-
RabbitMQ
1. 什么是MQ
MQ(Message Quene) : 翻译为消息队列,通过典型的生产者和消费者模型,生产者不断向消息队列中生产消息,消费者不断的从队列中获取消息。因为消息的生产和消费都是异
步的,而且只关心消息的发送和接收,没有业务逻辑的侵入,轻松的实现系统间解耦。别名为 消息中间件通过利用高效可靠的消息传递机制进行平台无关的数据交流,并基于数据通信来进行分布式系统的集成。2. MQ主流框架
1. ActiveMQ
- ActiveMQ 是Apache出品,最流行的,能力强劲的开源 消息总线。它是一个完全支持JMS规范的的消息中间件。
- 丰富的API,多种集群架构模式让ActiveMQ在业界成为老牌的消息中间件,在中小型企业 颇受欢迎!
2. Kafka
- Kafka是LinkedIn开源的分布式发布-订阅消息系统,目前归属于Apache顶级项目。Kafka主要特点是基于Pull的模式来处理消息消费,追求高吞吐量,一开始的目的就是用于日志收集和传输。
- 0.8版本开始支持复制,不支持事务,对消息的重复、丢失、错误没有严格要求,适合产生大量数据的互联网服务的数据收集业务。
3. RockerMQ
- RocketMQ是阿里开源的消息中间件,它是纯Java开发,具有高吞吐量、高可用性、适合大规模分布式系统应用的特点。
- RocketMQ思路起源于Kafka,但并不是Kafka的一个Copy,它对消息的可靠传输及事务性做了优化,目前在阿里集团被广泛应用于交 易、充值、流计算、消息推送、日志流式处理、binglog分发等场景。
4. RabbitMQ
- RabbitMQ是使用Erlang语言开发的开源消息队列系统,基于AMQP协议来实
- AMQP的主要特征是面向消息、队列、路由(包括点对点和发布/订阅)、可靠性、安全。
- AMQP协议更多用在企业系统内对数据一致性、稳定性和可靠性要求很高的场景,对性能和吞吐量的要求还在其次。
3. MQ的四大核心
1、生产者
2、消费者
3、交换机
4、队列
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-6ASrXjDW-1659410303870)(RabbitMQ.assets/image-20220522104445074.png)]
4. AMQP协议
-
AMQP(advanced message queuing protocol)在2003年时被提出,最早用于解决金融领域不同平台之间的消息传递交互问题。顾名思义,AMQP是一种协议,更准确的说是一种binary wire-level protocol(链接协议)。这是其和JMS的本质差别,AMQP不从API层进行限定,而是直接定义网络交换的数据格式。这使得实现了AMQP的provider天然性就是跨平台的。以下是AMQP协议模型:
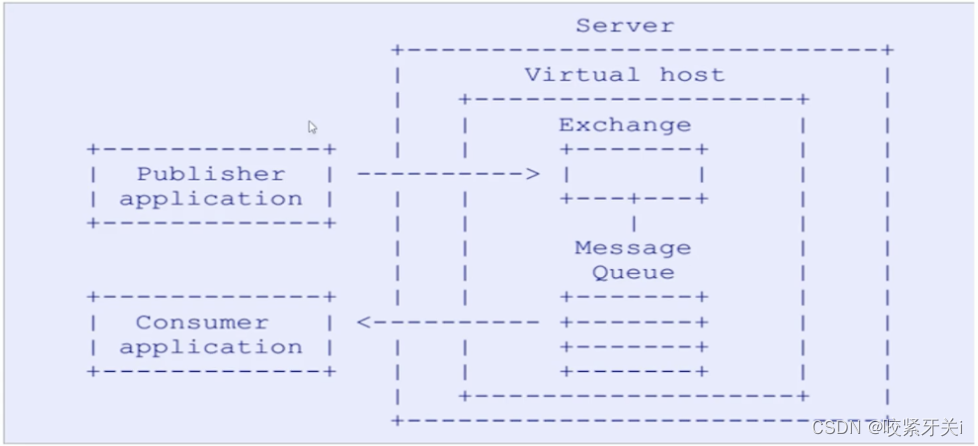
5. 安装RabbitMQ
- 使用docker安装
cd /opt/rabbitmq mkdir data # 拉取镜像 docker pull rabbitmq # 查看镜像 docker images # 拉取镜像到本地仓库,这里是直接安装最新的, # 如果需要安装其他版本在rabbitmq后面跟上版本号即可 # docker pull rabbitmq # 启动rabbitMq docker run -d \ -v /opt/rabbitmq/data:/var/lib/rabbitmq \ -p 5672:5672 -p 15672:15672 --name rabbitmq --restart=always \ --hostname myRabbit 镜像id # 启动rabbitmq_management, rabbitmq 为容器的名称,使用id也可以 docker exec -it 容器id /bin/bash- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
-
启动前端web界面
# 开启插件 rabbitmq-plugins enable rabbitmq_management # ip+端口号登录,用户名和密码默认都是guest ip:15672- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
6. RabbitMQ的七种消息模型
1.简单模式
- 一个生产者,一个消费者
- 生产者,也就是要发送消息的程序
消费者:消息的接受者,会一直等待消息到来。 - 缺点:当消息处理比较耗时的时候,可能生产消息的速度会 远远大于消息的消费速度。长此以往,消息就会堆积 越来越多,无法及时处理。

1. 导入依赖
<dependency> <groupId>com.rabbitmqgroupId> <artifactId>amqp-clientartifactId> <version>5.7.2version> dependency>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
2. 生产者
@Test public void sendMessage() throws IOException, TimeoutException { // 创建链接mq的工厂类 ConnectionFactory factory = new ConnectionFactory(); // 设置rabbitmq主机地址的ip factory.setHost("192.168.122.1"); // 设置端口号 factory.setPort(5672); //设置连接的虚拟机 factory.setVirtualHost("simple"); //设置访问虚拟主机的用户名和密码 factory.setUsername("guest"); factory.setPassword("guest"); // 获取连接对象 Connection connection = factory.newConnection(); // 获取连接中通道 Channel channel = connection.createChannel(); //通道绑定对应消息队列 //参数1: 队列名称 如果队列不存在自动创建 //参数2: 用来定义队列特性是否要持久化 true 持久化队列 false 不持久化 //参数3: exclusive 是否独占队列 true 独占队列 false 不独占 //参数4: autoDelete: 是否在消费完成后自动删除队列 true 自动删除 false 不自动删除 //参数5: 额外附加参数 channel.queueDeclare("hello", false, false, false, null); //发布消息 //参数1: 交换机名称 参数2:队列名称 //参数3:传递消息额外设置:不设置的话消息不会持久化,消息持久化:传参数MessageProperties.PERSISTENT_TEXT_PLAIN //参数4:消息的具体内容 channel.basicPublish("", "hello", null, "Hello RabbitMQ".getBytes()); //关闭 connection.close(); channel.close(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
3. 生产者
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException { //创建工厂连接 ConnectionFactory factory = new ConnectionFactory(); factory.setHost("192.168.122.1"); factory.setPort(5672); factory.setVirtualHost("simple"); factory.setUsername("guest"); factory.setPassword("guest"); Connection connection = factory.newConnection(); Channel channel = connection.createChannel(); channel.queueDeclare("hello", false, false, false, null); /** * 参数1:队列名称 * 是否自动确定收到消息 * 回调接口 */ String hello = channel.basicConsume("hello", true, new DefaultConsumer(channel) { @Override public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException { System.out.println("new String(body) = " + new String(body)); } }); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
4. 工厂连接工具类
package utils; import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel; import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection; import com.rabbitmq.client.ConnectionFactory; import java.util.Properties; public class RabbitMQUtils { private static ConnectionFactory connectionFactory; private static Properties properties; static{ //重量级资源 类加载执行之执行一次 connectionFactory = new ConnectionFactory(); connectionFactory.setHost("192.168.42.134"); connectionFactory.setPort(5672); connectionFactory.setVirtualHost("/"); connectionFactory.setUsername("admin"); connectionFactory.setPassword("admin"); } //定义提供连接对象的方法 public static Connection getConnection() { try { return connectionFactory.newConnection(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return null; } //关闭通道和关闭连接工具方法 public static void closeConnectionAndChanel(Channel channel, Connection conn) { try { if(channel!=null) channel.close(); if(conn!=null) conn.close(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static void main(String[] args) { //System.out.println("RabbitMQUtils.getConnection() = " + RabbitMQUtils.getConnection()); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
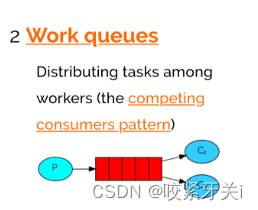
2. work模式
- 一个生产者,多个消费者,每个消费者获取到的消息唯一。
- 消息会平均分配给多个消费者,例如有10条消息,两个消费者那么消费者1:1、3、5、7、9。消费者2:2、4、6、8、10
消息提供者
@Test public void sendMessage() throws Exception { Connection connection = RabbitMQUtils.getConnection(); Channel channel = connection.createChannel(); channel.queueDeclare("work", false, false, false, null); for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) { channel.basicPublish("", "work", null, (i+"Hello Work").getBytes()); } RabbitMQUtils.closeConnectionAndChanel(channel, connection); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
消息消费者1
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { Connection connection = RabbitMQUtils.getConnection(); Channel channel = connection.createChannel(); channel.queueDeclare("work", false, false, false, null); channel.basicConsume("work", false, new DefaultConsumer(channel) { @Override public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException { System.out.println("消费者1--" + new String(body)); } }); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
消费者2
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { Connection connection = RabbitMQUtils.getConnection(); Channel channel = connection.createChannel(); channel.queueDeclare("work", false, false, false, null); channel.basicConsume("work", false, new DefaultConsumer(channel) { @Override public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException { System.out.println("消费者2--" + new String(body)); } }); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
-
取消平均分配,按执行顺序去消费,设置消息手动确定防止其中一个消费者挂了而导致的消息丢失现象发生
- 设置每次接受几条消息:channel.basicQos(1)
- 第二个参数设置为false:channel.basicConsume(“work”, false, …)
- 手动确定接收成功:channel.basicAck(envelope.getDeliveryTag(), false);
channel.basicQos(1); channel.queueDeclare("work",true,false,false,null); channel.basicConsume("work",false,new DefaultConsumer(channel){ @Override public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException { System.out.println("消费者-2: "+new String(body)); //手动确认 参数1:手动确认消息标识 参数2:false 每次确认一个 channel.basicAck(envelope.getDeliveryTag(), false); } });- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
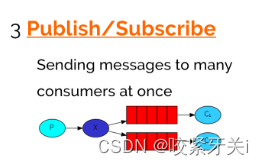
3. 订阅模式(Fonout)
一个生产者发送的消息会被多个消费者获取。
-
在广播模式下,消息发送流程是这样的:
-
可以有多个消费者每个消费者有自己的queue(队列)
-
每个队列都要绑定到Exchange(交换机)生产者发送的消息,只能发送到交换机,交换机来决定要发给哪个队列,生产者无法决定。
-
交换机把消息发送给绑定过的所有队列队列的消费者都能拿到消息。实现一条消息被多个消费者消费。
生产者
@Test public void sendMessage() throws IOException { Connection connection = RabbitMQUtils.getConnection(); Channel channel = connection.createChannel(); //将通道声明指定交换机 //参数1: 交换机名称 参数2: 交换机类型 fanout 广播类型 channel.exchangeDeclare("hello", BuiltinExchangeType.FANOUT); //发送消息 channel.basicPublish("hello", "", null, "Hello Fanout".getBytes()); RabbitMQUtils.closeConnectionAndChanel(channel, connection); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
消费者1
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { Connection connection = RabbitMQUtils.getConnection(); Channel channel = connection.createChannel(); // 通道绑定交换机 channel.exchangeDeclare("hello", BuiltinExchangeType.FANOUT); // 创建临时队列 String queue = channel.queueDeclare().getQueue(); // 绑定交换机和队列 channel.queueBind(queue, "hello", ""); // 消费消息 channel.basicConsume(queue, true, new DefaultConsumer(channel) { @Override public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException { System.out.println("消费者---1" + new String(body)); } }); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
消费者2
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { Connection connection = RabbitMQUtils.getConnection(); Channel channel = connection.createChannel(); // 通道绑定交换机 channel.exchangeDeclare("hello", BuiltinExchangeType.FANOUT); // 创建临时队列 String queue = channel.queueDeclare().getQueue(); // 绑定交换机和队列 channel.queueBind(queue, "hello", ""); // 消费消息 channel.basicConsume(queue, true, new DefaultConsumer(channel) { @Override public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException { System.out.println("消费者---2" + new String(body)); } }); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
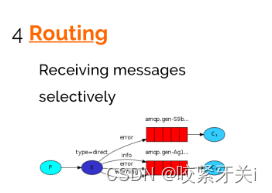
4. Routing路由模式–Direct直连
- 发送消息到交换机并且要指定路由key ,消费者将队列绑定到交换机时需要指定路由key。
- 在Direct模型下:队列与交换机的绑定,不能是任意绑定了,而是要指定一个RoutingKey(路由key)消息的发送方在 向 Exchange发送消息时,也必须指定消息的 RoutingKey。
- Exchange不再把消息交给每一个绑定的队列,而是根据消息的Routing Key进行判断,只有队列的Routingkey与消息的 Routing key完全一致,才会接收到消息。
- 生产者
@Test public void sendMessage() throws Exception { Connection connection = RabbitMQUtils.getConnection(); Channel channel = connection.createChannel(); // 创建交换机 channel.exchangeDeclare("routing-direct", BuiltinExchangeType.DIRECT); // routing-key String routingKey = "info"; //发送消息 channel.basicPublish("routing-direct", routingKey, null, ("我创造了一条"+routingKey+"的消息").getBytes()); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
-
消费者1
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Connection connection = RabbitMQUtils.getConnection(); Channel channel = connection.createChannel(); //创建交换机 channel.exchangeDeclare("routing-direct", BuiltinExchangeType.DIRECT); // 创建临时队列 String queue = channel.queueDeclare().getQueue(); // 绑定交换机和队列 channel.queueBind(queue, "routing-direct", "err"); channel.queueBind(queue, "routing-direct", "info"); //消费消息 channel.basicConsume(queue, true, new DefaultConsumer(channel) { @Override public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException { System.out.println("消费者---1" + new String(body)); } }); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
-
消费者2
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { Connection connection = RabbitMQUtils.getConnection(); Channel channel = connection.createChannel(); channel.exchangeDeclare("routing-direct", BuiltinExchangeType.DIRECT); String queue = channel.queueDeclare().getQueue(); channel.queueBind(queue, "routing-direct", "info"); channel.basicConsume(queue, true, new DefaultConsumer(channel) { @Override public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException { System.out.println("消费者----2" + new String(body)); } }); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
5. Routing路由模式–topic模式
- 将路由键和某模式进行匹配,此时队列需要绑定在一个模式上,“#”匹配一个词或多个词,“*”只匹配一个词。
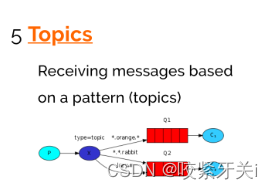
-
生产者
@Test public void sendMessage() throws IOException { Connection connection = RabbitMQUtils.getConnection(); Channel channel = connection.createChannel(); //声明交换机 channel.exchangeDeclare("routing-topic", BuiltinExchangeType.TOPIC); // 定义routingKey String routingKey = "user.add.admin"; //发送消息 channel.basicPublish("routing-topic", routingKey, null, ("我是一条"+routingKey+"消息").getBytes()); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
-
消费者1
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { Connection connection = RabbitMQUtils.getConnection(); Channel channel = connection.createChannel(); // 声明交换机 channel.exchangeDeclare("routing-topic", BuiltinExchangeType.TOPIC); //创建一个临时队列 String queue = channel.queueDeclare().getQueue(); // 绑定队列和交换机 channel.queueBind(queue, "routing-topic", "user.*"); // 消费消息 channel.basicConsume(queue, true, new DefaultConsumer(channel) { @Override public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException { System.out.println("消费者--1" + new String(body)); } }); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
-
消费者2
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { Connection connection = RabbitMQUtils.getConnection(); Channel channel = connection.createChannel(); // 声明交换机 channel.exchangeDeclare("routing-topic", BuiltinExchangeType.TOPIC); //创建一个临时队列 String queue = channel.queueDeclare().getQueue(); // 绑定队列和交换机 channel.queueBind(queue, "routing-topic", "user.#"); // 消费消息 channel.basicConsume(queue, true, new DefaultConsumer(channel) { @Override public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException { System.out.println("消费者--2" + new String(body)); } }); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
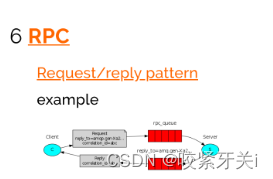
6. RPC模式
使用RabbitMQ构建RPC系统:客户端和可伸缩RPC服务器。
7. 发布确认
与发布者进行可靠的发布确认
7. RabbitMQ整合SpringBoot
-
生产者
@Autowired RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate; /** * routing的topic的生产者 */ @Test void routingTopic() { rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("routingTopic", "user.add.aaaa", "这是一条routingTopic的user.add消息"); } /** * routing的direct的生产者 */ @Test void routingDirect() { rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("routingDirect", "info", "这是一条routingDirect的Info消息"); rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("routingDirect", "error", "这是一条routingDirect的error消息"); rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("routingDirect", "add", "这是一条routingDirect的add消息"); } /** * fonout生产者 */ @Test void fanout() { rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("fonoutExchange", "fonoutKey", "这是一条fonout消息"); } /** * work消息生产者 */ @Test void work() { for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) { rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("work", "这是一条work消息模型消息" + i); } } /** * 简单消息生产者 */ @Test void simple() { rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("hello", "这是一条简单模型消息"); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
-
消费者
@Component public class Customer { @RabbitListener( bindings = @QueueBinding( value = @Queue, exchange = @Exchange(name = "routingTopic", type = ExchangeTypes.TOPIC), key = {"user.*"} ) ) void routingTopic(String message) { System.out.println("message = " + message); } /** * routing-direct消费者 * @param message */ @RabbitListener( bindings = @QueueBinding( value = @Queue, exchange = @Exchange(name = "routingDirect", type = ExchangeTypes.DIRECT),// ExchangeTypes.DIRECT为默认类型 key = {"info", "error"} // routingKey ) ) void routingDirect(String message) { System.out.println("message = " + message); } /** * fanout消费者2 * @param message */ @RabbitListener( bindings = @QueueBinding( value = @Queue, //没有指定名字就是创建临时队列 exchange = @Exchange(name = "fonoutExchange", type = ExchangeTypes.FANOUT) )) void fanout2(String message) { System.out.println("message2 = " + message); } /** * fanout消费者1 * @param message */ @RabbitListener( bindings = @QueueBinding( value = @Queue, //没有指定名字就是创建临时队列 exchange = @Exchange(name = "fonoutExchange", type = ExchangeTypes.FANOUT) )) void fanout1(String message) { System.out.println("message1 = " + message); } /** * 这是work消费者2 * @param message */ @RabbitListener(queuesToDeclare = @Queue(value = "work")) void work2(String message) { System.out.println("message2 = " + message); } /** * 这是work消费者1 * @param message */ @RabbitListener(queuesToDeclare = @Queue(value = "work")) void work1(String message) { System.out.println("message1 = " + message); } /** * 这是一个简单消息消费者 * 生产端没有指定交换机只有routingKey和Object。 * 消费方产生hello队列,放在默认的交换机(AMQP default)上。 * 而默认的交换机有一个特点,只要你的routerKey的名字与这个 * 交换机的队列有相同的名字,他就会自动路由上。 * 生产端routingKey 叫hello ,消费端生产hello队列。 * 他们就路由上了 */ @RabbitListener(queuesToDeclare = @Queue(value = "hello")) public void simple(String message) { System.out.println("message = " + message); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
8. 使用场景
1. 异步处理
2. 应用解耦
订单系统:用户下单后,订单系统完成持久化处理,将消息写入消息队列, 返回用户订单下单成功。 库存系统:订阅下单的消息,获取下单消息,进行库操作。 就算库存系统出现故障,消息队列也能保证消息的可靠投递, 不会导致消息丢失.
3. 流量削峰
作用: 1.可以控制活动人数,超过此一定阀值的订单直接丢弃(我为什么 秒杀一次都没有成功过呢^^) 2.可以缓解短时间的高流量压垮应用(应用程序按自己的最大处理能力 获取订单)
9. 集群搭建
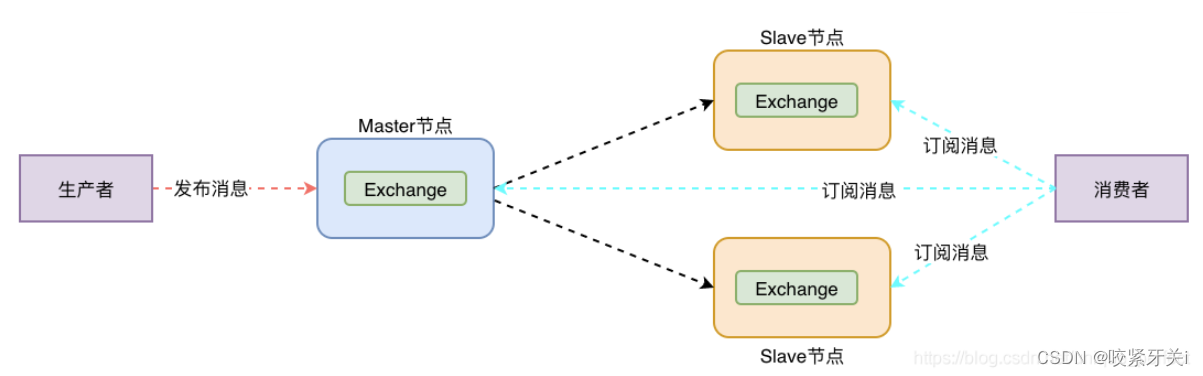
1. 普通集群(副本集群)
- 主从复制,从节点会复制主节点。
- 但是消息队列位于一个节点上,尽管它们可以从所有节点看到和访问。
- 并且当主节点挂了,从节点全部都将不可用。
- 核心解决问题: 当集群中某一时刻master节点宕机,可以对Quene中信息,进行备份
# 0.集群规划 node1: 10.15.0.3 mq1 master 主节点 node2: 10.15.0.4 mq2 repl1 副本节点 node3: 10.15.0.5 mq3 repl2 副本节点 # 1.克隆三台机器主机名和ip映射 vim /etc/hosts加入: 10.15.0.3 mq1 10.15.0.4 mq2 10.15.0.5 mq3 node1: vim /etc/hostname 加入: mq1 node2: vim /etc/hostname 加入: mq2 node3: vim /etc/hostname 加入: mq3 # 2.三个机器安装rabbitmq,并同步cookie文件,在node1上执行: scp /var/lib/rabbitmq/.erlang.cookie root@mq2:/var/lib/rabbitmq/ scp /var/lib/rabbitmq/.erlang.cookie root@mq3:/var/lib/rabbitmq/ # 3.查看cookie是否一致: node1: cat /var/lib/rabbitmq/.erlang.cookie node2: cat /var/lib/rabbitmq/.erlang.cookie node3: cat /var/lib/rabbitmq/.erlang.cookie # 4.后台启动rabbitmq所有节点执行如下命令,启动成功访问管理界面: rabbitmq-server -detached # 5.在node2和node3执行加入集群命令: 1.关闭 rabbitmqctl stop_app 2.加入集群 rabbitmqctl join_cluster rabbit@mq1 3.启动服务 rabbitmqctl start_app # 6.查看集群状态,任意节点执行: rabbitmqctl cluster_status # 7.如果出现如下显示,集群搭建成功: Cluster status of node rabbit@mq3 ... [{nodes,[{disc,[rabbit@mq1,rabbit@mq2,rabbit@mq3]}]}, {running_nodes,[rabbit@mq1,rabbit@mq2,rabbit@mq3]}, {cluster_name,<<"rabbit@mq1">>}, {partitions,[]}, {alarms,[{rabbit@mq1,[]},{rabbit@mq2,[]},{rabbit@mq3,[]}]}]- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
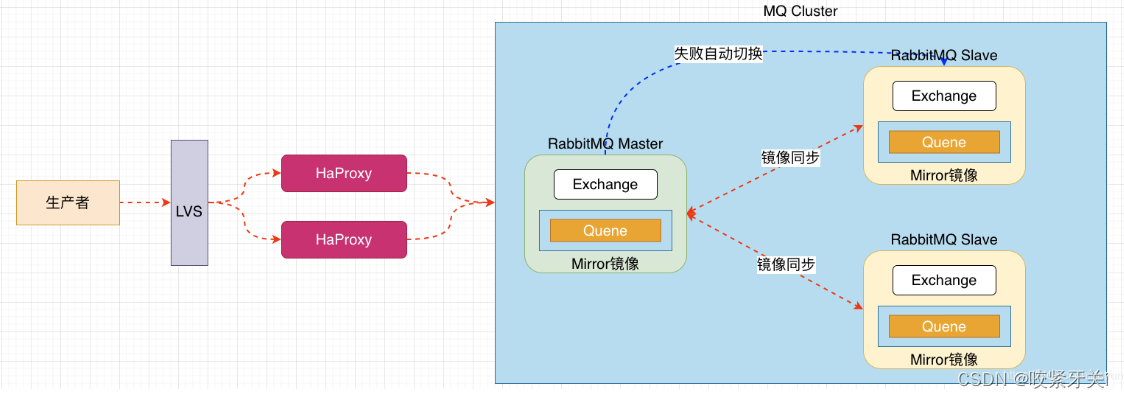
2. 镜像集群
镜像队列机制就是将队列在三个节点之间设置主从关系, 消息会在三个节点之间进行自动同步,且如果其中一个 节点不可用,并不会导致消息丢失或服务不可用的情况, 提升MQ集群的整体高可用性。
# 0.策略说明 rabbitmqctl set_policy [-p <vhost>] [--priority <priority>] [--apply-to <apply-to>] <name> <pattern> <definition> -p Vhost: 可选参数,针对指定vhost下的queue进行设置 Name: policy的名称 Pattern: queue的匹配模式(正则表达式) Definition:镜像定义,包括三个部分ha-mode, ha-params, ha-sync-mode ha-mode:指明镜像队列的模式,有效值为 all/exactly/nodes all:表示在集群中所有的节点上进行镜像 exactly:表示在指定个数的节点上进行镜像,节点的个数由ha-params指定 nodes:表示在指定的节点上进行镜像,节点名称通过ha-params指定 ha-params:ha-mode模式需要用到的参数 ha-sync-mode:进行队列中消息的同步方式,有效值为automatic和manual priority:可选参数,policy的优先级 # 1.查看当前策略 rabbitmqctl list_policies # 2.添加策略 rabbitmqctl set_policy ha-all '^hello' '{"ha-mode":"all","ha-sync-mode":"automatic"}' 说明:策略正则表达式为 “^” 表示所有匹配所有队列名称 ^hello:匹配hello开头队列 # 3.删除策略 rabbitmqctl clear_policy ha-all # 4.测试集群- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
0.策略说明
rabbitmqctl set_policy [-p ] [–priority ] [–apply-to ]
-p Vhost: 可选参数,针对指定vhost下的queue进行设置
Name: policy的名称
Pattern: queue的匹配模式(正则表达式)
Definition:镜像定义,包括三个部分ha-mode, ha-params, ha-sync-mode
ha-mode:指明镜像队列的模式,有效值为 all/exactly/nodes
all:表示在集群中所有的节点上进行镜像
exactly:表示在指定个数的节点上进行镜像,节点的个数由ha-params指定
nodes:表示在指定的节点上进行镜像,节点名称通过ha-params指定
ha-params:ha-mode模式需要用到的参数
ha-sync-mode:进行队列中消息的同步方式,有效值为automatic和manual
priority:可选参数,policy的优先级1.查看当前策略
rabbitmqctl list_policies
2.添加策略
rabbitmqctl set_policy ha-all ‘^hello’ ‘{“ha-mode”:“all”,“ha-sync-mode”:“automatic”}’
说明:策略正则表达式为 “^” 表示所有匹配所有队列名称 ^hello:匹配hello开头队列3.删除策略
rabbitmqctl clear_policy ha-all
4.测试集群
- 1
-
相关阅读:
Qt model/view 理解01
springmvc http请求,支持get,post,附件传输和参数传输
炼厂322℃工艺气余热换热器设计
es6运算符扩展
解决Nacos服务器连接问题:一次完整的排查经验分享
LAL v0.34.3发布,G711音频来了,Web UI也来了
浅析量化交易是什么类型的交易?
一文学会Intellij IDEA的Debug功能
LVGL v8学习笔记 | 07 - 字体的使用方法
JavaEE -- Spring的创建和使用
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_44255146/article/details/126118768
