-
C++新特性(3)
1.返回值优化技术
返回值优化技术本质上就是移动语义的应用,在代码运行中为了维护临时对象,对产生大量的创建和销毁等操作,严重影响运行性能,使用移动语义可以直接将右值过渡给目标对象,类似于剪切而不是复制,不用反复地调用构造和析构函数。
class String { public: String() = default; String(const char* string) { std::cout << "调用构造函数!" << std::endl; m_Size = strlen(string); m_Data = new char[m_Size]; memcpy(m_Data, string, m_Size); } String(const String& other) { std::cout << "调用拷贝函数!" << std::endl; m_Size = other.m_Size; m_Data = new char[m_Size]; memcpy(m_Data, other.m_Data, m_Size); } ~String() { std::cout << "调用析构函数!" << std::endl; delete m_Data; } private: char* m_Data; int m_Size; }; String func() { String s("返回"); return s; } int main() { String result = func(); return 0; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42

此时func()函数是将对象s利用拷贝构造函数赋值给一个临时变量作为返回值,但是这个临时返回值并再调用拷贝构造函数赋值给result,而是直接将内容过渡给了result,两次调用析构函数实际上第一次是析构s,第二次是析构临时变量(result)进一步优化可以使用move函数
String&& func() { String s("返回"); return std::move(s); } int main() { String&& s = func(); return 0; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12

2.闭包
闭包:闭包是带有上下文的函数,闭包的状态捆绑,必须发生在运行时。
闭包实现的方式:
- 仿函数:重载 operator()
- std::bind绑定器
- lambda表达式
1.仿函数:重载 operator()实现闭包
仿函数:仿函数就是使用函数对象代替函数指针class Myfunc { public: Myfunc(int x,int y):x(x),y(y){} int operator()(int z) { return (x+y)*z; } private: int x; int y; }; int main() { Myfunc mul(2, 5); cout << mul(3) << endl; return 0; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
 2.bind绑定器
2.bind绑定器- std::function
function<函数返回类型(参数类型)>
头文件:#include < functional >
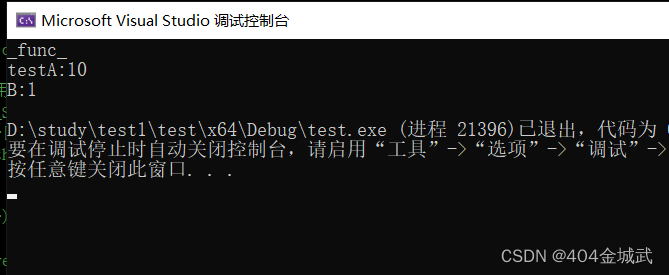
void func() { cout << "_func_" << endl; } class A { public: static int testA(int a) { cout << "testA:" << a << endl; return a; } }; class B { public: int operator()(char b) { cout << "B:" << b - 'a' << endl; return b - 'a'; } }; int main() { function<void()> f1 = func; f1(); function<int(int)> f2 = A::testA; f2(10); B b; function<int(char)> f3 = b; f3('b'); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
2.bind绑定器void func(int x, int y) { cout << x << " " << y << endl; } int main() { bind(func, 11, 22)(); bind(func, std::placeholders::_1, std::placeholders::_2)(11, 22); using namespace std::placeholders; bind(func, 11, _1)(22); bind(func, _2, 22)(22,11); return 0; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
_1表示被传进来的第一个参数所替换,_2表示被传进来的第二个参数所替换

3.bind和function结合使用using namespace std; using namespace std::placeholders; class Test { public: void func(int x, int y) { cout << x << " " << y << endl; } int a; }; int main() { Test obj; //绑定成员函数 function<void(int, int)> f1 = bind(&Test::func, &obj, _1, _2); f1(11, 22); function<int &()> f2 = bind(&Test::a, &obj); f2() = 111; cout << obj.a << endl; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23

-
相关阅读:
linux服务器集群分发scp与rsync
Postgresql数据类型-数字类型
聊聊Promise的使用
Scala的基本使用
企业IT资产设备折旧残值如何计算
【Pygame实战】只有一个币,投《勇者大冒险》还是《街霸》?(经典复刻,谁的青春回来了?)
leetcode 638. 大礼包-思路整理
练习副“产品”:自制七彩提示字符串展示工具(for循环、if条件判断)
【Linux】Linux系统编程(入门与系统编程)(三)(深入理解操作系统、进程、环境变量、内存分布)
算法与数据结构 --- 栈的表示和操作的实现
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44971209/article/details/126244179


