-
Leetcode刷题——单链表2
目录
练习题1 链表分割

思路:

将链表一分为2,以x为界限,大于x的尾插到新链表1,小于x的尾插到新链表2
,之后再将新链表1,头插到新链表2,跟归并排序有点像
- class Partition {
- public:
- ListNode* partition(ListNode* pHead, int x) {
- ListNode*Guard1=(ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
- ListNode*Guard2=(ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
- ListNode*tail1=Guard1;
- ListNode*tail2=Guard2;
- while(pHead)
- {
- if(pHead->val{tail1->next=pHead;tail1=tail1->next;}else{tail2->next=pHead;tail2=tail2->next;}pHead=pHead->next;}tail1->next=Guard2->next;tail2->next=NULL;free(Guard2);return Guard1->next;}};
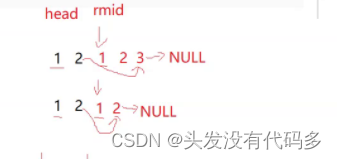
练习题2 链表的回文结构
思路:
1.先找到中间节点

2.从中间节点一直到末尾节点内的节点进行逆置

3. 用俩个节点分别指向头和中间位置,然后挨个进行数字比较,若不想等,直接退出

注:当奇数时候,第一个2,仍然指向3,因此判断相等
- struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head){
- struct ListNode*fast,*slow;
- fast=slow=head;
- while(fast&&fast->next)
- {
- fast=fast->next->next;
- slow=slow->next;
- }
- return slow;
- }
- struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head){
- struct ListNode*cur=head;
- struct ListNode*prve=NULL;
- while(cur)
- {
- struct ListNode*t=cur->next;
- cur->next=prve;
- prve=cur;
- cur=t;
- }
- return prve;
- }
- class PalindromeList {
- public:
- bool chkPalindrome(ListNode* A) {
- ListNode*mid=middleNode(A);
- struct ListNode*rmid=reverseList(mid);
- while(A&&rmid)
- {
- if(A->val!=rmid->val)
- return false;
- else
- {
- rmid=rmid->next;
- A=A->next;
- }
- }
- return true;
- }
- };
方法二:临时拷贝一份,然后一个一个比较
练习题3 链表相交
 相交链表特点:最后一个节点的地址相等
相交链表特点:最后一个节点的地址相等方法:1.求俩个出链表的长度,即让俩个链表都走到尾节点
2.求出他们的距离差d
3.较长的链表先走d步,然后俩个链表开始一起走,每次走一步
- struct ListNode *getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB) {
- struct ListNode *newhead1=headA;
- struct ListNode *newhead2=headB;
- int k=1;int z=1;int c=0;
- while(newhead1->next)
- {
- newhead1=newhead1->next;
- k++;
- }
- while(newhead2->next)
- {
- newhead2=newhead2->next;
- z++;
- }
- if(newhead1!=newhead2)
- return NULL;
- c=abs(k-z);
- while(c--)
- {
- if(k>z)
- headA=headA->next;
- else
- headB=headB->next;
- }
- while(headA&&headB)
- {
- if(headA==headB)
- return headA;
- else
- {
- headA=headA->next;
- headB=headB->next;
- }
- }
- return NULL;
- }
- struct ListNode *getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB) {
- struct ListNode *newhead1=headA;
- struct ListNode *newhead2=headB;
- int k=1;int z=1;
- while(newhead1->next)
- {
- newhead1=newhead1->next;
- k++;
- }
- while(newhead2->next)
- {
- newhead2=newhead2->next;
- z++;
- }
- if(newhead1!=newhead2)
- return NULL;
- int gap=abs(k-z);
- struct ListNode *Longlist=headA;
- struct ListNode *ShoreList=headB;
- if(k{Longlist=headB;ShoreList=headA;}while(gap--){Longlist=Longlist->next;}while(Longlist!=ShoreList){Longlist=Longlist->next;ShoreList=ShoreList->next;}return Longlist;}
练习题4 判断是否为环形链表

带环链表:1.不能遍历,会陷入死循环
利用快慢指针,快指针一次走俩步,慢指针走一步

当slow走到中间位置时,fast进入环内

当慢指针进环时,快指针在环内已经走了一小会了,具体走到了哪里,无法知晓 (要根据环的大小决定),但是可以知道fast在环里走的路程,是slow从中间到进环路程的2倍
slow进入环后,看作是fast追赶slow

假设在红色位置fast追上了slow
- bool hasCycle(struct ListNode *head) {
- struct ListNode *fast=head;
- struct ListNode *slow=head;
- while(fast&&fast->next)
- {
- fast=fast->next->next;
- slow=slow->next;
- if(slow==fast)
- return true;
- }
- return false;
- }
快慢指针延伸问题


证明:slow走一步,fast走俩步,fast能追上slow
假设:slow进环以后,fast和slow之间的差距是N,即追赶距离为N

slow和fast每移动一次,他们的距离会缩小一格
因此距离由:N,N-1,N-2,N-3……0
所以,能追上
证明:slow走一步,fast走三部,能否追得上
假设:slow进环以后,fast和slow之间的差距是N,即追赶距离为N

一开始fast在3,slow进入圆环
slow和fast每移动一次,他们的距离会缩小2格,他们的距离N=9

此时距离是-1,-1意味着,他们之间的距离变成了C-1(C是环的长度)
最终距离是0还是其他数字,由N决定
如果N是奇数,N=9
9,7,5,3,1,-1
-1意味着,他们之间的距离变成了C-1(C是环的长度)
如果C-1是偶数,即他们的距离是偶数每次-2,一定追得上,如果C-1是奇数,又得去判断下一次C-1是偶数还是奇数
因此,能否追的上如果距离是偶数,则追得上
如果距离是奇数,得看C-1是否为偶
练习题5 找环形链表的节点
方式1.公式证明
用快慢指针:fast走的距离=2*slow的距离
公式推导
假设进环前的长度L,假设环的长度C,入口点到相遇点距离x
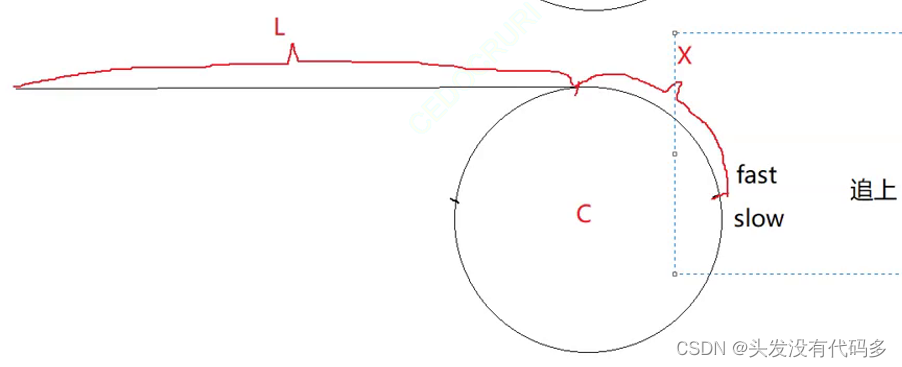
slow所走距离:L+X,慢指针所走的距离不可能超过一圈,因为N最大是C-1
fast所走距离:L+NC+X,N代表fast走过的圈数,N>=1
2(L+X)=L+X+NC
(L+X)=NC
L=NC-X
L=(N-1)*C+C-X
左边是A所走距离,右边是B所走距离
可证明:一个指针A从头开始走,另一个指针B从相遇点开始走,最终会在入口点相遇
- struct ListNode* detectCycle(struct ListNode* head) {
- struct ListNode* slow = head;
- struct ListNode* fast = head;
- struct ListNode* meetnextl =NULL;
- while (fast && fast->next)
- {
- slow = slow->next;
- fast = fast->next->next;
- if (fast == slow)
- {
- meetnextl = fast;
- while(head!=meetnextl)
- {
- meetnextl=meetnextl->next;
- head=head->next;
- }
- return head;
- }
- }
- return NULL;
- }
方法2:转换成相交问题

fast旁白的黑色是相遇点,下面蓝色是相遇点的下一个点,A和B链表的交点,就是入口点 ,
然后让长的先走,接着同时走,跟上面的题一样
- struct ListNode *getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB) {
- struct ListNode *newhead1=headA;
- struct ListNode *newhead2=headB;
- int k=1;int z=1;
- while(newhead1->next)
- {
- newhead1=newhead1->next;
- k++;
- }
- while(newhead2->next)
- {
- newhead2=newhead2->next;
- z++;
- }
- if(newhead1!=newhead2)
- return NULL;
- int gap=abs(k-z);
- struct ListNode *Longlist=headA;
- struct ListNode *ShoreList=headB;
- if(k{Longlist=headB;ShoreList=headA;}while(gap--){Longlist=Longlist->next;}while(Longlist!=ShoreList){Longlist=Longlist->next;ShoreList=ShoreList->next;}return Longlist;}struct ListNode *hasCycle(struct ListNode *head) {struct ListNode *fast=head;struct ListNode *slow=head;while(fast&&fast->next){fast=fast->next->next;slow=slow->next;if(slow==fast)return slow;}return fast;}struct ListNode* detectCycle(struct ListNode* head) {struct ListNode* guard1 = hasCycle(head);if(guard1==NULL)return NULL;struct ListNode*fast=head;struct ListNode*slow=head;struct ListNode* meetnextl =NULL;while (fast && fast->next){slow = slow->next;fast = fast->next->next;if (fast == slow){meetnextl = fast->next;fast->next=NULL;struct ListNode* guard2 = getIntersectionNode(head, meetnextl);return guard2;}}return NULL;}
练习题6 复制带随机指针的链表
138. 复制带随机指针的链表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
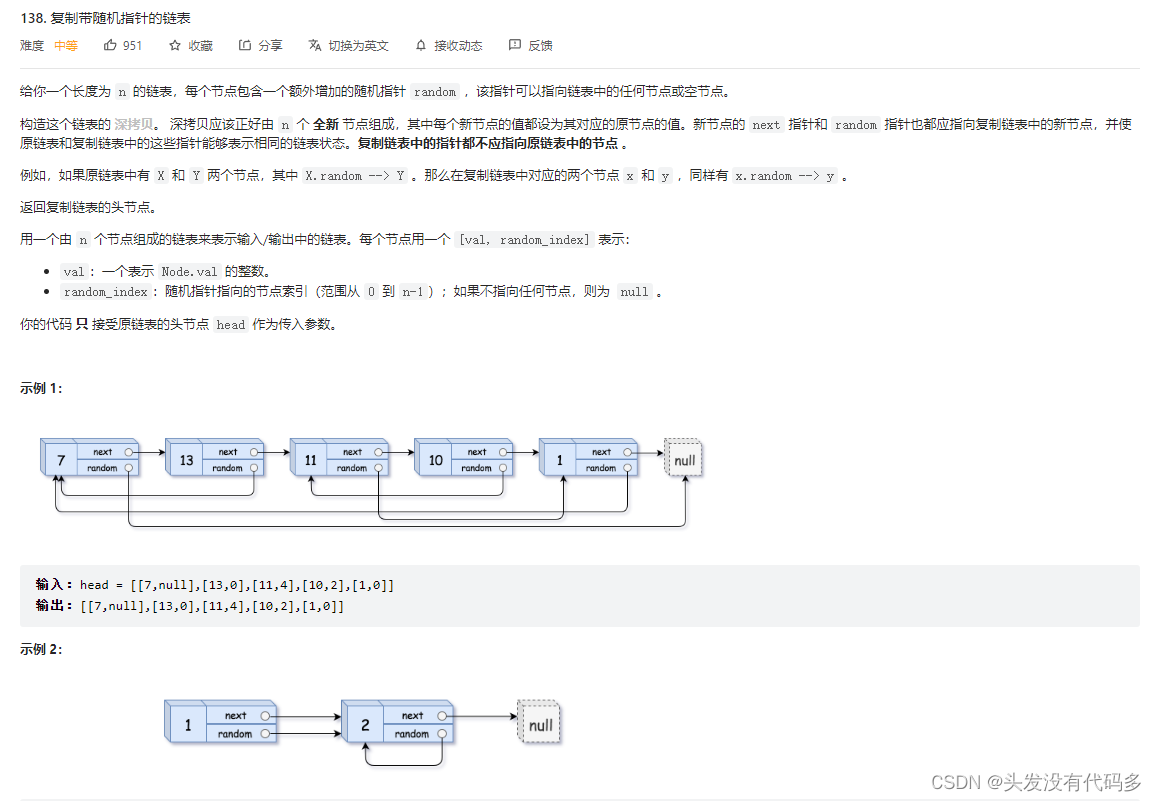
思路:

1.先拷贝各个节点,插到相对应的节点后面,然后将链表连接起来
2.然后将cur的random所指指针赋值给copy的random
if(cur->random!=NULL)
copy->random=cur->random->next
3.将各节点拷贝下来进行链接,顺便链接原链表

- * struct Node {
- * int val;
- * struct Node *next;
- * struct Node *random;
- * };
- */
- struct Node* copyRandomList(struct Node* head) {
- struct Node*cur=head;
- struct Node* next=NULL;
- struct Node*copy=NULL;
- while(cur)
- {
- //1.拷贝一份插入链表内
- copy=(struct Node*)malloc(sizeof( struct Node));
- next=cur->next;
- copy->val=cur->val;
- cur->next=copy;
- copy->next=next;
- cur=next;
- }
- cur=head;
- while(cur)
- { //2.链接random
- copy=cur->next;
- if(cur->random==NULL)
- copy->random=NULL;
- else
- copy->random=cur->random->next;
- cur=cur->next->next;
- }
- cur=head;
- struct Node*newhead=NULL;
- struct Node*tail=NULL;
- while(cur)
- {
- copy=cur->next;
- next=copy->next;
- if(newhead==NULL)
- newhead=tail=copy;
- else
- {
- tail->next=copy;
- tail=tail->next;
- }
- cur->next=next;
- cur=next;
- }
- return newhead;
- }
-
相关阅读:
vertx的学习总结2
设计模式 -- 单例模式(Singleton Pattern)
Java Array、List、Set互相转化
(2)达梦数据库匹配
Llama2开源大模型的新篇章以及在阿里云的实践
Linux Kernel 之十 虚拟化、VirtIO 架构及规范、VirtQueue & VRing
机器学习概述
Vue 组件和插件:探索细节与差异
计算机毕业设计springboot+vue+elementUI球员转会管理系统
docker入门配置
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_49449676/article/details/126105052
