-
VS2015+windows10编译配置Ceres库
一、准备工作:软件下载
1、cmake:是一种跨平台的编译工具,它可以应用于Windows、Linux等系统
2、VS2015:这就不用怎么介绍了,使用很广泛的一个软件。
3、Eigen:一个矩阵库,Ceres官方建议下载3.3版本及之上的Eigen包。
4、glog:在Ceres中,glog被广泛用于记录关于内存分配、解决过程中不同部分所消耗的时间、内部错误情况等详细信息。
5、gflags:一套命令行参数解析工具,比getopt功能更强大,使用起来更加方便,gflags还支持从环境变量、配置文件读取参数,通常需要依赖于glog。
6、Ceres:一个开源的c++库,用于建模和解决大型、复杂的优化问题。它可用于求解有界约束的非线性最小二乘问题和一般的无约束优化问题。它是一个成熟的、功能丰富的和性能良好的库,自2010年以来一直在谷歌上用于生产。由于这里我使用的是VS2015,所以Ceres版本选择了V1.14.0;若是VS2019或VS2022,可以下载最新的版本。
上述的相关包的源代码均可以在GitHub中进行下载。注:由于以前SuiteSparse在Windows上是不可用的,所以VS2015并不需要编译SuiteSparse库,最近该库已经支持了Windows系统,不过只有VS2019和VS2022支持对该库的调用。二、实现过程
其中的Eigen、glog以及gflags库,均是正常的cmake操作,指定源目录和构建目录,点击configure和generate即可。之后在各个项目中进行编译、安装。
在上述的库全部都编译安装好了之后,就可以编译Ceres了,如下所示:
1、指定源目录和构建目录。

2、对CMake进行如下设置。

Eigen_Dir也需要指定相关的路径"_"。

这里修改一下Ceres的安装路径,方便后续的使用。
3、之后点击configure与generate生成VS项目。
4、对Ceres进行编译与安装。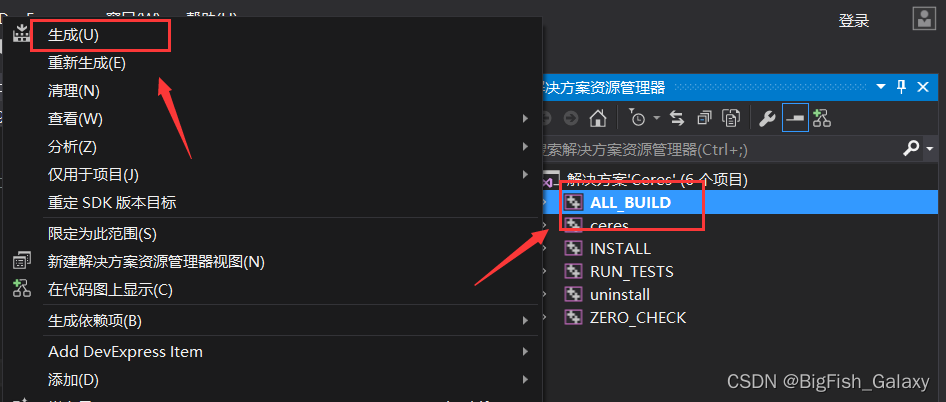

最终的效果:
5、最后,添加相关的环境变量,方便后面程序的调用。

三、实现效果
添加一个Ceres示例:
#include#include using namespace std; using namespace ceres; struct CostFunctor { template <typename T> bool operator()(const T* const x, T* residual) const { residual[0] = 10.0 - x[0]; return true; } }; int main(int argc, char** argv) { google::InitGoogleLogging(argv[0]); // The variable to solve for with its initial value. double initial_x = 5.0; double x = initial_x; // Build the problem. Problem problem; // Set up the only cost function (also known as residual). This uses // auto-differentiation to obtain the derivative (jacobian). CostFunction* cost_function = new AutoDiffCostFunction<CostFunctor, 1, 1>(new CostFunctor); problem.AddResidualBlock(cost_function, nullptr, &x); // Run the solver! Solver::Options options; options.linear_solver_type = ceres::DENSE_QR; options.minimizer_progress_to_stdout = true; Solver::Summary summary; Solve(options, &problem, &summary); std::cout << summary.BriefReport() << "\n"; std::cout << "x : " << initial_x << " -> " << x << "\n"; system("pause"); return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45

参考资料
-
相关阅读:
linux奇技淫巧
flink 8081 web页面无法被局域网内其他机器访问
MobLink iOS端快速集成文档
Elasticsearch:Rank feature query - 排名功能查询
小程序中计算距离信息
【教3妹学编程-java基础6】详解父子类变量、代码块、构造函数执行顺序
harbor portal密码错误
Centos升级Openssh版本至openssh-9.3p2
ROS2 中的轻量级、自动化、受控回放
【SQL解析】- Druid SQL AST 01
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/dayuhaitang1/article/details/126494164
