-
外边距合并出现bug的两种情况
1.相邻块元素垂直外边距的合并
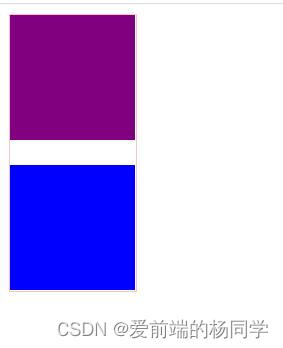
<style> .box { width: 100px; height: 220px; border: 1px solid pink; } .box1 { width: 100%; height: 100px; background-color: purple; margin-bottom: 5px; } .box2 { width: 100%; height: 100px; background-color: blue; margin-top: 20px; } style> head> <body> <div class="box"> <div class="box1">div> <div class="box2">div> div> body>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
当上下相邻的两个块级元素(兄弟关系)相遇时,如果上面的元素有下外边距 margin-bottom,下面的元素有上外边距 margin-top,则它们之间的垂直间距不是margin-bottom和margin-top之和。而是
取两个值中的较大者。

解决方案:
尽量只给一个盒子添加margin值。
2.嵌套块元素垂直外边距的塌陷

<style> .father { width: 200px; height: 220px; background-color: pink; margin-top: 20px; } .child { width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color: purple; margin-bottom: 5px; margin-top: 40px; } style> head> <body> <div class="father"> <div class="child">div> div> body>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
对于两个嵌套关系(父子关系)的块级元素,父元素有上外边距,同时子元素也有上外边距,此时父元素会塌陷较大的外边距值。
解决方案:
(1)可以为父元素定义上边框。
(2)可以为父元素定义上内边距。
(3)可以为父元素添加 overflow:hidden。<style> .father { width: 200px; height: 220px; background-color: pink; margin-top: 20px; /* border-top: 1px solid black; */ /* padding-top: 1px; */ overflow: hidden; } .child { width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color: purple; margin-bottom: 5px; margin-top: 40px; } style> head> <body> <div class="father"> <div class="child">div> div> body>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26

-
相关阅读:
json-server搭建mock服务
vue_day3
【JavaEE】锁策略、CAS和synchronized的优化
python+django固定资产管理系统项目源码
vue3 v-html中使用v-viewer
【深入浅出 Yarn 架构与实现】6-3 NodeManager 分布式缓存
CentOS 7 安装 JDK11(注意版本号要与自己的版本一致)
数据类型优化
游戏性能优化
node.js基础
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_55879104/article/details/126474049
