-
Java随记 —— Servlet 教程笔记
文章目录
1. 概念
Servlet:server applet
Servlet即运行在服务器端的小程序- Servlet 就是一个接口,定义了 Java 类被浏览器访问到(Tomcat识别)的规则。
- 将来我们自定义一个类,实现 Servlet 接口,复写方法。

2.步骤
1. 创建 JavaEE 项目

2. 定义一个类,实现 Servlet 接口
package com.example.webdemo; import javax.servlet.*; import java.io.IOException; public class HelloServlet implements Servlet { }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
3. 实现接口中的抽象方法

package com.example.webdemo; import javax.servlet.*; import java.io.IOException; public class HelloServlet implements Servlet { @Override public void init(ServletConfig servletConfig) throws ServletException { } @Override public ServletConfig getServletConfig() { return null; } @Override public void service(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse) throws ServletException, IOException { System.out.println("Hello Servlet"); } @Override public String getServletInfo() { return null; } @Override public void destroy() { } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
4. 配置 Servlet
- 在
- 注意不要写到根标签外
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd" version="4.0"> <servlet> <servlet-name>demo1servlet-name> <servlet-class>com.example.webdemo.HelloServletservlet-class> servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>demo1servlet-name> <url-pattern>/demo1url-pattern> servlet-mapping> web-app>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
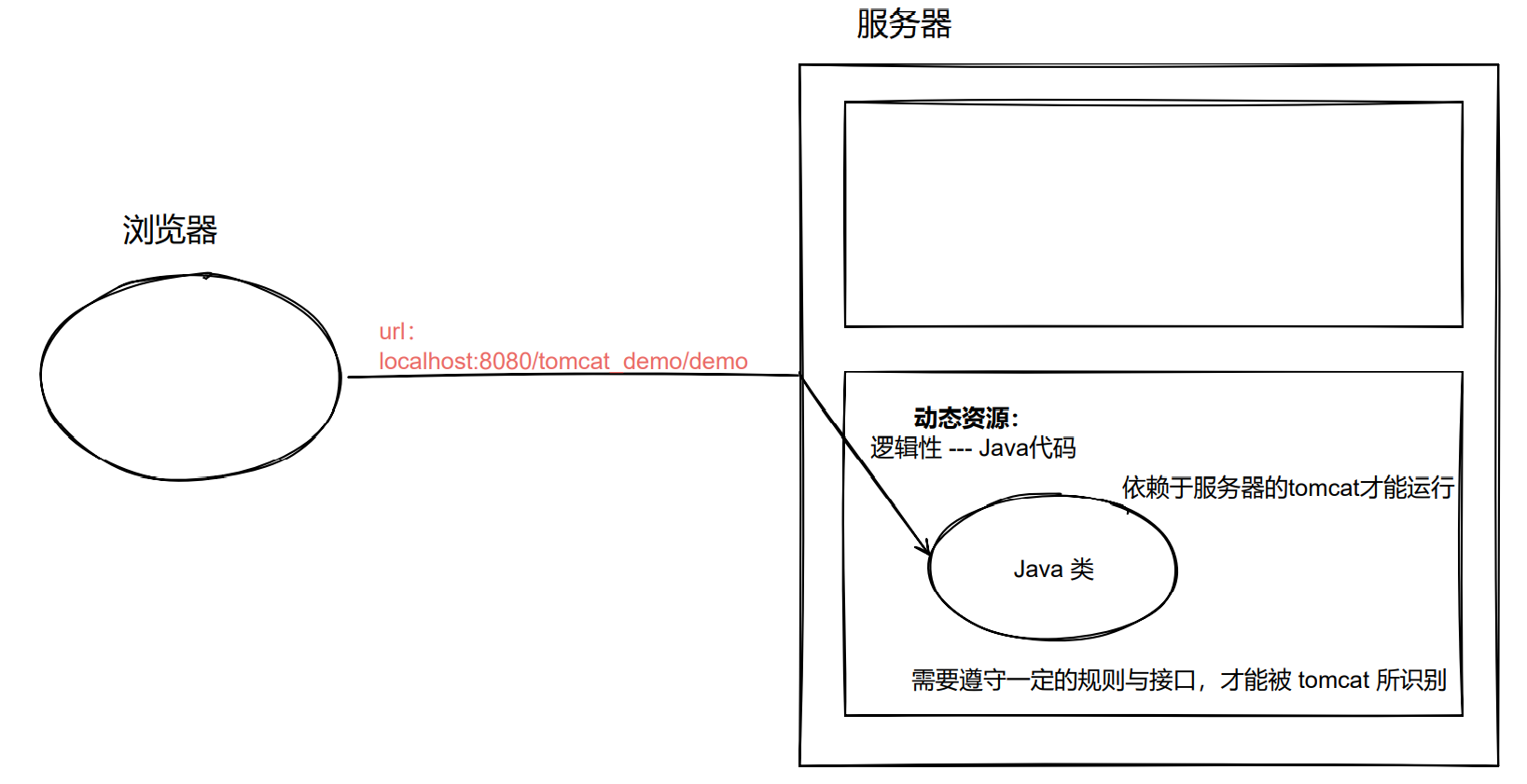
3. 执行原理
配置 Tomcat 虚拟目录
- 后期项目数量增加,配置 Tomcat 虚拟目录方便管理。
Run-->Edit Configurations...-->Tomcat 9.0.46-->Deployment-->Application context

Servlet 执行原理
- 当服务器接收到客户端浏览器的请求后,会解析请求 URL路径,获取访问的 Servlet 的资源路径
- 查找
web.xml文件,是否有对应的 - 如果有,则再找到对应的
- Tomcat 会将字节码文件加载进内存,并创建其对象
- 调用其方法

4. 生命周期
1. 被创建:执行
init方法,只执行一次Servlet 什么时候被创建 ?
- 默认情况下,第一次被访问时,Servlet 被创建
- 可以配置执行 Servlet 的创建时机。[[1. Servlet 教程#配置执行 Servlet 的创建时机]]
配置执行 Servlet 的创建时机
- 配置
-
- 第一次访问时,创建 -->
- 第一次访问时,创建 -->
-
- 服务器启动时,创建 -->
- 服务器启动时,创建 -->
-
<servlet> <servlet-name>Demo1servlet-name> <servlet-class>com.example.webdemo.Demo1servlet-class> <load-on-startup>5load-on-startup> servlet>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17

Servlet 的线程安全问题
- Servlet 的 init 方法,只执行一次,说明一个 Servlet 在内存中只存在一个对象,Servlet 是单例的。
- 多个用户同时访问时,可能存在线程安全问题
- 解决:尽量不要在 Servlet 中定义成员变量。即使定义了成员变量,也不要对其修改值
- number 不共享(解决问题)

- number 不共享(解决问题)
2. 提供服务:执行
service方法,执行多次- 每次访问 Servlet 时,Servlet 方法都会被调用一次
3. 被销毁:执行
destroy方法,只执行一次- Servlet 被销毁时执行。 服务器关闭时,Servlet 被销毁
- 只有服务器正常关闭时,才会执行
destroy方法 destroy方法在 Servlet 被销毁之前执行,一般用于释放资源(临终交代遗言)
代码
package com.example.webdemo; import javax.servlet.*; import java.io.IOException; public class HelloServlet implements Servlet { /** * 初始化方法 * 在 Servlet 被创建时,执行。只会执行一次 * * @param servletConfig * @throws ServletException */ @Override public void init(ServletConfig servletConfig) throws ServletException { System.out.println("init......"); } /** * 提供服务方法 * 每一次Servlet被访问,执行。执行多次 * * @return */ @Override public ServletConfig getServletConfig() { return null; } /** * 提供服务方法 * 每一次 Servlet 被访问是,执行,执行多次 * * @param servletRequest * @param servletResponse * @throws ServletException * @throws IOException */ @Override public void service(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse) throws ServletException, IOException { System.out.println("service......"); } /** * 获取 Servlet 的一些信息,版本,作者等等。。。 * * @return */ @Override public String getServletInfo() { return null; } /** * 销毁方法 * 在服务器正常关闭是,执行,执行一次 * */ @Override public void destroy() { System.out.println("destroy......"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
配置执行 Servlet 的创建时机
- 配置
-
- 第一次访问时,创建 -->
- 第一次访问时,创建 -->
-
- 服务器启动时,创建 -->
- 服务器启动时,创建 -->
-
<servlet> <servlet-name>Demo1servlet-name> <servlet-class>com.example.webdemo.Demo1servlet-class> <load-on-startup>5load-on-startup> servlet>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17

5. Servlet 3.0
Servlet 3.0 的好处
支持注解配置。可以不需要 web.xml 了
步骤:
- 创建 JavaEE 项目,选择 Servlet 的
3.0以上的版本,可以不创建 web.xml - 定义一个类,实现 Servlet 接口
- 复写方法
- 在类上使用
@WebServlet注解,进行配置
Servlet 3.0 注解配置方法
WebServlet("资源路径")- 1
方法一
在类前加入
@WebServlet注解并配置urlPatterns即可。- 示例
WebServlet(urlPatterns = "/demo1")- 1

方法二
value 的特性: 表示最重要的属性
由于注解
@WebServlet括号中只有一个属性,value 可以不写示例:
@WebServlet(value = "/demo1") //value 可以不写 @WebServlet("/demo1")- 1
- 2
- 3

注意
- 从 Java EE 6 才开始支持 Web 3.0 --> 支持 Servlet 3.0

6. IDEA 与 Tomcat 的相关配置
-
IDEA 会为每一个 Tomcat 部署的项目单独建立一份配置文件
- 查看控制台的 log:Using CATALINA_BASE:
- “C:\Users\fqy.IntelliJIdea2018.1\system\tomcat_itcast”
- 查看控制台的 log:Using CATALINA_BASE:
-
工作空间项目 和 Tomcat部署的web项目
- Tomcat真正访问的是“tomcat部署的web项目”,
- “Tomcat 部署的web项目"对应着"工作空间项目” 的web目录下的所有资源
- WEB-INF目录下的资源不能被浏览器直接访问。
-
断点调试:使用"小虫子"启动 dubug 启动
6. Servlet 的体系结构
1. Servlet 的结构体系
Servlet – 接口
↓
GenericServlet – 抽象类
↓
HttpServlet – 抽象类2. GenericServlet
代码 【GenericServlet.java】
// // Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA // (powered by FernFlower decompiler) // package javax.servlet; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.Serializable; import java.util.Enumeration; import java.util.ResourceBundle; public abstract class GenericServlet implements Servlet, ServletConfig, Serializable { private static final String LSTRING_FILE = "javax.servlet.LocalStrings"; private static ResourceBundle lStrings = ResourceBundle.getBundle("javax.servlet.LocalStrings"); private transient ServletConfig config; public GenericServlet() { } public void destroy() { } public String getInitParameter(String name) { ServletConfig sc = this.getServletConfig(); if (sc == null) { throw new IllegalStateException(lStrings.getString("err.servlet_config_not_initialized")); } else { return sc.getInitParameter(name); } } public Enumeration<String> getInitParameterNames() { ServletConfig sc = this.getServletConfig(); if (sc == null) { throw new IllegalStateException(lStrings.getString("err.servlet_config_not_initialized")); } else { return sc.getInitParameterNames(); } } public ServletConfig getServletConfig() { return this.config; } public ServletContext getServletContext() { ServletConfig sc = this.getServletConfig(); if (sc == null) { throw new IllegalStateException(lStrings.getString("err.servlet_config_not_initialized")); } else { return sc.getServletContext(); } } public String getServletInfo() { return ""; } public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException { this.config = config; this.init(); } public void init() throws ServletException { } public void log(String msg) { this.getServletContext().log(this.getServletName() + ": " + msg); } public void log(String message, Throwable t) { this.getServletContext().log(this.getServletName() + ": " + message, t); } public abstract void service(ServletRequest var1, ServletResponse var2) throws ServletException, IOException; public String getServletName() { ServletConfig sc = this.getServletConfig(); if (sc == null) { throw new IllegalStateException(lStrings.getString("err.servlet_config_not_initialized")); } else { return sc.getServletName(); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
由于我们常用的只有 service 方法,所以 GenericServlet 就将其它方法默认空实现,只把 service 方法抽象实现。
- GenericServlet:将Servlet接口中其他的方法做了默认空实现,只将service()方法作为抽象
- 将来定义Servlet类时,可以继承GenericServlet,实现service()方法即可
- 需要其它方法直接复写即可。
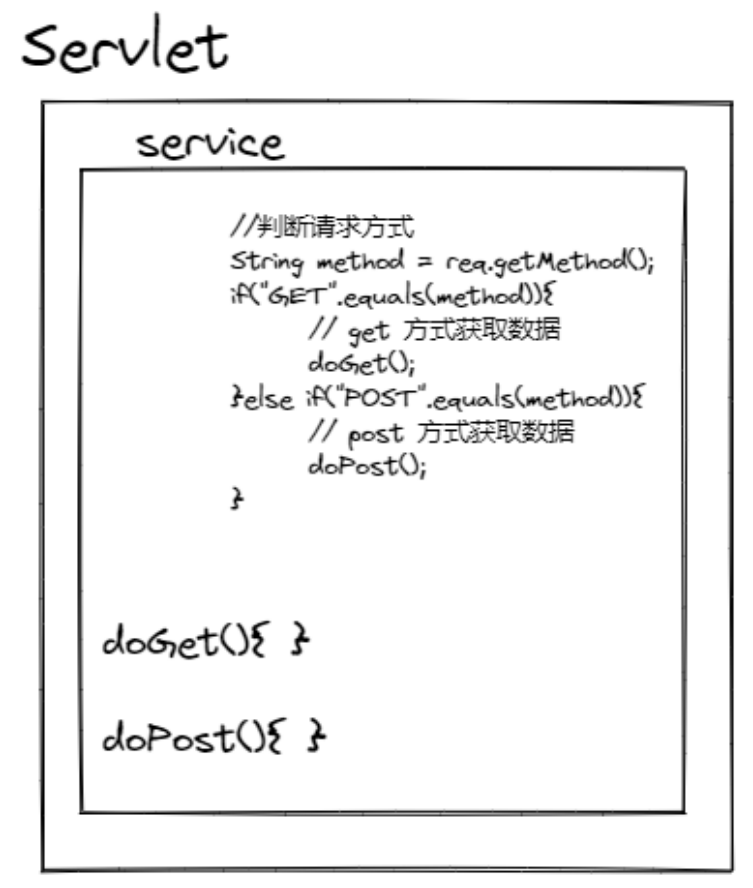
3. HttpServlet
- HttpServlet:对http协议的一种封装,简化操作
- 定义类继承 HttpServlet
- 复写 doGet/doPost 方法
7. Servlet 相关配置
- urlpartten:Servlet访问路径
- 一个Servlet可以定义多个访问路径
@WebServlet({"/d4","/dd4","/ddd4"})
- 路径定义规则:
/xxx:路径匹配 -->@WebServlet({"/user/demo4"})/xxx/xxx:多层路径,目录结构 -->@WebServlet("/user/demo4")*.do:扩展名匹配 -->@WebServlet("/*")
- 一个Servlet可以定义多个访问路径
-
相关阅读:
Hugging Face 年度回顾:2023,开源大模型之年
绝了《记一次数据库CPU使用率100%排查》
10.网络编程套接字Socket
【BI看板】Superset2.0+图表二次开发初探
2022.6.30-----leetcode.1175
二手车之家业务缓存应用实战
为什么用Selenium做自动化测试,你真的知道吗?
Vue | Vue.js 全家桶 Vuex状态管理
maven 私有仓库配置
凝思系统ftp只能下载文件,不能上传文件
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_21484461/article/details/126311773
