-
JavaSE---类和对象
1、 面向对象的初步认知
1.1 什么是面向对象
Java是一门纯面向对象的语言 (Object Oriented Program ,继承 OOP) ,在面向对象的世界里,一切皆为对象。 面 向对象是解决问题的一种思想,主要依靠对象之间的交互完成一件事情 。用面向对象的思想来涉及程序,更符合人们对事物的认知,对于大型程序的设计、扩展以及维护都非常友好。2.1 简单认识类
类是用来对一个实体( 对象 ) 来进行描述的 ,主要描述该实体 ( 对象 ) 具有哪些属性 ( 外观尺寸等 ) ,哪些功能 ( 用来干啥) ,描述完成后计算机就可以识别了。2.2 类的定义格式
在java 中定义类时需要用到 class 关键字 ,具体语法如下// 创建类class ClassName{fifield ; // 字段 ( 属性 ) 或者 成员变量method ; // 行为 或者 成员方法}class为 定义类的关键字, ClassName 为类的名字, {} 中为类的主体。类中包含的内容称为类的成员。属性主要是用来描述类的,称之为类的成员属性或者类成员变量。方法主要说明类具有哪些功能,称为类的成员方法。class WashMachine {public String brand ; // 品牌public String type ; // 型号public double weight ; // 重量public double lenght ; // 长public double weidth ; // 宽public double height ; // 高public String color ; // 颜色public void WashClothes (){ // 洗衣服System . out . println ( " 洗衣功能 " );}public void dryClothes (){ // 脱水System . out . println ( " 脱水功能 " );}public void SetTime (){ // 定时System . out . println ( " 定时功能 " );}}注意事项- 类名注意采用大驼峰定义
- 成员前写法统一为public,后面会详细解释
- 此处写的方法不带 static 关键字.
注意:1. 一般一个文件当中只定义一个类2. main 方法所在的类一般要使用 public 修饰 ( 注意: Eclipse 默认会在 public 修饰的类中找 main 方法 )3. public 修饰的类必须要和文件名相同4. 不要轻易去修改 public 修饰的类的名称,如果要修改,通过开发工具修改3、类的实例化
3.1 什么是实例化
定义了一个类,就相当于在计算机中定义了一种新的类型,与 int , double 类似,只不过 int 和 double 是 java 语言自带的内置类型,而类是用户自定义了一个新的类型,比如上述的:PetDog 类和 Student 类。它们都是类 ( 一种新定义的类型) 有了这些自定义的类型之后,就可以使用这些类来定义实例 ( 或者称为对象 ) 。用类类型创建对象的过程,称为类的实例化,在 java 中采用 new 关键字,配合类名来实例化对象。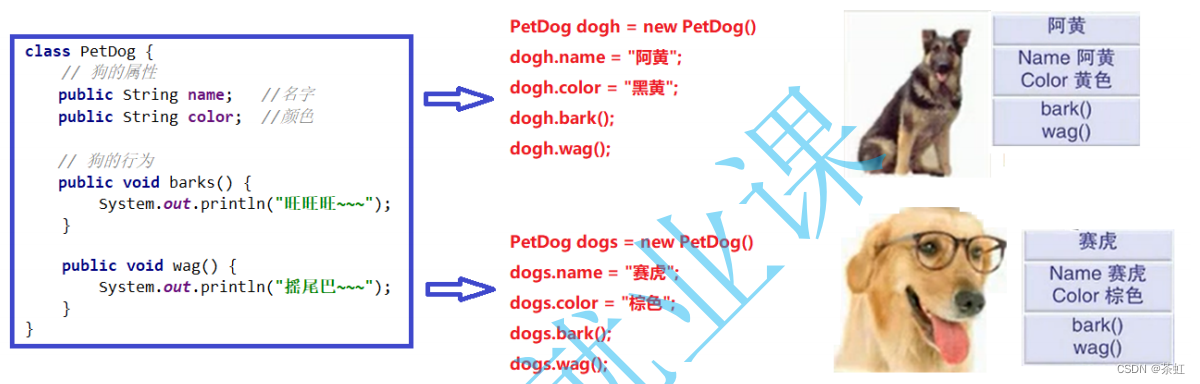
- public class Main
- {
- public static void main(String[] args)
- {
- PetDog dogh = new PetDog(); //通过new实例化对象
- dogh.name = "阿黄";
- dogh.color = "黑黄";
- dogh.barks();
- dogh.wag();
- PetDog dogs = new PetDog();
- dogs.name = "阿黄";
- dogs.color = "黑黄";
- dogs.barks();
- dogs.wag();
- }
- }
输出结果: 阿黄: 旺旺旺~~~ 阿黄: 摇尾巴~~~ 赛虎: 旺旺旺~~~ 赛虎: 摇尾巴~~~
注意事项- new 关键字用于创建一个对象的实例.
- 使用 . 来访问对象中的属性和方法.
- 同一个类可以创建对个实例.
3.2 类和对象的说明
1. 类只是 一个 模型 一样的东西,用来对一个实体进行描述,限定了类有哪些成员 .2. 类是一种自定义的类型 ,可以用来定义变量 .3. 一个类可以实例化出多个对象, 实例化出的对象 占用实际的物理空间,存储类成员变量4. 做个比方。 类实例化出对象就像现实中使用建筑设计图建造出房子,类就像是设计图 ,只设计出需要什么东西,但是并没有实体的建筑存在,同样类也只是一个设计,实例化出的对象才能实际存储数据,占用物理空间。
4、this引用
4.1 为什么要有this引用
先看一个日期类的例子:- public class Date
- {
- public int year;
- public int month;
- public int day;
- public void setDay(int y, int m, int d)
- {
- year = y;
- month = m;
- day = d;
- }
- public void printDate()
- {
- System.out.println(year + "/" + month + "/" + day);
- }
- public static void main(String[] args)
- {
- // 构造三个日期类型的对象 d1 d2 d3
- Date d1 = new Date();
- Date d2 = new Date();
- Date d3 = new Date();
- // 对d1,d2,d3的日期设置
- d1.setDay(2020,9,15);
- d2.setDay(2020,9,16);
- d3.setDay(2020,9,17);
- // 打印日期中的内容
- d1.printDate();
- d2.printDate();
- d3.printDate();
- }
- }
以上代码定义了一个日期类,然后main 方法中创建了三个对象,并通过 Date 类中的成员方法对对象进行设置和打印,代码整体逻辑非常简单,没有任何问题。但是细思之下有以下两个疑问:1. 形参名不小心与成员变量名相同 :public void setDay ( int year , int month , int day ){year = year ;month = month ;day = day ;}那函数体中到底是谁给谁赋值?成员变量给成员变量?参数给参数?参数给成员变量?成员变量参数?2. 三个对象都在调用 setDate 和 printDate 函数,但是这两个函数中没有任何有关对象的说明, setDate 和 printDate 函数如何知道打印的是那个对象的数据呢 ?
4.2 什么是this引用
this引用指向当前对象 ( 成员方法运行时调用该成员方法的对象 ) ,在成员方法中所有成员变量的操作,都是通过该 引用去访问 。只不过所有的操作对用户是透明的,即用户不需要来传递,编译器自动完成。- public class Date
- {
- public int year;
- public int month;
- public int day;
- public void setDay(int year, int month, int day)
- {
- this.year = year;
- this.month = month;
- this.day = day;
- }
- public void printDate()
- {
- System.out.println(this.year + "/" + this.month + "/" + this.day);
- }
- }
注意: this 引用的是调用成员方法的对象 。- public static void main(String[] args)
- {
- Date d = new Date();
- d.setDay(2020,9,15);
- d.printDate();
- }

4.3 this引用的特性
1. this的类型:对应类类型引用,即哪个对象调用就是哪个对象的引用类型2. this只能在 " 成员方法 " 中使用3. 在 " 成员方法 " 中, this 只能引用当前对象,不能再引用其他对象5、 对象的构造及初始化
5.1 如何初始化对象
通过前面知识点的学习知道,在Java 方法内部定义一个局部变量时,必须要初始化,否则会编译失败。public static void main ( String [] args ) {int a ;System . out . println ( a );}// Error:(26, 28) java: 可能尚未初始化变量 a要让上述代码通过编译,非常简单,只需在正式使用a 之前,给 a 设置一个初始值即可。如果是对象:public static void main ( String [] args ) {Date d = new Date ();d . printDate ();d . setDate ( 2021 , 6 , 9 );d . printDate ();}// 代码可以正常通过编译需要调用之前写的 SetDate 方法才可以将具体的日期设置到对象中。 通过上述例子发现两个问题:1. 每次对象创建好后调用 SetDate 方法设置具体日期,比较麻烦,那对象该如何初始化?2. 局部变量必须要初始化才能使用,为什么字段声明之后没有给值依然可以使用?5.2 构造方法
5.2.1 概念构造方法( 也称为构造器 ) 是一个特殊的成员方法, 名字必须与类名相同,在创建对象时,由编译器自动调用,并且 在整个对象的生命周期内只调用一次 。- public class Date
- {
- public int year;
- public int month;
- public int day;
- // 构造方法:
- // 名字与类名相同,没有返回值类型,设置为void也不行
- // 一般情况下使用public修饰
- // 在创建对象时由编译器自动调用,并且在对象的生命周期内只调用一次
- public Date(int year, int month, int day)
- {
- this.year = year;
- this.month = month;
- this.day = day;
- System.out.println("Date(int,int,int)方法被调用了");
- }
- public void printDate()
- {
- System.out.println(year + "-" + month + "-" + day);
- }
- public static void main(String[] args)
- {
- // 此处创建了一个Date类型的对象,并没有显式调用构造方法
- Date d = new Date(2021,6,9); // 输出Date(int,int,int)方法被调用了
- d.printDate(); // 2021-6-9
- }
- }
注意:构造方法的作用就是对对象中的成员进行初始化,并不负责给对象开辟空间。5.2.2 特性1. 名字必须与类名相同2. 没有返回值类型,设置为 void 也不行3. 创建对象时由编译器自动调用,并且在对象的生命周期内只调用一次 ( 相当于人的出生,每个人只能出生一次 )4. 构造方法可以重载 ( 用户根据自己的需求提供不同参数的构造方法 )- public class Date
- {
- public int year;
- public int month;
- public int day;
- // 无参构造方法
- public Date()
- {
- this.year = 1900;
- this.month = 1;
- this.day = 1;
- }
- // 带有三个参数的构造方法
- public Date(int year, int month, int day)
- {
- this.year = year;
- this.month = month;
- this.day = day;
- }
- public void printDate()
- {
- System.out.println(year + "-" + month + "-" + day);
- }
- public static void main(String[] args)
- {
- Date d = new Date();
- d.printDate();
- }
- }
上述两个构造方法:名字相同,参数列表不同,因此构成了方法重载。5. 如果用户没有显式定义,编译器会生成一份默认的构造方法,生成的默认构造方法一定是无参的。- public class Date
- {
- public int year;
- public int month;
- public int day;
- public void printDate()
- {
- System.out.println(year + "-" + month + "-" + day);
- }
- public static void main(String[] args)
- {
- Date d = new Date(); d.printDate();
- }
- }
上述Date类中,没有定义任何构造方法,编译器会默认生成一个不带参数的构造方法。注意:一旦用户定义,编译器则不再生成。- public class Date
- {
- public int year;
- public int month;
- public int day;
- public Date(int year, int month, int day)
- {
- this.year = year;
- this.month = month;
- this.day = day;
- }
- public void printDate()
- {
- System.out.println(year + "-" + month + "-" + day);
- }
- public static void main(String[] args)
- {
- // 如果编译器会生成,则生成的构造方法一定是无参的
- // 则此处创建对象是可以通过编译的
- // 但实际情况是:编译期报错
- Date d = new Date();
- d.printDate();
- }
- }
- /*
- Error:(26, 18) java: 无法将类 extend01.Date中的构造器 Date应用到给定类型;
- 需要: int,int,int
- 找到: 没有参数
- 原因: 实际参数列表和形式参数列表长度不同
- */
6. 构造方法中,可以通过 this 调用其他构造方法来简化代码- public class Date
- {
- public int year;
- public int month;
- public int day;
- // 无参构造方法--内部给各个成员赋值初始值,该部分功能与三个参数的构造方法重复
- // 此处可以在无参构造方法中通过this调用带有三个参数的构造方法
- // 但是this(1900,1,1);必须是构造方法中第一条语句
- public Date()
- {
- //System.out.println(year); 注释取消掉,编译会失败
- this(1900, 1, 1);
- //this.year = 1900;
- //this.month = 1;
- //this.day = 1;
- }
- // 带有三个参数的构造方法
- public Date(int year, int month, int day)
- {
- this.year = year;
- this.month = month;
- this.day = day;
- }
- }
注意:- this(...)必须是构造方法中第一条语句
- 不能形成环
- public Date()
- {
- this(1900,1,1);
- }
- public Date(int year, int month, int day)
- {
- this();
- }
- /*
- 无参构造器调用三个参数的构造器,而三个参数构造器有调用无参的构造器,形成构造器的递归调用 编译报错:Error:(19, 12) java: 递归构造器调用
- */
7. 绝大多数情况下使用 public 来修饰,特殊场景下会被 private 修饰 ( 后序讲单例模式时会遇到 )5.3 默认初始化
在上文中提出的第二个问题:为什么局部变量在使用时必须要初始化,而成员变量可以不用呢?- public class Date
- {
- public int year;
- public int month;
- public int day;
- public Date(int year, int month, int day)
- {
- // 成员变量在定义时,并没有给初始值, 为什么就可以使用呢?
- System.out.println(this.year); System.out.println(this.month);
- System.out.println(this.day);
- }
- public static void main(String[] args)
- {
- // 此处a没有初始化,编译时报错:
- // Error:(24, 28) java: 可能尚未初始化变量a
- // int a;
- // System.out.println(a);
- Date d = new Date(2021,6,9);
- }
- }

要搞清楚这个过程,就需要知道 new 关键字背后所发生的一些事情:
Date d = new Date ( 2021 , 6 , 9 );在程序层面只是简单的一条语句,在 JVM 层面需要做好多事情,下面简单介绍下:1. 检测对象对应的类是否加载了,如果没有加载则加载2. 为对象分配内存空间3. 处理并发安全问题 比如:多个线程同时申请对象,JVM 要保证给对象分配的空间不冲突4. 初始化所分配的空间即:对象空间被申请好之后,对象中包含的成员已经设置好了初始值,比如:
5. 设置对象头信息(关于对象内存模型后面会介绍)
6. 调用构造方法,给对象中各个成员赋值5.4 就地初始化
在声明成员变量时,就直接给出了初始值。- public class Date
- {
- public int year = 1900;
- public int month = 1;
- public int day = 1;
- public Date()
- {
- }
- public Date(int year, int month, int day)
- {
- }
- public static void main(String[] args)
- {
- Date d1 = new Date(2021,6,9);
- Date d2 = new Date();
- }
- }
注意:代码编译完成后,编译器会将所有给成员初始化的这些语句添加到各个构造函数中6、封装
6.1 封装的概念
面向对象程序三大特性:封装、继承、多态。而类和对象阶段,主要研究的就是封装特性。何为封装呢?简单来说就是套壳屏蔽细节 。比如:对于电脑这样一个复杂的设备,提供给用户的就只是:开关机、通过键盘输入,显示器,USB 插孔等,让用户来和计算机进行交互,完成日常事务。但实际上:电脑真正工作的却是CPU 、显卡、内存等一些硬件元件。对于计算机使用者而言,不用关心内部核心部件,比如主板上线路是如何布局的,CPU 内部是如何设计的等,用户只需要知道,怎么开机、怎么通过键盘和鼠标与计算机进行交互即可。因此计算机厂商在出厂时,在外部套上壳 子,将内部实现细节隐藏起来,仅仅对外提供开关机、鼠标以及键盘插孔等,让用户可以与计算机进行交互即可 。 封装:将数据和操作数据的方法进行有机结合,隐藏对象的属性和实现细节,仅对外公开接口来和对象进行 交互6.2 访问限定符
Java中主要通过类和访问权限来实现封装: 类可以将数据以及封装数据的方法结合在一起 ,更符合人类对事物的认知,而访问权限用来控制方法或者字段能否直接在类外使用 。 Java 中提供了四种访问限定符: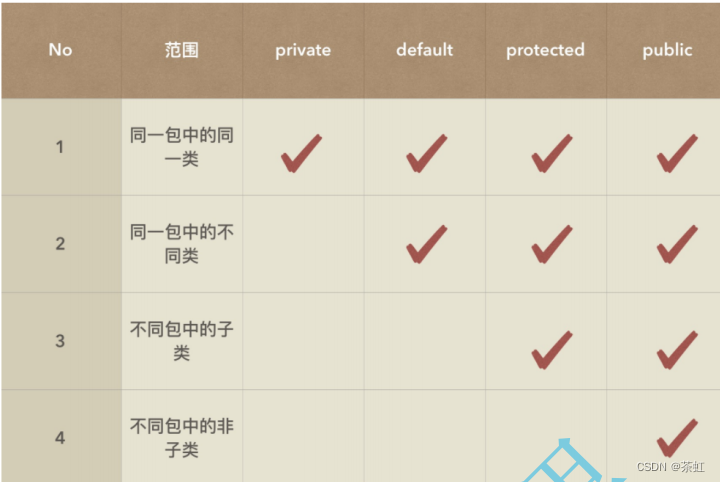
比如:
public:可以理解为一个人的外貌特征,谁都可以看得到default: 对于自己家族中 ( 同一个包中 ) 不是什么秘密,对于其他人来说就是隐私了private:只有自己知道,其他人都不知道【 说明 】- protected主要是用在继承中,继承部分详细介绍
- default权限指:什么都不写时的默认权限
- 访问权限除了可以限定类中成员的可见性,也可以控制类的可见性
- public class Computer
- {
- private String cpu; // cpu
- private String memory; // 内存
- public String screen; // 屏幕
- String brand; // 品牌---->default属性
- public Computer(String brand, String cpu, String memory, String screen)
- {
- this.brand = brand;
- this.cpu = cpu;
- this.memory = memory;
- this.screen = screen;
- }
- public void Boot()
- {
- System.out.println("开机~~~");
- }
- public void PowerOff()
- {
- System.out.println("关机~~~");
- }
- public void SurfInternet()
- {
- System.out.println("上网~~~");
- }
- }
- public class TestComputer
- {
- public static void main(String[] args)
- {
- Computer p = new Computer("HW", "i7", "8G", "13*14");
- System.out.println(p.brand); // default属性:只能被本包中类访问
- System.out.println(p.screen);// public属性: 可以任何其他类访问
- //System.out.println(p.cpu);// private属性:只能在Computer类中访问,不能被其他类访问
- }
- }
注意:一般情况下成员变量设置为private ,成员方法设置为 public 。6.3 封装扩展之包
6.3.1 包的概念在面向对象体系中,提出了一个软件包的概念,即:为了更好的管理类,把多个类收集在一起成为一组,称为软件 包 。有点类似于目录。比如:为了更好的管理电脑中的歌曲,一种好的方式就是将相同属性的歌曲放在相同文件下,也可以对某个文件夹下的音乐进行更详细的分类在Java 中也引入了包,包是对类、接口等的封装机制的体现,是一种对类或者接口等的很好的组织方式,比如:一个包中的类不想被其他包中的类使用。包还有一个重要的作用:在同一个工程中允许存在相同名称的类,只要处在 不同的包中即可 。6.3.2 导入包中的类Java 中已经提供了很多现成的类供我们使用 . 例如 Date 类:可以使用 java.util.Date 导入 java.util 这个包中的 Date类.- public class Test
- {
- public static void main(String[] args)
- {
- java.util.Date date = new java.util.Date(); // 得到一个毫秒级别的时间戳
- System.out.println(date.getTime());
- }
- }
但是这种写法比较麻烦一些, 可以 使用 import 语句导入包 .- import java.util.Date;
- public class Test
- {
- public static void main(String[] args)
- {
- Date date = new Date();
- // 得到一个毫秒级别的时间戳
- System.out.println(date.getTime());
- }
- }
如果需要使用 java.util 中的其他类 , 可以使用 import java.util.*- import java.util.*;
- public class Test
- {
- public static void main(String[] args)
- {
- Date date = new Date(); // 得到一个毫秒级别的时间戳
- System.out.println(date.getTime());
- }
- }
但是我们更建议显式的指定要导入的类名 . 否则还是容易出现冲突 的情况 .import java . util . * ;import java . sql . * ;public class Test {public static void main ( String [] args ) {// util 和 sql 中都存在一个 Date 这样的类 , 此时就会出现歧义 , 编译出错Date date = new Date ();System . out . println ( date . getTime ());}}// 编译出错Error :( 5 , 9 ) java : 对 Date 的引用不明确java . sql 中的类 java . sql . Date 和 java . util 中的类 java . util . Date 都匹配在这种情况下需要使用完整的类名- import java.util.*; import java.sql.*;
- public class Test
- {
- public static void main(String[] args)
- {
- java.util.Date date = new java.util.Date();
- System.out.println(date.getTime());
- }
- }
可以使用import static 导入包中静态的方法和字段。- import static java.lang.Math.*;
- public class Test
- {
- public static void main(String[] args)
- {
- double x = 30;
- double y = 40;
- // 静态导入的方式写起来更方便一些.
- // double result = Math.sqrt(Math.pow(x, 2) + Math.pow(y, 2));
- double result = sqrt(pow(x, 2) + pow(y, 2));
- System.out.println(result);
- }
- }
注意事项: import 和 C++ 的 #include 差别很大 . C++ 必须 #include 来引入其他文件内容 , 但是 Java 不需要 . import 只是为了写代码的时候更方便 . import 更类似于 C++ 的 namespace 和 using6.3.3 自定义包基本规则- 在文件的最上方加上一个 package 语句指定该代码在哪个包中.
- 包名需要尽量指定成唯一的名字, 通常会用公司的域名的颠倒形式(例如 com.bit.demo1 ).
- 包名要和代码路径相匹配. 例如创建 com.bit.demo1 的包, 那么会存在一个对应的路径 com/bit/demo1 来存储
- 代码.
- 如果一个类没有 package 语句, 则该类被放到一个默认包中.
操作步骤1. 在 IDEA 中先新建一个包 : 右键 src -> 新建 -> 包
2. 在弹出的对话框中输入包名, 例如 com.bit.demo1

3. 在包中创建类, 右键包名 -> 新建 -> 类, 然后输入类名即可

4. 此时可以看到我们的磁盘上的目录结构已经被 IDEA 自动创建出来了

5. 同时我们也看到了, 在新创建的 Test.java 文件的最上方, 就出现了一个 package 语句

6.3.4 包的访问权限控制举例
Computer类位于 com.bit.demo1 包中, TestComputer 位置 com.bit.demo2 包中:- package com.bit.demo1;
- public class Computer
- {
- private String cpu; // cpu
- private String memory; // 内存
- public String screen; // 屏幕
- String brand; // 品牌
- public Computer(String brand, String cpu, String memory, String screen)
- {
- this.brand = brand;
- this.cpu = cpu;
- this.memory = memory;
- this.screen = screen;
- }
- public void Boot()
- {
- System.out.println("开机~~~");
- }
- public void PowerOff()
- {
- System.out.println("关机~~~");
- }
- public void SurfInternet()
- {
- System.out.println("上网~~~");
- }
- }
- ///
- package com.bite.demo2;
- import com.bite.demo1.Computer;
- public class TestComputer
- {
- public static void main(String[] args)
- {
- Computer p = new Computer("HW", "i7", "8G", "13*14");
- System.out.println(p.screen);
- // System.out.println(p.cpu); // 报错:cup是私有的,不允许被其他类访问
- // System.out.println(p.brand); // 报错:brand是default,不允许被其他包中的类访问
- }
- }
- // 注意:如果去掉Computer类之前的public修饰符,代码也会编译失败
6.3.5 常见的包
1. java.lang:系统常用基础类 (String 、 Object), 此包从 JDK1.1 后自动导入。2. java.lang.reflflect:java 反射编程包 ;3. java.net:进行网络编程开发包。4. java.sql:进行数据库开发的支持包。5. java.util:是 java 提供的工具程序包。 ( 集合类等 ) 非常重要6. java.io:I/O编程开发包。7、 static成员
7.1 再谈学生类
使用前文中介绍的学生类实例化三个对象s1 、 s2 、 s3 ,每个对象都有自己特有的名字、性别,年龄,学分绩点等成员信息,这些信息就是对不同学生来进行描述的,如下所示:public class Student {// ...public static void main ( String [] args ) {Student s1 = new Student ( "Li leilei" , " 男 " , 18 , 3.8 );Student s2 = new Student ( "Han MeiMei" , " 女 " , 19 , 4.0 );Student s3 = new Student ( "Jim" , " 男 " , 18 , 2.6 );}}
假设三个同学是同一个班的,那么他们上课肯定是在同一个教室,那既然在同一个教室,那能否给类中再加一个成员变量,来保存同学上课时的教室呢?答案是不行的。
之前在Student 类中定义的成员变量,每个对象中都会包含一份 ( 称之为实例变量 ) ,因为需要使用这些信息来描述具体的学生。而现在要表示学生上课的教室,这个教室的属性并不需要每个学生对象中都存储一份,而是需要让所有的学生来共享。在 Java 中,被 static 修饰的成员,称之为静态成员,也可以称为类成员,其不属于某个具体的对 象,是所有对象所共享的 。7.2 static修饰成员变量
static修饰的成员变量,称为静态成员变量 ,静态成员变量最大的特性: 不属于某个具体的对象,是所有对象所共 享的 。【静态成员变量特性】1. 不属于某个具体的对象,是类的属性,所有对象共享的,不存储在某个对象的空间中2. 既可以通过对象访问,也可以通过类名访问,但一般更推荐使用类名访问3. 类变量存储在方法区当中4. 生命周期伴随类的一生 ( 即:随类的加载而创建,随类的卸载而销毁 )public class Student {public String name ;public String gender ;public int age ;public double score ;public static String classRoom = "Bit306" ;// ...public static void main ( String [] args ) {// 静态成员变量可以直接通过类名访问System . out . println ( Student . classRoom );Student s1 = new Student ( "Li leilei" , " 男 " , 18 , 3.8 );Student s2 = new Student ( "Han MeiMei" , " 女 " , 19 , 4.0 );Student s3 = new Student ( "Jim" , " 男 " , 18 , 2.6 );// 也可以通过对象访问:但是 classRoom 是三个对象共享的System . out . println ( s1 . classRoom );System . out . println ( s2 . classRoom );System . out . println ( s3 . classRoom );}}7.3 static修饰成员方法
一般类中的数据成员都设置为private ,而成员方法设置为 public ,那设置之后, Student 类中 classRoom 属性如何在类外访问呢?public class Student {private String name ;private String gender ;private int age ;private double score ;private static String classRoom = "Bit306" ;// ...}public class TestStudent {public static void main ( String [] args ) {System . out . println ( Student . classRoom );}}编译失败:Error :( 10 , 35 ) java : classRoom 在 extend01 . Student 中是 private 访问控制那static 属性应该如何访问呢?Java中, 被 static 修饰的成员方法称为静态成员方法,是类的方法,不是某个对象所特有的。静态成员一般是通过静态方法来访问的。public class Student {// ...private static String classRoom = "Bit306" ;// ...public static String getClassRoom (){return classRoom ;}}public class TestStudent {public static void main ( String [] args ) {System . out . println ( Student . getClassRoom ());}}输出: Bit306【 静态方法特性 】1. 不属于某个具体的对象,是类方法2. 可以通过对象调用,也可以通过类名. 静态方法名 (...) 方式调用,更推荐使用后者3. 不能在静态方法中访问任何非静态成员变量public static String getClassRoom (){System . out . println ( this );return classRoom ;}// 编译失败: Error:(35, 28) java: 无法从静态上下文中引用非静态 变量 thispublic static String getClassRoom (){age += 1 ;return classRoom ;}// 编译失败: Error:(35, 9) java: 无法从静态上下文中引用非静态 变量 age4. 静态方法中不能调用任何非静态方法,因为非静态方法有 this 参数,在静态方法中调用时候无法传递 this 引用public static String getClassRoom (){doClass ();return classRoom ;}// 编译报错: Error:(35, 9) java: 无法从静态上下文中引用非静态 方法 doClass()5. 静态方法无法重写,不能用来实现多态 ( 此处大家暂时不用管,后序多态位置详细讲解 ) 。7.4 static成员变量初始化
注意:静态成员变量一般不会放在构造方法中来初始化,构造方法中初始化的是与对象相关的实例属性静态成员变量的初始化分为两种:就地初始化 和 静态代码块初始化 。1. 就地初始化就地初始化指的是:在定义时直接给出初始值public class Student {private String name ;private String gender ;private int age ;private double score ;private static String classRoom = "Bit306" ;// ...}2. 静态代码块初始化8、 代码块
8.1 代码块概念以及分类
使用 {} 定义的一段代码称为代码块 。根据代码块定义的位置以及关键字,又可分为以下四种:- 普通代码块
- 构造块
- 静态块
- 同步代码块(后续讲解多线程部分再谈)
8.2 普通代码块
普通代码块:定义在方法中的代码块- public class Main
- {
- public static void main(String[] args)
- {
- {
- //直接使用{}定义,普通方法块
- int x = 10 ;
- System.out.println("x1 = " +x);
- }
- int x = 100 ;
- System.out.println("x2 = " +x);
- }
- }
- // 执行结果 x1 = 10 x2 = 100
这种用法较少见8.3 构造代码块
构造块:定义在类中的代码块( 不加修饰符 ) 。也叫: 实例代码块 。 构造代码块一般用于初始化实例成员变量 。- public class Student
- {
- //实例成员变量
- private String name;
- private String gender;
- private int age;
- private double score;
- public Student()
- {
- System.out.println("I am Student init()!");
- }
- //实例代码块
- {
- this.name = "bit";
- this.age = 12;
- this.sex = "man";
- System.out.println("I am instance init()!");
- }
- public void show()
- {
- System.out.println("name: "+name+" age: "+age+" sex: "+sex);
- }
- }
- public class Main
- {
- public static void main(String[] args)
- {
- Student stu = new Student();
- stu.show();
- }
- }
- // 运行结果
- I am instance init()!
- I am Student init()!
- name: bit age: 12 sex: man
8.4 静态代码块
使用static 定义的代码块称为静态代码块。 一般用于初始化静态成员变量。- public class Student
- {
- private String name;
- private String gender;
- private int age;
- private double score;
- private static String classRoom;
- //实例代码块
- {
- this.name = "bit";
- this.age = 12;
- this.gender = "man";
- System.out.println("I am instance init()!");
- }
- //
- 静态代码块
- static
- {
- classRoom = "bit306";
- System.out.println("I am static init()!");
- }
- public Student()
- {
- System.out.println("I am Student init()!");
- }
- public static void main(String[] args)
- {
- Student s1 = new Student();
- Student s2 = new Student();
- }
- }
注意事项- 静态代码块不管生成多少个对象,其只会执行一次
- 静态成员变量是类的属性,因此是在JVM加载类时开辟空间并初始化的
- 如果一个类中包含多个静态代码块,在编译代码时,编译器会按照定义的先后次序依次合并
- 实例代码块只有在创建对象时才会执行
9、内部类
当一个事物的内部,还有一个部分需要一个完整的结构进行描述,而这个内部的完整的结构又只为外部事物提供服务,那么整个内部的完整结构最好使用内部类。在 Java 中, 可以将一个类定义在另一个类或者一个方法的内部, 前者称为内部类,后者称为外部类 。内部类也是封装的一种体现。public class OutClass {class InnerClass {}}// OutClass 是外部类// InnerClass 是内部类【注意事项】1. 定义在 class 类名 {} 花括号外部的,即使是在一个文件里,都不能称为内部类public class A {}class B {}// A 和 B 是两个独立的类,彼此之前没有关系2. 内部类和外部类共用同一个 java 源文件,但是经过编译之后,内部类会形成单独的字节码文件9.1 内部类的分类
先来看下,内部类都可以在一个类的那些位置进行定义public class OutClass {// 成员位置定义:未被 static 修饰 ---> 实例内部类public class InnerClass1 {}// 成员位置定义:被 static 修饰 ---> 静态内部类static class InnerClass2 {}public void method (){// 方法中也可以定义内部类 ---> 局部内部类:几乎不用class InnerClass5 {}}}根据内部类定义的位置不同,一般可以分为以下几种形式:1. 成员内部类 ( 普通内部类:未 static 修饰的成员内部类 和 静态内部类:被 static 修饰的成员内部类 )2. 局部内部类 ( 不谈修饰符 ) 、匿名内部类注意:内部类其实日常开发中使用并不是非常多,大家在看一些库中的代码时候可能会遇到的比较多,日常开始中使用最多的是匿名内部类。9.1 内部类在外部类中,内部类定义位置与外部类成员所处的位置相同,因此称为成员内部类。9.1.1 实例内部类即未被static 修饰的成员内部类。- public class OutClass
- {
- private int a; static int b; int c;
- public void methodA()
- {
- a = 10;
- System.out.println(a);
- }
- public static void methodB()
- {
- System.out.println(b);
- }
- // 实例内部类:未被static修饰
- class InnerClass
- {
- int c;
- public void methodInner()
- {
- // 在实例内部类中可以直接访问外部类中:任意访问限定符修饰的成员
- a = 100;
- b =200;
- methodA();
- methodB();
- // 如果外部类和实例内部类中具有相同名称成员时,优先访问的是内部类自己的
- c = 300;
- System.out.println(c);
- // 如果要访问外部类同名成员时候,必须:外部类名称.this.同名成员名字
- OutClass.this.c = 400;
- System.out.println(OutClass.this.c);
- }
- }
- public static void main(String[] args)
- {
- // 外部类:对象创建 以及 成员访问
- OutClass outClass = new OutClass();
- System.out.println(outClass.a);
- System.out.println(OutClass.b);
- System.out.println(outClass.c);
- outClass.methodA();
- outClass.methodB();
- System.out.println("=============实例内部类的访问=============");
- // 要访问实例内部类中成员,必须要创建实例内部类的对象
- // 而普通内部类定义与外部类成员定义位置相同,因此创建实例内部类对象时必须借助外部类
- // 创建实例内部类对象
- OutClass.InnerClass innerClass1 = new OutClass().new InnerClass();
- // 上述语法比较怪异,也可以先将外部类对象先创建出来,然后再创建实例内部类对象
- OutClass.InnerClass innerClass2 = outClass.new InnerClass();
- innerClass2.methodInner();
- }
- }
9.1.2 静态内部类被static 修饰的内部成员类称为静态内部类。- public class OutClass
- {
- private int a; static int b;
- public void methodA()
- {
- a = 10;
- System.out.println(a);
- }
- public static void methodB()
- {
- System.out.println(b);
- }
- // 静态内部类:被static修饰的成员内部类
- static class InnerClass
- {
- public void methodInner()
- {
- // 在内部类中只能访问外部类的静态成员
- // a = 100; // 编译失败,因为a不是类成员变量
- b =200;
- // methodA(); // 编译失败,因为methodB()不是类成员方法
- methodB();
- }
- }
- public static void main(String[] args)
- {
- // 静态内部类对象创建 & 成员访问
- OutClass.InnerClass innerClass = new OutClass.InnerClass();
- innerClass.methodInner();
- }
- }
【 注意事项 】1. 在静态内部类中只能访问外部类中的静态成员2. 创建静态内部类对象时,不需要先创建外部类对象9.2 局部内部类
定义在外部类的方法体或者{} 中,该种内部类只能在其定义的位置使用,一般使用的非常少,此处简单了解下语法格式。- public class OutClass
- {
- int a = 10;
- public void method()
- {
- int b = 10;
- // 局部内部类:定义在方法体内部
- // 不能被public、static等访问限定符修饰
- class InnerClass
- {
- public void methodInnerClass()
- {
- System.out.println(a);
- System.out.println(b);
- }
- }
- // 只能在该方法体内部使用,其他位置都不能用
- InnerClass innerClass = new InnerClass();
- innerClass.methodInnerClass();
- }
- public static void main(String[] args)
- {
- // OutClass.InnerClass innerClass = null; 编译失败
- }
- }
【 注意事项 】1. 局部内部类只能在所定义的方法体内部使用2. 不能被 public 、 static 等修饰符修饰3. 编译器也有自己独立的字节码文件,命名格式:外部类名字 $ 内部类名字 .class4. 几乎不会使用9.3 匿名内部类
10、对象的打印
- public class Person
- {
- String name;
- String gender;
- int age;
- public Person(String name, String gender, int age)
- {
- this.name = name;
- this.gender = gender;
- this.age = age;
- }
- public static void main(String[] args
- {
- Person person = new Person("Jim","男", 18);
- System.out.println(person);
- }
- }
- // 打印结果:day20210829.Person@1b6d3586
如果想要默认打印对象中的属性该如何处理呢?答案:重写toString 方法即可。- public class Person
- {
- String name;
- String gender;
- int age;
- public Person(String name, String gender, int age)
- {
- this.name = name;
- this.gender = gender;
- this.age = age;
- }
- @Override
- public String toString()
- {
- return "[" + name + "," + gender + "," + age + "]";
- }
- public static void main(String[] args)
- {
- Person person = new Person("Jim","男", 18);
- System.out.println(person);
- }
- }
- // 输出结果:[Jim,男,18]
-
相关阅读:
蔡司光学:儿童近视眼镜的匠心之选
ElasticSearch学习笔记之二:Filebeat日志收集
数据分析入门全攻略:从新手到专家
源码安装nginx及其配置
会话管理——Cookie和 Session
Swift使用Embassy库进行数据采集:热点新闻自动生成器
spark(day05)
C语言控制台程序添加图标(基于GCC编译器)
ApplicationContext接口解读
使用CFimagehost源码搭建免费的PHP图片托管私人图床,无需数据库支持
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_51912875/article/details/125718549
