-
c++:二叉搜索树的简析与详细实现(万字)
目录
一:什么是二叉搜索树
该树的任意一个子树都要满足
左子树的值<根<右子树的值
如图:

二:优点
查找非常迅速,最多查找高度次
列如我查找7,
(1)8>7,进入左边
(2)7>3,进入右边
(3)7>6, 进入右边
(4)7=7,找到

缺点:查找时间复杂度:O(N)
如下图的极端情况:

三:实现二叉搜索树
(1)定义头文件和test函数

(2)创建二叉树的基本结构
- template<class k>//模板
- //struct BinarySearchTree全名
- struct BSTree//缩写名,孩子兄弟表示法
- {
- BSTree
* _left; - BSTree
* _right; - k _key;
- };
不清楚孩子兄弟表示法看这里:树的孩子兄弟表示法_幻荼的博客-CSDN博客
(3)创建二叉树
- template<class k>
- class BSTree
- {
- typedef BSTreeNode
Node;//简写一下名字,不简写也行 - public:
- private:
- Node* _root=nullptr;//创建了一个名为_root的空树
- };
(4)Insert非递归版本
我们可以设定两个数记录位置,一个记录插入数的位置(cur),一个记录插入数的上一个位置(parent),当插入的数走到空,就new一个结点然后链接起来
假设我有这么一个树,需要插入数字’7’

根据二叉搜索树的特性,7会走到6的右边空位置处

然后7就new一个结点出来,6再和7相连接

注意这里链接还需要判断是链接在左边还是在右边,这里 7>6所以链接在右边
假如这里不是6而是8,那么7就应该链接在左边

insert 代码如下:
- bool Insert(const k& key)
- {
- if (_root == nullptr)//如果是一个空树,就直接new一个结点出来就好了
- {
- _root = new Node(key);
- return true;
- }
- Node* parent = nullptr;//设置一个记录该数字位置的上一个位置
- Node* cur = _root;//记录该数字的位置
- while (cur)
- {
- if (cur->_key < key)//该数字的值大于结点值,就朝该结点的右走
- {
- parent = cur;
- cur = cur->_right;
- }
- else if (cur->_key > key)//该数字的值小于结点值,就朝该结点的左走
- {
- parent = cur;
- cur = cur->_left;
- }
- else//不能插入同样得值
- {
- return false;
- }
- }
- cur = new Node(key);//此时走到空,new一个结点出来
- if (parent->_key < key)//如果该数字大于该数字的上一个结点,就需要链接到右边
- {
- parent->_right = cur;
- }
- else//如果该数字小于该数字的上一个结点,就需要链接到左边
- {
- parent->_left = cur;
- }
- return true;
- }
(5)中序遍历(打印)
先在private:里面写一个递归
- void _InOrder(Node* root)
- {
- if (root == nullptr)
- {
- return;
- }
- _InOrder(root->_left);
- cout<< root->_key << " ";
- _InOrder(root->_right);
- }
然后public嵌套一下
- void InOrder()
- {
- _InOrder(_root);
- cout << endl;
- }
这样嵌套一层,我们就可以直接用,不用传参就可以打印。
- void TestTree()
- {
- BSTree<int> t;//创建一个树
- int a[] = { 8,3,1,10,6,4,7,14,13 };
- for (auto e : a)//将数字插入树
- {
- t.Insert(e);
- }
- t.InOrder();//打印
- t.Insert(16);//插入
- t.Insert(9);//插入
- t.InOrder();//打印
- }
不明白_InOrder递归怎么实现的?
好吧
差不多是这样的(没画完,理解就行):
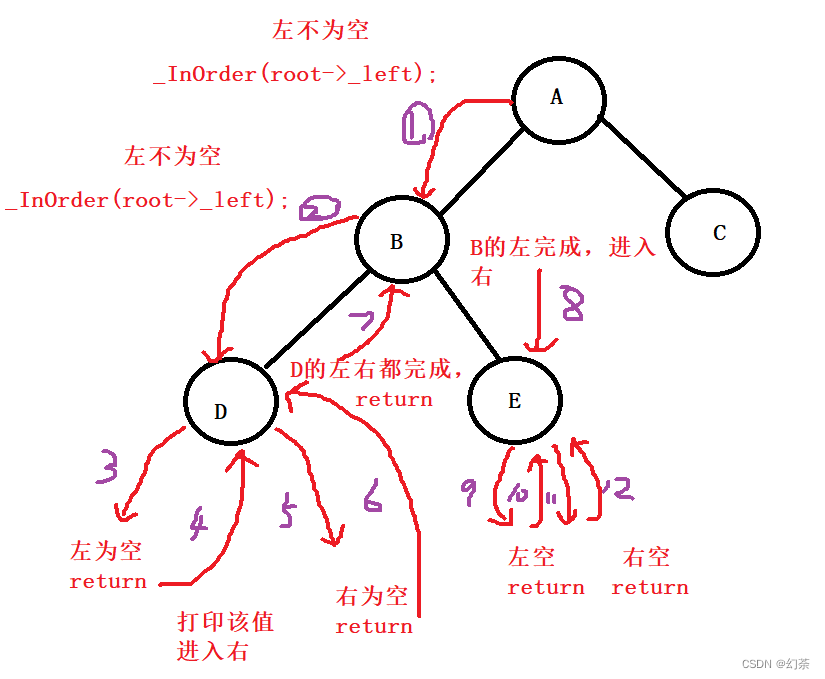
(6)查找Find(非递归版本)
不就是把刚才的代码截取一半吗?
- bool Find(const k& key)
- {
- Node* parent=nullptr;
- Node* cur = _root;//传根节点
- while (cur)
- {
- if (cur->_key < key)//大就右走
- {
- parent = cur;
- cur = cur->_right;
- }
- else if (cur->_key > key)//小就左走
- {
- parent = cur;
- cur = cur->_left;
- }
- else//找到return true
- {
- return true;
- }
- }
- return false;//找不到return false
- }
(7)删除Erase(非递归版本)
我们删除这里分三种情况
(1)该结点没有孩子,比如4,7,13,1
(2)该节点只有一个孩子(不论左孩子还是右孩子),比如10,14
(3)该结点有两个孩子(左孩子+右孩子),比如3,6.
其实对于情况一和情况二,我们可以直接删除该结点,让该结点的父节点指向空或者自己的孩子结点。
比如我要删除7和14
7:因为7后面没有子节点,所以只需要干掉7的空间,然后让7的父亲6,指向7的左还是或者右孩子(反正都是空,随意)就可以了

14:因为14有一个孩子13,所以删除14的时候,我们需要把14的父亲10链接到13上面

这两种情况其实都非常好处理,难处理的是有两个孩子的情况
比如根节点8和3
这个时候就需要运用到一个叫做替换法的方法
替换法:该结点与该节点左子树的最大值结点或者右子树的最小值结点的值进行交换
我们拿3举例
3:对于3这个结点而言,他左子树的最大值是1,右子树的最小值是4,假如我们和4进行交换

假如我们和1进行交换

实际上和直接删除相比,只是多了一个交换而已
理解了上门的理论之后,我们就需要更深入的来完善各种细节
(1)在只有一个或者没有子节点删除的时候我们需要谨慎的判断到底父节点指向子节点的左还是子节点的右。
假如我们删除4和14.(这里是一个孩子或者没有孩子的情况)
这个时候6的左指向4的右,10的右指向14的左。
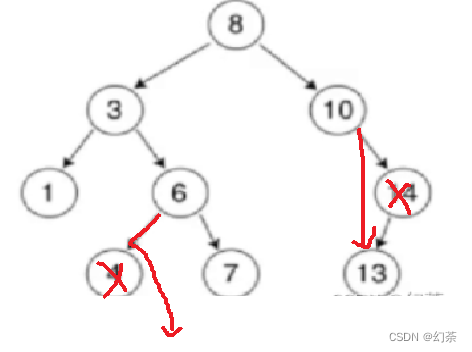
所以我们这里就需要分两种情况来讨论,子节点的左为空,子节点的右为空
- Node* parent = nullptr;//这里就是find,重点在下面的else
- Node* cur = _root;
- while (cur)//找到该节点
- {
- if (cur->_key < key)
- {
- parent = cur;
- cur = cur->_right;
- }
- else if (cur->_key > key)
- {
- parent = cur;
- cur = cur->_left;
- }
- else{ //重点在这里
- if (cur->_left == nullptr)//如果左为空
- {
- if (cur == parent->_left)//我是左结点,父节点的左指向我的右
- {
- parent->_left = cur->_right;
- }
- else//我是右结点,父节点的右指向我的右
- {
- parent->_right = cur->_right;
- }
- delete cur;
- }
- else if (cur->_right == nullptr)//如果右为空
- {
- if (cur == parent->_left)//我是左孩子
- {
- parent->_left = cur->_left;//父亲的左指向我的左
- }
- else//我是右孩子
- {
- parent->_right = cur->_left;//父亲的右指向我的左
- }
- delete cur;
- }
- }
这里还有一个极端情况
假如该树只有左孩子,或者该树只有右孩子,然后删除根节点

在这种情况下,我们的parent就会为空,所以我们只需要将根节点变为第二个结点就好
- if (parent == nullptr)
- {
- _root = cur->_right;//左数就left,右树就right
- }

好了,上面是1个或者没有孩子的情况
下面是有两个孩子的情况
我们来删除3和8,默认找右树最小值(当然你也可以找左数最大值)
其实最关键的还是看父节点的左和右指向子节点的哪
3:3和4交换,父节点的左指向子节点的右

8:10和8交换,父节点的右,指向子节点的右

- Node* minParent = cur;//注意父节点需要给根节点,防止为空
- Node* minRight = cur->_right;
- while (minRight->_left)
- {
- minParent = minRight;
- minRight = minRight->_left;
- }
- swap(minRight->_key, cur->_key);
- if (minParent->_left == minRight)
- {
- minParent->_left = minRight->_right;
- }
- else
- {
- minParent->_right = minRight->_right;
- }
- delete minRight;
erase的总代码:
- bool Erase(const k& key)
- {
- Node* parent = nullptr;
- Node* cur = _root;
- while (cur)
- {
- if (cur->_key < key)//值大走右边
- {
- parent = cur;
- cur = cur->_right;
- }
- else if (cur->_key > key)//值小走左边
- {
- parent = cur;
- cur = cur->_left;
- }
- else//找到该结点
- {
- //一个孩子--左为空 or 右为空
- //两个孩子--替换法
- if (cur->_left == nullptr)//左为空,有右孩子
- {
- if (parent == nullptr)//如果该树只有右孩子,又直接删除根节点会导致parent为空,所以直接将根结点变为右边的下一个孩子,然后删除根节点
- {
- _root = cur->_right;
- }
- else//这里就是正常情况
- {
- if (cur == parent->_left)//如果我是你的左孩子,那么父节点的左就要指向我的右
- {
- parent->_left = cur->_right;
- }
- else//如果我是你的右孩子,那么父节点的右就要指向我的右
- {
- parent->_right = cur->_right;
- }
- }
- delete cur;//删除结点
- }
- else if (cur->_right == nullptr)//右为空,有左孩子
- {
- if (parent == nullptr)//还是判断极端情况
- {
- parent = cur->_left;
- }
- else//正常情况
- {
- if (cur == parent->_left)//我是你的左孩子,父节点的左指向我的左
- {
- parent->_left = cur->_left;
- }
- else//我是你的右孩子,父节点的右指向我的左
- {
- parent->_right = cur->_left;
- }
- }
- delete cur;
- }
- else//两个孩子都不为空,替换法
- {
- //找右子树的最小结点替代
- Node* minParent = cur;
- Node* minRight = cur->_right;
- while (minRight->_left)//找右子树的最小值结点
- {
- minParent = minRight;
- minRight = minRight->_left;
- }
- swap(minRight->_key, cur->_key);//交换两个结点的值
- if (minParent->_left == minRight)//如果我是左孩子,父节点的左指向我的右
- {
- minParent->_left = minRight->_right;
- }
- else//如果我是你的右孩子,父节点的右指向我的右。
- {
- minParent->_right = minRight->_right;
- }
- delete minRight;
- }
- return true;
- }
- }
- return false;//找不到结点return false
- }
注意:这里捋不清的小伙伴,自己多画画图,一定要判断清楚父节点的指针究竟指向哪里,这是删除里面最重要的
(7)拷贝和析构
不是重点看看就行了直接上代码
- public:
- ~BSTree()
- {
- DestoryTree(_root);
- _root = nullptr;
- }
- //强制编译器自己生成构造
- BSTree() = default;
- BSTree(const BSTree
& t) - {
- _root = CopyTree(t._root);
- }
- BSTree
& operator=(BSTree t) - {
- swap(_root, t._root);
- return *this;
- }
- private:
- void DestoryTree(Node* root)//递归逐步销毁
- {
- if (root == nullptr)
- {
- return;
- }
- DestoryTree(root->_left);
- DestoryTree(root->_right);
- delete root;
- }
- Node* CopyTree(Node* root)//递归逐步创建结点
- {
- if (root == nullptr)
- {
- return nullptr;
- }
- Node* copyNode = new Node(root->_key);
- copyNode->_left = CopyTree(root->_left);
- copyNode->_right = CopyTree(root->_right);
- return copyNode;
- }
以上就是非递归版本,大家理解之后就可以看递归版本了
(8)查找(递归版本)
- public:
- bool FindR(const k& key)//嵌套一层而已
- {
- return _FindR(_root, key);
- }
- private:
- bool _FindR(Node* root, const k& key)//这里是递归的实现
- {
- if (root == nullptr)//找不到
- {
- return false;
- }
- if (root->_key < key)//值大,往右查找
- {
- return _FindR(root->_right, key);
- }
- else if (root->_key > key)//值小,往左查找
- {
- return _FindR(root->_left, key);
- }
- else//找到
- {
- return true;
- }
- }
(9)插入(递归版本)
我这里先上代码,然后再来解释
- public:
- bool InsertR(const k& key)//嵌套一层
- {
- return _InsertR(_root, key);
- }
- private:
- bool _InsertR(Node*& root, const k& key)
- {
- if (root == nullptr)//找到了,插入
- {
- root = new Node(key);
- return true;
- }
- //下面是查找插入的位置
- if (root->_key < key)
- {
- return _InsertR(root->_right, key);
- }
- else if (root->_key > key)
- {
- return _InsertR(root->_left, key);
- }
- else
- {
- return false;
- }
- }
小伙伴们其实找插入的位置是看的明白的,但是不明白new出来的结点是怎么和原来的树链接起来的。
我们以前是使用了一个parent来记录插入结点的上一个位置(当然这里也可以),但是这里我们没有parent,究竟是怎么链接起来的呢?
这里我们有一个小知识:引用C++引用_幻荼的博客-CSDN博客
(不清楚引用的同学一定要先看我的这篇文章,很简短,不然后面看不懂)
bool _InsertR(Node*& root, const k& key)//仔细看这里的root有个&符号我们举例,插入一个9:结果应该是这样的

关键就是在数字10这里,我们深入看看
(1)根节点是10,10>9,进入下面else if内

(2)此时返回10的左(null)给InsertR,insertR把null传给插入

(3)关键来了因为这里是&,所以root是root->_left的别名。
这样就相当于10->left=new Node(key)

(10)删除Erase(递归版本)
我们理解了上面的别名之后,我们看看Erase的递归是如何巧用别名的
还是先上代码
- public:
- bool EraseR(const k& key)//嵌套一层
- {
- return _EraseR(_root, key);
- }
- private:
- bool _EraseR(Node*& root, const k& key)
- {
- if (root == nullptr)//没找到
- {
- return false;
- }
- if (root->_key < key)//大往右走
- {
- return _EraseR(root->_right, key);
- }
- else if (root->_key > key)//小往左走
- {
- return _EraseR(root->_left, key);
- }
- else//找到了
- {
- Node* del = root;//创建一个指针记录root方便删除
- if (root->_left == nullptr)
- {
- root = root->_right;
- }
- else if (root->_right == nullptr)
- {
- root = root->_left;
- }
- else
- {
- Node* minRight = root->_right;
- while (minRight->_left)
- {
- minRight = minRight->_left;
- }
- swap(root->_key, minRight->_key);
- return _EraseR(root->_right, key);
- }
- delete del;
- return true;
- }
- }
我们举例,我们删除14(有一个孩子或者没有孩子的情况):

(1)14右为空进入这个代码

(2)而14其实是10->rigth的别名
这个代码翻译一下就是
- else if(14->right==nullptr)
- {
- 10->right=14->left;
- }
是不是就链接起来了
再看我们删除3(有两个孩子):

(1)找到右树最小值,然后交换两个值
(2)因为别名不能改变,我现在的别名是8->left,所以我们return,root->right;
就等于是重新在一个树里面删除

就是在这个根为6的树里面删除3这个结点,那么就和我们原来的一模一样了
以上就是所有的讲解,最后附上总代码
-------------------------------------
总代码:
BinarySearchTree.h
- #pragma once
- #include
- using namespace std;
- template<class k>
- struct BSTreeNode
- {
- BSTreeNode
* _left; - BSTreeNode
* _right; - k _key;
- BSTreeNode(const k& key)
- :_left(nullptr)
- ,_right(nullptr)
- ,_key(key)
- {}
- };
- template<class k>
- class BSTree
- {
- typedef BSTreeNode
Node; - public:
- ~BSTree()
- {
- DestoryTree(_root);
- _root = nullptr;
- }
- //t1=t2
- BSTree
& operator=(BSTree t) - {
- swap(_root, t._root);
- return *this;
- }
- //强制编译器自己生成构造
- BSTree() = default;
- BSTree(const BSTree
& t) - {
- _root = CopyTree(t._root);
- }
- bool Insert(const k& key)
- {
- if (_root == nullptr)
- {
- _root = new Node(key);
- return true;
- }
- Node* cur = _root;
- Node* parent = nullptr;
- while (cur)
- {
- if (cur->_key < key)
- {
- parent = cur;
- cur = cur->_right;
- }
- else if (cur->_key > key)
- {
- parent = cur;
- cur = cur->_left;
- }
- else
- {
- return false;
- }
- }
- cur = new Node(key);
- if (parent->_key < key)
- {
- parent->_right = cur;
- }
- else
- {
- parent->_left = cur;
- }
- return true;
- }
- bool Find(const k& key)
- {
- Node* cur = _root;
- while (cur)
- {
- if (cur->_key < key)
- {
- cur = cur->_right;
- }
- else if (cur->_key > key)
- {
- cur = cur->_left;
- }
- else
- {
- return true;
- }
- }
- return false;
- }
- bool Erase(const k& key)
- {
- Node* parent = nullptr;
- Node* cur = _root;
- while (cur)
- {
- if (cur->_key < key)
- {
- parent = cur;
- cur = cur->_right;
- }
- else if (cur->_key > key)
- {
- parent = cur;
- cur = cur->_left;
- }
- else//两个孩子,左为空或者右为空
- {
- if (cur->_left == nullptr)
- {
- if (cur == _root)
- {
- _root = cur->_right;
- }
- else
- {
- if (cur == parent->_left)
- {
- parent->_left = cur->_right;
- }
- else
- {
- parent->_right = cur->_right;
- }
- }
- delete cur;
- }
- else if (cur->_right == nullptr)
- {
- if (cur == _root)
- {
- _root = cur->_left;
- }
- else
- {
- if (cur == parent->_left)
- {
- parent->_left = cur->_left;
- }
- else
- {
- parent->_right = cur->_left;
- }
- }
- delete cur;
- }
- else//两个孩子都不为空
- {
- //右子树的最小结点替代
- Node* minRight = cur->_right;
- Node* minParent = cur;
- while (minRight->_left)
- {
- minParent = minRight;
- minRight = minRight->_left;
- }
- swap(minRight->_key, cur->_key);
- //cur->_key = minRight->_key;
- if (minParent->_left == minRight)
- {
- minParent->_left = minRight->_right;
- }
- else
- {
- minParent->_right = minRight->_right;
- }
- delete minRight;
- }
- return true;
- }
- }
- return false;
- }
- void InOrder()
- {
- _InOrder(_root);
- cout << endl;
- }
- bool FindR(const k& key)
- {
- return _FindR(_root, key);
- }
- bool InsertR(const k& key)
- {
- return _InsertR(_root, key);
- }
- bool EraseR(const k& key)
- {
- return _EraseR(_root, key);
- }
- private:
- bool _EraseR(Node* & root,const k& key)
- {
- if (root == nullptr)
- {
- return false;
- }
- if (root->_key < key)
- {
- return _EraseR(root->_right, key);
- }
- else if (root->_key > key)
- {
- return _EraseR(root->_left, key);
- }
- else
- {
- Node* del = root;
- //删除
- if (root->_left == nullptr)
- {
- root = root->_right;
- }
- else if (root->_right == nullptr)
- {
- root = root->_left;
- }
- else
- {
- Node* minRight = root->_right;
- while (minRight->_left)
- {
- minRight = minRight->_left;
- }
- swap(root->_key, minRight->_key);
- return _EraseR(root->_right,key);
- }
- }
- }
- bool _FindR(Node* root, const k& key)
- {
- if (root == nullptr)
- {
- return false;
- }
- if (root->_key < key)
- {
- return _FindR(root->_right, key);
- }
- else if (root->_key > key)
- {
- return _FindR(root->_left, key);
- }
- else
- {
- return true;
- }
- }
- bool _InsertR(Node*& root,const k& key)
- {
- if (root == nullptr)
- {
- root = new Node(key);
- return true;
- }
- if (root->_key < key)
- {
- return _InsertR(root->_right, key);
- }
- else if (root->_key > key)
- {
- return _InsertR(root->_left, key);
- }
- else
- {
- return false;
- }
- }
- Node* _root = nullptr;
- void _InOrder(Node* root)
- {
- if (root == nullptr)
- {
- return;
- }
- _InOrder(root->_left);
- cout << root->_key << " ";
- _InOrder(root->_right);
- }
- void DestoryTree(Node* root)
- {
- if (root == nullptr)
- {
- return;
- }
- DestoryTree(root->_left);
- DestoryTree(root->_right);
- delete root;
- }
- Node* CopyTree(Node* root)
- {
- if (root == nullptr)
- {
- return nullptr;
- }
- Node* copyNode = new Node(root->_key);
- copyNode->_left = CopyTree(root->_left);
- copyNode->_right = CopyTree(root->_right);
- return copyNode;
- }
- };
- void TestBSTree()
- {
- BSTree<int> t;
- int a[] = { 8,3,1,10,6,4,7,14,13 };
- for (auto e : a)
- {
- t.Insert(e);
- }
- t.InOrder();
- t.Insert(16);
- t.Insert(9);
- t.InOrder();
- }
- void TestBSTree2()
- {
- BSTree<int> t;
- int a[] = { 8,7,9,12,5,19,20,30 };
- for (auto e : a)
- {
- t.Insert(e);
- }
- t.InOrder();
- }
- void TestBSTree3()
- {
- BSTree<int> t;
- int a[] = { 8,3,1,10,6,4,7,14,13 };
- for (auto e : a)
- {
- t.Insert(e);
- }
- t.InOrder();
- cout << endl;
- t.Erase(3);
- t.Erase(8);
- for (auto e : a)
- {
- t.Erase(e);
- }
- t.InOrder();
- }
- void TestBSTree4()
- {
- BSTree<int> t;
- int a[] = { 8,3,1,10,6,4,7,14,13 };
- for (auto e : a)
- {
- t.Insert(e);
- }
- t.InOrder();
- BSTree<int> copy = t;
- copy.InOrder();
- }
- void TestBSTree5()
- {
- BSTree<int> t;
- int a[] = { 8,3,1,10,6,4,7,14,13 };
- for (auto e : a)
- {
- t.Insert(e);
- }
- t.InOrder();
- t.InsertR(9);
- BSTree<int> copy = t;
- copy.InOrder();
- }
- void TestBSTree6()
- {
- BSTree<int> t;
- int a[] = { 8,3,1,10,6,4,7,14,13 };
- for (auto e : a)
- {
- t.Insert(e);
- }
- t.InOrder();
- t.EraseR(3);
- t.EraseR(8);
- t.InOrder();
- t.EraseR(14);
- t.EraseR(7);
- t.InOrder();
- }
test.cpp
- #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
- #include"BinarySearchTree.h"
- int main()
- {
- TestBSTree6();
- return 0;
- }
-
相关阅读:
c++访问修饰符与继承关系
Dubbo-Adaptive实现原理
11.10记录纪要
查询或解析solidity智能合约事件event或logs日志
程序员必看内容连续集之 SpringBoot05 整合Druid&Redis
原生小程序一键获取手机号
MySQL的enum类型的踩坑记录
Python编程基础:深入理解值类型与引用类型及其在数据处理中的关键作用
MyBatisPlus-条件构造器/分页/多数据源/MyBatisX插件(生成代码)
js 监控 浏览器关闭前 调用
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_62718027/article/details/126009024
