-
一起刷算法与数据结构-树篇1
大家好,我是工藤学编程 🦉 大二在读 作业侠系列最新文章😉 Java实现聊天程序 一起备战ccf-csp与蓝桥杯系列最新文章🐷 一起备战蓝桥杯与CCF-CSP之大模拟炉石传说 一起刷算法与数据结构最新文章🐷 一起刷算法与数据结构-树篇1 之前我们的链表篇已经完结:
一起刷算法与数据结构-链表篇1
一起刷算法与数据结构-链表篇2
说明:
在此栏中,我不生产题解,但我是题解的搬运工,写此栏主要用于自己后续的复习
今天这篇内容如下:
今天咱们的内容如下:
题目1.重建二叉树
题目2.二叉树的下一个节点
题目3.树的子结构
题目4.二叉树的镜像
题目5.对称的二叉树
题目6.不分行从上往下打印二叉树
题目7.二叉搜索树的后续遍历序列
题目8:二叉树中和为某一值的路径
题目9.二叉搜索树的第K个节点
题目10.二叉树的深度题目1.重建二叉树
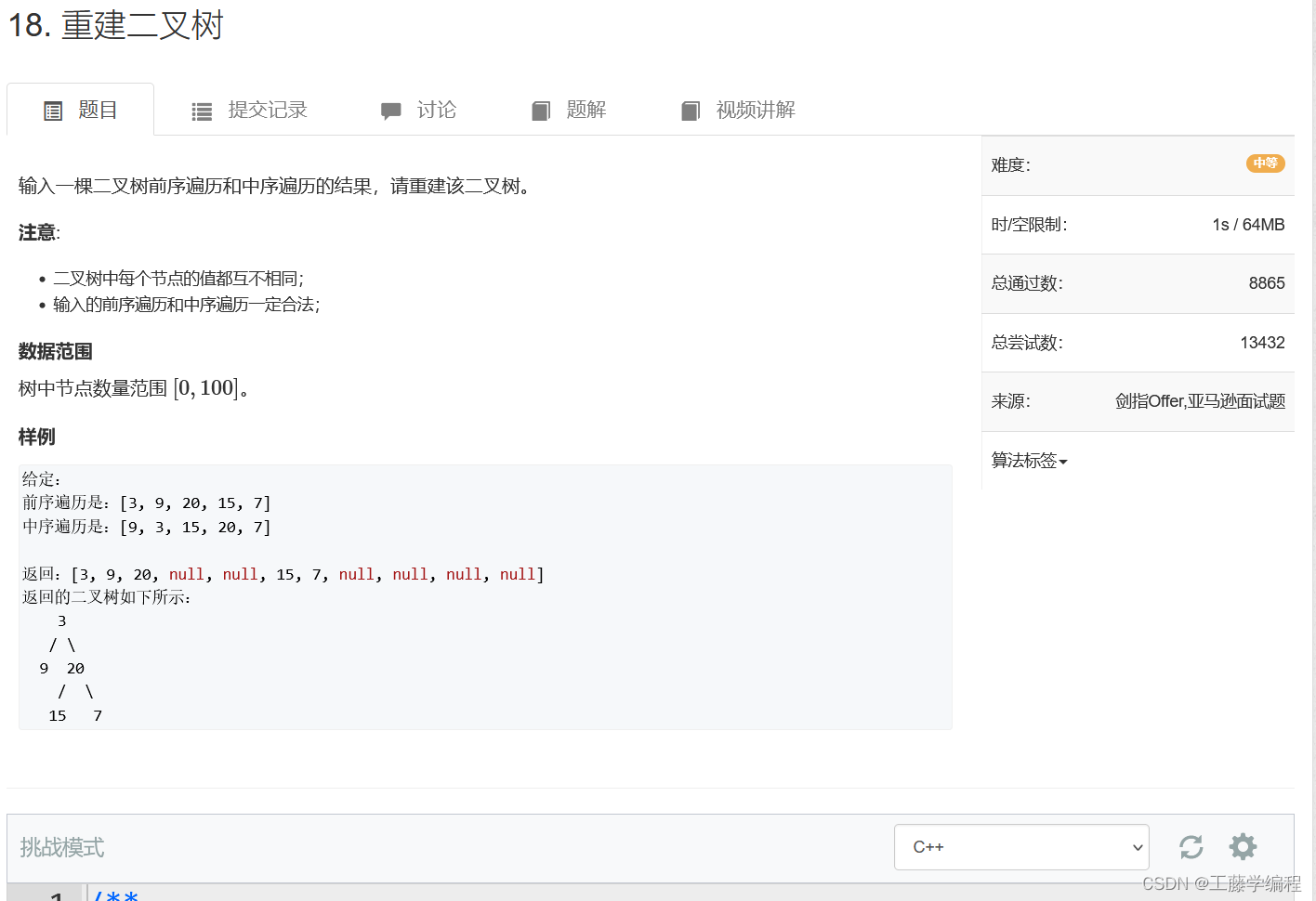
解决思路:
看y总:
 参考代码:
参考代码:class Solution { public: unordered_map<int,int>pos; TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder) { int n = preorder.size(); for(int i=0;i<n;i++) pos[inorder[i]]=i; return dfs(preorder,inorder,0,n-1,0,n-1); } TreeNode* dfs(vector<int>& pre, vector<int>& in,int pl,int pr,int il,int ir) { if(pl>pr) return NULL; int k = pos[pre[pl]]-il; auto root = new TreeNode(pre[pl]); root->left=dfs(pre,in,pl+1,pl+k,il,il+k-1); root->right=dfs(pre,in,pl+k+1,pr,il+k+1,ir); return root; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
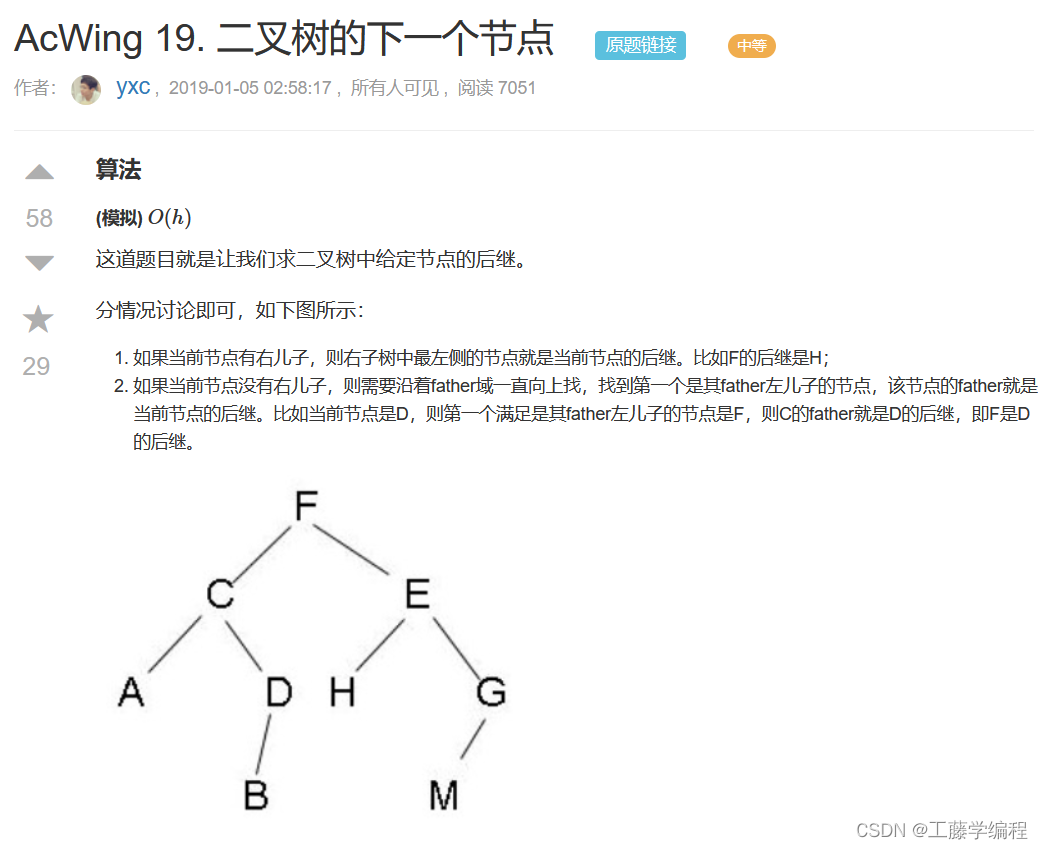
题目2.二叉树的下一个节点
 解题思路:
解题思路:
继续看y总:
参考代码:class Solution { public: TreeNode* inorderSuccessor(TreeNode* p) { if(p->right) { p=p->right; while(p->left) p = p->left; return p; } while(p->father && p==p->father->right) p=p->father; return p->father; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
题目3.树的子结构

y总yyds
 参考代码:
参考代码:class Solution { public: bool hasSubtree(TreeNode* pRoot1, TreeNode* pRoot2) { if(!pRoot1 || !pRoot2) return false; if(ispart(pRoot1,pRoot2)) return true; return hasSubtree(pRoot1->left,pRoot2) || hasSubtree(pRoot1->right,pRoot2); } bool ispart(TreeNode* p1,TreeNode* p2) { if(!p2) return true; if(!p1) return false; if(p1->val == p2->val) return ispart(p1->left,p2->left) && ispart(p1->right,p2->right); return false; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
题目4.二叉树的镜像

题解:
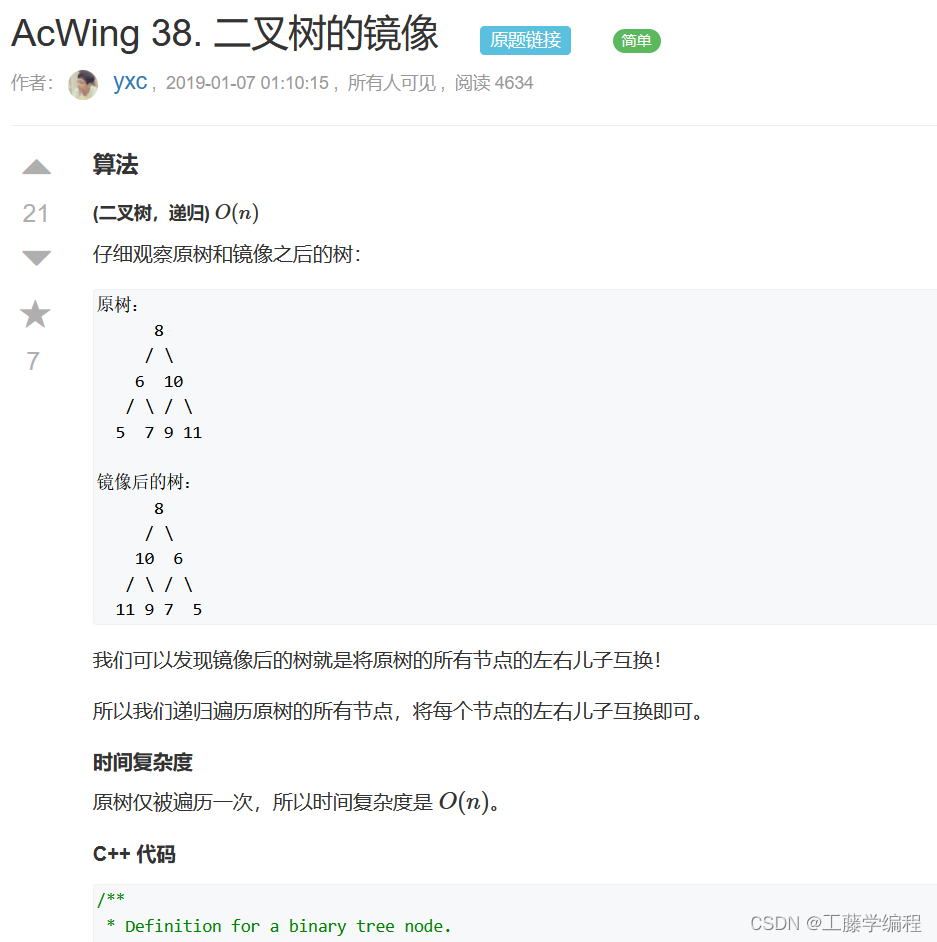
参考代码class Solution { public: void mirror(TreeNode* root) { if(!root) return; mirror(root->right); mirror(root->left); swap(root->left,root->right); } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
题目5.对称的二叉树
 解题思路:
解题思路:两个子树互为镜像当且仅当:
两个子树的根节点值相等;
第一棵子树的左子树和第二棵子树的右子树互为镜像,且第一棵子树的右子树和第二棵子树的左子树互为镜像;参考代码:
class Solution { public: bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) { if(!root) return true; return dfs(root->left,root->right); } bool dfs(TreeNode* l,TreeNode* r) { if(!l || !r) return !l && !r; if(l->val != r->val ) return false; return dfs(l->left,r->right) && dfs(l->right,r->left); } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
题目6.不分行从上往下打印二叉树

解题思路:我们从根节点开始按宽度优先的顺序遍历整棵树,每次先扩展左儿子,再扩展右儿子。
这样我们会:
先扩展根节点;
再依次扩展根节点的左右儿子,也就是从左到右扩展第二层节点;
再依次从左到右扩展第三层节点;
依次类推
所以BFS的顺序就是这道题目要求的顺序。
也就是树的层序遍历参考代码:
class Solution { public: vector<int> printFromTopToBottom(TreeNode* root) { vector<int>ans; if(!root) return ans; queue<TreeNode*>q; q.push(root); while(!q.empty()) { auto t = q.front(); q.pop(); ans.push_back(t->val); if(t->left) q.push(t->left); if(t->right) q.push(t->right); } return ans; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
题目7.二叉搜索树的后续遍历序列
前置知识:什么是二叉搜索树:
它或者是一棵空树,或者是具有下列性质的二叉树:
若它的左子树不空,则左子树上所有结点的值均小于它的根结点的值;
若它的右子树不空,则右子树上所有结点的值均大于它的根结点的值; 它的左、右子树也分别为二叉排序树。解题思路:
根据其性质,递归判断是否符合即可
参考代码:class Solution { public: vector<int>se; bool verifySequenceOfBST(vector<int> sequence) { se=sequence; return dfs(0,se.size()-1); } bool dfs(int l,int r) { if(l>=r) return true; int root=se[r]; int k=l; while(k<r && se[k]<root) k++; for(int i=k;i<r;i++) if(se[i]<root) return false; return dfs(l,k-1) && dfs(k,r-1); } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
题目8:二叉树中和为某一值的路径

解题思路:递归直到树的叶子节点,如果sum等于0,则说明是符合要求
参考代码:
class Solution { public: vector<vector<int>>ans; vector<int>cur; vector<vector<int>> findPath(TreeNode* root, int sum) { dfs(root,sum); return ans; } void dfs(TreeNode* root,int sum) { if(!root) return; cur.push_back(root->val); sum-=root->val; if(!sum && !root->left && !root->right ) ans.push_back(cur); dfs(root->left,sum); dfs(root->right,sum); cur.pop_back(); } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
题目9.二叉搜索树的第K个节点
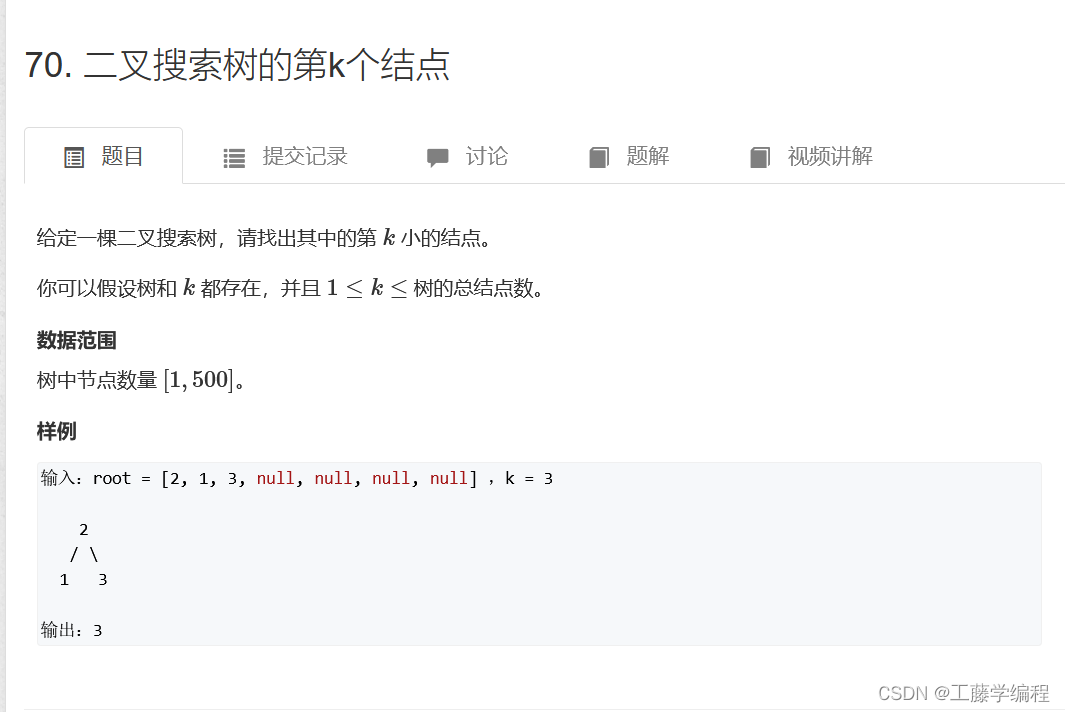
参考大佬题解:
第k大k小问题参考代码:
class Solution { public: TreeNode* ans; TreeNode* kthNode(TreeNode* root, int k) { dfs(root,k); return ans; } // TreeNode* dfs(TreeNode* root,int& k) // { // if(!root) return NULL; // dfs(root->left,k); // k--; // if(k==0) // { // ans=root; // } // if(k>0) dfs(root->right,k); // } void dfs(TreeNode* root,int& k) { if(!root) return ; dfs(root->left,k); k--; if(k==0) { ans=root; } if(k>0) dfs(root->right,k); } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
注意,如果是这样写是
不正确的:class Solution { public: TreeNode* kthNode(TreeNode* root, int k) { return dfs(root,k); } TreeNode* dfs(TreeNode* root,int& k) { if(!root) return NULL; dfs(root->left,k); k--; if(k==0) { return root; } dfs(root->right,k); } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
题目10.二叉树的深度
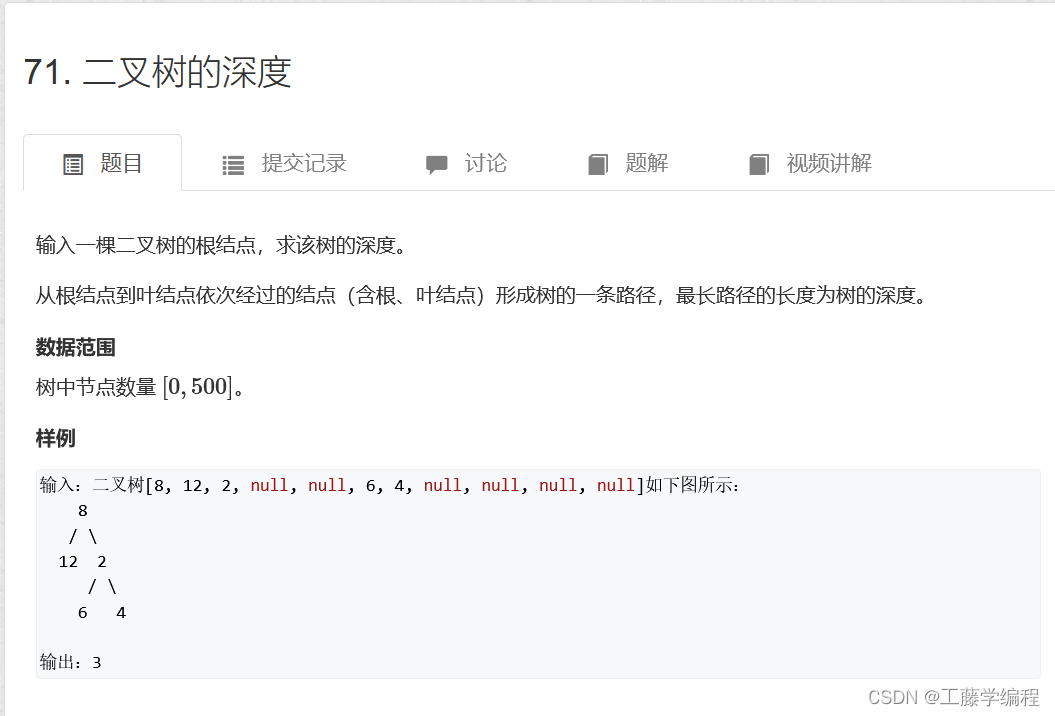
解题思路:递归遍历,找到最长的即可
参考代码:
class Solution { public: int mmax; int treeDepth(TreeNode* root) { dfs(root,1); return mmax; } void dfs(TreeNode* root,int k) { if(!root) return; if(root->left) dfs(root->left,k+1); if(root->right) dfs(root->right,k+1); if(k>mmax) mmax=k; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
-
相关阅读:
python模拟表格任意输入位置
Linux防火墙firewall常用的命令集合
ElasticSearch系列-索引原理与数据读写流程详解
MongoDB集群之分片集群 Shard Cluster
MyBatis-Flex学习手册
Dotnet 序列化枚举为字符串
zabbix监控中间件服务
数据分析:小红书品牌“共情力”缔造指南
《HTML表单》
SV-315C 15寸触模屏 I3工控机 网络广播主机
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/chandfy/article/details/125834104
