useState,useEffect,useMemo} from 'react' export default function CustomHookPage(props) { const [count,setCount] = useState(0) useEffect(() => { document.title = count },[count]) return ( <div> <h3>⾃定义Hook</h3> <p>{count}</p> <button onClick={() => setCount(count + 1)}>add</button> <p>{useClock().toLocaleTimeString()}</p> </div> ); } //⾃定义hook,命名必须以use开头 function useClock() { const [data, setDate] = useState(new Date()) useEffect(()=> { //只需要在didMount时候执⾏就可以 const timer = setInterval(()=> { setDate(new Date()) },1000) //清除定时器,类似willUnmount return () => clearInterval(timer) },[]) }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
hook使用规则
- 只能在函数最外层调⽤ Hook。不要在循环、条件判断或者⼦函数中调⽤。
- 只能在 React 的函数组件中调⽤ Hook。不要在其他 JavaScript 函数中调⽤。(还有⼀个地⽅可以调⽤ Hook —— 就是⾃定义的 Hook 中。)
Hook api (useMemo、useCallback)
useMemo
把“创建”函数和依赖项数组作为参数传⼊ useMemo ,它仅会在某个依赖项改变时才重新计算 memoized 值。这种优化有助于避免在每次渲染时都进⾏⾼开销的计算。- 1
- 2
import React, {useState,useMemo} from 'react' export default function UseMemoPage(props){ const [count,setCount] = useState(0) const expensive = useMemo(() =>{ let sum = 0 for(let i = 0; i<count;i++){ sum+=i } return sum //只有count变化,这⾥才重新执⾏ },[count]) const [value, setValue] = useState('') return ( <div> <p>expensive:{expensive}</p> <p>{count}</p> <button onClick={() => setCount(count + 1)}>add</button> <input value={value} onChange={event => setValue(event.target.value)} /> </div> ) }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
useCallback
把内联回调函数及依赖项数组作为参数传⼊ useCallback ,它将返回该回调函数的 memoized 版本, 该回调函数仅在某个依赖项改变时才会更新。当你把回调函数传递给经过优化的并使⽤引⽤相等性去避免⾮必要渲染(例如 shouldComponentUpdate )的⼦组件时,它将⾮常有⽤- 1
- 2
import React, {useState,useCallback,PureComponent} from 'react' export default function useCallbackPage(props){ const [count, setCount] = useState(0) const addClick = useCallback(() => { let sum = 0 for(let i = 0; i< count; i++){ sum += i } return sum },[count]) const [value, setValue] = useState('') return ( <div> <p>{count}</p> <button onClick={() => setCount(count + 1)}>add</button> <input value={value} onChange={event => setValue(event.target.value)} /> <Child addClick={addClick} /> </div> ) } class Child extends PureComponent { render() { const {addClick} = this.props return ( <h3>Child</h3> <button onClick={() => console.log(addClick())}>add</button> ) } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
useCallback(fn, deps) 相当于 useMemo(() => fn, deps) 。注意:依赖项数组不会作为参数传给“创建”函数。虽然从概念上来说它表现为:所有“创建”函数中引⽤的值都应该出现在依赖项数组中。未来编译器会更加智能,届时⾃动创建数组将成为可能。 -
相关阅读:
wifi感知技术
SpringBoot RabbitMQ 注解版 基本概念与基本案例
扫描车牌是什么神经网络,卷积神经网络车牌识别
排序归纳 Java版
dbLinq最新版linq sqlite
阿里内部面试官手册熬夜也要啃完的,吃透直接拿下大厂offer
百趣代谢组学资讯:植物挥发性有机物生物合成机理及抗菌性研究IF14.46
自定义注解+AOP实现字典值的翻译
透明度和透明贴图制作玻璃水杯
Spring Boot——Thymeleaf生成PDF实战教程
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/hhhhhhhhhtr/article/details/126478968
