-
Linux学习之:进程间通信(匿名管道、命名管道、共享内存)
进程间通信目的
1.数据传输:一个进程需要将它的数据发送给另一个进程
2.资源共享:多个进程之间共享同样的资源。
3.通知事件:一个进程需要向另一个或一组进程发送消息,通知它(它们)发生了某种事件(如进程终止时要通知父进程)。
4.进程控制:有些进程希望完全控制另一个进程的执行(如Debug进程),此时控制进程希望能够拦截另一个进程的所有陷入和异常,并能够及时知道它的状态改变。

进程间通信分类
管道
1.匿名管道pipe
2.命名管道System V IPC
1.System V 消息队列
2.System V 共享内存
3.System V 信号量POSIX IPC
1.消息队列
2.共享内存
3.信号量
4.互斥量
5.条件变量
6.读写锁匿名管道(半双工)
父子进程间匿名管道通信基本原理

站在文件描述符角度-深度理解管道

Linux匿名管道函数

匿名管道的限制


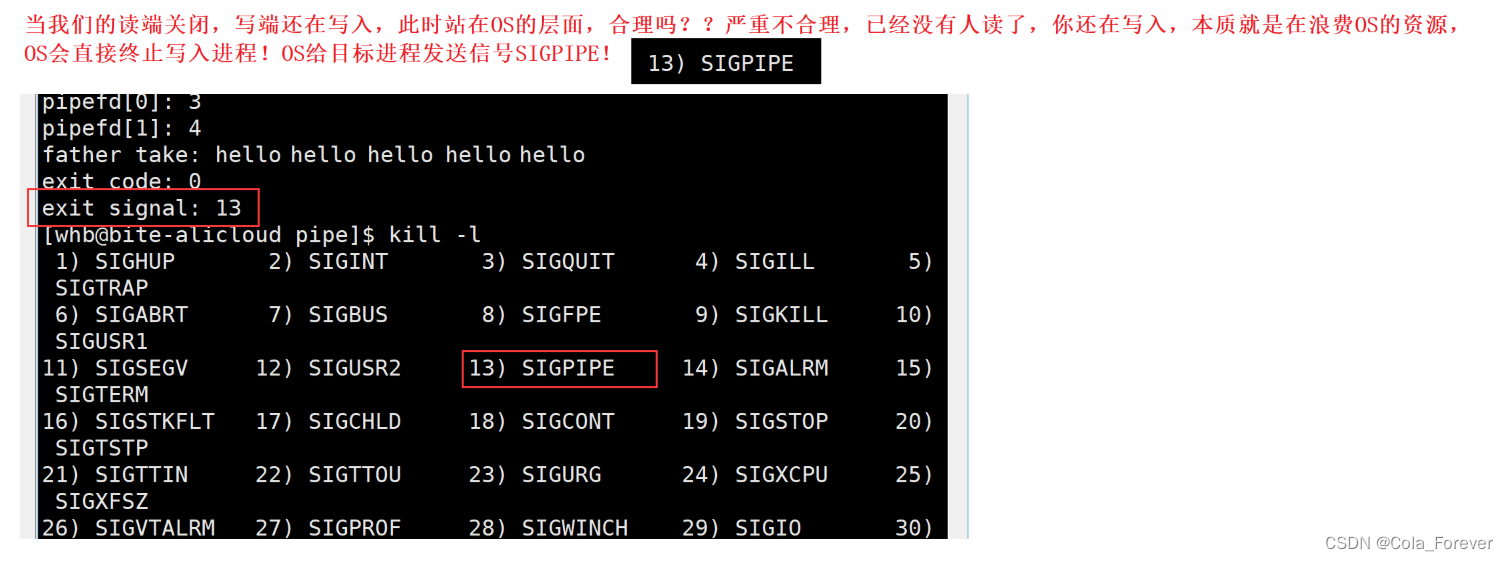
匿名管道总结(重要!看总结就可以了解基本机制了)

匿名管道实验代码(很简单)
#include#include #include #include #include int main() { int pipe_fd[2] = {0}; if(pipe(pipe_fd) < 0){ perror("pipe"); return 1; } printf("%d, %d\n", pipe_fd[0], pipe_fd[1]); int id = fork(); if(id < 0){ perror("fork"); return 2; } else if(id == 0) { //write //child close(pipe_fd[0]); const char *msg = "hello parent, I am child"; while(1){ write(pipe_fd[1], msg, strlen(msg)); //strlen(msg) + 1?? sleep(1); } close(pipe_fd[1]); exit(0); } else{ //read //parent close(pipe_fd[1]); char buffer[64]; while(1){ //sleep(100); buffer[0] = 0; ssize_t size = read(pipe_fd[0], buffer, sizeof(buffer)-1); if(size > 0){ buffer[size] = 0; printf("parent get messge from child# %s\n", buffer); } else if(size == 0){ printf("pipe file close, child quit!\n"); break; } else{ //TODO break; } } // int status = 0; // if(waitpid(id, &status,0) > 0){ // printf("child quit, wait success!, sig: %d\n", status&0x7F); // } close(pipe_fd[0]); } return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
命名管道(半双工,最多64KB,与匿名管道相同,都是管道文件,只不过实现方式不同)
管道应用的一个限制就是只能在具有共同祖先(具有亲缘关系)的进程间通信。
如果我们想在不相关的进程之间交换数据,可以使用FIFO文件来做这项工作,它经常被称为命名管道。
命名管道是一种特殊类型的文件命名管道通信原理

创建命名管道函数

匿名管道与命名管道的区别
匿名管道由pipe函数创建并打开。
命名管道由mkfifo函数创建,打开用open
FIFO(命名管道)与pipe(匿名管道)之间唯一的区别在它们创建与打开的方式不同,一但这些工作完
成之后,它们具有相同的语义。

命名管道实验代码(搞懂匿名与命名区别基本就都会了)
server.c
#include "comm.h" #include#include #include #include int main() { umask(0); if(mkfifo(MY_FIFO, 0666) < 0){ perror("mkfifo"); return 1; } //只需要文件操作即可 int fd = open(MY_FIFO, O_RDONLY); if(fd < 0){ perror("open"); return 2; } //业务逻辑,可以进行对应的读写了 while(1){ char buffer[64] = {0}; sleep(50); ssize_t s = read(fd, buffer, sizeof(buffer)-1); //键盘输入的时候,\n也是输入字符的一部分 if(s > 0){ //success buffer[s] = 0; if(strcmp(buffer, "show") == 0){ if(fork() == 0){ execl("/usr/bin/ls", "ls", "-l", NULL); exit(1); } waitpid(-1, NULL, 0); } else if(strcmp(buffer, "run") == 0){ if(fork() == 0){ execl("/usr/bin/sl", "sl", NULL); } waitpid(-1, NULL, 0); } else{ printf("client# %s\n", buffer); } } else if(s == 0){ //peer close printf("client quit ...\n"); break; } else{ //error perror("read"); break; } } close(fd); return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
client.c
#include "comm.h" //此时是不是两个程序,又能看到同一个资源的能力啦! #includeint main() { //用不用在创建fifo?? 我只要获取即可 int fd = open(MY_FIFO, O_WRONLY); //不需要O_CREAT if(fd < 0){ perror("open"); return 1; } //业务逻辑 while(1){ printf("请输入# "); fflush(stdout); char buffer[64] = {0}; //先把数据从标准输入拿到我们的client进程内部 ssize_t s = read(0, buffer, sizeof(buffer)-1); if(s > 0){ buffer[s-1] = 0; printf("%s\n", buffer); //拿到了数据 write(fd, buffer, strlen(buffer)); //要不要-1,不需要 } } close(fd); return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
comm.h
#pragma once #include#include #include #include #include #define MY_FIFO "./fifo" - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
共享内存(全双工,是IPC通信方式中速度最快的。它的数据传输不需要通过内核,直接在物理内存上进行通信。)
共享内存区是最快的IPC形式。一旦这样的内存映射到共享它的进程的地址空间,这些进程间数据传递不再涉及到
内核,换句话说是进程不再通过执行进入内核的系统调用来传递彼此的数据

通信原理

准备工作

创建共享内存函数

修改共享内存函数


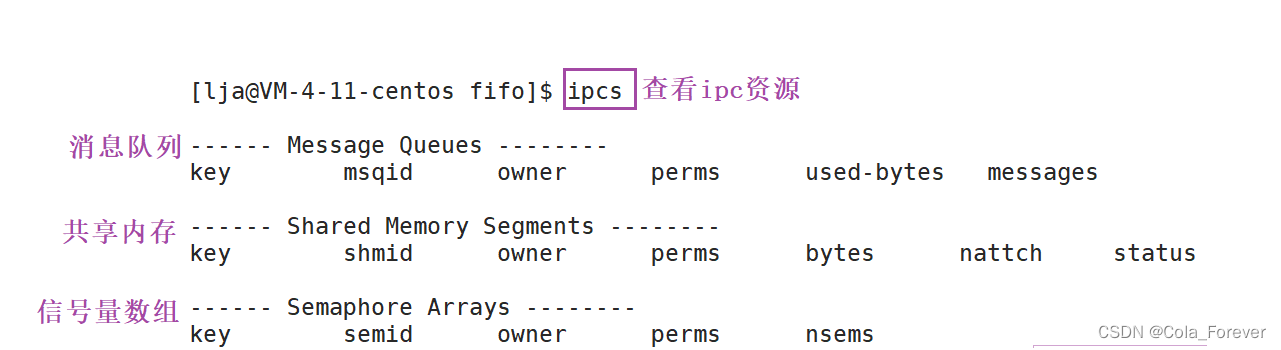

挂接与取消挂接共享内存函数

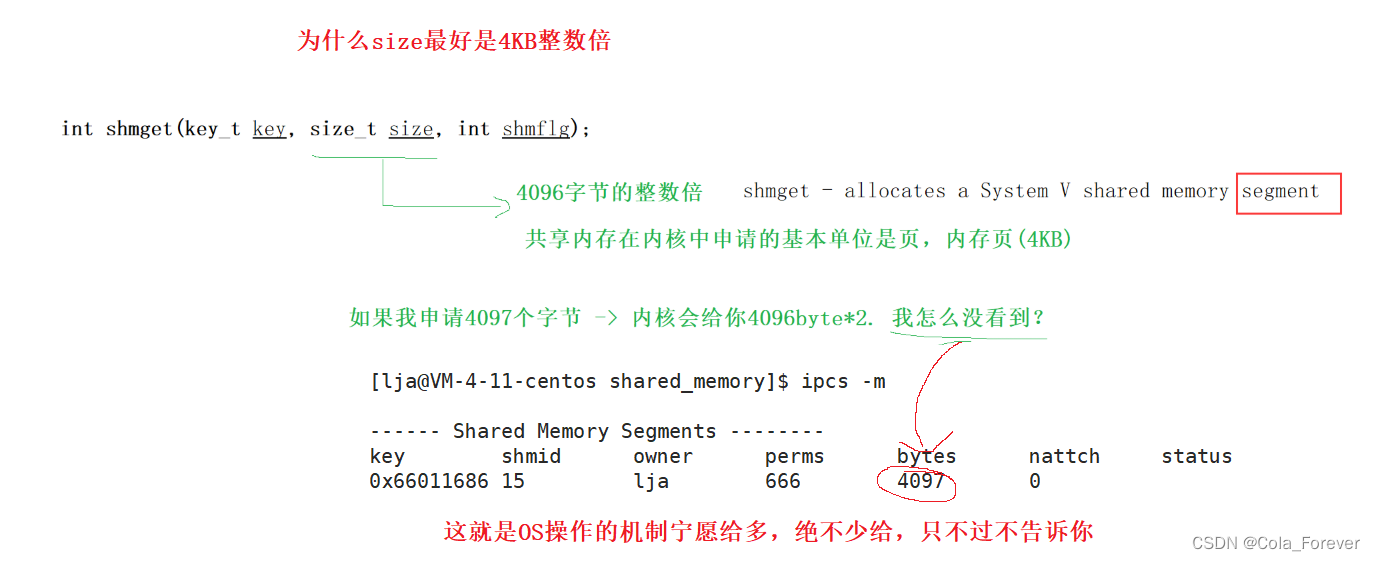
为什么size做好是4KB整数倍
命令行删除共享内存方式

为什么共享内存id是0 1 2。。。(与消息队列、信号量对比)
共享内存使用代码(搞懂每个函数都是干嘛的,使用起来就不难了)
server.c
#include"comm.h" int main() { key_t key = ftok(PATH_NAME, PROJ_ID); if(key < 0) { perror("ftok"); return 2; } int shmid = shmget(key, SIZE, IPC_CREAT|IPC_EXCL|0666); if(shmid < 0) { perror("shmget"); return 2; } printf("key: %u, shmid: %d\n", key, shmid); char * mem = (char *)shmat(shmid, NULL, 0); printf("attaches shm success\n"); //通信逻辑 //int a = 10; while(1) { sleep(1); printf("%s\n", mem); } shmdt(mem); printf("detaches shm success\n"); shmctl(shmid, IPC_RMID, NULL); printf("key: 0x%x, shmid: %d -> shm delete success\n", key, shmid); return 0; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
client.c
#include"comm.h" int main() { key_t key = ftok(PATH_NAME, PROJ_ID); if(key < 0) { perror("ftok"); return 1; } printf("%u\n", key); int shmid = shmget(key, SIZE, IPC_CREAT); if(shmid < 0) { perror("shmget"); return 2; } char * mem = (char *)shmat(shmid, NULL, 0); printf("client process attaches success!\n"); //通信逻辑 //fgets(mem, 64, stdin); char c = 'A'; while(c <= 'Z') { mem[c-'A'] = c; c++; mem[c-'A'] = 0; sleep(2); } shmdt(mem); printf("client process detaches success\n"); return 0; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
comm.h
#pragma once #include#include #include #include #include #include #define PATH_NAME "./" #define PROJ_ID 0X6666 #define SIZE 4097 - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
Makefile
.PHONY:all all:client server client:client.c gcc -o $@ $^ server:server.c gcc -o $@ $^ .PHONY:clean clean: rm -f client server- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
-
相关阅读:
使用Docker+PHP搭建苹果Maccms的影视站详细教程
拆解一下任务队列、消息队列、任务调度系统
kafka保证消息有序性
java SpringBoot基础
Mysql主从复制之skip-slave-start,slave-parallel-type,slave-parallel-workers参数详解和测试
[转]MySQL索引底层实现原理(此文个人觉得非常好收藏一下)
linux正则表达式
Nginx 市场份额全球第一,10月全球Web服务器调查报告出炉!
软件开发提效工具——低代码(Low-Code)
java设计模式之策略模式
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/jiaao666/article/details/126399373
