-
不就是Java吗之类和对象 Part I
1、面向对象
1.1 什么是面向对象?
Java是一门纯面向对象的语言(Object Oriented Program,继承OOP),在面向对象的世界里,一切皆为对象。面向对象思想就是对象和对象之间相互协作,完成一件事情
OOP主要思想:封装,继承,多态1.2 面向对象与面向过程
举个栗子:假设你要买手机

面向对象的方式就不用考虑具体过程,而面向过程的方法就需要考虑具体
那么我们想要面向对象的话,就需要先有一个对象!那么对象从何而来,我们需要创建一个类!
2、类的定义和使用
2.1 类的定义格式
2.1.1 语法
class 类名 { 成员变量(字段/属性): 成员方法(行为): }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
举个栗子:创建一个人这个类
class Person { //成员变量(字段/属性) public String name; public int age; //成员方法(行为) public void sleep() { System.out.println(name + "正在睡觉!"); } public void eat() { System.out.println(name + "正在吃饭!"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
举几个栗子吧:
栗子1:定义一个小狗类
class Dog { //成员变量(字段/属性) public String name; public String color; //成员方法(行为) public void bark() { System.out.println(name + "正在叫!"); } public void shake() { System.out.println(name + "正在晃!"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
栗子2:定义一个学生类
class Student { //成员变量(字段/属性) public String name; public int age; public double score; public String sex; //成员方法(行为) public void doClass() { System.out.println(name + "正在上课!"); } public void doStudy() { System.out.println(name + "正在学习!"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
2.1.2 注意事项
-
类名要用大驼峰命名
-
一般一个文件中最好只写一个类
-
main方法也是一个类,只不过这个类必须要用public修饰,且一个文件内只能有一个public修饰的类
-
public修饰的类(也就是main方法),要和文件名相同
3、类的实例化
3.1 语法
类名 变量 = new 类名();- 1
举个栗子:
对
Person这个类进行实例化public class PersonDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { Person person = new Person(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
对
Student这个类进行实例化public class StudentDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { Student student = new Student(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
对
Dog这个类进行实例化public class DogDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { Dog dog = new Dog(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
实例化之后,我们就可以通过
.来访问类中的成员变量以及成员方法了我们以
Person这个类来做栗子class Person { //成员变量(字段/属性) public String name; public int age; //成员方法(行为) public void sleep() { System.out.println(name + "正在睡觉!"); } public void eat() { System.out.println(name + "正在吃饭!"); } } public class PersonDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { Person person = new Person(); //给成员变量赋值 person.age = 20; person.name = "安陵容"; //调用成员方法 person.eat(); person.sleep(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
运行结果如下:

3.2 注意事项
-
同一个类可以创建多个实例
class Person { //成员变量(字段/属性) public String name; public int age; //成员方法(行为) public void sleep() { System.out.println(name + "正在睡觉!"); } public void eat() { System.out.println(name + "正在吃饭!"); } } public class PersonDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { Person person1 = new Person(); person1.age = 20; person1.name = "安陵容"; person1.eat(); person1.sleep(); System.out.println("-------------------"); Person person2 = new Person(); person2.age = 21; person2.name = "沈眉庄"; person2.eat(); person2.sleep(); System.out.println("-------------------"); Person person3 = new Person(); person3.age = 22; person3.name = "甄嬛"; person3.eat(); person3.sleep(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37

-
当成员变量没有赋初值的时候,每个成员变量就是他默认的初值
引用类型:
nullboolean:falsechar:\u0000->空格(IDEA里面打印不出来)//我们在这里面新增加了一个char类型的性别,增加了一个show方法 class Person { //成员变量(字段/属性) public String name; public int age; public char sex; //成员方法(行为) public void sleep() { System.out.println(name + "正在睡觉!"); } public void eat() { System.out.println(name + "正在吃饭!"); } public void show() { System.out.println("姓名:" + name + " 年龄:" + age + " 性别:" + sex); } } public class PersonDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { Person person = new Person(); person.show(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
我们可以看到,由于未初始化,对应的成员变量都是对应的初值,
char元素的性别处没打印出来
-
局部变量存放在栈上,成员变量存放在堆上

3.3 说明
- 类其实就相当于一个图纸,你必须在实例化之后,才能有成果。实例化之后的对象占用实际的物理空间,来存储类的成员
4、this引用
4.1 为什么要有this引用?
我们来看一个栗子:实现一个日期类(这次我们都在
public修饰的类里面写)public class Date { public int year; public int month; public int day; //我们要写一个函数,来设置日期 public void setDate(int myYear,int myMonth,int myDay) { year = myYear; month = myMonth; day = myDay; } //打印日期 public void printDate() { System.out.println(year + "年" + month + "月" + day + "日"); } public static void main(String[] args) { Date date1 = new Date(); date1.setDate(2022,05,23); date1.printDate(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
这样的代码当然是没问题的

那我要是这么写呢?把
setDate的参数改成了与成员变量同名的情况package Demo4; public class Date { public int year; public int month; public int day; //我们要写一个函数,来设置日期 public void setDate(int year,int month,int day) { year = year; month = month; day = day; } //打印日期 public void printDate() { System.out.println(year + "年" + month + "月" + day + "日"); } public static void main(String[] args) { Date date1 = new Date(); date1.setDate(2022,05,23); date1.printDate(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
这时候我们来看结果:

怎么变成了0???
其实是这样的,因为我们最刚开始成员变量没有初始化,默认为0。而恰好
year,month,day作为了函数参数,他们三个为局部变量,这代表函数体内所有的这三个值都为0。那么我们就需要this了。4.2 this引用
我们会慢慢的给大家讲解
那么我们先把刚才的代码用
this解决一下吧public class Date { public int year; public int month; public int day; //我们要写一个函数,来设置日期 public void setDate(int year,int month,int day) { this.year = year;//this表示对当前对象的引用 this.month = month; this.day = day; } //打印日期 public void printDate() { System.out.println(year + "年" + month + "月" + day + "日"); } public static void main(String[] args) { Date date1 = new Date(); date1.setDate(2022,05,23); date1.printDate(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23

4.3 注意点
-
this类型:哪个对象调用哪个就是public static void main(String[] args) { MyDate myDate = new MyDate();//MyDate就是 myDate.setDate(2022,3,25); myDate.printDate(); MyDate myDate2 = new MyDate(); myDate2.setDate(2022,3,28); myDate2.printDate(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
-
this不能在静态方法中使用(main方法更不可以)public static void main(String[] args) { //this.printDate(); MyDate myDate = new MyDate();//MyDate就是 myDate.setDate(2022,3,25); myDate.printDate(); MyDate myDate2 = new MyDate(); myDate2.setDate(2022,3,28); myDate2.printDate(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
-
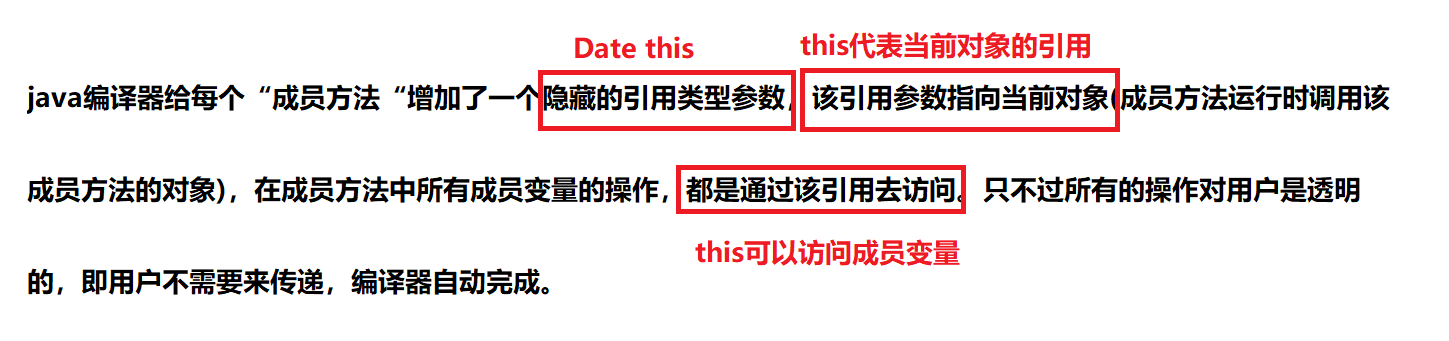
在"成员方法"中,
this只能引用当前对象,不能再引用其他对象this要么指向Date1,要么指向Date2 -
this是“成员方法”第一个隐藏的参数,编译器会自动传递,在成员方法执行时,编译器会负责将调用成员方法
对象的引用传递给该成员方法,this负责来接收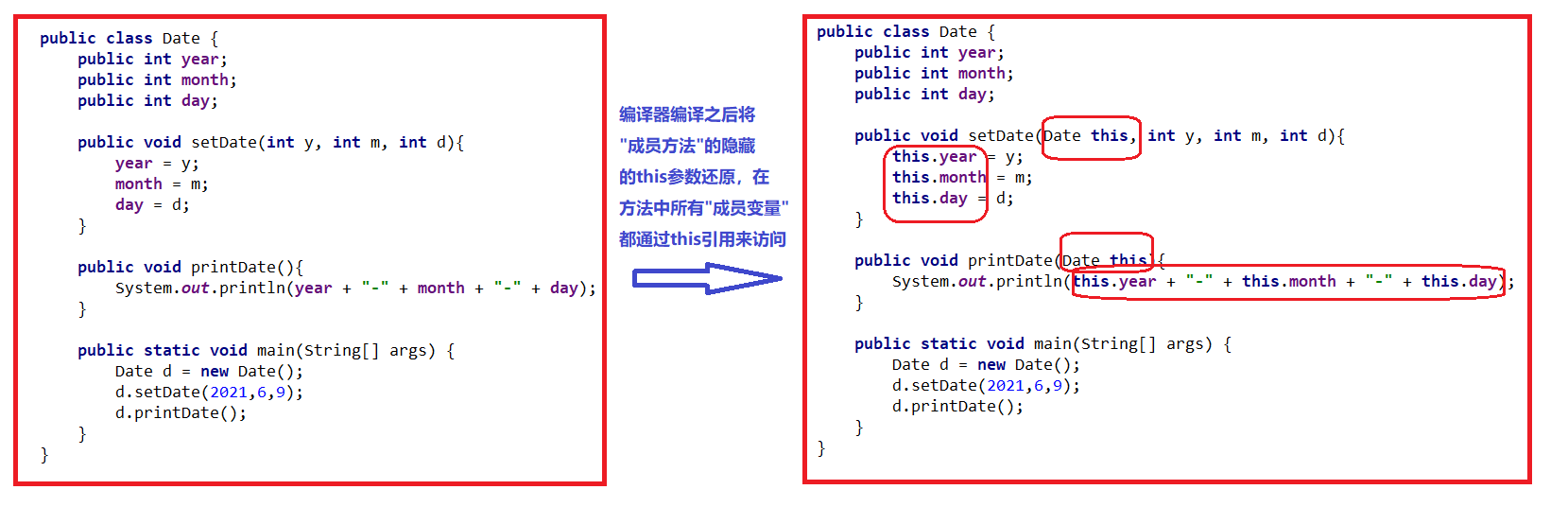
我们目前知道的
this的用法:- 代表当前对象的引用
- 可以区别,函数参数和成员变量名字冲突的时候
this是个隐式的参数,默认放在第一个- 只要是在当前类中去访问你自己的成员变量和成员方法时,建议加
this
-
相关阅读:
心理咨询预约微信小程序开发制作步骤
今天零九的雪
SpringBoot SpringBoot 开发实用篇 4 数据层解决方案 4.1 内置数据源
辅助驾驶功能开发-功能规范篇(22)-3-L2级辅助驾驶方案功能规范
都 2022 年了,你真的会用 Python 的 pip 吗?
python毕业设计作品基于django框架 教室图书馆座位预约系统毕设成品(7)中期检查报告
【算法系列篇】模拟算法
[ACNOI2022]王校长的构造
Java Interview 200 Questions —— Day01 —— 备战2022年秋招 —— 经典 200 问
在c#中使用CancellationToken取消任务
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_53117341/article/details/126091387
