-
单链表的基本操作
目录
1 链表的引入
链表的每个节点由数据域和指针域构成。数据域存放数据元素信息,指针域存放后继节点的地址。最后一个节点是没有后继节点,因此其指针域一般设置为NULL。

链表与数组的区别?
数组是线性存储结构,在内存地址是连续的,增加一个数组元素和删除一个数组元素都是非常不方便;而链表是链式存储结构,在内存空间中地址不一定是连续的,因为地址不连续所以插入一个节点或者删除一个节点都是非常方便,可以看出链表比较灵活。
如何使用链表存放三个整数1,2,3 ?
- #include
- struct Test{
- int data;
- struct Test *next;
- };
- int main(void)
- {
- /*申明了三个节点,存放数据1,2,3;但是这三个
- 节点之间并没有联系,因为他们的指针域并没有存放
- 后继节点的地址*/
- struct Test t1 = {1, NULL};
- struct Test t2 = {2, NULL};
- struct Test t3 = {3, NULL};
- /*让指针存放后继节点的地址*/
- t1.next = &t2;
- t2.next = &t3;
- /*现在通过变量t1就可以访问到t2,t3里面的数据*/
- printf("t1 = %d\nt2 = %d\nt3 = %d\n",t1.data,t1.next->data,t1.next->next->data);
- return 0;
- }
2 链表的动态遍历
链表的最后一个节点是没有后继节点;因此可以通过判断当前节点的指针是否为NULL来遍历循环链表。
- struct Test *print_link(struct Test *head)
- {
- struct Test *temp = head;
- while(temp)//因为最后一个节点是没有后继节点的,所以可以通过判断后继节点是否为NULL来遍历链表
- {
- printf("%d\n",temp->data);
- temp = temp->next; //让temp指向后继节点
- }
- }
3 遍历链表中的p = p - next

4 统计链表的个数
在动态遍历链表的时候,设置一个计算器变量i;通过i来统计链表的个数
- int Get_link_nodeNum(struct Test *head)
- {
- struct Test *temp = head;
- int i = 0;
- while(temp)
- {
- i++;
- temp = temp->next;
- }
- return i;
- }
5 查找指定的节点
在动态遍历链表的时候,判断当前节点的数据是否等于我们所需要的数据;如果查找到了我们所需要的数据让函数返回该节点的地址;如果未查找到让函数返回NULL;
- struct Test *findNode_byDate(struct Test *head,int data)
- {
- struct Test *temp = head;
- while(temp)
- {
- if(temp->data = data)
- {
- printf("找到data=%d的指定节点\n",data);
- return temp;
- }
- temp = temp->next;
- }
- printf("未找到data=%d的指定节点\n",data);
- return NULL;
- }
6 从指定节点后方插入新节点

如上图所示在指定节点的后方插入,共分为三步:
1 找到指定的节点p
2 将新节点new的后继节点设置为指定节点的后继节点,即new->next = p ->next;
3 将指定节点的后继节点设置为新节点,即p->next = new;
如果插入成功,提示插入成功并返回1;插入失败,提示插入失败并返回0;
- int insertNode_Rear(struct Test *head,struct Test *new,int data)
- {
- struct Test *temp = head;
- while(temp)
- {
- if(temp->data = data)
- {
- new->next = temp->next;
- temp->next = new;
- printf("插入成功\n");
- return 1;
- }
- temp = temp->next;
- }
- printf("未找到指定节点,插入失败!\n");
- return 0;
- }
7 从指定节点前方插入新节点
情况1:
如果指定节点是头节点,让新节点的后继节点设置为头节点,即new->next = head;此时新节点变成了头节点,所以要让head = new。

情况2:
如果指定节点不是头节点,则通过判断头节点下一个节点是否是否我们需要找的指定节点(通过p->next->data == data来判断);

- struct Test *insertNode_front(struct Test *head,struct Test *new,int data)
- {
- struct Test *temp = head;
- if(temp->data == data)
- {
- new->next = temp;
- head = new;
- return new;
- }
- while(temp->next != NULL)
- {
- if(temp->next->data == data)
- {
- new-next = temp->next;
- temp->next = new;
- return head;
- }
- temp = temp->next;
- }
- printf("找不到指定data=%d的节点,插入失败!\n",data);
- return NULL;
- }
8 链表删除指定节点
情况1:
如果删除的节点是头节点,让头节点直接指向第二个节点,即head = head->next;

情况2:
如果删除的节点不是头节点, 则通过判断头节点下一个节点是否是我们需要找的删除的节点(通过p->next->data == data来判断);
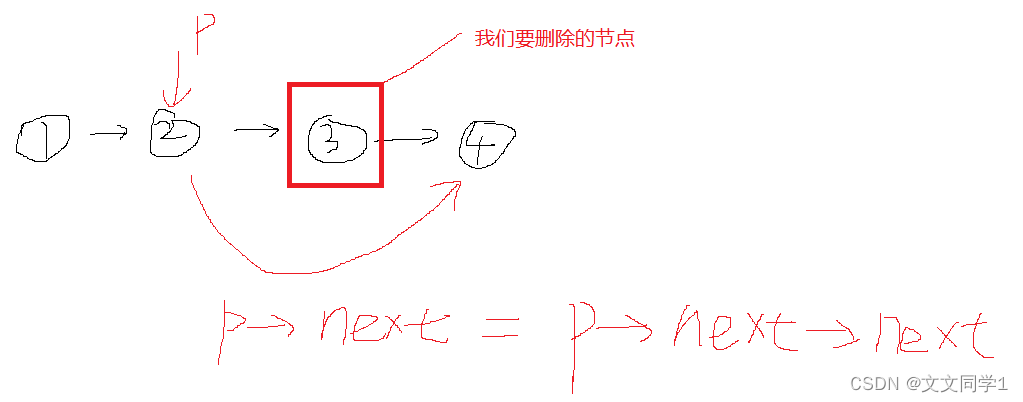
如果是使用malloc开辟的空间,在删除节点后需要及时使用free( )函数进行释放,否则会造成内存泄漏。
- struct Test *deleteNode(struct Test *head, int data)
- {
- struct Test *temp = head;
- struct Test *temp_free = NULL; //用来存放删除的节点,以便使用free()函数释放内存
- if(temp->data == data)
- {
- //temp_free = temp;
- temp = temp->next;
- // free(temp_free);
- return temp;
- }
- else
- {
- while(temp->next != NULL)
- {
- if(temp->next->data == data)
- {
- //temp_free = temp->next;
- temp->next = temp->next->next;
- //free(temp_free);
- return head;
- }
- p = p->next;
- }
- }
- return head;
- }
9 头插法创建链表
让新节点的后继节点设置原来的头节点,即new->next = head;让后将头节点设置为新节点,即head = new

- struct Test *create_front(struct Test *head)
- {
- struct Test *new;
- int i,n;
- printf("请输入要插入的节点个数:\n");
- scanf("%d",&n);
- if(head == NULL)
- {
- head = (struct Test*)malloc(sizeof(struct Test));
- printf("请输入数据:\n");
- scanf("%d",&head->data);
- head->next = NULL;
- n = n - 1;
- }
- for(i = 0;i < n;i++)
- {
- new = (struct Test*)malloc(sizeof(struct Test));
- printf("请输入数据:\n");
- scanf("%d",&new->data);
- new->next = head;
- head = new;
- }
- return head;
- }
10 尾插法创建链表
定义一个尾节点tail,刚刚开始tail = head;然后动态遍历到尾节点,让尾节点的后继节点设置为新节点,即tail->next = new;同时尾节点设置为新节点,即tail = new;

- struct Test *create_rear(struct Test *head)
- {
- int n,i;
- struct Test *new;
- struct Test *tail;
- printf("请输入插入的节点个数:\n");
- scanf("%d",&n);
- if(head == NULL)
- {
- head =(struct Test*)malloc(sizeof(struct Test));
- printf("请输入数据:\n");
- scanf("%d",&head->data);
- n = n-1;
- head->next = NULL;
- }
- tail = head;
- //遍历至尾节点
- while(tail->next != NULL)
- {
- tail = tail->next;
- }
- for(i = 0;i < n; i++)
- {
- new = (struct Test*)malloc(sizeof(struct Test));
- printf("请输入数据:\n");
- scanf("%d",&new->data);
- tail->next = new;
- tail = new;
- }
- return head;
- }
-
相关阅读:
关于DatagridviewComboBox控件的若干技术问题
C/C++编译器配置——MinGW下载安装
c++builder 6.0 使用TRichView最基本的方法
Windows右键菜单美化(适用版本:Win7-Win11) 奇怪的美化教程 #1
DC进阶-多周期约束详解
苏宁API接口
selenium(练习)提取dou yu网站上的数据
使用宝塔部署项目
Vue3 数据响应式原理:Proxy和Reflect
如何选择安全可靠的跨网文件安全交换一体机?
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_55299368/article/details/126002301
