-
leetcode94 -- 二叉树的中序遍历
一、问题描述
给定一个二叉树的根节点root ,返回 它的中序遍历 。
示例 1:
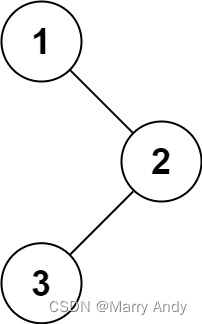
输入:root = [1,null,2,3]
输出:[1,3,2]示例 2:
输入:root = []
输出:[]示例 3:
输入:root = [1]
输出:[1]提示:
树中节点数目在范围 [0, 100] 内
-100 <= Node.val <= 100二、解决问题
法一:递归
class Solution { public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) { List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>(); inOrder(root, res); return res; } public void inOrder(TreeNode root, List res){ if(root == null) return; inOrder(root.left, res); res.add(root.val); inOrder(root.right, res); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 时间复杂度:O(n)
(其中 n 为二叉树节点的个数。二叉树的遍历中每个节点会被访问一次且只会被访问一次。) - 空间复杂度:O(n)
(空间复杂度取决于递归的栈深度,而栈深度在二叉树为一条链的情况下会达到 O(n) 的级别。)
法二:非递归
class Solution { public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) { List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>(); Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<TreeNode>(); while(root != null || !stack.isEmpty()){ while(root != null){ stack.push(root); root = root.left; } root = stack.pop(); res.add(root.val); root = root.right; } return res; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 时间复杂度:O(n)
(其中 n 为二叉树节点的个数。二叉树的遍历中每个节点会被访问一次且只会被访问一次。) - 空间复杂度:O(n)
(空间复杂度取决于栈深度,而栈深度在二叉树为一条链的情况下会达到 O(n) 的级别。)
法三:Morris 中序遍历
class Solution { public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) { List<Integer> ans=new LinkedList<>(); while(root!=null){ //没有左子树,直接访问该节点,再访问右子树 if(root.left==null){ ans.add(root.val); root=root.right; }else{ //有左子树,找前驱节点,判断是第一次访问还是第二次访问 TreeNode pre=root.left; while(pre.right!=null&&pre.right!=root) pre=pre.right; //是第一次访问,访问左子树 if(pre.right==null){ pre.right=root; root=root.left; } //第二次访问了,那么应当消除链接 //该节点访问完了,接下来应该访问其右子树 else{ pre.right=null; ans.add(root.val); root=root.right; } } } return ans; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 时间复杂度:O(n)
(其中 n 为二叉搜索树的节点个数。Morris 遍历中每个节点会被访问两次,因此总时间复杂度为 O(2n)=O(n)。) - 空间复杂度:O(1)
参考:https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-inorder-traversal/solution/
-
相关阅读:
vue3组件的通信方式
2024第三届全国大学生数据分析大赛,有没有没有思路的朋友?
H3C交换机设置时间命令
决策树模型(4)Cart算法
亚商投资顾问 早餐FM/1129冰雪消费升温
OpenJudge NOI 2.1 15:Counterfeit Dollar
Vue3 源码阅读(5):响应式系统 —— Vue2 中的 watch 和 computed
dubbo 2.5.3 升级记录 to 2.7.10
搭建SSH服务器
Z-Score模型的进阶版:Zeta模型
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_39671159/article/details/126031370
