-
剑指Offer 07 重建二叉树 -- 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
剑指 Offer 07. 重建二叉树
输入某二叉树的前序遍历和中序遍历的结果,请构建该二叉树并返回其根节点。
假设输入的前序遍历和中序遍历的结果中都不含重复的数字。
示例 1:
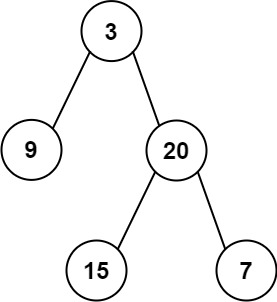
Input: preorder = [3,9,20,15,7], inorder = [9,3,15,20,7] Output: [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]- 1
- 2
示例 2:
Input: preorder = [-1], inorder = [-1] Output: [-1]- 1
- 2
思路分析
首先要知道遍历后的数组都有什么样的特点
- 在前序遍历序列中,第一个元素为树的根节点
- 在中序遍历序列中,根节点的左边为左子树,根节点的右边为右子树
根据上面的理论知识可以清楚本题的解题策略,就是以 前序数组的第一个元素【根节点】为切割点,先切中序数组,根据中序数组,反过来在切前序数组。一层一层切下去,每次前序数组的第一个元素就是节点元素。

前序遍历的第一个元素就是他的头节点。知道了头节点,我们可以在中序遍历中找到头节点的位置
index。通过index我们就可以求出来左子树在数组中的长度:index - inorder_start。(inorder_start是中序遍历的起点)。-
获取树的头节点
int root_val = preorder[preorder_start](preorder_start是前序遍历的起始值)。然后我们直接构建二叉树 的根节点TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(root_val) -
构建左树:
root->left我们知道该二叉树的左子树的长度为left_length = index - inorder_start所以我们可以推出二叉树的左子树在前序遍历的位置是
[preorder_start+1,preorder_start+left_length]。
同理:二叉树的左子树在中序遍历的位置是[inorder_start, index - 1]。 -
构建右树:
root->right
二叉树的右子树在前序遍历的位置是[preorder_start+left_length+1,preorder_end]。
同理:二叉树右子树在中序遍历的位置是[index + 1 , inorder_end]。
代码如下:👇👇👇👇
class Solution { public: //递归代码 TreeNode* buildcore(const vector<int>& preorder, const vector<int>& inorder, int preorder_start, int preorder_end, int inorder_start, int inorder_end) { if(preorder_start>preorder_end||inorder_start>inorder_end) { return nullptr; } //前序遍历的第一个数字是根节点的值 int root_val = preorder[preorder_start]; TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(root_val); //区间里只有一个值,返回 if(preorder_start == preorder_end) { return root; } //中序遍历找到根节点的位置 int index = 0; //可以等于,在范围内 while(index <= inorder_end && inorder[index] != root_val) { index++; } //如果index大于inorder_end,说明没找到,报错,题目所给的意思是肯定能找到,所以这里就不判断了。 //左右子树区间大小。 int left_length = index - inorder_start; root->left = buildcore(preorder,inorder,preorder_start+1,preorder_start+left_length,inorder_start,index-1); root->right = buildcore(preorder,inorder,preorder_start+left_length+1,preorder_end,index+1,inorder_end); return root; } TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder) { int n = preorder.size(); if(n==0) { return 0; } return buildcore(preorder,inorder,0,n-1,0,n-1); } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
106. 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
该题与上题类似,可以使用相同的解法递归解决。
思路分析
-
在后序遍历序列中,最后一个元素为树的根节点
-
在中序遍历序列中,根节点的左边为左子树,根节点的右边为右子树
以 后序数组的最后一个元素【根节点】为切割点,先切中序数组,根据中序数组,反过来在切后序数组。一层一层切下去,每次后序数组最后一个元素就是节点元素。
class Solution { public: TreeNode* buildcore(const vector<int>& inorder, const vector<int>& postorder, int inorder_start, int inorder_end, int post_start, int post_end) { if(inorder_start>inorder_end||post_start>post_end) { return nullptr; } //后序遍历的最后一个值是根节点 int root_val = postorder[post_end]; TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(root_val); //遍历找根节点在中序遍历的的位置 int index = 0; for(index = 0; index<= inorder_end; index++) { if(inorder[index] == root_val) { break; } } //计算左子树的长度 int left_length = index - inorder_start; //构建左子树 root->left = buildcore(inorder,postorder,inorder_start,index-1,post_start,post_start+left_length-1); //构建右子树 root->right = buildcore(inorder,postorder,index+1,inorder_end,post_start+left_length,post_end-1); return root; } TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder) { int n = inorder.size(); if(n==0) { return nullptr; } return buildcore(inorder,postorder,0,n-1,0,n-1); } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
-
相关阅读:
“终于懂了” 系列:组件化框架 ARouter 完全解析(二)APT技术
【数据分析】:什么是数据分析?
Ti AM335X工控模块矩阵键盘电路的设计与驱动移植
报错与解决 | 应用程序无法启动0x7b mysql
基于PHP+MySQL医药信息查询系统的设计与开发
如何实现 MySQL 增删改查操作
C#操作PPT动画窗格并插入音频文件的一些思路
如何让电脑永不息屏?Python:这事我熟,只需5行代码...
React事件绑定的方式有哪些?区别?
音频文件元数据修改:批量操作的技巧和方法
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/Y673789476/article/details/126007155