-
【数据结构阶级】链表面试题(万字详解带你手撕链表)
大家好我是沐曦希💕
1.移除链表元素
题目链接:203. 移除链表元素

方法一
直接在原头节点进行删除。
第一种情况:头节点的val不等于给的val,此时只要边遍历边删除就可以了。

第二种情况:头节点的val等于给的val,此时要更改头节点head的指向,指向下一个节点,再继续遍历。

struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val){ struct ListNode* cur = head; struct ListNode* prev = NULL; while(cur) { if(cur->val == val) { if(cur==head) { head = head->next; free(cur); cur=head; } else { prev->next=cur->next; free(cur); cur=prev->next; } } else { prev=cur; cur=cur->next; } } return head; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
方法二
把不是val的节点尾插到新链表中。

struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val){ struct ListNode* cur = head; struct ListNode* newhead = NULL; struct ListNode* tail = NULL; while(cur) { if(cur->val !=val) { if(tail==NULL) { tail = cur; newhead = tail; } else { tail->next = cur; tail = tail->next; } } else { struct ListNode* del = cur; cur = cur->next; free(del); } } tail->next = NULL; return newhead; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
方法三
可以在通过增加哨兵位的方法来解决,这样可以不用分开来更改新链表的指向。这里要注意的是:返回的应该是新链表的下一个节点,因为哨兵位是我们新增的,没有值的。

struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val){ struct ListNode* newhead = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode)); newhead->next = NULL; struct ListNode* tail = newhead; struct ListNode* cur = head; struct ListNode* next = head; while(cur) { if(cur->val!=val) { next = cur->next; tail->next = cur; tail = tail->next; cur = next; } else { next = cur->next; free(cur); cur = next; } } tail->next = NULL; head = newhead->next; free(newhead); return head; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
2.反转链表
题目链接:206. 反转链表

方法一
1.一次取一个节点头插到新链表中,一个指针cur来头插节点,另一个指针来记录下一个节点的位置。每次插入节点时候,把改节点的next指向newhead的节点,每插入一个节点newhead就更改一下位置即newhead指向cur的节点。最后cur指向next的节点。

struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head) { struct ListNode* newhead = NULL; struct ListNode* cur = head; struct ListNode* next = head; while(cur) { next = cur->next; cur->next = newhead; newhead = cur; cur = next; } return newhead; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
方法二
通过三个指针在原链表进行逆置。

struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head) { struct ListNode* n1 =NULL; struct ListNode* n2 =head; struct ListNode* n3 =head; while(n2) { n3 = n2->next; n2->next = n1; n1 = n2; n2 = n3; } return n1; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
3.链表的中间结点
题目链接:876. 链表的中间结点

有两种求解方法:
第一种:暴力求解,先遍历一遍,求出链表的长度,在通过另一个指针走链表长度的一半,改指针所指的节点为链表的中间节点。
第二种方法:只遍历一遍,通过快指针fast每次走两步,慢指针slow一次走一步。当fast走到尾节点或者fast为NULL时候,slow所指的节点即为链表的中间节点。

struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head){ struct ListNode* fast = head; struct ListNode* slow = head; while(fast && fast->next) { fast = fast->next->next; slow = slow->next; } return slow; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
4.链表中倒数第k个结点
题目链接:链表中倒数第k个结点

方法一
暴力求解,先用tail指针遍历一遍链表,求出链表的长度count,最后通过另一个指针走(count-k)步。
struct ListNode* FindKthToTail(struct ListNode* pListHead, int k ) { // write code here struct ListNode* cur = pListHead; struct ListNode* node = pListHead; int count = 0; while(cur!=NULL) { count++; cur = cur->next; } if(k>count) return NULL; int i = 0; while(i<(count-k)) { i++; node = node->next; } return node; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
方法二
通过快慢指针来求解,快指针fast先走k步,之后快慢指针一起走,一次走一步,当fast为NULL时候,slow即为链表中倒数第k个节点。
注意:k有可能大于链表的长度,所以在快指针先走时候,应该检查一下fast是否为NULL,如果fast为NULL,返回NULL。
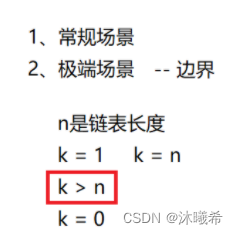

struct ListNode* FindKthToTail(struct ListNode* pListHead, int k ) { // write code here struct ListNode* fast = pListHead; struct ListNode* slow = pListHead; while(k--) { if(fast==NULL) { return NULL; } fast = fast->next; } while(fast) { fast = fast->next; slow = slow->next; } return slow; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
5.合并两个有序链表
题目链接:21. 合并两个有序链表

此时可以创建一个有哨兵位的新链表,通过比较链表一和二,把小的尾插到新链表中。如果链表一或者二其中一个已经尾插完,直接把未尾插的节点直接尾插到新链表中。
注意的是新链表的尾节点的next必须为NULL。struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2) { struct ListNode* newhead = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode)); newhead->next = NULL; struct ListNode* cur1 = list1; struct ListNode* cur2 = list2; struct ListNode* tail = newhead; while(cur1!=NULL&&cur2!=NULL) { if(cur1->val<cur2->val) { tail->next = cur1; cur1=cur1->next; } else { tail->next = cur2; cur2 = cur2->next; } tail = tail->next; } if(cur1!=NULL) { tail->next = cur1; } else if(cur2!=NULL) { tail->next = cur2; } struct ListNode* head = newhead->next; free(newhead); return head; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
6.分割链表
Leetcode题目链接: 面试题 02.04. 分割链表
牛客题目链接:CM11 链表分割


此时可以设置两个新带哨兵位的链表(带哨兵位会很方便),一个链表用来尾插比x小的节点,另一个链表用来尾插比x大的节点。最后将大于x的链表尾插到小于x的链表中。
注意:大的链表的尾节点必须为NULL。极端场景:1.所有值都比x小。
2.所有值都比x大。
3.空链表
4.最后一个值小于x,倒数第二个值大于x。

struct ListNode* partition(struct ListNode* head, int x){ struct ListNode* lessGuard = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode)); lessGuard->next = NULL; struct ListNode* lesstail = lessGuard; struct ListNode* greaterGuard = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode)); greaterGuard->next = NULL; struct ListNode* greatertail = greaterGuard; struct ListNode* cur = head; while(cur) { if(cur->val<x) { lesstail->next = cur; lesstail = lesstail->next; } else { greatertail->next = cur; greatertail = greatertail->next; } cur = cur->next; } greatertail->next = NULL; lesstail->next = greaterGuard->next; free(greaterGuard); head = lessGuard->next; free(lessGuard); return head; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
7.回文链表
Leetcode题目链接:剑指 Offer II 027. 回文链表
牛客题目链接:OR36 链表的回文结构

那么可以通过快慢指针来找到链表的中间节点,然后逆转中间节点之后的节点。用一个rmid指针来接受逆转后的头节点,通过一一比对rmid和head的节点,直到rmid或者head其中一个为空。
需要注意的是中间节点的前一个节点的next依然指向中间的那个节点。
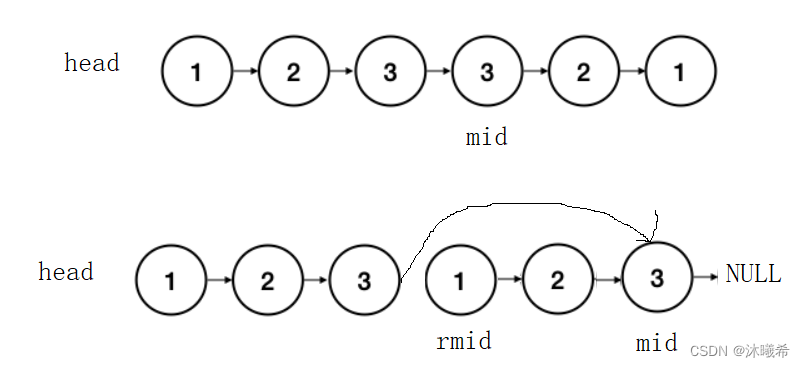
struct ListNode* MiddleNode(struct ListNode* head) { struct ListNode* fast = head; struct ListNode* slow = head; while(fast && fast->next) { fast = fast->next->next; slow = slow->next; } return slow; } struct ListNode* ReverseList(struct ListNode* head) { struct ListNode* n1 = NULL; struct ListNode* n2 = head; struct ListNode* n3 = head; while(n2) { n3 = n3->next; n2->next = n1; n1 = n2; n2 = n3; } return n1; } bool isPalindrome(struct ListNode* head){ struct ListNode* mid = MiddleNode(head); struct ListNode* rmid = ReverseList(mid); while(rmid && head) { if(head->val != rmid->val) { return false; } head = head->next; rmid = rmid->next; } return true; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
8.相交链表
题目链接:160. 相交链表




这里需要注意的是不能比对节点的val是否相等,应该比对节点的地址。
首先应该判断链表A和链表B是否相交,可以想到不管在哪个节点相交的两个链表的尾节点的地址必相等。
那么此时就可以设两个指针tailA和tailB,分别遍历A链表和B链表,并用lenA和lenB分别记录链表A和链表B的长度。
最后通过快慢指针来来找到相交的节点,长度较短的为慢指针,长度较长的为快指针,快指针先走差距k步(k=abs(lenA-lenB))。之后快慢指针同时走,每次走一步。

struct ListNode *getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB) { struct ListNode* curA = headA; struct ListNode* curB = headB; if(headA==NULL || headB==NULL) { return NULL; } int lenA = 1; while(curA->next) { ++lenA; curA = curA->next; } int lenB = 1; while(curB->next) { ++lenB; curB = curB->next; } if(curA!=curB) { return NULL; } int gap = abs(lenA - lenB); struct ListNode* longlist = headA; struct ListNode* lesslist = headB; if(lenA<lenB) { longlist = headB; lesslist = headA; } while(gap--) { longlist = longlist->next; } while(longlist != lesslist) { longlist = longlist->next; lesslist = lesslist->next; } return longlist; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
9.环形链表
题目链接:141. 环形链表

环形链表:

可以通过快慢指针来求解,快指针一次走两步,慢指针一次走一步。当快指针fast进入环时,慢指针slow未进入环。当慢指针进入环时,快指针已经在环上走了。此时就变成了快指针追赶慢指针的问题了。
设它们之间距离为N,一次距离缩减1步,那么N终有一次被缩减为0,此时快指针就追上了慢指针。那么就可以说明该链表是有环的,返回true。
当fast或者fast->next为NULL时,说明改链表没有环,返回false。

bool hasCycle(struct ListNode *head) { struct ListNode* fast = head; struct ListNode* slow = head; while(fast && fast->next) { fast = fast->next->next; slow = slow->next; if(slow == fast) { return true; } } return false; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
如果slow一次走一步,fast走一次走三步,fast是否能追上slow?
答案是不一定
假设slow进环以后,fast和slow之间差距为N。设C为环的长度。
每追赶一次,距离缩减2步。
分情况讨论:
1.当N是偶数时:距离:N->N-2->N-4->N-6…2-> 0,会追上。
2.当N是奇数时:距离:N->N-2->N-4->N-6…3->1->-1,它们之间距离变成了C-1,即fast在slow的前面一个位置。
(如果想要判断环的话,可以加判断条件:if(slow==fast||slow->next==fast))
那么此时又要分C为奇数和偶数。
当C为奇数时,C-1为偶数,那么(C-1)%2 = 0,那么再追一圈可以追上。
当C为偶数时,C-1为奇数,那么(C-1)%2 = 1,那么不可能追上。

如果slow一次走一步,fast走一次走x步,fast是否能追上slow?
答案是不一定
假设slow进环以后,fast和slow之间差距为N。设C为环的长度。
每追赶一次,距离缩减x-1步。- 当x=1时,此时fast和slow并排同行。
- 当x!=1时,分两种情况:
2.1. 当N%(x-1)=0时,fast能追上slow。
2.2.当N%(x-1)!=0时,那么它们之间的差距又变成了C-x+2。
又要分情况讨论:
2.2.1当(C-x+2)%(x-1)=0时,fast可以追上slow。
2.2.2当(C-x+2)%(x-1)!=0时,fast追不上slow。
如果slow一次走y步,fast走一次走x步,fast是否能追上slow?
答案是不一定【扩展问题】
为什么快指针每次走两步,慢指针走一步可以?
假设链表带环,两个指针最后都会进入环,快指针先进环,慢指针后进环。当慢指针刚进环时,可能就和快指针相遇了,最差情况下两个指针之间的距离刚好就是环的长度。此时,两个指针每移动一次,之间的距离就缩小一步,不会出现每次刚好是套圈的情况,因此:在满指针走到一圈之前,快指针肯定是可以追上慢指针的,即相遇。
快指针一次走3步,走4步,…n步行吗?

10.环形链表 II
题目链接:142.环形链表 II

此时应该找到相遇点,可以通过快慢指针来找到相遇点,快指针fast一次走两步,慢指针slow一次走一步。slow和fast相遇时则为相遇点。
struct ListNode* fast = head; struct ListNode* slow = head; while(fast && fast->next) { fast = fast->next->next; slow = slow->next; if(slow==fast) { break; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
方法一
公式证明:
结论:
让一个指针从链表起始位置开始遍历链表,同时让一个指针从判环时相遇点的位置开始绕环运行,两个指针都是每次均走一步,最终肯定会在入口点的位置相遇。
证明:

truct ListNode *detectCycle(struct ListNode *head) { struct ListNode* fast = head; struct ListNode* slow = head; while(fast && fast->next) { fast = fast->next->next; slow = slow->next; if(slow==fast) { break; } } struct ListNode* cur = head; while(cur&&fast&&cur->next) { if(cur==fast) { return fast; } fast = fast->next; cur = cur->next; } return NULL; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
方法二
转换成两个链表相交的问题,通过一个meet指针来记录相遇节点和以meet->next节点为新链表的头newhead,并把meet->next置为空,在最后再把meet->next置为新节点的头newhead。因为题目明确要求了不能更改链表的结构。
通过一一比对原链表head和新链表newhead的节点的地址是否一样,从而确定环的入口节点。

struct ListNode* getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode* headA, struct ListNode* headB) { if (headA == NULL || headB == NULL) { return NULL; } struct ListNode* curA = headA, * curB = headB; int lenA = 1; //找尾节点 while (curA->next) { curA = curA->next; ++lenA; } int lenB = 1; while (curB->next) { curB = curB->next; ++lenB; } if (curA != curB) { return NULL; } struct ListNode* longList = headA, * shortList = headB; if (lenA < lenB) { longList = headB; shortList = headA; } //长的链表先走差距步 int gap = abs(lenA - lenB); while (gap--) { longList = longList->next; } //同时走找交点 while (longList != shortList) { longList = longList->next; shortList = shortList->next; } return longList; } struct ListNode* detectCycle(struct ListNode* head){ struct ListNode* slow = head, * fast = head; while (fast && fast->next) { slow = slow->next; fast = fast->next->next; if (slow == fast) { //转换相交 struct ListNode* meet = slow; struct ListNode* next = meet->next; meet->next = NULL; struct ListNode* entryNode = getIntersectionNode(head, next); //恢复环 meet->next = next; return entryNode; } } return NULL; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
11.复制带随机指针的链表
题目链接:138.复制带随机指针的链表


struct Node* copyRandomList(struct Node* head) { //copy节点 struct Node* cur = head; struct Node* copy = NULL; struct Node* next = NULL; while (cur) { //赋值链接 next = cur->next; copy = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); copy->val = cur->val; cur->next = copy; copy->next = next; //迭代 cur = next; } //更新copy的random cur = head; while (cur) { copy = cur->next; if (cur->random == NULL) { copy->random = NULL; } else { copy->random = cur->random->next; } //迭代 cur = cur->next->next; } //copy节点解下来链接在一起,恢复原链表 struct Node* copyHead = NULL, * copyTail = NULL; cur = head; while (cur) { copy = cur->next; next = copy->next; //取节点尾插 if (copyTail == NULL) { copyHead = copyTail = copy; } else { copyTail->next = copy; copyTail = copyTail->next; } //恢复原链表 cur->next = next; cur = next; } return copyHead; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
12.写在最后
那么链表的面试题就到这里了。

-
相关阅读:
django的update和create高级操作
OpenLayer通过WMTSCapabilities.xml加载GeoServer发布的标准vmts地图服务
线程的状态简介说明
golang---锁
常见的linux命令
SpringCloud面试题(附源码)
点云深度学习——点云配准网络DCP复现
ref实现input自动获取光标并执行多次
Kubernetes学习-概念2
刚爆火就下线的 ZAO 换脸,背后是另一场技术人的狂欢
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_68931081/article/details/126087569