-
39.【C/C++ 全局变量和局部变量 (详解)】
(一)、什么是全局变量
全局变量也称外部变量,是编程中的一种术语,对象函数是在外部定义变量,也可以在程序任何地方进行创建,当然也可以是程序和对象进行引用。
(二)、全局变量的定义
1.类外定义
#includeusing namesapce std; int a=3; int main() {} - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
2.静态定义
#incldue <iostream> using namespace std; static int a=3; int main() {}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
3.宏定义
#incldue <iostream> using namespace std; #define PI 3.1415962 int main().{}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
(三)、全局变量的访问
::变量名- 1
代码展示
#includeusing namespace std; int a = 10; int main() { int a = 3; cout << "局部变量a的值是:" << a << endl; ::a; cout << "全局变量a的值是:" << ::a << endl; int c; c=(a += a); cout << "局部变量a的和为:" << c << endl; int d; d = (a += ::a); cout << "改变后的局部变量a(即做了加法后)与全局变量a的和为:" << d << endl; return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
效果展示:

(四)、全局变量和局部变量
当全局变量与局部变量同名时:在定义局部变量的子程序内,局部变量起作用:在其它地方全局变量起作用.
①【定义一个局部不同名,一个局部同名。不同函数体】
代码展示:
#includeusing namespace std; int a = 0; void fun1() { int b = 3; //定义不同名局部变量 a += 5+b; } void fun2() { int a = 0; //定义同名局部变量. a += 10; } int main() { cout << a << endl; fun1(); cout << a << endl; fun2(); cout << a << endl; return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
效果展示:

②【定义一个局部不同名,一个局部同名。同一个函数体】
代码展示
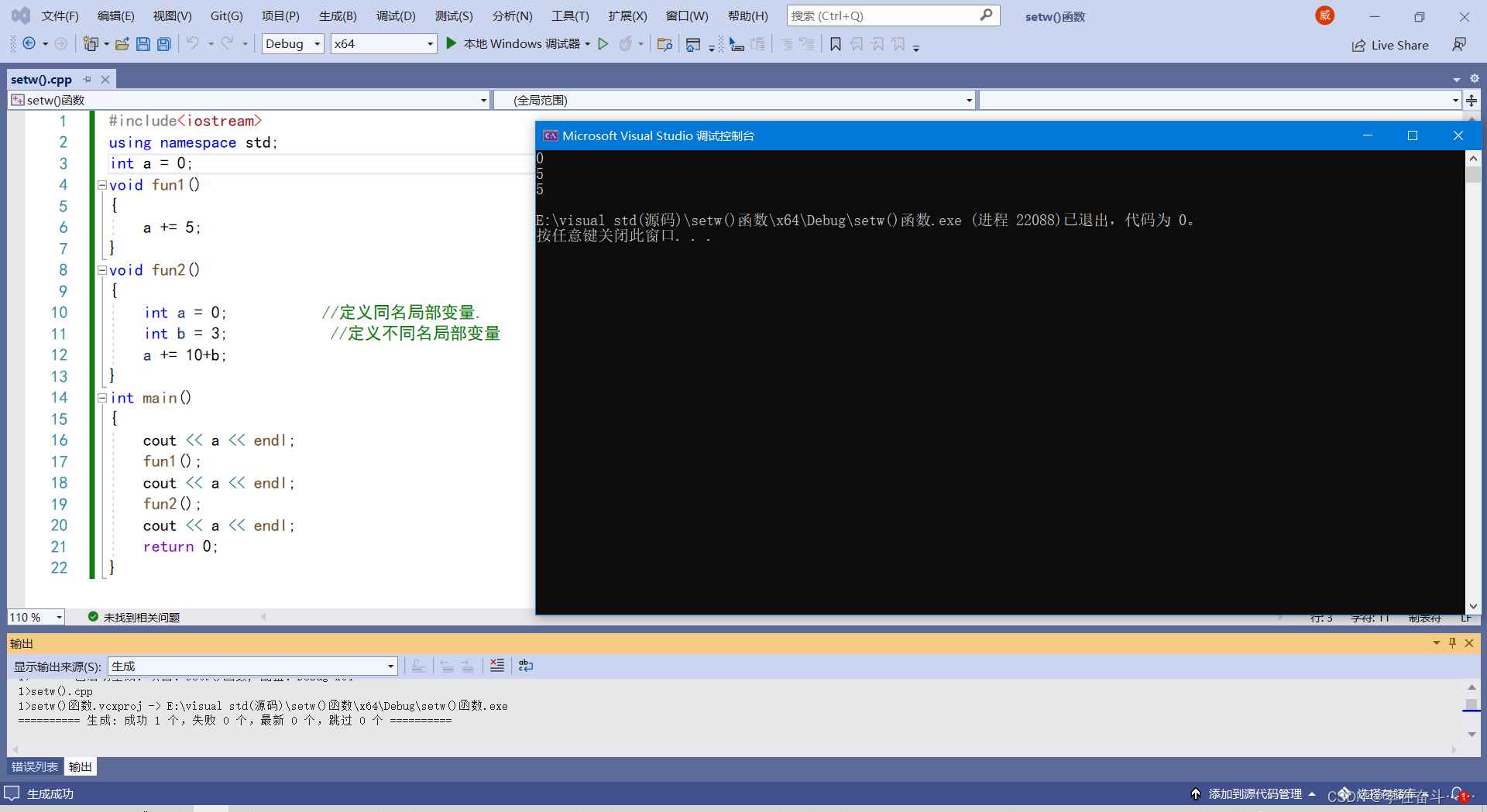
#includeusing namespace std; int a = 0; void fun1() { a += 5; } void fun2() { int a = 0; //定义同名局部变量. int b = 3; //定义不同名局部变量 a += 10+b; } int main() { cout << a << endl; fun1(); cout << a << endl; fun2(); cout << a << endl; return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
效果展示:

完结!!!!! 如有不解,可私聊 -
相关阅读:
集成hibeaver的血泪史 -- Ambiguous method overloading for method java.io.File#<init>
【python学习】AC自动机 高效敏感词过滤与文本匹配:全面掌握pyahocorasick库 (NLP自然语言处理项目实战)
Java开发基础_04
小程序自定义tabBar——原生
Linux下 Mysql 互为主从
Java:既然有了synchronized,为什么还要提供Lock?
基于JAVA天津城建大学校友录管理系统计算机毕业设计源码+系统+mysql数据库+lw文档+部署
分享从零开始学习网络设备配置--任务3.8 使用动态路由OSPF实现网络连通
【appium】APP元素操作Api、androidDriver操作Api
[Linux] shell脚本
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_69683957/article/details/126398200
