-
1.2 w字+!Java IO 基础知识系统总结 | JavaGuide
IO 流简介
IO 即
Input/Output,输入和输出。数据输入到计算机内存的过程即输入,反之输出到外部存储(比如数据库,文件,远程主机)的过程即输出。数据传输过程类似于水流,因此称为 IO 流。IO 流在 Java 中分为输入流和输出流,而根据数据的处理方式又分为字节流和字符流。Java IO 流的 40 多个类都是从如下 4 个抽象类基类中派生出来的。
InputStream/Reader: 所有的输入流的基类,前者是字节输入流,后者是字符输入流。OutputStream/Writer: 所有输出流的基类,前者是字节输出流,后者是字符输出流。
字节流
InputStream(字节输入流)
InputStream用于从源头(通常是文件)读取数据(字节信息)到内存中,java.io.InputStream抽象类是所有字节输入流的父类。InputStream常用方法 :read():返回输入流中下一个字节的数据。返回的值介于 0 到 255 之间。如果未读取任何字节,则代码返回-1,表示文件结束。read(byte b[ ]): 从输入流中读取一些字节存储到数组b中。如果数组b的长度为零,则不读取。如果没有可用字节读取,返回-1。如果有可用字节读取,则最多读取的字节数最多等于b.length, 返回读取的字节数。这个方法等价于read(b, 0, b.length)。read(byte b[], int off, int len):在read(byte b[ ])方法的基础上增加了off参数(偏移量)和len参数(要读取的最大字节数)。skip(long n):忽略输入流中的 n 个字节 ,返回实际忽略的字节数。available():返回输入流中可以读取的字节数。close():关闭输入流释放相关的系统资源。
从 Java 9 开始,
InputStream新增加了多个实用的方法:readAllBytes():读取输入流中的所有字节,返回字节数组。readNBytes(byte[] b, int off, int len):阻塞直到读取len个字节。transferTo(OutputStream out): 将所有字节从一个输入流传递到一个输出流。
FileInputStream是一个比较常用的字节输入流对象,可直接指定文件路径,可以直接读取单字节数据,也可以读取至字节数组中。FileInputStream代码示例:try (InputStream fis = new FileInputStream("input.txt")) { System.out.println("Number of remaining bytes:" + fis.available()); int content; long skip = fis.skip(2); System.out.println("The actual number of bytes skipped:" + skip); System.out.print("The content read from file:"); while ((content = fis.read()) != -1) { System.out.print((char) content); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }input.txt文件内容: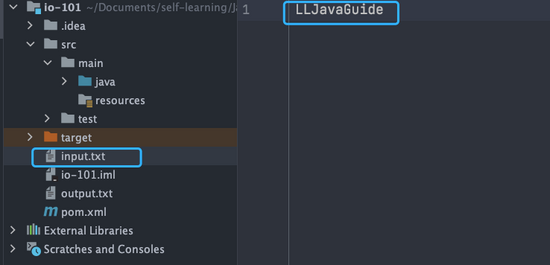
输出:
Number of remaining bytes:11 The actual number of bytes skipped:2 The content read from file:JavaGuide
不过,一般我们是不会直接单独使用
FileInputStream,通常会配合BufferedInputStream(字节缓冲输入流,后文会讲到)来使用。像下面这段代码在我们的项目中就比较常见,我们通过
readAllBytes()读取输入流所有字节并将其直接赋值给一个String对象。// 新建一个 BufferedInputStream 对象 BufferedInputStream bufferedInputStream = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("input.txt")); // 读取文件的内容并复制到 String 对象中 String result = new String(bufferedInputStream.readAllBytes()); System.out.println(result);DataInputStream用于读取指定类型数据,不能单独使用,必须结合FileInputStream。FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("input.txt"); //必须将fileInputStream作为构造参数才能使用 DataInputStream dataInputStream = new DataInputStream(fileInputStream); //可以读取任意具体的类型数据 dataInputStream.readBoolean(); dataInputStream.readInt(); dataInputStream.readUTF();ObjectInputStream用于从输入流中读取 Java 对象(反序列化),ObjectOutputStream用于将对象写入到输出流(序列化)。ObjectInputStream input = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("object.data")); MyClass object = (MyClass) input.readObject(); input.close();另外,用于序列化和反序列化的类必须实现
Serializable接口,对象中如果有属性不想被序列化,使用transient修饰。OutputStream(字节输出流)
OutputStream用 -
相关阅读:
ClickHouse—物理机部署
MinIO实现数据迁移(mc)
#include <> 与 #include “ “ : 尖括号和双撇号的区别、何时用
【QT系列教程】之二创建项目和helloworld案例
超牛逼的 Feed 流系统设计!
【云原生】K8S--负载均衡详细介绍;什么是K8S的负载均衡?
Vue - 实现任意内容展开 / 收起功能组件(支持自定义高度、动态展开与折叠、自定义展开与收起文案、动态增删数据自动计算高度、过渡动画等)
【毕业设计】深度学习行人车辆流量计数系统 - 目标检测 python
css:两栏三栏布局
线下实体店铺会员引流的四种方法-未完待续
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/lt_xiaodou/article/details/126408919