-
Java NIO :如何为通道注册多个事件及多线程处理 Accetp 请求
背景
上周梳理了一下 IO 的发展过程,从 BIO 、NIO 到 多路复用,每一个 IO 模型背后的 Java 应用是怎么样的呢?
本文记录 NIO 的入门案例,巩固一下 Java NIO 编码知识。
基本概念
Java NIO 有四个基本概念,分别是:
- Channel,事件注册的通道
- Selector,事件监听器
- Buffer,缓冲区
- SelectionKey,就绪事件
服务端基本流程:
1、创建 ServerSocketChannel; 2、ServerSocketChannel 注册到 Selector 并监听 OP_ACCEPT 事件; 3、主程序轮询 Selector 的就绪事件,根据时间类型进行处理,如果是 OP_ACCEPT 事件,执行 accept 事件处理:获取接收到的 SocketChannel ,并注册 OP_READ 事件; 4、主程序轮询到的接收到的 SocketChannel 的 READ 事件,则分发该数据通道给线程池处理,并取消该事件的监听,代表一个 Socket 请求处理完成。- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
客户端基本流程:
1、创建 SocketChannel; 2、将 SocketChannel 注册到 Selector 上,同时监听 OP_CONNECT 和 OP_READ 两个事件; 3、轮询 Selector 的就绪事件,如果是 OP_CONNECT 事件,就发送请求数据;如果是 OP_READ,就读取响应,并关闭 SocketChannel,客户端流程结束。- 1
- 2
- 3
NioServer 端编码
public class NioServer { private int port ; private Selector selector; private ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5); public NioServer(int port) { this.port = port; } public void init() { ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = null; try { // Channel 定义 serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open(); serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false); serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(port)); // 创建选择器 selector = Selector.open(); // 注册到 Selector ,监听 Accept 事件 serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT); System.out.println("Start server"); }catch (Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } public void accept(SelectionKey key) { try{ // ServerSocketChannel 监听到了 Accept 事件后的处理过程,从通道中获取 SocketChannel ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel(); SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept(); socketChannel.configureBlocking(false); // 注册客户端 Channel 的读事件,因为注册的通道对象不一样了,是收到的 Socket 对象 socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ); System.out.println("Start to process accepted socket."); // 打印客户端地址 String clientInfo = socketChannel.socket().getInetAddress().getHostAddress(); int portInfo = socketChannel.socket().getPort(); System.out.println("Receive client info "+clientInfo + ",portInfo:"+portInfo); }catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public void start() { this.init(); // 轮询 Select 的事件 while (true) { try { int event = selector.select(); // 轮询到了 完成就绪事件,遍历并分发处理 if (event >0) { Iterator<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys().iterator(); while(selectionKeys.hasNext()) { SelectionKey key = selectionKeys.next(); selectionKeys.remove(); if (key.isAcceptable()) { this.accept(key); } else { if (!key.isReadable()) { System.out.println("Key is not read able."); continue; } // 把请求数据的通道提交给线程池处理 service.submit(new NioServerHandler((SocketChannel)key.channel())); // 该 Client 请求提交给客户端后,key.cancel 可以解除监听 key.cancel(); System.out.println("Submit task and cancel."); } } } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } public static void main(String[] args) { NioServer server = new NioServer(8800); server.start(); } /** * 线程池任务:接收通道对象,处理数据,而不是接收 Key */ private class NioServerHandler implements Runnable { SocketChannel socketChannel; public NioServerHandler(SocketChannel socketChannel) { this.socketChannel = socketChannel; } @Override public void run() { try { ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); socketChannel.read(buffer); buffer.flip(); buffer.clear(); // 响应数据 ByteBuffer outBuffer = ByteBuffer.wrap("ok".getBytes()); socketChannel.write(outBuffer);// 将消息回送给客户端 System.out.println("接收到 client request :"+ new String (buffer.array())); System.out.println("response finished"); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
关键逻辑:
ACCEPT事件中,再对收到的SocketChannel注册读事件;- 处理
SocketChannel的 READ 事件时,把通道对象提交给线程池处理类,同时解除该通道的监听事件,这里模拟的是一次 Socket 请求的处理。
NioClient 编码
public class NioClient { private static final String host = "127.0.0.1"; private static final int port = 8800; private Selector selector; public static void main(String[] args){ for (int i=0;i<1;i++) { new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { System.out.println("Client is started listened "); NioClient client = new NioClient(); client.connect(host, port); client.listen(); System.out.println("finished start"); } }).start(); } } public void connect(String host, int port) { try { SocketChannel sc = SocketChannel.open(); sc.configureBlocking(false); this.selector = Selector.open(); // 一次注册多个事件,要用 | 来进行操作,而不是执行多次 register ,否则最后一次会覆盖前面的事件的 sc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT|SelectionKey.OP_READ); sc.connect(new InetSocketAddress(host, port)); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } /** * 轮询就绪的事件 */ public void listen() { boolean isClose = false; while (!isClose) { try { int events = selector.select(); if (events > 0) { // 迭代器遍历 Iterator<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys().iterator(); while (selectionKeys.hasNext()) { SelectionKey selectionKey = selectionKeys.next(); selectionKeys.remove(); //连接事件:连接成功后发送数据 if (selectionKey.isConnectable()) { SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) selectionKey.channel(); if (socketChannel.isConnectionPending()) { socketChannel.finishConnect(); } // 发送数据给服务器端 String data = "Hello this is " + Thread.currentThread().getName(); socketChannel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap(data.getBytes())); System.out.println("send data to server "+data); } else if (selectionKey.isReadable()) { // 监听到响应结果,读取响应结果 SocketChannel sc = (SocketChannel) selectionKey.channel(); ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); sc.read(buffer); buffer.flip(); buffer.clear(); System.out.println("收到服务端的数据:"+new String(buffer.array())); // 结束请求 sc.shutdownOutput(); sc.close(); System.out.println("sc connected {}"+sc.isConnected()); isClose = true; break; } } } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
运行结果
客户端发送请求,收到响应后结束流程:
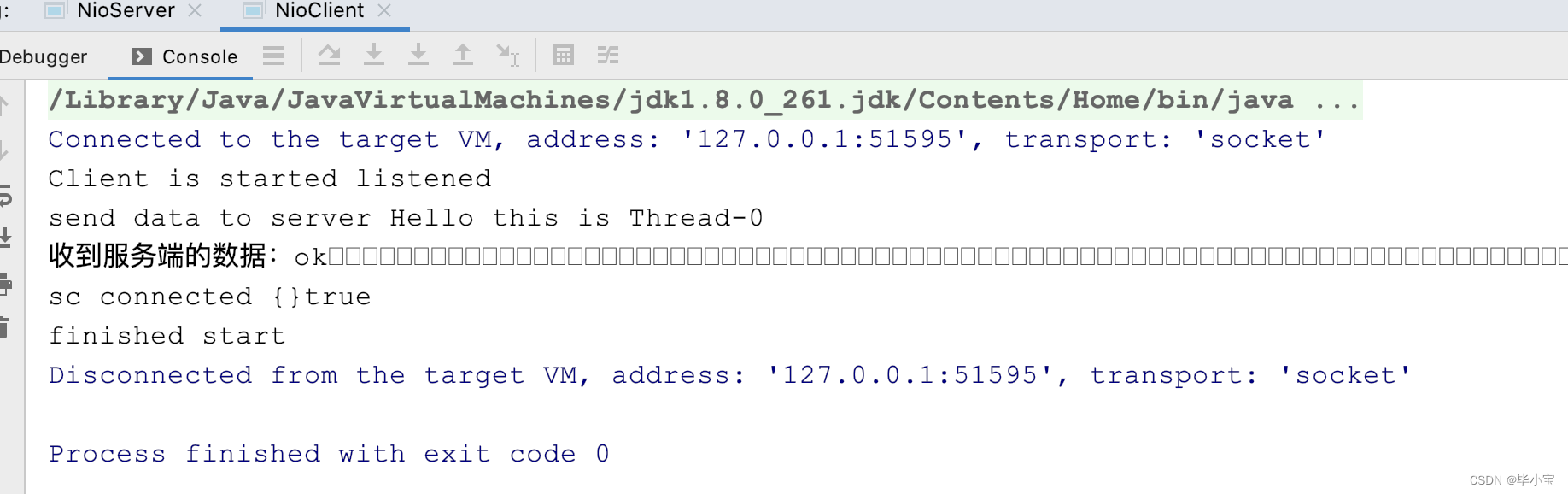
服务端,处理完一个客户端请求后,阻塞等待:

编程启示录
上面两个类,是在网上随便找到并搬来,记录一下修正的问题有两个。
第一,服务器端提交请求给处理线程时,不应该将
SelectionKey提交给线程池取消调用,因为这个异步过程,无法保证主程序轮询时SelectionKey的 isValid 状态的实时性。线程池处理的时候,具体获取到SocketChannel对象,由它去完成响应操作。主程序分发处理任务后,直接取消该SocketChannel的监听事件即可。第二,可以同时为某一
Channel注册多个事件,但方法不是调用多次register,而是一次调用的事件参数多个用|进行操作。正确:
sc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT|SelectionKey.OP_READ);错误,后面的注册事件会覆盖:
sc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ); sc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT);- 1
- 2
-
相关阅读:
python版本3.10.12 pyinstaller打包exe程序出现错误,No module named_bootlocale?
Servlet的基础详解与架构解析
Linux:文件搜索
红黑树--讲解以及详细实现过程
MyBatis使用<foreach>标签like查询报错解决
2023.8.13百度之星(第二场)第一题官方题解注释说明
sklearn混淆矩阵的计算和seaborn可视化
nacos不同局域网如何相互调用?nacos微服务云开发,远程联调部署,内网穿透,frp部署
雷达仿真:FMCW DDMA-MIMO 3D点云获取方法
彩色稻高食用价值 国稻种芯-何登骥:功能农业诠释农业大健康
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/wojiushiwo945you/article/details/126343452
