-
Netty学习笔记之Java I/O
Java IO
I/O模型
Java BIO:同步阻塞(传统阻塞型),服务器实现模式为一个连接一个线程,对每个客户端的连接服务器都会新建一个线程进行处理,如果这个连接不做任何事情会造成不必要的线程开销。
Java BIO模型示意图: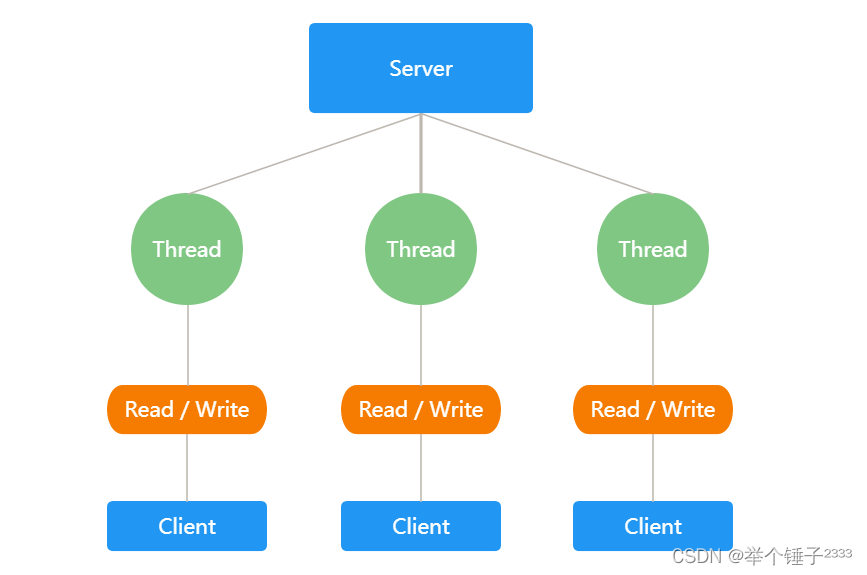
Java NIO:同步非阻塞,服务器实现模式为一个线程处理多个请求(连接),服务器将客户端的连接注册到多路复用器上,多路复用器轮询到连接有 I/O 请求就进行处理。
Java NIO模型示意图:

Java AIO:异步非阻塞,AIO 引入异步通道的概念,采用了 Proactor 模式,简化了程序编写,有效的请求才启动线程,它的特点是先由操作系统完成后才通知服务端程序启动线程去处理,一般适用于连接数较多且连接时间较长的应用。BIO、NIO、AIO适用场景
- BIO 方式适用于连接数目比较小且固定的架构,这种方式对服务器资源要求比较高,并发局限于应用中,JDK1.4以前的唯一选择,但程序简单易理解。
- NIO 方式适用于连接数目多且连接比较短(轻操作) 的架构,比如聊天服务器,弹幕系统,服务器间通讯等。编程比较复杂,JDK1.4 开始支持。
- AIO 方式使用于连接数目多且连接比较长(重操作) 的架构,比如相册服务器,充分调用 OS 参与并发操作,编程比较复杂,JDK7 开始支持。
BIO、NIO、AIO 对比
BIO NIO AIO IO模型 同步阻塞 同步非阻塞(多路复用) 异步非阻塞 可靠性 低 高 高 吞吐量 低 高 高 编程难度 简单 复杂 复杂 BIO、NIO不同点
- BIO 以流的方式处理数据,而 NIO 以块的方式处理数据,块I/O 的效率比流 I/O高很多
- BIO 是阻塞的,NIO 则是非阻塞的
- BIO 基于字节流和字符流进行操作,而 NIO 基于 Channel(通道) 和Buffer(缓冲区) 进行操作,数据总是从通道读取到缓冲区中,或者从缓冲区写入到通道中。Selector(选择器)用于监听多个通道的事件(比如:连接请求,数据到达等),因此使用单个线程就可以监听多个客户端通道
BIO
BIO工作流程
- 服务器启动ServerSocket
- 客户端发起连接请求,服务器对该客户端新建一个线程进行通信
- 客户端发送请求后,先咨询服务器是否有线程响应,如果没有则会等待,或者被拒绝
- 如果有响应,客户端线程会等待请求结束后,再继续执行
代码示例
package com.atguigu.bio; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.net.ServerSocket; import java.net.Socket; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; /** * @author RedStar * @date 2022/06/09 15:16 * @description */ public class BIOServer { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); // 创建ServerSocket ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(6666); System.out.println("服务器启动"); while (true) { // 监听等待客户端连接 final Socket socket = serverSocket.accept(); System.out.println("新客户端连接"); // 启动新线程 newCachedThreadPool.execute(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { handler(socket); } }); } } /** * @author RedStar * @date 2022/6/9 15:22 * @description socket的handler方法 */ public static void handler(Socket socket) { try { byte[] bytes = new byte[1024]; // 通过socket获取输入流 InputStream inputStream = socket.getInputStream(); // 循环读取客户端发来的数据 while (true) { int read = inputStream.read(bytes); if (read != -1) { System.out.println(new String(bytes, 0, read)); } else { break; } } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { System.out.println("关闭socket连接"); try { socket.close(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
缺点
- 每个请求都需要创建独立的线程,与对应的客户端进行数据 Read、业务处理、数据 Write
- 当并发数较大时,需要创建大量线程来处理连接,系统资源占用较大
- 连接建立后,如果当前线程暂时没有数据可读,则线程就阻塞在 Read 操作上,造成线程资源浪费
NIO
基本介绍
- NIO 相关类都被放在java.nio包及子包下,并且对原 java.io 包中的很多类进行改写
- NIO 有三大核心部分:Channel(通道),Buffer(缓冲区), Selector(选择器)
- NIO 是 面向缓冲区 ,或者面向块编程的。数据读取到一个它稍后处理的缓冲区,需要时可在缓冲区中前后移动,这就增加了处理过程中的灵活性,使用它可以提供非阻塞式的高伸缩性网络
Selector 、 Channel 和 Buffer 的关系
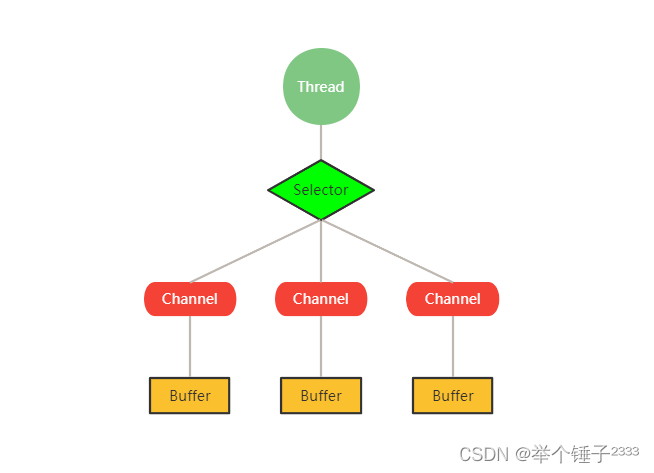
- 每个channel都会对应一个Buffer
- Selector 对应一个线程,一个线程对应多个channel(连接)
- 该图反应了有三个channel注册到该selector程序
- 程序切换到哪个channel是有事件决定的, Event 就是一个重要的概念
- Selector 会根据不同的事件,在各个通道上切换
- Buffer 就是一个内存块 , 底层是有一个数组
- 数据的读取写入是通过Buffer实现,BIO中要么是输入流,或者是输出流,不能双向。但是NIO的Buffer是可以读也可以写, 需要 flip 方法切换channel,Buffer操作是双向的。
Buffer
缓冲区(Buffer):缓冲区本质上是一个可以读写数据的内存块,可以理解成是一个容器对象(含数组),该对象提供了一组方法,可以更轻松地使用内存块,缓冲区对象内置了一些机制,能够跟踪和记录缓冲区的状态变化。Channel提供从文件、网络读取数据的渠道,但是读取或写入的数据都必须经由 Buffer。
Buffer子类
- ByteBuffer,存储字节数据到缓冲区
- ShortBuffer,存储字符串数据到缓冲区
- CharBuffer,存储字符数据到缓冲区
- IntBuffer,存储整数数据到缓冲区
- LongBuffer,存储长整型数据到缓冲区
- DoubleBuffer,存储小数到缓冲区
- FloatBuffer,存储小数到缓冲区
Buffer及其子类共有属性
- Capacity 容量,即可以容纳的最大数据量;在缓冲区创建时被设定并且不能改变
- Limit 表示缓冲区的当前终点,不能对缓冲区超过极限的位置进行读写操作。且极限是可以修改的
- Position 位置,下一个要被读或写的元素的索引,每次读写缓冲区数据时都会改变改值,为下次读写作准备
- Mark 标记
Buffer常用方法
public abstract class Buffer { // JDK1.4时,引入的api public final int capacity( ); // 返回此缓冲区的容量 public final int position( ); // 返回此缓冲区的位置 public final Buffer position (int newPositio); // 设置此缓冲区的位置 public final int limit( ); // 返回此缓冲区的限制 public final Buffer limit (int newLimit); // 设置此缓冲区的限制 public final Buffer mark( ); // 在此缓冲区的位置设置标记 public final Buffer reset( ); // 将此缓冲区的位置重置为以前标记的位置 public final Buffer clear( ); // 清除此缓冲区, 即将各个标记恢复到初始状态,但是数据并没有真正擦除, 后面操作会覆盖 public final Buffer flip( ); // 反转此缓冲区 public final Buffer rewind( ); // 重绕此缓冲区 public final int remaining( ); // 返回当前位置与限制之间的元素数 public final boolean hasRemaining( ); // 告知在当前位置和限制之间是否有元素 public abstract boolean isReadOnly( ); // 告知此缓冲区是否为只读缓冲区 // JDK1.6时引入的api public abstract boolean hasArray(); // 告知此缓冲区是否具有可访问的底层实现数组 public abstract Object array(); // 返回此缓冲区的底层实现数组 public abstract int arrayOffset(); // 返回此缓冲区的底层实现数组中第一个缓冲区元素的偏移量 public abstract boolean isDirect(); // 告知此缓冲区是否为直接缓冲区 }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
ByteBuffer
Java的基本类型(除boolean)都有一个Buffer子类与之对应,最常用的是ByteBuffer类(二进制数据)
public abstract class ByteBuffer { // 缓冲区创建相关api public static ByteBuffer allocateDirect(int capacity) // 创建直接缓冲区 public static ByteBuffer allocate(int capacity) // 设置缓冲区的初始容量 public static ByteBuffer wrap(byte[] array) // 把一个数组放到缓冲区中使用 // 构造初始化位置offset和上界length的缓冲区 public static ByteBuffer wrap(byte[] array,int offset, int length) // 缓存区存取相关API public abstract byte get( ); // 从当前位置position上get,get之后,position会自动+1 public abstract byte get (int index); // 从绝对位置get public abstract ByteBuffer put (byte b); // 从当前位置上添加,put之后,position会自动+1 public abstract ByteBuffer put (int index, byte b); // 从绝对位置上put }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
Channel
基本介绍
- NIO 的通道类似于流
- NIO 中的通道(Channel)是双向的,可以读操作,也可以写操作。BIO 中的 stream 是单向的,例如 FileInputStream对象只能进行读取数据的操作
- Channel 在 NIO 中是一个接口,常用的Channel实现类有FileChannel 、 DatagramChannel 、 ServerSocketChannel 和 SocketChannel(ServerSocketChanne 类似 ServerSocket , SocketChannel 类似 Socket)
FileChannel
FileChannel 主要用来对本地文件进行 IO 操作
public int read(ByteBuffer dst); // 从通道读取数据并放到缓冲区中 public int write(ByteBuffer src); // 把缓冲区的数据写到通道中 public long transferFrom(ReadableByteChannel src, long position, long count); // 从目标通道中复制数据到当前通道 public long transferTo(long position, long count, WritableByteChannel target); // 把数据从当前通道复制给目标通道- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
FileChannel代码示例
读文件
package com.atguigu.channel; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.nio.ByteBuffer; import java.nio.channels.FileChannel; /** * @author RedStar * @date 2022/06/10 16:27 * @description */ public class FileChannelRead { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // 创建文件的输入流 File file = new File("d:\\file.txt"); FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(file); // 获取流对象的channel FileChannel channel = fileInputStream.getChannel(); // 创建buffer对象 ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); // 将channel中的数据读到buffer channel.read(byteBuffer); // 将buffer中的字节数据转化为string并输出 System.out.println(new String(byteBuffer.array())); // 关闭流对象 fileInputStream.close(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
写文件
package com.atguigu.channel; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.nio.ByteBuffer; import java.nio.channels.FileChannel; import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets; /** * @author RedStar * @date 2022/06/10 16:12 * @description */ public class FileChannelWrite { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { String str = "hello world"; // 新建文件输出流对象 FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("d:\\file.txt"); // 获取流对象的channel FileChannel channel = fileOutputStream.getChannel(); // 新建buffer、存入数据并读写反转 ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); byteBuffer.put(str.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)); byteBuffer.flip(); // 将buffer中的数据写到channel中 channel.write(byteBuffer); // 关闭channel fileOutputStream.close(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
拷贝文件
package com.atguigu.channel; import java.io.*; import java.nio.ByteBuffer; import java.nio.channels.FileChannel; /** * @author RedStar * @date 2022/06/10 16:36 * @description */ public class FileChannelCopy { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // 获取输入输出流对象 String filePathFrom = "d://file.txt"; String filePathTo = "d://file1.txt"; FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(filePathFrom); FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(filePathTo); // 获取输入输出channel FileChannel inputStreamChannel = fileInputStream.getChannel(); FileChannel outputStreamChannel = fileOutputStream.getChannel(); // 创建buffer ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); while (true) { // 清空buffer byteBuffer.clear(); // read为本次读取的长度,-1为读取完毕 int read = inputStreamChannel.read(byteBuffer); if (read == -1) { break; } // buffer读写操作反转 byteBuffer.flip(); // 将buffer中的数据写入outStreamChannel outputStreamChannel.write(byteBuffer); } // 关闭输入输出流 fileInputStream.close(); fileOutputStream.close(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
剪切文件
package com.atguigu.channel; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.nio.channels.FileChannel; /** * @author RedStar * @date 2022/06/10 16:56 * @description */ public class FileChannelDirect { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // 获取输入输出流对象 String filePathFrom = "d://file.txt"; String filePathTo = "d://file1.txt"; FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(filePathFrom); FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(filePathTo); // 获取输入输出channel FileChannel inputStreamChannel = fileInputStream.getChannel(); FileChannel outputStreamChannel = fileOutputStream.getChannel(); // 使用transferFrom完成拷贝 outputStreamChannel.transferFrom(inputStreamChannel, 0, inputStreamChannel.size()); // 关闭流对象 fileInputStream.close(); fileOutputStream.close(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
Selector
基本介绍
- Java的NIO,用非阻塞的 IO 方式。可以用一个线程,处理多个的客户端连接,就会使用到Selector(选择器) Selector
- 能够检测多个注册的通道上是否有事件发生(注意:多个 Channel以事件的方式可以注册到同一个Selector),如果有事件发生,便获取事件然后针对每个事件进行相应的处理。这样就可以只用一个单线程去管理多个通道,也就是管理多个连接和请求
- 只有在连接/通道真正有读写事件发生时,才会进行读写,就大大地减少了系统开销,并且不必为每个连接都创建一个线程,不用去维护多个线程,避免了多线程之间上下文切换导致额外的开销
Selector示意图:
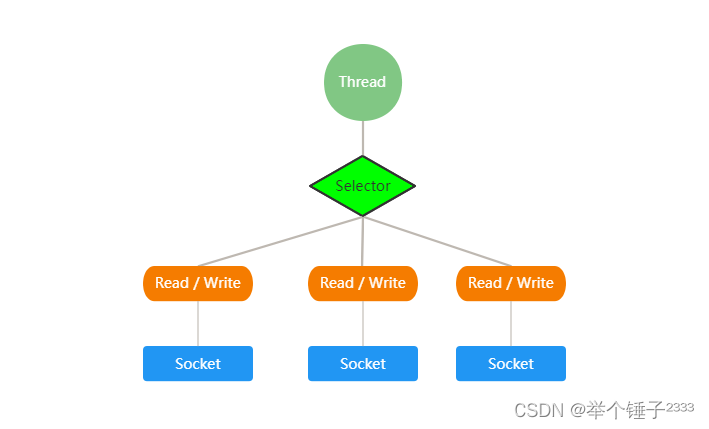
- Netty 的 IO 线程 NioEventLoop 聚合了 Selector(选择器,也叫多路复用器),可以同时并发处理成百上千个客
户端连接。 - 当线程从某客户端 Socket 通道进行读写数据时,若没有数据可用时,该线程可以进行其他任务。
- 线程通常将非阻塞 IO 的空闲时间用于在其他通道上执行 IO 操作,所以单独的线程可以管理多个输入和输出
通道。 - 由于读写操作都是非阻塞的,这就可以充分提升 IO 线程的运行效率,避免由于频繁 I/O 阻塞导致的线程挂
起。 - 一个 I/O 线程可以并发处理 N 个客户端连接和读写操作,这从根本上解决了传统同步阻塞 I/O 一连接一线
程模型,架构的性能、弹性伸缩能力和可靠性都得到了极大的提升。
Selector类及其相关方法
Selector是一个抽象类,常见方法和说明如下:
public abstract class Selector implements Closeable { public static Selector open(); // 得到一个选择器对象 public int select(long timeout); // 监控所有注册的通道,当其中有 IO 操作可以进行时,将对应的 SelectionKey 加入到内部集合中并返回,参数用来 设置超时时间 public Set<SelectionKey> selectedKeys(); // 从内部集合中得到所有的SelectionKey } selector.select() // 阻塞 selector.select(1000); // 阻塞1000毫秒,在1000毫秒后返回 selector.wakeup(); // 唤醒selector selector.selectNow(); // 不阻塞,立马返回- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
其他相关类
SelectionKey
SelectionKey表示Selector和网络通道的注册关系,该关系共四种:
public static final int OP_READ = 1 << 0; // 代表读操作,值为 1 public static final int OP_WRITE = 1 << 2; // 代表写操作,值为 4 public static final int OP_CONNECT = 1 << 3;// 代表连接已经建立,值为 8 public static final int OP_ACCEPT = 1 << 4; // 有新的网络连接可以 accept,值为 16- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
SelectionKey相关方法
public abstract class SelectionKey { public abstract Selector selector(); // 得到与之关联的Selector对象 public abstract SelectableChannel channel(); // 得到与之关联的通道 public final Object attachment(); // 得到与之关联的共享数据 public abstract SelectionKey interestOps(int ops); // 设置或改变监听事件 public final boolean isAcceptable(); // 是否可以 accept public final boolean isReadable(); // 是否可以读 public final boolean isWritable(); // 是否可以写 }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
Channel注册到Selector需要指定自己感兴趣的事件,感兴趣就是该通道需要关注的事件,如果channel1只有在客户端发来数据的时候执行相应操作,那么它只需要注册
SelectionKey.OP_READ, 当发生读事件时,此通道对应的selectionKey.isReadable()方法返回true。除此之外该通道上发生的其他事件并不会被感知。channel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ); // 可以通过|(或运算符)监听多个事件 // channel注册到同一个Selector两次, 那么第二次的注册其实就是相当于更新这个Channel的interestSet为SelectionKey.OP_READ|SelectionKey.OP_WRITE channel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ | SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
Channel.register()方法实际上是得到第二个参数与运算后的结果,然后调用该通道对应的SelectionKey.interestOps()方法。也就是说SelectionKey的实现类有一个interestOps属性,该属性的值是对应通道想要监听的事件值与操作后的结果。ServerSocketChannel
ServerSocketChannel是一个可以监听新建TCP连接的通道ServerSocketChannel相关方法
public abstract class ServerSocketChannel extends AbstractSelectableChannel implements NetworkChannel{ public static ServerSocketChannel open(); // 得到一个 ServerSocketChannel 通道 public final ServerSocketChannel bind(SocketAddress local); // 设置服务器端端口号 public final SelectableChannel configureBlocking(boolean block); // 设置阻塞或非阻塞模式,取值 false 表示采用非阻塞模式 public SocketChannel accept(); // 接受一个连接,返回代表这个连接的通道对象SocketChannel public final SelectionKey register(Selector sel, int ops); // 注册一个选择器并设置监听事件 }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
阻塞模式
通过
ServerSocketChannel.accept()方法监听新进来的连接。当accept()方法返回的时候,它返回一个包含新进来的连接的 SocketChannel。因此,accept()方法会一直阻塞到有新连接到达。ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open(); serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(9999)); serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(true); while(true){ SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept(); // 业务处理 }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
非阻塞模式
当然
ServerSocketChannel也可以设置成非阻塞模式。在非阻塞模式下,accept()方法会立刻返回,如果还没有新进来的连接,返回的将是null。 因此,需要检查返回的SocketChannel是否是nullServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open(); serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(9999)); serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false); while(true){ SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept(); if(socketChannel != null){ // 业务处理 } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
SocketChannel
SocketChannel是一个连接到TCP网络套接字的通道,具体负责进行读写操作。NIO 把缓冲区的数据写入通道,或者把通道里的数据读到缓冲区SocketChannel相关方法
public abstract class SocketChannel extends AbstractSelectableChannel implements ByteChannel, ScatteringByteChannel, GatheringByteChannel, NetworkChannel{ public static SocketChannel open(); // 得到一个SocketChannel 通道 public final SelectableChannel configureBlocking(boolean block); // 设置阻塞或非阻塞模式,取值false表示采用非阻塞模式 public boolean connect(SocketAddress remote); // 连接服务器 public boolean finishConnect(); // 如果上面的方法连接失败,接下来就要通过该方法完成连接操作 public int write(ByteBuffer src); // 往通道里写数据 public int read(ByteBuffer dst); // 从通道里读数据 public final SelectionKey register(Selector sel, int ops, Object att); // 注册一个选择器并设置监听事件,最后一个参数可以设置共享数据 public final void close(); // 关闭通道 }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
NIO非阻塞网络编程原理分析
NIO核心组件关系图:
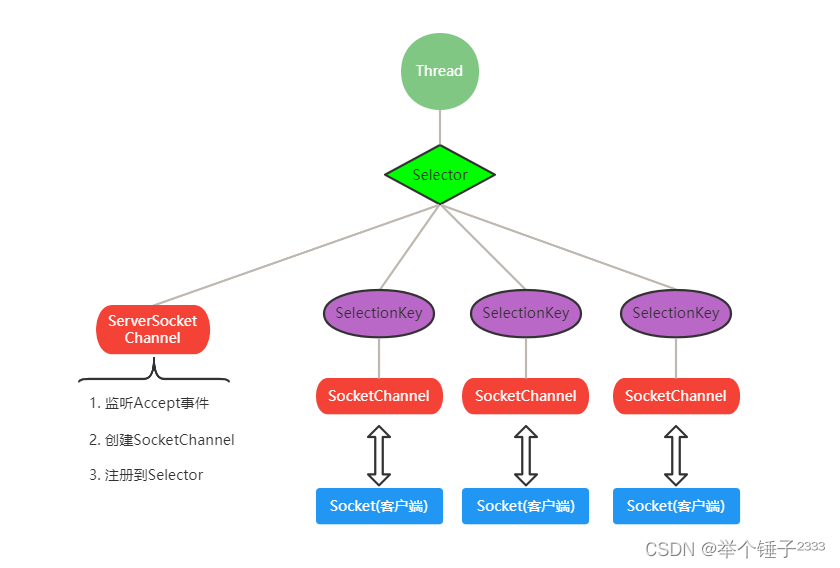
相关代码在群聊系统GroupChatServer中查看
- 当客户端连接时,
ServerSocketChannel监听到连接accept事件 - 创建新的
SocketChannel并注册到一个Selector上,一个Selector可以注册多个SocketChannel - 注册方法返回一个
SelectionKey, 会和该Selector关联(集合) Selector进行监听select()方法, 返回有事件发生的通道的个数Selector.selectedKeys()方法返回所有有事件发生的通道对应的SelectionKey集合- 通过集合进一步得到各个
SelectionKey SelectionKey.channel()方法反向获取 SocketChannel- 可以通过得到的channel, 完成业务处理
NIO群聊系统代码示例
服务端
package com.atguigu.nioGroupChat; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.InetSocketAddress; import java.nio.ByteBuffer; import java.nio.channels.*; import java.util.Iterator; /** * @author RedStar * @date 2022/07/20 15:45 * @description NIO群聊系统服务端 */ public class GroupChatServer { private Selector selector; private ServerSocketChannel listenChannel; private static final int PORT = 9528; /** * @author RedStar * @date 2022/7/20 15:47 * @description 构造器 */ public GroupChatServer() { try { // 获取选择器 selector = Selector.open(); // 获取serverSocketChannel listenChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open(); // 绑定端口 listenChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(PORT)); // 设置非阻塞模式 listenChannel.configureBlocking(false); // 将该listenChannel注册到selector listenChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } /** * @author RedStar * @date 2022/7/20 15:51 * @description 监听方法 */ public void listen() { try { while (true) { // selectCount为事件数量 int selectCount = selector.select(2000); if (selectCount > 0) { // 获取所有发生事件的SelectionKey集合 Iterator<SelectionKey> keyIterator = selector.selectedKeys().iterator(); while (keyIterator.hasNext()) { // 取出selectionKey SelectionKey key = keyIterator.next(); // 监听accept事件 if (key.isAcceptable()) { SocketChannel sc = listenChannel.accept(); // 设置为非阻塞 sc.configureBlocking(false); // 将socketChannel注册到seletor并监听读事件 sc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ); System.out.println(sc.getRemoteAddress() + " 上线"); } // 监听read事件 if (key.isReadable()) { SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) key.channel(); System.out.println("通道[" + channel.hashCode() + "] readable"); readData(key); } // 监听write事件 // if(key.isWritable()) { // SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) key.channel(); // System.out.println("通道[" + channel.hashCode() + "] writeable" ); // } // 监听connect事件 // if(key.isConnectable()) { // SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) key.channel(); // System.out.println("通道[" + channel.hashCode() + "] connectable" ); // } // 删除当前的事件key,防止重复处理 keyIterator.remove(); } } else { System.out.println("等待连接..."); } } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } /** * @author RedStar * @date 2022/7/20 16:08 * @description 读取客户端消息 */ public void readData(SelectionKey key) { // 定义一个socketChannel SocketChannel channel = null; try { // 取到关联的channel channel = (SocketChannel) key.channel(); // 创建buffer ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); // 获取数据长度 int len = channel.read(buffer); if (len > 0) { // 把缓冲区的数据转换成字符串 String msg = new String(buffer.array()); System.out.println("from 客户端:" + msg); // 向其他客户端转发消息 sendInfoToOtherClients(msg, channel); } } catch (IOException e) { try { System.err.println(channel.getRemoteAddress() + " 离线了"); // 取消注册 key.cancel(); // 关闭通道 channel.close(); } catch (IOException e2) { e2.printStackTrace(); } } } /** * @author RedStar * @date 2022/7/20 16:17 * @description 消息转发方法 */ private void sendInfoToOtherClients(String msg, SocketChannel selfChannel) throws IOException { System.out.println("服务器转发消息..."); for (SelectionKey key : selector.keys()) { // 通过key获取对应的socketChannel SelectableChannel targetChannel = key.channel(); if (targetChannel instanceof SocketChannel && targetChannel != selfChannel) { SocketChannel dest = (SocketChannel) targetChannel; // 将msg存储到buffer中 ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(msg.getBytes()); // 将buffer数据写入到channel dest.write(buffer); } } } public static void main(String[] args) { GroupChatServer groupChatServer = new GroupChatServer(); groupChatServer.listen(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
客户端
package com.atguigu.nioGroupChat; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.InetSocketAddress; import java.nio.ByteBuffer; import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey; import java.nio.channels.Selector; import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.Scanner; /** * @author RedStar * @date 2022/07/20 16:30 * @description NIO群聊系统客户端 */ public class GroupChatClient { private final String HOST = "127.0.0.1"; private final int PORT = 9528; private Selector selector; private SocketChannel socketChannel; private String userName; public GroupChatClient() { try { selector = Selector.open(); // 连接服务器 socketChannel = SocketChannel.open(new InetSocketAddress(HOST, PORT)); // 设置非阻塞 socketChannel.configureBlocking(false); // 将socketChannel注册到selector socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ); // 得到userName userName = socketChannel.getLocalAddress().toString().substring(1); System.out.println(userName + " is ok"); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } /** * @author RedStar * @date 2022/7/20 16:35 * @description 向服务器发送消息 */ public void sendMsg(String message) { message = userName + ":" + message; try { socketChannel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap(message.getBytes())); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } /** * @author RedStar * @date 2022/7/20 16:38 * @description 接收服务器发来的消息 */ public void receiveMsg() { try { // 获取发生事件的数量,客户端只能是0或1 int readCount = selector.select(); if (readCount > 0) { Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selector.selectedKeys().iterator(); while (iterator.hasNext()) { SelectionKey key = iterator.next(); if (key.isReadable()) { // 得到相关SocketChannel SocketChannel sc = (SocketChannel) key.channel(); // 申请buffer ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); // 读取消息 sc.read(buffer); //把缓冲区的数据转换成字符串 String msg = new String(buffer.array()); System.out.println(msg.trim()); } iterator.remove(); } } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { GroupChatClient groupChatClient = new GroupChatClient(); // 启动新线程 new Thread(() -> { while (true) { groupChatClient.receiveMsg(); try { Thread.sleep(3000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }).start(); // 获取键盘输入并发送到服务端 Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); while (scanner.hasNextLine()) { String s = scanner.nextLine(); groupChatClient.sendMsg(s); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
AIO
- JDK 7 引入了 Asynchronous I/O,即 AIO。在进行 I/O 编程中,常用到两种模式:Reactor 和 Proactor。Java 的NIO 就是Reactor,当有事件触发时,服务器端得到通知,进行相应的处理
- AIO即NIO2.0,叫做异步不阻塞的IO。AIO 引入异步通道的概念,采用了 Proactor 模式,简化了程序编写,有效的请求才启动线程,它的特点是先由操作系统完成后才通知服务端程序启动线程去处理,一般适用于连接数较多且连接时间较长的应用
- 目前AIO还没有广泛应用,Netty也是基于NIO, 而不是AIO
零拷贝
传统文件拷贝模式示意图:

- Java程序无法直接从磁盘读取文件,通过调用系统层api获取文件,由用户态进入内核态
- 第1次拷贝操作系统将文件从磁盘拷贝到内核的文件缓冲区
- 第2次拷贝操作系统将文件从内核文件缓冲区拷贝到应用缓冲区,由内核态转换成用户态
- 第3次拷贝操作系统将文件从应用缓冲区拷贝到Socket缓冲区,由用户态进入内核态
- 第4次拷贝操作系统将文件从内核Socket缓冲区拷贝到网卡,拷贝完成,由内核态转换成用户态
由此可见,传统拷贝方式经过4次拷贝、4次状态切换才完成了文件的拷贝操作
mmap
mmap 即 memory map,也就是内存映射。mmap 是一种内存映射文件的方法,即将一个文件或者其它对象映射到进程的地址空间,实现文件磁盘地址和进程虚拟地址空间中一段虚拟地址的一一对映关系。
通过mmap方式,能够在系统内存中开辟一片空间和用户进程共享使用,这样就能够将应用缓冲区省掉,从而减少一次拷贝。
mmap拷贝示意图:

- Java程序调用系统层api获取文件,由用户态进入内核态
- 第1次拷贝操作系统将文件从磁盘拷贝到公共地址映射空间,由内核态转换成用户态
- 第2次拷贝操作系统将文件从公共地址映射空间拷贝到Socket缓冲区,由用户态进入内核态
- 第3次拷贝操作系统将文件从内核Socket缓冲区拷贝到网卡,拷贝完成,由内核态转换成用户态
由此可见,mmap优化后的拷贝方式经过3次拷贝、4次状态切换完成了文件的拷贝操作
sendFile
sendfile()系统调用利用DMA引擎将文件中的数据拷贝到操作系统的内核缓冲区中,然后又将数据被拷贝从内核文件缓冲区拷贝到协议栈(网卡)。其中有一次拷贝是从内核文件缓冲区到Socket缓冲区,但是由于只拷贝文件描述符(文件的描述信息),数据量很小忽略不计。sendFile拷贝示意图:

- Java程序调用系统层api获取文件,由用户态进入内核态
- 第1次拷贝操作系统将文件从磁盘拷贝到内核文件缓冲区
- 第2次拷贝操作系统将文件从内核文件缓冲区拷贝到网卡,操作系统同时将文件描述符从内核文件缓冲区拷贝到Socket缓冲区,由内核态转换成用户态
由此可见,sendFile优化后的拷贝方式经过2次拷贝、2次状态切换完成了文件的拷贝操作
mmap和sendFile区别
- mmap 适合小数据量读写,sendFile 适合大文件传输
- mmap 需要4次上下文切换,3次数据拷贝;sendFile 需要2次上下文切换,最少2次数据拷贝
- sendFile 可以利用DMA方式,减少 CPU 拷贝,mmap 则不能(必须从内核拷贝到 Socket 缓冲区)
其他
- 所谓零拷贝,是从操作系统的角度来说的。因为内核缓冲区之间,没有数据是重复的(只有内核文件缓冲区有一份数据)
- 零拷贝不仅仅带来更少的数据复制,还能带来其他的性能优势,例如更少的上下文切换,更少的CPU缓存共享以及无CPU校验和计算
文章参考:尚硅谷韩顺平Netty视频教程
原文链接: https://www.jhxblog.cn/#/home/read?articleid=37 -
相关阅读:
windows docker desktop==spark环境搭建
AI辅助研发,引领科技新潮流
controller-informer
C#WPF通过串口(232协议)调用基恩士打标机进行打标
[附源码]Python计算机毕业设计SSM江西婺源旅游文化推广系统(程序+LW)
2023.10.7 Java 创建线程的七种方法
6-3漏洞利用-SSH环境搭建
聊一聊装饰者模式
使用全局配置处理字段名和属性名不一致的情况+使用resultMap处理字段名和属性名不一致的情况
【步态识别】GaitMPL
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_26024785/article/details/126230919
