-
完善系统的最后一公里,增加系统日志功能
当我们在开发一个系统的时候,随着规划的功能越来越多,按照复杂度和稳定性相反的原则,为了保证系统能够按照我们设想的目标运行,我们需要对系统的运行状况进行监控。
那么什么时候介入监控比较好?在系统功能开发的前期(还没有任何实质性的功能),似乎不太合适,那么在系统一切功能开发接近尾声的时候好像也不太合适,最好在这中间,选择一个迭代不是很紧急的阶段,系统已经有那么一个成熟的功能在用的时候,并且随着用户量的不断增大,我们需要对系统的运营情况进行一些了解的时候。
前期我们对系统日志进行设计的时候,可以不必考虑的那么周全,就一些必要的信息进行收集。日志大概分为两种:1. 操作日志;2. 异常日志
操作日志用来监控用户在使用系统时候的一些行为,比如请求了什么接口可以推断出他在系统前台进行了什么操作;异常日志则是用户在请求某个接口的时候,接口内部出现了程序上的错误,这个日志主要提供给程序员进行问题追踪的。随后我们还可以从这些日志中分析出很多有需要的数据,包括系统的健康度,功能的使用频率和频次等。
1. 日志表设计
梳理出一些必要的字段后,我们可以设计出如下的两张不同功能的日志表,它们有些字段是相同的,都需要记录谁在请求某个接口、请求的Uri、请求人的访问IP等信息。
CREATE TABLE `sys_log_operation` ( `id` INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '自动编号', `opera_module` VARCHAR(64) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '功能模块', `opera_type` VARCHAR(64) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '操作类型', `opera_desc` VARCHAR(500) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '操作描述', `opera_req_param` TEXT DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '请求参数', `opera_resp_param` TEXT DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '返回参数', `opera_employee_account` VARCHAR(11) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '操作人账号', `opera_method` VARCHAR(255) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '操作方法', `opera_uri` VARCHAR(255) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '请求URI', `opera_ip` VARCHAR(64) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '请求IP', `created_time` DATETIME DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '创建时间', `modified_time` DATETIME DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '修改时间', PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE ) COMMENT = '操作日志表' ROW_FORMAT = COMPACT; CREATE TABLE `sys_log_exception` ( `id` INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '自动编号', `exc_req_param` TEXT DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '请求参数', `exc_name` VARCHAR(255) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '异常名称', `exc_message` TEXT DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '异常信息', `opera_employee_account` VARCHAR(11) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '操作人账号', `opera_method` VARCHAR(255) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '操作方法', `opera_uri` VARCHAR(255) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '请求URI', `opera_ip` VARCHAR(64) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '请求IP', `created_time` DATETIME DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '创建时间', `modified_time` DATETIME DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '修改时间', PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE ) COMMENT = '异常日志表' ROW_FORMAT = COMPACT;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
2. 后台系统日志收集
到了后端编码的阶段,我们来构思下这个代码架构如何去实现?因为日志代码是需要穿插在业务代码中的,这样必然带来一个问题,导致代码过于混乱的问题。有没有一种途径,通过 Spring 里注解的方式,只需要在接口的入口增加携带参数的注解,然后在注解的代码里就实现具体的日志收集功能。
Spring 里的特性 AOP(面向切面)就很适合用来实现日志记录,性能统计,安全控制,事务处理,异常处理等功能,将代码从业务逻辑代码中划分出来。
我们在项目代码的 Utils 目录创建注解接口
OperLogpackage com.lead.utils; import java.lang.annotation.Retention; import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; import java.lang.annotation.Documented; import java.lang.annotation.Target; /** * 自定义操作日志注解 * @author Fan */ @Target(ElementType.METHOD) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented public @interface OperLog { String operModule() default ""; // 操作模块 String operType() default ""; // 操作类型 String operDesc() default ""; // 操作说明 }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
具体的功能,我们创建一个 OperLogAspect 切面处理类来实现。这里面通过
@Pointcut注解定义了日志的切入点和执行范围package com.lead.utils; import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON; import com.lead.entity.System.ExceptionLog; import com.lead.entity.System.OperationLog; import com.lead.service.System.IExceptionLogService; import com.lead.service.System.IOperationLogService; import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterReturning; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterThrowing; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut; import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import org.springframework.util.Assert; import org.springframework.web.context.request.RequestAttributes; import org.springframework.web.context.request.RequestContextHolder; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; /** * 切面处理类,操作日志异常日志记录处理 * @author Fan */ @Aspect @Component public class OperLogAspect { private final IOperationLogService operationLogService; private final IExceptionLogService exceptionLogService; public OperLogAspect( IOperationLogService operationLogService, IExceptionLogService exceptionLogService) { Assert.notNull(operationLogService, "operationLogService must not be null!"); Assert.notNull(exceptionLogService, "exceptionLogService must not be null!"); this.operationLogService = operationLogService; this.exceptionLogService = exceptionLogService; } /** * 设置操作日志切入点 记录操作日志 在注解的位置切入代码 */ @Pointcut("@annotation(com.lead.utils.OperLog)") public void operLogPoinCut() { } /** * 设置操作异常切入点记录异常日志 扫描所有controller包下操作 */ @Pointcut("execution(* com.lead.controller..*.*(..))") public void exceptionLogPoinCut() { } /** * 正常返回通知,拦截用户操作日志,连接点正常执行完成后执行, 如果连接点抛出异常,则不会执行 * @param joinPoint 切入点 * @param keys 返回结果 */ @AfterReturning(value = "operLogPoinCut()", returning = "keys") public void saveOperLog(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object keys) { RequestAttributes requestAttributes = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes(); HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) requestAttributes.resolveReference(RequestAttributes.REFERENCE_REQUEST); OperationLog operlog = new OperationLog(); String token = request.getHeader("accessToken"); String employeeAccount = ""; Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs(); Object params = args[0]; // 请求参数对象 if (token != null && !token.equals("")) { employeeAccount = JwtUtil.getUserId(token); } else { Map argMap = (Map) params; String resp = JSON.toJSONString(keys); if (argMap.get("account") != null && argMap.get("passWord") != null && resp.indexOf("用户登录成功") > -1) { employeeAccount = argMap.get("account").toString(); } } try { MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature(); Method method = signature.getMethod(); OperLog opLog = method.getAnnotation(OperLog.class); if (opLog != null) { String operaModule = opLog.operModule(); String operaType = opLog.operType(); String operaDesc = opLog.operDesc(); operlog.setOperaModule(operaModule); operlog.setOperaType(operaType); operlog.setOperaDesc(operaDesc); } // 获取请求的类名 String className = joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getName(); // 获取请求的方法名 String methodName = method.getName(); methodName = className + '.' + methodName; operlog.setOperaMethod(methodName); // Map<String, String> rtnMap = converMap(request.getParameterMap()); // 将参数所在的数组转换成json operlog.setOperaReqParam(JSON.toJSONString(params)); operlog.setOperaRespParam(JSON.toJSONString(keys)); operlog.setOperaEmployeeAccount(employeeAccount); operlog.setOperaUri(request.getRequestURI()); operlog.setOperaIp(IPUtil.getIpAddress(request)); operationLogService.addOperationLog(operlog); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } /** * 异常返回通知,用于拦截异常日志信息 连接点抛出异常后执行 */ @AfterThrowing(pointcut = "exceptionLogPoinCut()", throwing = "e") public void saveExceptionLog(JoinPoint joinPoint, Throwable e) { RequestAttributes requestAttributes = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes(); HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) requestAttributes.resolveReference(RequestAttributes.REFERENCE_REQUEST); ExceptionLog exceptLog = new ExceptionLog(); String token = request.getHeader("accessToken"); String employeeAccount = ""; Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs(); Object params = args[0]; // 请求参数对象 if (token != null && !token.equals("")) { employeeAccount = JwtUtil.getUserId(token); } else { employeeAccount = request.getParameter("account"); } try { MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature(); Method method = signature.getMethod(); // 获取请求的类名 String className = joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getName(); // 获取请求的方法名 String methodName = method.getName(); methodName = className + '.' + methodName; exceptLog.setExcReqParam(JSON.toJSONString(params)); // 请求参数 exceptLog.setOperaMethod(methodName); // 请求方法名 exceptLog.setExcName(e.getClass().getName()); // 异常名称 exceptLog.setExcMessage(stackTraceToString(e.getClass().getName(), e.getMessage(), e.getStackTrace())); // 异常信息 exceptLog.setOperaEmployeeAccount(employeeAccount); exceptLog.setOperaUri(request.getRequestURI()); exceptLog.setOperaIp(IPUtil.getIpAddress(request)); exceptionLogService.addExceptionLog(exceptLog); } catch (Exception e2) { e2.printStackTrace(); } } /** * 转换request 请求参数 * @param paramMap request获取的参数数组 */ public Map<String, String> converMap(Map<String, String[]> paramMap) { Map<String, String> rtnMap = new HashMap<String, String>(); for (String key : paramMap.keySet()) { rtnMap.put(key, paramMap.get(key)[0]); } return rtnMap; } /** * 转换异常信息为字符串 * @param exceptionName 异常名称 * @param exceptionMessage 异常信息 * @param elements 堆栈信息 */ public String stackTraceToString(String exceptionName, String exceptionMessage, StackTraceElement[] elements) { StringBuffer strbuff = new StringBuffer(); for (StackTraceElement stet : elements) { strbuff.append(stet + "\n"); } String message = exceptionName + ":" + exceptionMessage + "\n\t" + strbuff.toString(); return message; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
具体的日志数据处理分别封装在
saveOperLog和saveExceptionLog方法中,这里主要说下他们共同的一些字段数据的获取。用户的账号是通过请求头参数accessToken获取的token信息然后解析出来的,这里为了获取未登录情况也就是请求登录接口的时候,直接获取登录提交的用户账号RequestAttributes requestAttributes = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes(); HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) requestAttributes.resolveReference(RequestAttributes.REFERENCE_REQUEST); OperationLog operlog = new OperationLog(); String token = request.getHeader("accessToken"); String employeeAccount = ""; if (token != null && !token.equals("")) { employeeAccount = JwtUtil.getUserId(token); } else { Map argMap = (Map) params; String resp = JSON.toJSONString(keys); if (argMap.get("account") != null && argMap.get("passWord") != null && resp.indexOf("用户登录成功") > -1) { employeeAccount = argMap.get("account").toString(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
获取接口类名和方法名
MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature(); Method method = signature.getMethod(); // 获取请求的类名 String className = joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getName(); // 获取请求的方法名 String methodName = method.getName(); methodName = className + '.' + methodName; operlog.setOperaMethod(methodName);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
这里直接获取的注解携带的参数,也就是我们在接口端添加的代码
OperLog opLog = method.getAnnotation(OperLog.class); if (opLog != null) { String operaModule = opLog.operModule(); String operaType = opLog.operType(); String operaDesc = opLog.operDesc(); operlog.setOperaModule(operaModule); operlog.setOperaType(operaType); operlog.setOperaDesc(operaDesc); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
在业务代码中添加日志注解,给每个参数赋予带有一定含义的值:
@OperLog(operModule = "培训模块", operType = "用户获取培训课程列表", operDesc = "用户获取培训课程列表") @RequestMapping(value = "/get-training", method = RequestMethod.POST) public Result getTrainings(@RequestBody Map<String, Object> params, HttpServletRequest request) {}- 1
- 2
- 3
3. 前台日志查询
前台拿到日志接口请求过来的数据,我们用一张表格展示就好,在该接口中提供了操作人、操作模块、操作类型和起始时间等查询参数,前台可以通过输入参数值进行过滤。

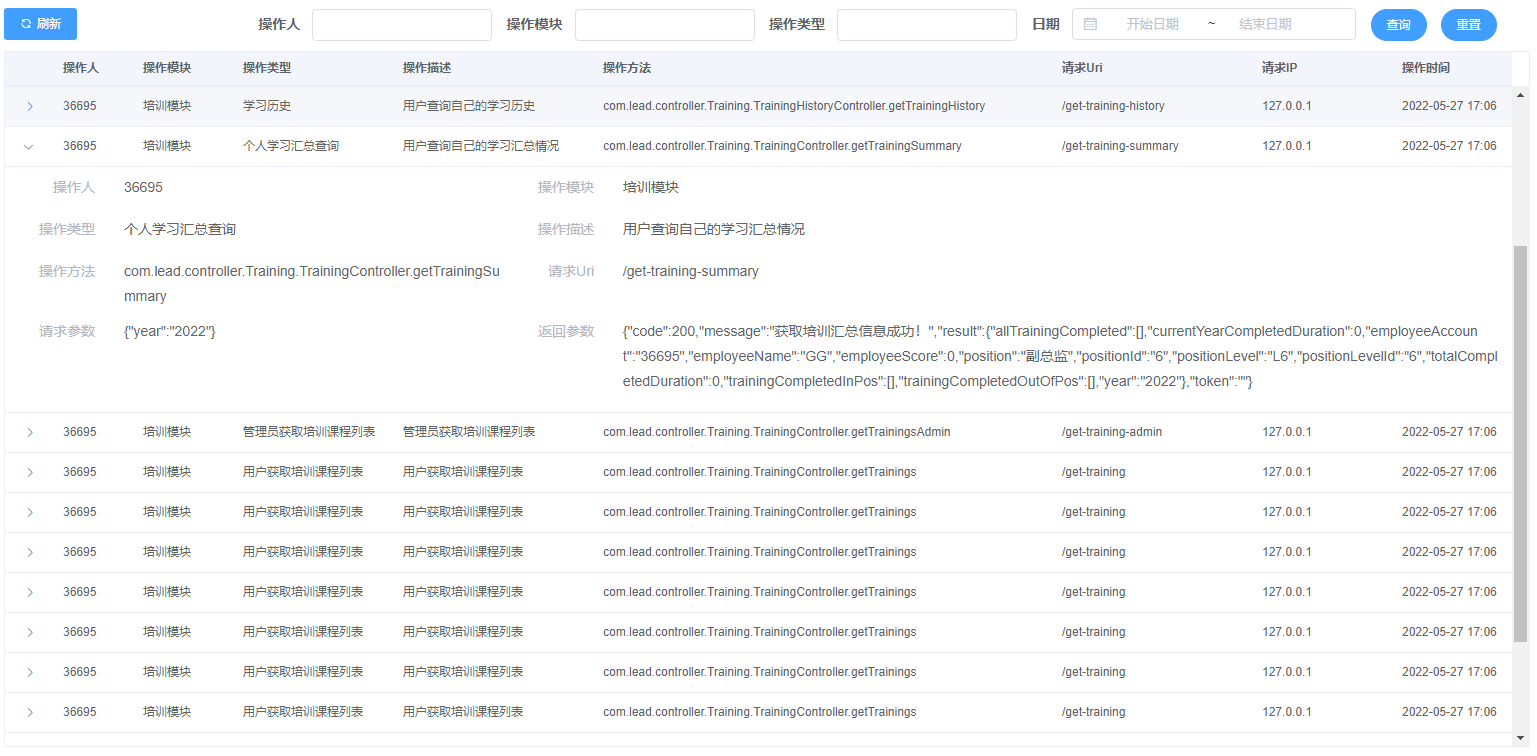
为了展示的信息更全,我们在表格中增加展开行的功能,点击表格中的行任何位置,出现该条日志的详细信息。

-
相关阅读:
西安某1000M3浮顶油罐设计(成品油库1000m³油罐设计与制造工艺)
ubuntu18.04上遇到的一些bug修复
C++ 不知图系列之基于邻接矩阵实现广度、深度搜索
SD NAND 的 SDIO在STM32上的应用详解(上篇)
MyBatis-Plus公共字段自动填充
【ROS入门】实现参数服务器参数的增删改查操作
2024年,我又开始用Linux桌面作为主力系统了~
滴滴弹性云基于 K8S 的调度实践
高德 Android 地图SDK 绘制面不显示
通过百度翻译API完成Java中的中英文翻译
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/u013919171/article/details/125604789
