-
字符串算法
一、KMP(单模式)
KMP算法是一种改进的字符串匹配算法,其算法的核心是利用匹配失败后的信息,尽量减少模式串与主串的匹配次数以达到快速匹配的目的。具体实现就是通过一个next() 函数实现,函数本身包含了模式串的局部匹配信息。KMP算法的时间复杂度O(m+n)

图解:
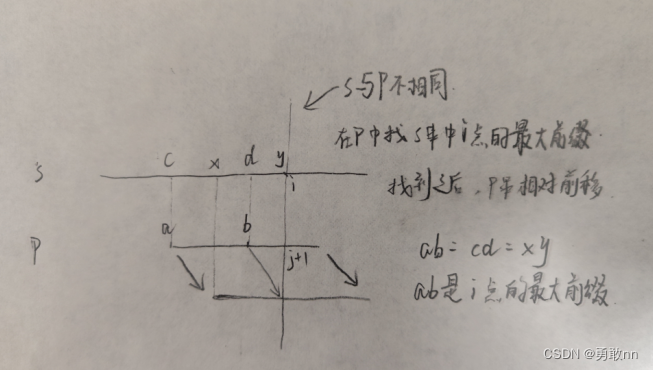
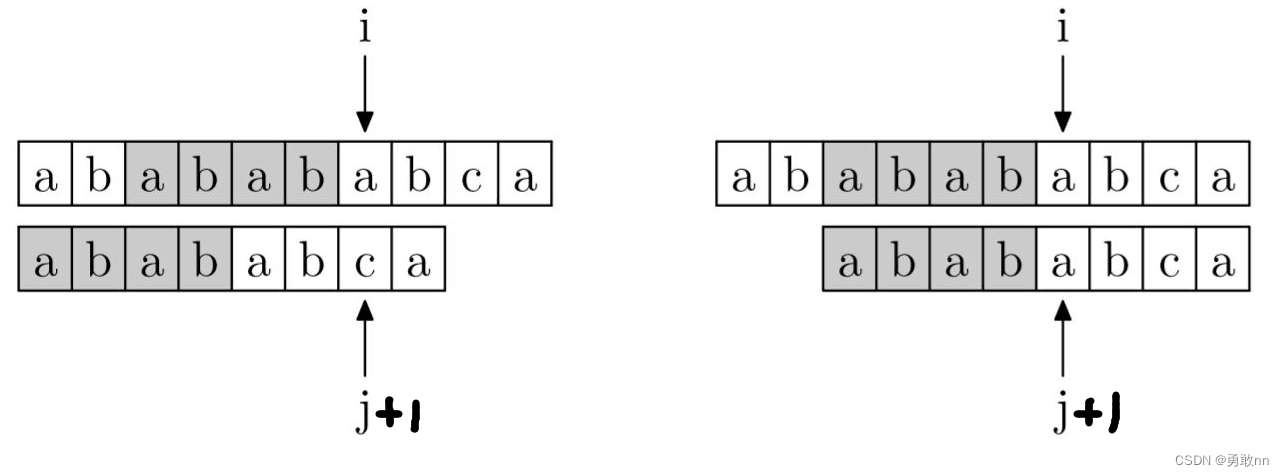
输入: 3 aba 5 ababa 输出: 0 2- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
#includeusing namespace std; int n,m; int ne[100010]; char p[100010],s[1000010]; int main() { cin>>n>>p+1>>m>>s+1; //初始化next数组 for(int i=2,j=0;i<=n;i++) { while(j&&p[i]!=p[j+1]) j=ne[j]; //j!=0防止进入死循环,如果当前位置(j+1)与模板的位置i不匹配,就向前找 当前位置前一个位置(j)的最大前缀的尾部,然后继续比较下一个位置 if(p[i]==p[j+1]) j++; ne[i]=j; } //kmp匹配过程 for(int i=1,j=0;i<=m;i++) { while(j&&s[i]!=p[j+1]) j=ne[j]; if(s[i]==p[j+1]) j++; if(j==n) //匹配成功 { printf("%d ",i-n); j=ne[j]; } } return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
二、Trie(字典树,多模式)
Trie是一种高效地存储和查找字符串集合地数据结构,又称单词查找树,是一种树形结构,是一种哈希树的变种。典型应用是用于统计,排序和保存大量的字符串(但不仅限于字符串),所以经常被搜索引擎系统用于文本词频统计。它的优点是:利用字符串的公共前缀来减少查询时间,最大限度地减少无谓的字符串比较,查询效率比哈希树高。
1. Trie字符串统计

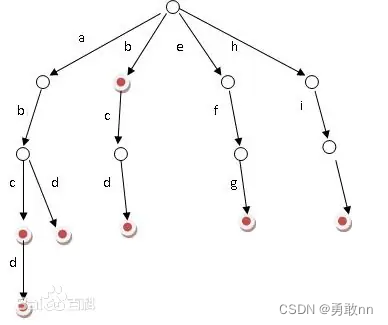
输入: 5 I abc Q abc Q ab I ab Q ab 输出: 1 0 1- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
代码如下:
#includeusing namespace std; const int N=100010; int son[N][26],cnt[N],idx; //cnt存每一个单词地个数 char str[N]; void insert(char str[]) { int p=0; //根节点地idx为0,根节点不存储字母 for(int i=0; str[i]; i++) { int u=str[i]-'a'; if(!son[p][u]) son[p][u]=++idx; //每一个节点都有一个单独的idx p=son[p][u];//存下一个节点的编号 } cnt[p]++; } int query(char str[]) { int p=0; for(int i=0; str[i]; i++) { int u=str[i]-'a'; if(!son[p][u]) return 0; p=son[p][u]; } return cnt[p]; } int main() { int n; scanf("%d",&n); while(n--) { char op[2]; scanf("%s %s",op,str); if(op[0]=='I') insert(str); else printf("%d\n",query(str)); } return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
2. 最大异或对
题目描述:
在给定的 N 个整数 A1,A2……AN 中选出两个进行异或运算,得到的结果最大是多少?输入: 3 1 2 3 输出: 3- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
#include#include using namespace std; const int N = 100010, M = 3100010; int n; int a[N], son[M][2], idx; void insert(int x) { int p = 0; for (int i = 30; i >= 0; i -- ) { int &s = son[p][x >> i & 1];//x的第i+1位 if (!s) s = ++ idx;//建立一个新结点 p = s; } } int search(int x) { int p = 0, res = 0; for (int i = 30; i >= 0; i -- ) { int s = x >> i & 1; if (son[p][!s])//存在相反位 { res += 1 << i; p = son[p][!s]; } else p = son[p][s];//不存在相反位 } return res; } int main() { scanf("%d", &n); for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) { scanf("%d", &a[i]); insert(a[i]); } int res = 0; for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) res = max(res, search(a[i])); printf("%d\n", res); return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
三、AC自动机(多模式)
输入:1 5 she he say shr her yasherhs 输出: 3- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
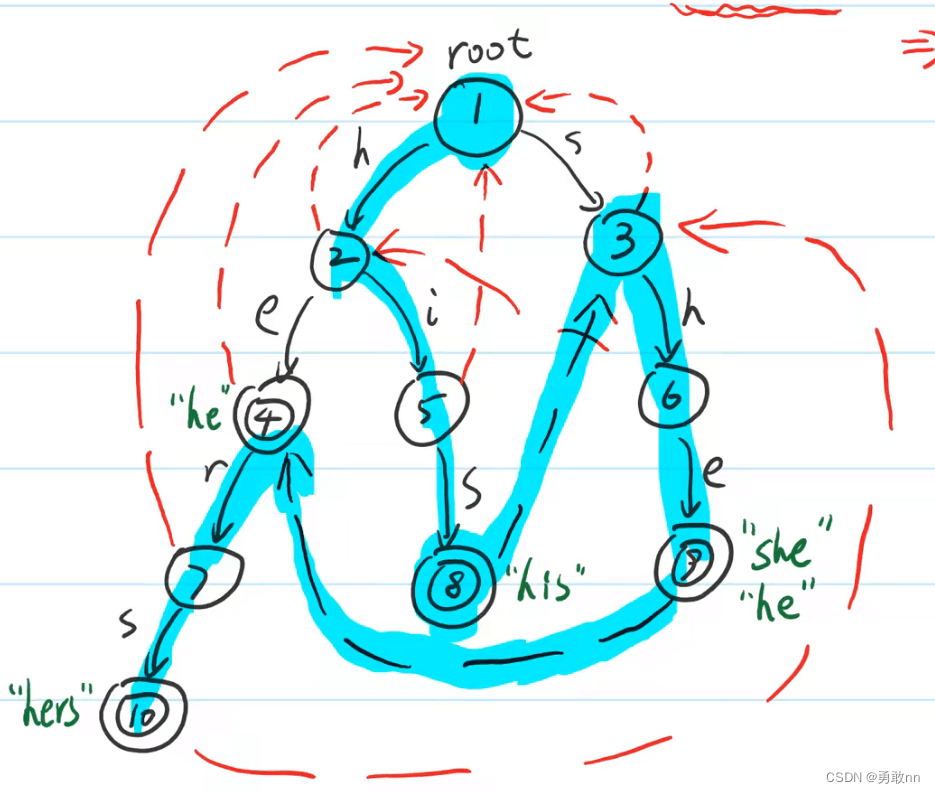
#include#include #include #include using namespace std; typedef long long ll; ll n,idx=1; ll trie[500050][26]; ll cnt[500050]; //cnt存单词的尾部,统计该单词出现的次数 ll ne[500050]; //next数组找到其最大后缀所在的位置 ll ans; void INSERT(string s) { ll root=1; for(int i=0; i<s.size(); i++) { int id=s[i]-'a'; if(!trie[root][id]) trie[root][id]=++idx; root=trie[root][id]; } cnt[root]++; } void bfs_next() { queue<ll> q; for(int i=0;i<26;i++) { trie[0][i]=1; } q.push(1); //将根节点放入队列 ne[1]=0; while(q.size()) { int u=q.front(); q.pop(); for(int i=0;i<26;i++) { if(!trie[u][i]) trie[u][i]=trie[ne[u]][i]; //剪枝 else { q.push(trie[u][i]); int v=ne[u]; ne[trie[u][i]]=trie[v][i]; //儿子指向父节点next数组指向的位置的子节点,如果该节点不存在,则指向root } } } } void FIND(string s) { int root=1; for(int i=0;i<s.size();i++) { int id=s[i]-'a'; int k=trie[root][id]; while(k>1) //从当前节点开始,递归遍历完每个节点对应的最长后缀,直到后缀长度为0,即回到root { ans+=cnt[k]; cnt[k]=0; k=ne[k]; } root=trie[root][id]; //儿子变成父亲 } } int main() { ios::sync_with_stdio(false); //此时只能用cin,而不能用scanf int t; cin>>t; while(t--) { ans=0; memset(cnt,0,sizeof cnt); memset(trie,0,sizeof trie); memset(ne,0,sizeof ne); cin>>n; string s; for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) { cin>>s; INSERT(s); } bfs_next(); cin>>s; FIND(s); cout<<ans<<endl; } return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
-
相关阅读:
Redisson集成SpringBoot
项目部署之持续集成
Java-数据结构-链表<三>
第59章 ApplicationPart内置依赖注入中间件
湖仓一体电商项目(十五):实时统计商品及一级种类、二级种类访问排行业务需求和分层设计及流程图
顺序表和链表
字节跳动java面试题,附详细答案解析
Day 46 Redis缓存集群
IoC和DI
机器学习-决策树
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_53726614/article/details/126237639