-
C++内存管理机制—Primitives笔记
Primitives -基本实体
文章目录
C++语言中与内存相关的所有基础构件 (constructs),包括 malloc/free, new/delete,
operator new/operator delete, placement new/placement delete,探讨它们的意
义、运用方式和重载方式。并以此开发一个极小型内存池 (memory pool)。1、c++应用程序,使用memoryde 途径

1.1 不同方式分配内存

不管什么方式在CRT都是使用的malloc和free。
void* p1 = malloc(512); //512 bytes free(p1); complex<int>* p2 = new complex<int>; //one object delete p2; void* p3 = ::operator new(512); //512 bytes ::operator delete(p3); //以下使用 C++ 标準库提供的 allocators。 //其接口虽有标准规格,但实现厂商并未完全遵守;下面叁者形式略异。 #ifdef _MSC_VER //以下两个函数都是 non-static,定要通过 object 调用。以下分配 3 個 ints. int* p4 = allocator<int>().allocate(3, (int*)0); allocator<int>().deallocate(p4,3); #endif #ifdef __BORLANDC__ //以下兩函數都是 non-static,定要通過 object 調用。以下分配 5 個 ints. int* p4 = allocator<int>().allocate(5); allocator<int>().deallocate(p4,5); #endif #ifdef __GNUC__ //以下兩函數都是 static,可通過全名調用之。以下分配 512 bytes. //void* p4 = alloc::allocate(512); //alloc::deallocate(p4,512); //以下兩函數都是 non-static,定要通過 object 調用。以下分配 7 個 ints. void* p4 = allocator<int>().allocate(7); allocator<int>().deallocate((int*)p4,7); //以下兩函數都是 non-static,定要通過 object 調用。以下分配 9 個 ints. void* p5 = __gnu_cxx::__pool_alloc<int>().allocate(9); __gnu_cxx::__pool_alloc<int>().deallocate((int*)p5,9); #endif- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
2 、基本构件之一 new/delete expressions
2.1 当用New分配空间时
complex* pc = new complex(1, 2);- 1
转化成编辑器
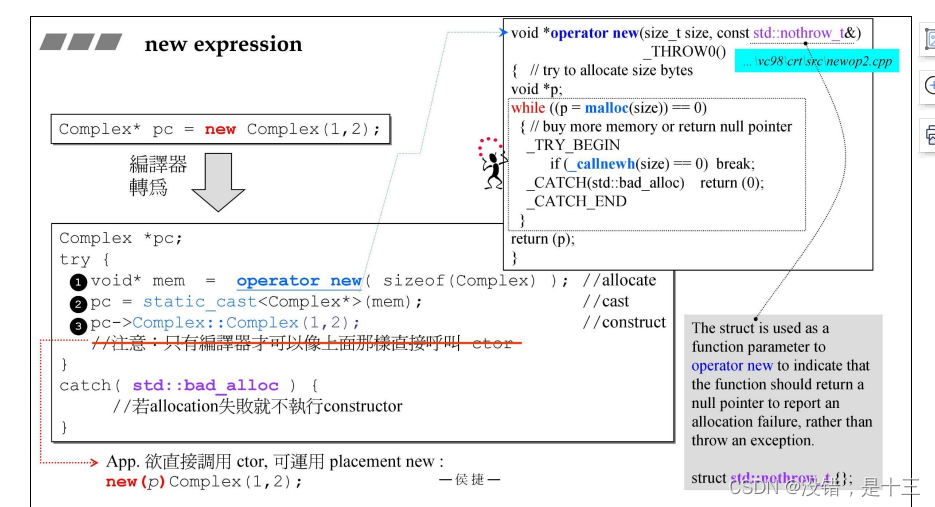
2.2 释放空间
delete pc;- 1
编译器转化为

2.3 Ctor和Dotor的调用

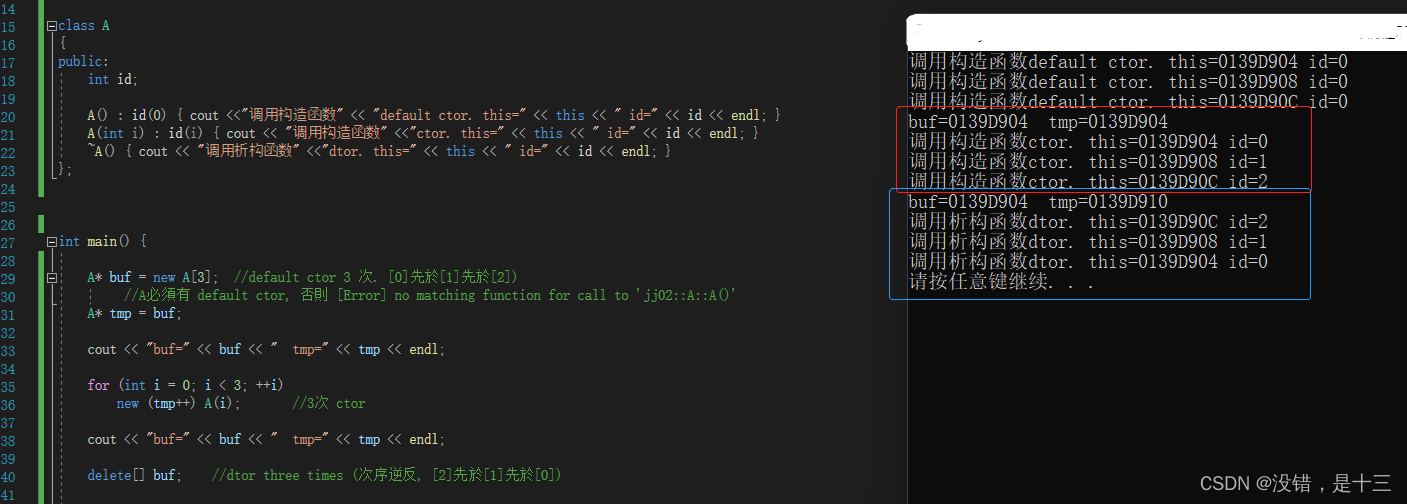
在分配空间时调用构造函数和释放是调用析构函数的顺序是相反的。3、基本构件之二 array new/delete
当数组类型分配连续的空间时。
complex * pca=new complex[3];//分配空间,调用了三次构造函数 ..... delete[] pca;//加上[] 调用了三次析构函数 string* psa=new string[3]; ... delete pca;//此时只调用了一次析构函数- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8

如果是object类型,在delete时候必须加上[]否则会存在内存部分释放完的清空。
4、基本构件之三 placement new/delete
- placement new允许我们将object构建于allocated memory中。
- 没有所谓的placement delete,因为placement new根本没有分配memory。
- placement是将前面分配的内存这给变量,没有重新分配内存。
char* buf = new char[sizeof(Complex)*3]; Complex* pc = new(buf)Complex(1,2);- 1
- 2
编译器转化为
try { void* mem = operator new(sizeof(Complex), buf); // operator new()里面啥也没做,直接返回buf pc = static_case<Complex*>(mem); pc->Complex::Complex(1,2); } catch(std::bad_alloc) { // 若allocation失败就不执行ctor }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10

5、C++应用程序,分配内存的途径


可以看到到最后面CRT都是使用的malloc和free。
6、基本构件之重载
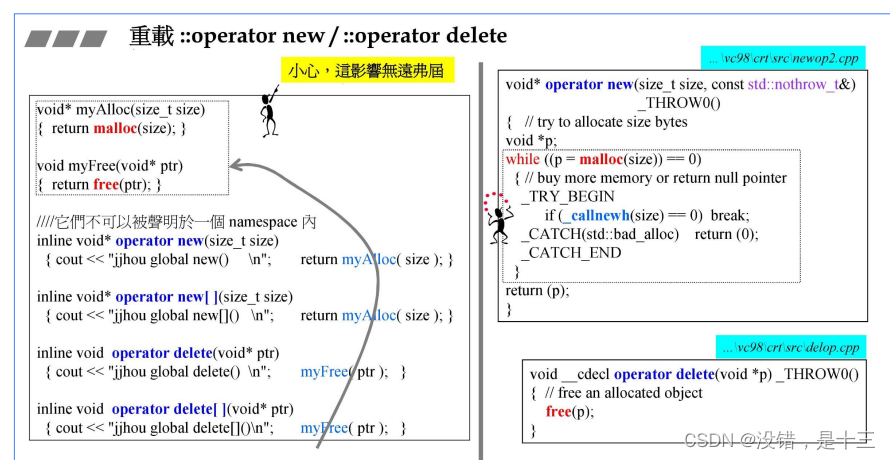
理解: 重载全局的operator new/opeartor delete,即类外重载 可以把分配空间和释放空间接管过来,自定义一些额外操作。
- 我们可以重载class member operator new(),写出多个版本,前提是每一版本的声明都必须有独特的参数列,其中第一参数必须是size_t,其余参数以new所指定的placement arguments为初值。
事例//定义一个Foo类,重载new和delete class Foo { public: int _id; long _data; string _str; public: static void* operator new(size_t size); static void operator delete(void* deadObject, size_t size); static void* operator new[](size_t size); static void operator delete[](void* deadObject, size_t size); Foo() : _id(0) { cout << "default ctor. this=" << this << " id=" << _id << endl; } Foo(int i) : _id(i) { cout << "ctor. this=" << this << " id=" << _id << endl; } //virtual ~Foo() { cout << "dtor. this=" << this << " id=" << _id << endl; } //不加 virtual dtor, sizeof = 12, new Foo[5] => operator new[]() 的 size 參數是 64, //加了 virtual dtor, sizeof = 16, new Foo[5] => operator new[]() 的 size 參數是 84, //上述二例,多出來的 4 可能就是個 size_t 欄位用來放置 array size. }; void* Foo::operator new(size_t size) { Foo* p = (Foo*)malloc(size); cout << "Foo::operator new(), size=" << size << "\t return: " << p << endl; return p; } void Foo::operator delete(void* pdead, size_t size) { cout << "Foo::operator delete(), pdead= " << pdead << " size= " << size << endl; free(pdead); } void* Foo::operator new[](size_t size) { Foo* p = (Foo*)malloc(size); //crash, 問題可能出在這兒 cout << "Foo::operator new[](), size=" << size << "\t return: " << p << endl; return p; } void Foo::operator delete[](void* pdead, size_t size) { cout << "Foo::operator delete[](), pdead= " << pdead << " size= " << size << endl; free(pdead); } //方法调用 void test_overload_operator_new_and_array_new() { cout << "\ntest_overload_operator_new_and_array_new().......... \n"; cout << "sizeof(Foo)= " << sizeof(Foo) << endl; { Foo* p = new Foo(7); delete p; Foo* pArray = new Foo[5]; //無法給 array elements 以 initializer delete [] pArray; } { cout << "testing global expression ::new and ::new[] \n"; // 這會繞過 overloaded new(), delete(), new[](), delete[]() // 但當然 ctor, dtor 都會被正常呼叫. Foo* p = ::new Foo(7); ::delete p; Foo* pArray = ::new Foo[5]; ::delete [] pArray; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
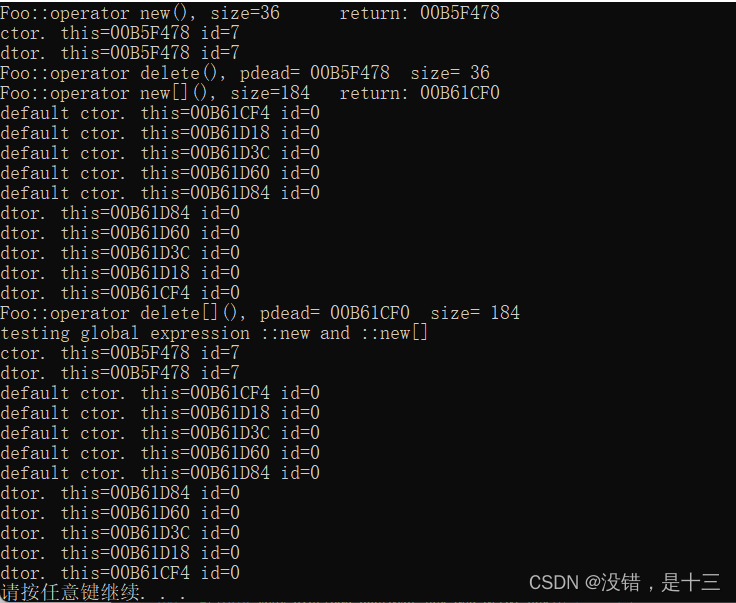

注意:如果加上::,就会使用全局版本,通过自定义重载的部分。
7、Allocator 小型内存管理
分配器分配途径:allocator—>allocate—>::operator new—>malloc
我们想要把operator new / delete抽取出来形成单独的一个类allocator,是的这个类和内存分配的分配细节剥离开,这样,需要内存管理的类,就调用allocator。这就是STL中分配器的实现思路。
减少malloc调用次数,减少cookie。一次性性分配多个连续的空间。连续创建几个只有8个字节大小的对象,如果使用自己预先申请到的一大片内存的方式,那就没有cookie(但这大块内存的上下还是有cookie的),每个对象的地址间隔(一般,因为malloc拿到的内存可能是分散的)是8字节。
但是如果是没有使用自己的内存池,那么每个对象的地址间隔是16字节,在内存布局上是上下各多了4个字节的cookie。7.1 v1版本
第一版本的opeartor new 和 operator delete:

效果
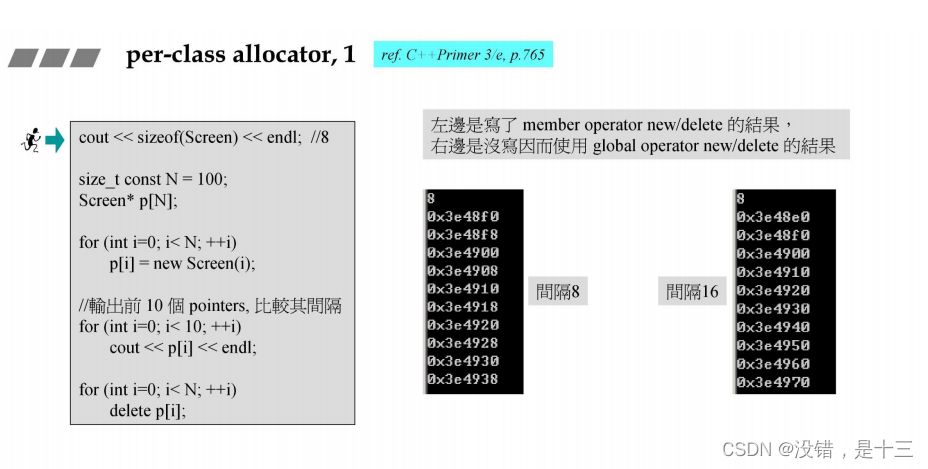
class Screen { public: Screen(int x) : i(x) { }; int get() { return i; } void* operator new(size_t); void operator delete(void*, size_t); //(2) //! void operator delete(void*); //(1) 二擇一. 若(1)(2)並存,會有很奇怪的報錯 (摸不著頭緒) private: Screen* next; static Screen* freeStore; static const int screenChunk; private: int i; }; Screen* Screen::freeStore = 0; const int Screen::screenChunk = 24; void* Screen::operator new(size_t size) { Screen *p; if (!freeStore) { //linked list 是空的,所以攫取一大塊 memory //以下呼叫的是 global operator new size_t chunk = screenChunk * size; freeStore = p = reinterpret_cast<Screen*>(new char[chunk]); //將分配得來的一大塊 memory 當做 linked list 般小塊小塊串接起來 for (; p != &freeStore[screenChunk-1]; ++p) p->next = p+1; p->next = 0; } p = freeStore; freeStore = freeStore->next; return p; } //! void Screen::operator delete(void *p) //(1) void Screen::operator delete(void *p, size_t) //(2)二擇一 { //將 deleted object 收回插入 free list 前端 (static_cast<Screen*>(p))->next = freeStore; freeStore = static_cast<Screen*>(p); } //------------- void test_per_class_allocator_1() { cout << "\ntest_per_class_allocator_1().......... \n"; cout << sizeof(Screen) << endl; //8 size_t const N = 100; Screen* p[N]; for (int i=0; i< N; ++i) p[i] = new Screen(i); //輸出前 10 個 pointers, 用以比較其間隔 for (int i=0; i< 10; ++i) cout << p[i] << endl; for (int i=0; i< N; ++i) delete p[i]; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
7.2 v2版本
使用了union ,用前4个字节当成指针来使用,即“embedded pointer”方法。
但是还是有个小缺点:收回来的指针全部累计起来了,如果能还给操作系统就更好了。
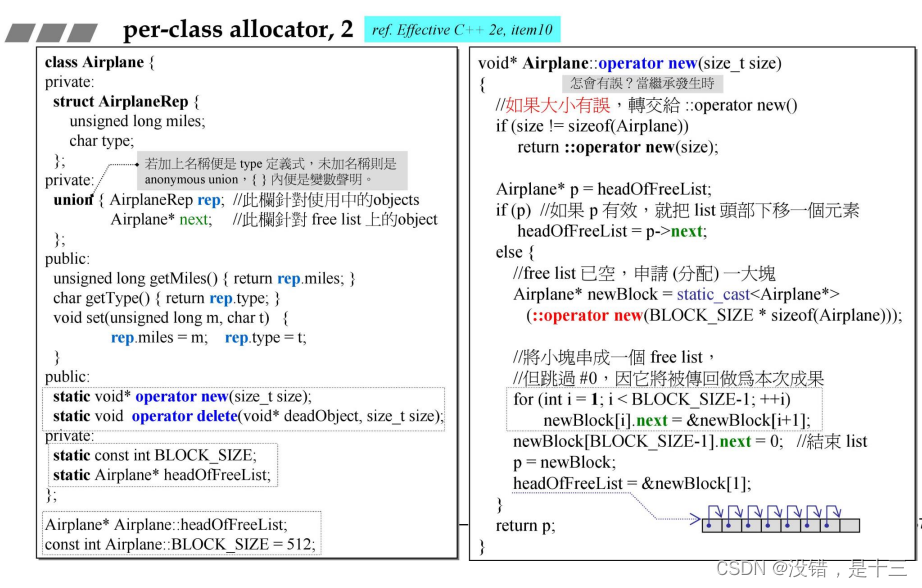

class Airplane { //支援 customized memory management private: struct AirplaneRep { unsigned long miles; char type; }; private: union { AirplaneRep rep; //此針對 used object Airplane* next; //此針對 free list }; public: unsigned long getMiles() { return rep.miles; } char getType() { return rep.type; } void set(unsigned long m, char t) { rep.miles = m; rep.type = t; } public: static void* operator new(size_t size); static void operator delete(void* deadObject, size_t size); private: static const int BLOCK_SIZE; static Airplane* headOfFreeList; }; Airplane* Airplane::headOfFreeList; const int Airplane::BLOCK_SIZE = 512; void* Airplane::operator new(size_t size) { //如果大小錯誤,轉交給 ::operator new() if (size != sizeof(Airplane)) return ::operator new(size); Airplane* p = headOfFreeList; //如果 p 有效,就把list頭部移往下一個元素 if (p) headOfFreeList = p->next; else { //free list 已空。配置一塊夠大記憶體, //令足夠容納 BLOCK_SIZE 個 Airplanes Airplane* newBlock = static_cast<Airplane*> (::operator new(BLOCK_SIZE * sizeof(Airplane))); //組成一個新的 free list:將小區塊串在一起,但跳過 //#0 元素,因為要將它傳回給呼叫者。 for (int i = 1; i < BLOCK_SIZE-1; ++i) newBlock[i].next = &newBlock[i+1]; newBlock[BLOCK_SIZE-1].next = 0; //以null結束 // 將 p 設至頭部,將 headOfFreeList 設至 // 下一個可被運用的小區塊。 p = newBlock; headOfFreeList = &newBlock[1]; } return p; } // operator delete 接獲一塊記憶體。 // 如果它的大小正確,就把它加到 free list 的前端 void Airplane::operator delete(void* deadObject, size_t size) { if (deadObject == 0) return; if (size != sizeof(Airplane)) { ::operator delete(deadObject); return; } Airplane *carcass = static_cast<Airplane*>(deadObject); carcass->next = headOfFreeList; headOfFreeList = carcass; } //------------- void test_per_class_allocator_2() { cout << "\ntest_per_class_allocator_2().......... \n"; cout << sizeof(Airplane) << endl; //8 size_t const N = 100; Airplane* p[N]; for (int i=0; i< N; ++i) p[i] = new Airplane; //隨機測試 object 正常否 p[1]->set(1000,'A'); p[5]->set(2000,'B'); p[9]->set(500000,'C'); cout << p[1] << ' ' << p[1]->getType() << ' ' << p[1]->getMiles() << endl; cout << p[5] << ' ' << p[5]->getType() << ' ' << p[5]->getMiles() << endl; cout << p[9] << ' ' << p[9]->getType() << ' ' << p[9]->getMiles() << endl; //輸出前 10 個 pointers, 用以比較其間隔 for (int i=0; i< 10; ++i) cout << p[i] << endl; for (int i=0; i< N; ++i) delete p[i]; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
7.3 v3版本 static allocator
特点:将内存的动作抽取到单一的class——allocator 中;
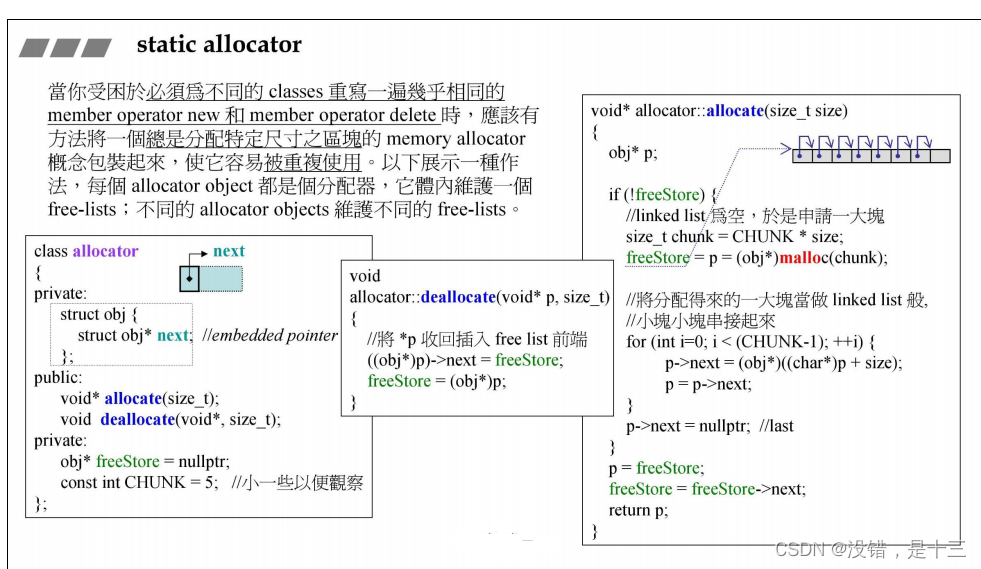

效果:

7.4 v4版本 marco for static allocator
因为每个使用allocator 的类的几处写法是固定的,于是将它们写成宏:


7.5 global allocator(with multiple free-lists)

-
相关阅读:
k8s Pod简介与探针实现零宕机发布
️️️Vue3+Element-Plus二次封装一个可定制化的table组件
通信原理学习笔记3-2:数字通信系统概述(信源编码/压缩编码、信道编码和交织)
Javascript 常见的循环方式总结
免费 AI 编程助手 Amazon CodeWhisperer 体验
python-数据描述与分析(1)
【Mybatis源码】IDEA中Mybatis源码环境搭建
旅游住宿酒店14页
Python多平台word转pdf
为什么避免在循环、条件或嵌套函数中调用 Hooks
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43482965/article/details/126324256
