-
1325. Delete Leaves With a Given Value
Given a binary tree
rootand an integertarget, delete all the leaf nodes with valuetarget.Note that once you delete a leaf node with value
target, if its parent node becomes a leaf node and has the valuetarget, it should also be deleted (you need to continue doing that until you cannot).Example 1:
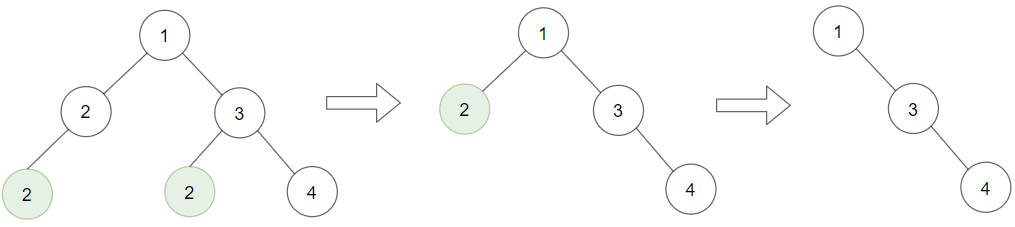
Input: root = [1,2,3,2,null,2,4], target = 2 Output: [1,null,3,null,4] Explanation: Leaf nodes in green with value (target = 2) are removed (Picture in left). After removing, new nodes become leaf nodes with value (target = 2) (Picture in center).
Example 2:

Input: root = [1,3,3,3,2], target = 3 Output: [1,3,null,null,2]
Example 3:

Input: root = [1,2,null,2,null,2], target = 2 Output: [1] Explanation: Leaf nodes in green with value (target = 2) are removed at each step.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 3000]. 1 <= Node.val, target <= 1000
题目:给定一个二叉树,将与给定target值相等的叶结点删除。注意,删除之后其父结点可能变为叶结点。
思路:一看就是递归,从下网上删就完了。代码:
- /**
- * Definition for a binary tree node.
- * struct TreeNode {
- * int val;
- * TreeNode *left;
- * TreeNode *right;
- * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
- * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
- * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
- * };
- */
- class Solution {
- public:
- TreeNode* removeLeafNodes(TreeNode* root, int target) {
- if(!root) return NULL;
- root->left = removeLeafNodes(root->left, target);
- root->right = removeLeafNodes(root->right, target);
- if(!root->left && !root->right && root->val == target)
- return NULL;
- return root;
- }
- };
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
-
相关阅读:
删除有序数组里的重复项 -力扣(Java)
Flutter快学快用11 多样式导航栏:掌握所有 Flutter 导航栏的设计
Qt day5
Stretched mesh
GPT带我学-设计模式-10观察者模式
[C++ 从入门到精通] 12.重载运算符、赋值运算符重载、析构函数
72B大模型分片部署
力扣刷题-数组-数组理论基础
考研数学|汤家凤《1800》vs 张宇《1000》怎么选?
存储器、I/O组织、微处理器
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qing2019/article/details/126383539
