-
LeetCode-404. Sum of Left Leaves [C++][Java]
Given the
rootof a binary tree, return the sum of all left leaves.A leaf is a node with no children. A left leaf is a leaf that is the left child of another node.
Example 1:
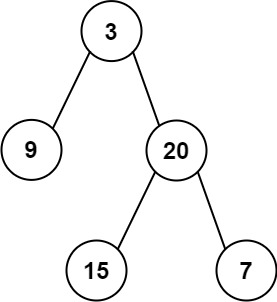
Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] Output: 24 Explanation: There are two left leaves in the binary tree, with values 9 and 15 respectively.
Example 2:
Input: root = [1] Output: 0
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 1000]. -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
【C++】
- /**
- * Definition for a binary tree node.
- * struct TreeNode {
- * int val;
- * TreeNode *left;
- * TreeNode *right;
- * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
- * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
- * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
- * };
- */
- class Solution {
- public:
- int sumOfLeftLeaves(TreeNode* root) {
- if (!root) {return 0;}
- if (isLeaf(root->left)) {
- return root->left->val + sumOfLeftLeaves(root->right);
- }
- return sumOfLeftLeaves(root->left) + sumOfLeftLeaves(root->right);
- }
- bool isLeaf(TreeNode* node){
- return node && !node->left && !node->right;
- }
- };
【Java】
- /**
- * Definition for a binary tree node.
- * public class TreeNode {
- * int val;
- * TreeNode left;
- * TreeNode right;
- * TreeNode() {}
- * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
- * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
- * this.val = val;
- * this.left = left;
- * this.right = right;
- * }
- * }
- */
- class Solution {
- public int sumOfLeftLeaves(TreeNode root) {
- if (root == null) {return 0;}
- return (isLeaf(root.left)
- ? root.left.val
- : sumOfLeftLeaves(root.left))
- + sumOfLeftLeaves(root.right);
- }
- boolean isLeaf(TreeNode node){
- return node != null
- && node.left == null
- && node.right == null;
- }
- }
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
-
相关阅读:
达梦数据库MAIN表空间导致磁盘满问题的处理和总结
flutter(学习日记篇-1)
文件复制到u盘后文件夹是空的,怎么恢复?
科技资讯|苹果新款手机支持 4.5W 反向充电,耳机手表不怕没电
v-model绑定input、textarea、checkbox、radio、select
网络安全数字孪生:一种新颖的汽车软件解决方案
基于STM32与FreeRTOS的消息传递详解(HAL库)
C++基础第9章:序列与关联容器(2)——序列容器
重新整理 .net core 实践篇 ———— dotnet-dump [外篇]
小程序中Java后台调用接口(getAccessToken)获取调用凭据,调用接口(msgSecCheck)检测文本内容是否安全--最终版
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_15711195/article/details/126331670
 https://leetcode.com/problems/sum-of-left-leaves/
https://leetcode.com/problems/sum-of-left-leaves/