-
Pytest 的高级用法之 插件开发
前言用过pytest的小伙伴应该都知道,pytest之所以功能强大,是因为pytest的插件非常的多。这是插件大多是pytest的使用者所开发的,今天咱们专门来聊聊如何去自己开发Pytest的插件。
一 pytest插件的介绍pytest框架采用的是插件系统的模式来设计的,pytest运行的所有流程都是基于插件实现的钩子来实现的。一个插件包含一个或多个钩子函数。编写钩子 解释了如何自己编写钩子函数的基础知识和细节。pytest通过调用插件的指定钩子来实现配置、收集、运行和报告的各个方面:
内置插件:从 pytest 的内部_pytest目录加载。
外部插件:通过 setuptools 入口点发现的模块
conftest.py 插件:在测试目录中自动发现的模块
原则上,每个钩子调用都是一个1:NPython 函数调用,其中N是给定钩子的已注册实现函数的数量。所有钩子都遵循pytest_前缀命名约定,使其易于区分和查找。
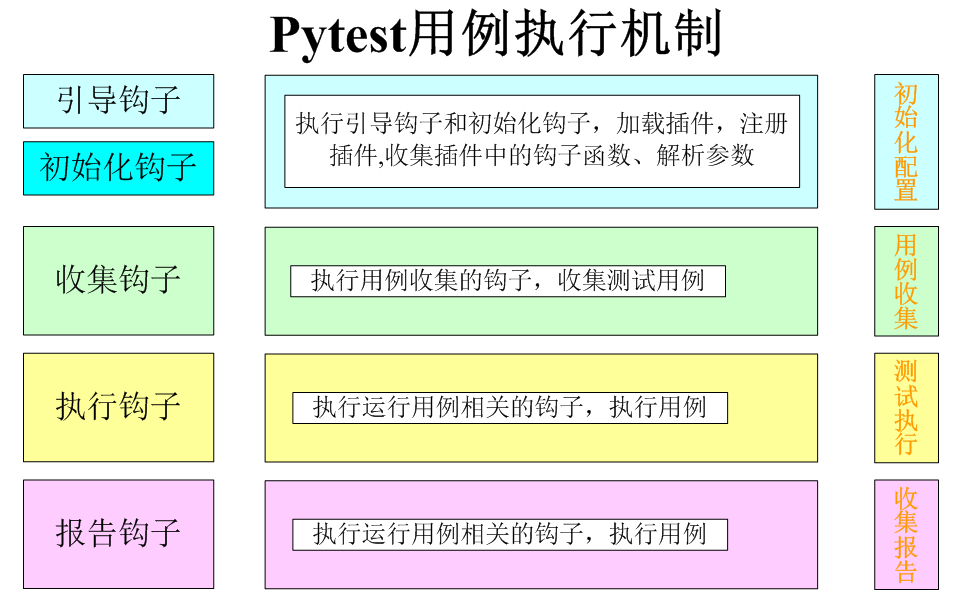
二 pytest启动时插件发现顺序pytest通过以下方式在工具启动时加载插件模块:
1.通过扫描命令行中的选项并阻止加载该插件(即使是内置插件也可以通过这种方式阻止)。这发生在正常的命令行解析之前。-p no:name
2.通过加载所有内置插件。
3.通过扫描命令行选项并加载指定的插件。这发生在正常的命令行解析之前。-p name
4.通过加载通过setuptools 入口点注册的所有插件。
5.通过加载通过PYTEST_PLUGINS环境变量。
6.通过加载conftest.py命令行调用推断的所有文件:
如果没有指定测试路径,则使用当前目录作为测试路径
如果存在,则加载 conftest.py 并 test*/conftest.py 相对于第一个测试路径的目录部分。加载文件后conftest.py ,加载其 pytest_plugins 变量中指定的所有插件(如果存在)。
请注意,pytest 在工具启动时不会conftest.py 在更深的嵌套子目录中找到文件。conftest.py 将文件保存在顶级测试或项目根目录中通常是个好主意。
7.通过递归加载 文件中pytest_plugins变量指定的所有插件conftest.py。
三 插件开发的流程明确需求:开发一个什么功能的插件?
分析需求:这个功能在pytest执行的那个阶段执行?
找出实现需要用到的钩子函数
在conftest.py中定义对应的钩子函数实现相关的功能
四 案例:并发执行用例的插件开发1、需求
需求一:开发一个并发执行测试的插件
通过pytest执行测试时,可以使用参数指定并发执行的线程数量和并发执行的最小任务- 1
需求二:插件需要实现以下几个命令行参数
–runTask : 指定并发执行的最小任务可传以下几个参数值
mod: 测试文件为并发最小执行任务(可以保证测试文件中的用例执行先后顺序)case: 测试用例为并发最小执行任务
–current: 最大的并发执行数
2、需求分析
1、需求一:在测试执行的阶段
pytest执行负责用例执行的钩子函数:
https://www.osgeo.cn/pytest/reference.html#test-running-runtest-hooksdef pytest_runtestloop(session): for item in session.items: item.ihook.pytest_runtest_protocol(item=item, nextitem=None) return True- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
2、需求二:实现自己写自定义参数,在初始化阶段,需要使用的钩子函数为:pytest_addoption
pytest添加运行参数的钩子函数:
https://www.osgeo.cn/pytest/writing_plugins.html#writing-hook-functionsdef pytest_addoption(parser): # 添加参数分组 group = parser.getgroup('pytest-thread') # 添加参数信息 group.addoption('--current', default=None, help='运行的线程数量')- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
pytest中的更多的钩子函数文档:
https://www.osgeo.cn/pytest/reference.html#hooks参数的获取:在pytest钩子函数中,可以通过session.config.getoption(‘–current’)去获取参数
3、代码实现
def pytest_addoption(parser): """添加参数名称""" # 添加参数分组 group = parser.getgroup('pytest-current') # 添加参数和帮助信息 group.addoption('--unit', default=None, help='并发执行的任务单位',type="string") group.addoption('--current', default=None, help='运行的并发数量',type="int") def pytest_runtestloop(session): # 获取并发数量 Count = session.config.getoption('--current') # 并发执行的任务单位 unit = session.config.getoption('--unit') # 将测试用例按模块进行拆分 dictCase = {} for item in session.items: # 获取用例所属模块 mod = item.module # 判断dictCase是否有该测试模块 if dictCase.get(mod): dictCase[mod].append(item) else: dictCase[mod] = [] dictCase[mod].append(item) # 开启协程并发执行 gs = [] for cases in dictCase.values(): g = gevent.spawn(run_test_mod, cases) gs.append(g) gevent.joinall(gs) return True def run_test_mod(cases): """ :param cases: 用例列表 :return: """ for item in cases: item.ihook.pytest_runtest_protocol(item=item, nextitem=None)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
五 插件打包和上传参照官方文档:
https://packaging.python.org/en/latest/tutorials/packaging-projects/#packaging-your-project1、创建一个pytest插件项目
源码目录:(编写插件源码)
readme.md (说明文档)
setup.py(打包配置文件)
LICENSE:开源许可协议
2、编写插件功能代码
在src目录下创建py文件,编写插件核心代码
def pytest_addoption(parser): """添加参数名称""" # 添加参数分组 group = parser.getgroup('pytest-current') # 添加参数和帮助信息 group.addoption('--unit', default=None, help='并发执行的任务单位',type="string") group.addoption('--current', default=None, help='运行的并发数量',type="int") def pytest_runtestloop(session): # 获取并发数量 Count = session.config.getoption('--current') # 并发执行的任务单位 unit = session.config.getoption('--unit') # 将测试用例按模块进行拆分 dictCase = {} for item in session.items: # 获取用例所属模块 mod = item.module # 判断dictCase是否有该测试模块 if dictCase.get(mod): dictCase[mod].append(item) else: dictCase[mod] = [] dictCase[mod].append(item) # 开启协程并发执行 gs = [] for cases in dictCase.values(): g = gevent.spawn(run_test_mod, cases) gs.append(g) gevent.joinall(gs) return True def run_test_mod(cases): """ :param cases: 用例列表 :return: """ for item in cases: item.ihook.pytest_runtest_protocol(item=item, nextitem=None)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
3、配置打包信息
1、在项目目录下创建setup.py文件,
from setuptools import setup
setup( name="pytest-musen", version='0.0.1', packages=["pytest_musen"], # 指定插件文件 entry_points={"pytest11": ["pytest-lemon = pytest_musen.musen"]}, # pypi插件分类器 classifiers=["Framework :: Pytest"], )- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
注意点:pytest 查找插件是根据pytest11入口来查找的安装的第三方包的
Writing plugins — pytest documentation2、对项目进行打包
python setup.py sdist bdist_wheel- 1
4、发布插件到PYPI
1、在PYPI上注册账号
https://pypi.org/account/register/- 1
2、安装twine
pip install twine- 1
3、使用twine发布插件到pypi
twine upload dist/* twine upload --repository testpypi dist/*- 1
- 2
- 3
并发执行的插件pytest_parallel
现在我邀请你进入我们的软件测试学习交流群:【
746506216】,备注“入群”, 大家可以一起探讨交流软件测试,共同学习软件测试技术、面试等软件测试方方面面,还会有免费直播课,收获更多测试技巧,我们一起进阶Python自动化测试/测试开发,走向高薪之路。喜欢软件测试的小伙伴们,如果我的博客对你有帮助、如果你喜欢我的博客内容,请 “点赞” “评论” “收藏” 一 键三连哦!
软件测试工程师自学教程:
这才是2022最精细的自动化测试自学教程,我把它刷了无数遍才上岸字节跳动,做到涨薪20K【值得自学软件测试的人刷】
软件测试工程师月薪2W以上薪资必学技能 — Python接口自动化框架封装.
美团面试真题_高级测试25K岗位面试 — 软件测试人都应该看看
软件测试必会_Jmeter大厂实战 — 仅6步可实现接口自动化测试


-
相关阅读:
2022年最全教程:如何做大数据的采集数据及数据分析?
haproxy使用
【Endnote】插入文献时,自动弹出select matching reference
Web安全开发 | 青训营笔记
数据库公共字段自动填充
C语言数据结构之数据结构入门
盘点一下今年世界杯中国赞助商及联名入圈品牌
Java中的自动装箱和拆箱
android移植dbus
【王道代码】【2.3链表】d4
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_67695717/article/details/126389299
