-
Django-图书管理系统(含源码)
前段时间翻文件发现了以前学习python和django时做的一个系统,当时的想法是将这玩意做出来应付web开发大作业、课程设计作业甚至是毕设用的,实际上也确实应付了课程设计,功能虽然不算多,但是应付课程设计或者大作业绰绰有余了。
项目使用python开发,采用Django框架,数据库采用MySQL,根据用户人员的不同分成两套系统,分别是学生系统和管理员系统,功能模块具体分成四个,分别是用户管理模块、图书管理模块、数据管理模块、前端模块。
1、用户管理模块
用户管理模块实现的功能包括用户注册(分为学生注册和管理员注册)、用户信息修改、用户登录和判定
用户注册和登录

views.py中用户注册及登陆判定代码段
- def login(request):#登录
- return render(request, 'login.html')
- def student_register(request): # 学生注册
- name = request.POST.get("student_name") # 获取学生输入的姓名
- id = request.POST.get("student_id") # 获取学生输入的学号
- major = request.POST.get("student_major") # 获取学生输入的学院
- email = request.POST.get("student_email") # 获取学生输入的邮箱
- telephone = request.POST.get("student_telephone")
- password = request.POST.get("student_password")
- result1 = User.objects.filter(account=telephone) # 在用户表中搜索该用户名的记录
- result2 = Student.objects.filter(student_id=id) # 在学生表中搜索该学号的记录
- context = {}
- if len(result1) == 1: # 判断该账户是否存在(即判断是否注册过),如果后台存在记录,则返回相应的提示语句
- context["info"] = "该账户已注册!!!"
- context["status"] = 0 #零表示注册失败
- return render(request, 'login.html', context=context)
- else: #该账户是新用户
- if len(result2) == 1:#判断该学号是否有学生已使用
- context["info"] = "该学号已占用!!!"
- context["status"] = 4
- return render(request, 'login.html', context=context)
- else:
- User.objects.create(account=telephone, user_password=password,user_identity='学生')#用create为user表添加一条记录
- Student.objects.create(student_name=name,student_id=id,student_major=major,student_tel=telephone,student_email=email)#用create为student表添加一条记录
- context["info"] = "注册成功!"
- context["status"] = 1 #1表示注册成功
- return render(request, 'login.html', context=context)
- def manager_register(request): # 管理员注册
- name = request.POST.get("manager_name") # 获取管理员输入的姓名
- id = request.POST.get("manager_id") # 获取管理员输入的工号
- stack = request.POST.get("manager_stack") # 获取管理员输入的书库
- email = request.POST.get("manager_email") # 获取管理员输入的邮箱
- telephone = request.POST.get("manager_telephone")
- password = request.POST.get("manager_password")
- result1 = User.objects.filter(account=telephone) # 在用户表中搜索该用户名的记录
- result2 = Manager.objects.filter(manager_id=id) # 在管理员表中搜索该工号的使用记录
- context = {}
- if len(result1) == 1: # 判断该账户是否存在(即判断是否注册过),如果后台存在记录,则返回相应的提示语句
- context["info"] = "该账户已注册!!!"
- context["status"] = 0 #零表示注册失败
- return render(request, 'login.html', context=context)
- else: #该账户是新用户
- if len(result2) == 1:#判断该工号号是否有管理员已使用
- context["info"] = "该工号已占用!!!"
- context["status"] = 5
- return render(request, 'login.html', context=context)
- else:
- User.objects.create(account=telephone, user_password=password,user_identity='管理员')#用create为user表添加一条记录
- Manager.objects.create(manager_name=name, manager_id=id, manager_stack=stack, manager_tel=telephone,manager_email=email)#用create为manager表添加一条记录
- context["info"] = "注册成功!"
- context["status"] = 1 #1表示注册成功
- return render(request, 'login.html', context=context)
- def login_judge(request):#登入判定
- global account ,global_sname,global_mname #定义全局变量account,存储该用户的账户,global_sname保存一下该学生的姓名,global_mname保存一下该学生的姓名
- account = request.POST.get("telephone")#获取前端输入的账户(手机号)
- user_password = request.POST.get("password")
- result1 = User.objects.filter(account=account)#在user表里检索是否存在该账户
- if len(result1) == 1: # 判断后台是否存在该用户,有则进一步判断密码是否正确
- password = result1[0].user_password # 获取后台的密码
- identity = result1[0].user_identity # 获取该账户的身份信息
- if user_password == password: # 将用户输入的密码和后台密码进行比对,如何正确,判断该账户身份
- if identity == '学生':
- result2 = Student.objects.filter(student_tel=account)
- global_sname = result2[0].student_name # 用全局变量保存一下该学生的姓名
- context={
- "name":result2[0].student_name,
- "id":result2[0].student_id,
- "major":result2[0].student_major,
- "telephone":result2[0].student_tel,
- "email":result2[0].student_email,
- }
- return render(request, 'student/student_information.html',context) # 跳转到学生主页界面
- else:
- result = Manager.objects.filter(manager_tel=account) # account为全局变量
- global_mname = result[0].manager_name # 用全局变量保存一下该管理员的姓名
- context = {
- "name": result[0].manager_name,
- "id": result[0].manager_id,
- "stack": result[0].manager_stack,
- "telephone": result[0].manager_tel,
- "email": result[0].manager_email,
- }
- return render(request, 'manager/manager_information.html',context) # 跳转到管理员主页界面
- else: # 如果不一致则返回相应提示语句
- context = {
- "info": "密码错误!!!",
- "status": 2
- }
- return render(request, 'login.html', context=context) # 密码错误回到登入界面
- else: # 如果不存在该用户则返回相应的提示语句
- context = {
- "info": "该账户不存在!!!",
- "status": 3
- }
- return render(request, 'login.html', context=context) # 账户不存在则继续回到登入界面
用户信息管理

views.py中用户信息管理代码段
- def student_information(request):#个人信息
- if request.method == "GET": #此部分是当每次点击侧边导航栏的“个人信息”选项时,都重新显示该用户的个人资料
- result = Student.objects.filter(student_tel=account) #account为全局变量
- context = {
- "name": result[0].student_name,
- "id": result[0].student_id,
- "major": result[0].student_major,
- "telephone": result[0].student_tel,
- "email": result[0].student_email,
- }
- return render(request, 'student/student_information.html', context)#将该用户的个人信息再次传到前端页面
- else: #在student_information.html页面的第44行中通过post方式的“保存”按钮跳转到此处,即完成更新数据操作(保存)
- email = request.POST.get("email") # 获取邮箱
- Student.objects.filter(student_tel=account).update(student_email=email)#更新数据
- result = Student.objects.filter(student_tel=account) # account为全局变量 此处再次传值到前端
- context = {
- "name": result[0].student_name,
- "id": result[0].student_id,
- "major": result[0].student_major,
- "telephone": result[0].student_tel,
- "email": result[0].student_email,
- }
- return render(request, 'student/student_information.html', context) # 将该用户的个人信息再次传到前端页面
- def manager_information(request):#个人信息
- if request.method == "GET": #此部分是当每次点击侧边导航栏的“个人信息”选项时,都重新显示该管理员的个人资料
- result = Manager.objects.filter(manager_tel=account) #account为全局变量
- context = {
- "name": result[0].manager_name,
- "id": result[0].manager_id,
- "stack": result[0].manager_stack,
- "telephone": result[0].manager_tel,
- "email": result[0].manager_email,
- }
- return render(request, 'manager/manager_information.html', context)#将该用户的个人信息再次传到前端页面
- else: #在manager_information.html页面的第44行中通过post方式的“保存”按钮跳转到此处,即完成更新数据操作(保存)
- stack = request.POST.get("stack") # 获取书库信息
- email = request.POST.get("email") # 获取邮箱
- Manager.objects.filter(manager_tel=account).update(manager_email=email,manager_stack=stack)#更新数据
- result = Manager.objects.filter(manager_tel=account) # account为全局变量 此处再次传值到前端
- context = {
- "name": result[0].manager_name,
- "id": result[0].manager_id,
- "stack": result[0].manager_stack,
- "telephone": result[0].manager_tel,
- "email": result[0].manager_email,
- }
- return render(request, 'manager/manager_information.html', context) # 将该用户的个人信息再次传到前端页面
用户密码修改

views.py中用户密码修改代码段
- def change_password(request):#修改密码
- result = User.objects.filter(account=account).first()
- password = result.user_password
- if request.method == "GET": #此部分是当每次点击侧边导航栏的“修改密码”选项时,显示该界面
- return render(request,'student/change_password.html',context={"password":password,"name":global_sname})
- else:#此部分是在change_password.html页面中点击保存按钮时完成修改密码的操作
- oldPassword = request.POST.get("oldPassword")
- newPassword = request.POST.get("newPassword")
- reNewPassword = request.POST.get("reNewPassword")#以下是先判断输入的旧密码是否正确,并且两次输入的密码是否一致且都不为空
- if password == oldPassword and newPassword == reNewPassword and newPassword and reNewPassword:
- User.objects.filter(account=account).update(user_password = newPassword)#更新该用户的密码
- password = newPassword
- return render(request, 'student/change_password.html', context={"password": password, "name": global_sname})
- def change_manager_password(request):#修改管理员的密码
- result = User.objects.filter(account=account).first()
- password = result.user_password
- if request.method == "GET":#此部分是当每次点击侧边导航栏的“修改密码”选项时,显示该界面
- return render(request,'manager/change_manager_password.html',context={"password":password,"name":global_mname})
- else:#此部分是在change_manager_password.html页面中点击保存按钮时完成修改密码的操作
- oldPassword = request.POST.get("oldPassword")
- newPassword = request.POST.get("newPassword")
- reNewPassword = request.POST.get("reNewPassword")#以下是先判断输入的旧密码是否正确,并且两次输入的密码是否一致且都不为空
- if password == oldPassword and newPassword == reNewPassword and newPassword and reNewPassword:
- User.objects.filter(account=account).update(user_password = newPassword)#更新该用户的密码
- password = newPassword
- return render(request, 'manager/change_manager_password.html', context={"password": password, "name": global_mname})
2、图书管理模块
图书馆里模块实现的功能与我们日常图书馆的借阅系统相似,学生端包括书籍查询、书籍借阅、书记归还;管理员端包括书籍采购、书籍信息修改等更多扩展功能
书籍查询及借阅归还,可选择按书籍名或类型查找

views代码段
- def search_book(request):#查找书籍
- if request.method == "GET":#此部分是当用户每次点击侧边导航栏的“查找书籍”选项时,都要显示出所有书籍资料
- books = Book.objects.all()
- types = Type.objects.all()
- return render(request, 'student/search_book.html',context={"books": books,"types":types,"name":global_sname }) # 向前端传递所有查找到的书籍信息的集合
- else:#student/search_book.html页面的第56行中通过post方式的“搜索”按钮跳转到此处,即完成搜索操作
- book_name = request.POST.get("book_name")
- type_id = request.POST.get("type_id")
- types = Type.objects.all()
- if book_name:#如果书名非空,则按书名查找
- book_result = Book.objects.filter(book_name=book_name)
- if book_result:#如果找到的结果集非空,则输出
- return render(request,'student/search_book.html',context={"books":book_result,"types":types,"name":global_sname})
- else:#若搜索的结果集为0,那么输出未找到该本书!
- book_result = Book.objects.all()
- return render(request, 'student/search_book.html',context={"books": book_result, "types": types, "name": global_sname, "status": 0})
- else:
- if type_id:#如果获取的类型输入框内容不为空,则按类型查找
- book_result = Book.objects.filter(book_type=type_id)
- if book_result:#如果找到的结果集非空,则输出
- return render(request, 'student/search_book.html', context={"books": book_result,"types":types,"name":global_sname})
- else:#若搜索的结果集为0,那么输出未找到类型的书!
- book_result = Book.objects.all()
- return render(request, 'student/search_book.html',context={"books": book_result, "types": types, "name": global_sname,"status":1})
- else:#都为空,则显示空列表
- return render(request, 'student/search_book.html')
- def borrow_book(request):
- book_ISBN = request.GET.get("book_ISBN")
- result = Book.objects.filter(ISBN=book_ISBN).first()
- books = Book.objects.all()
- types = Type.objects.all()
- if result.book_rest:#如果可借数不为0,则进行book_rest--
- rest = result.book_rest-1
- Book.objects.filter(ISBN=book_ISBN).update(book_rest=rest)
- now_time = datetime.datetime.now().strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M")#获取当前借书的系统时间
- student = Student.objects.filter(student_tel=account).first()
- Borrow.objects.create(student_id=student.student_id,student_name=student.student_name,student_tel=account,book_id=book_ISBN,book_name=result.book_name,borrow_time=now_time,rest_time=60)
- return render(request, 'student/search_book.html',context={"books": books, "types": types, "name": global_sname}) # 向前端传递所有查找到的书籍信息的集合
- else:#可借数为0,则不予借出
- return render(request, 'student/search_book.html',context={"books": books, "types": types, "name": global_sname}) # 向前端传递所有查找到的书籍信息的集合
- def borrow_record(request):#借书记录
- if request.method == "GET":
- records = Borrow.objects.filter(student_tel=account)#把当前用户的借阅记录搜索出来
- #计算剩余天数
- for record in records:
- borrow_t = record.borrow_time #获取借阅时间如:2019-11-1 11:40
- print(borrow_t)
- str1 = borrow_t.split(' ') # 先用空格分割该时间字符串,并保存到列表,str1[0]='2019-11-1' ,str1[1]='11:40'
- str2 = str1[0].split('-') #再讲时间按'-'分割开,得到str2,str2[0]='2019',str2[1]='11',str2[2]='1'
- borrow_time = datetime.date(int(str2[0]), int(str2[1]), int(str2[2]))#利用date函数得到相对应的借阅时间
- now_time = datetime.date(datetime.datetime.now().year, datetime.datetime.now().month,
- datetime.datetime.now().day) # 获取当前日期
- rest_day = 60 - (now_time - borrow_time).days #最多借阅60天
- print(rest_day)
- if rest_day>=0:
- Borrow.objects.filter(borrow_time = record.borrow_time).update(rest_time = rest_day)
- else:
- Borrow.objects.filter(borrow_time = record.borrow_time).update(rest_time = 0)
- return render(request,'student/borrow_record.html',context={"records":records,"name":global_sname})
- def return_book(request):#还书操作,在borrow_record.html页面中点击还书按钮后跳转到此处
- borrow_id = request.GET.get("borrow_id")
- result1 = Borrow.objects.filter(id = borrow_id).first()
- result2 = Book.objects.filter(ISBN = result1.book_id).first()
- rest = result2.book_rest+1 #还书后库存+1
- Book.objects.filter(ISBN = result2.ISBN).update(book_rest = rest)
- Borrow.objects.filter(id=borrow_id).delete() # 当点击还书按钮后,删除该用户的借阅记录
- records = Borrow.objects.filter(student_tel=account) # 把当前用户的借阅记录搜索出来
- return render(request, 'student/borrow_record.html', context={"records": records, "name": global_sname})
书籍采购(既书籍入库)以及书籍信息修改等
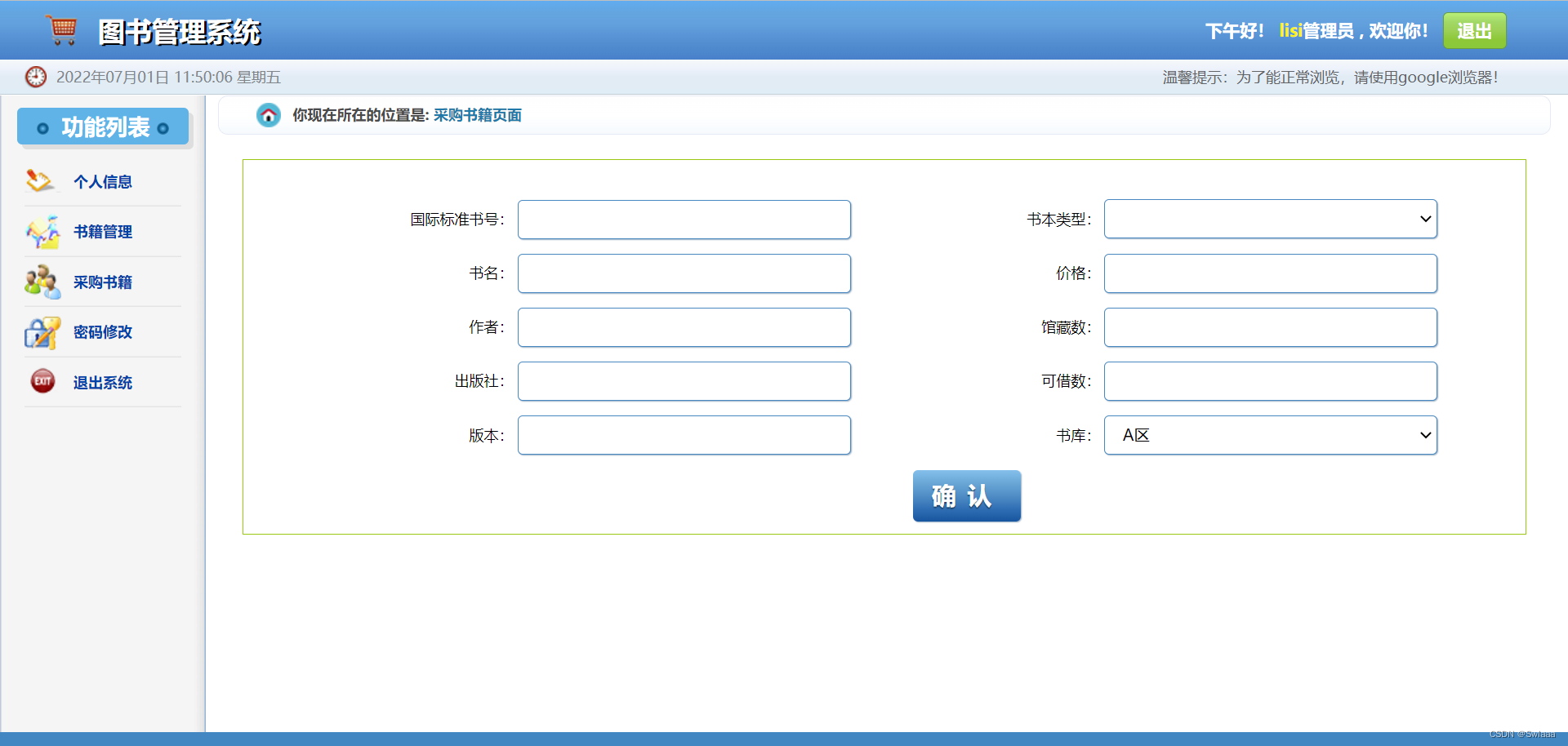

views代码段
- def manage_book(request):#管理书籍
- if request.method == "GET": # 此部分是当用户每次点击侧边导航栏的“管理书籍”选项时,都要显示出所有书籍资料
- books = Book.objects.all()
- types = Type.objects.all()
- return render(request, 'manager/manage_book.html',context={"books": books, "types": types, "name": global_mname}) # 向前端传递所有查找到的书籍信息的集合
- else: # 在manager/manage_bok.html页面中通过post方式的“搜索”按钮跳转到此处,即完成搜索操作
- book_name = request.POST.get("book_name")
- type_id = request.POST.get("type_id")
- types = Type.objects.all()
- if book_name: # 如果书名非空,则按书名查找
- book_result = Book.objects.filter(book_name=book_name)
- if book_result: # 如果找到的结果集非空,则输出
- return render(request, 'manager/manage_book.html',context={"books": book_result, "types": types, "name": global_mname})
- else: # 若搜索的结果集为0,那么输出未找到该本书!
- book_result = Book.objects.all()
- return render(request, 'manager/manage_book.html',
- context={"books": book_result, "types": types, "name": global_mname, "status": 0})
- else:
- if type_id: # 如果获取的类型输入框内容不为空,则按类型查找
- book_result = Book.objects.filter(book_type=type_id)
- if book_result: # 如果找到的结果集非空,则输出
- return render(request, 'manager/manage_book.html',
- context={"books": book_result, "types": types, "name": global_mname})
- else: # 若搜索的结果集为0,那么输出未找到类型的书!
- book_result = Book.objects.all()
- return render(request, 'manager/manage_book.html',
- context={"books": book_result, "types": types, "name": global_mname, "status": 1})
- else: # 都为空,则显示空列表
- return render(request, 'manager/manage_book.html')
- def add_book(request):#增加书籍的馆藏数量
- if request.method == "GET":
- ISBN = request.GET.get("book_ISBN1")
- result = Book.objects.filter(ISBN=ISBN).first()
- number = result.book_number+1 #让该书本的馆藏数量和可借数++
- rest = result.book_rest+1
- Book.objects.filter(ISBN=ISBN).update(book_number = number,book_rest = rest)
- books = Book.objects.all()
- types = Type.objects.all()
- return render(request, 'manager/manage_book.html',context={"books": books, "types": types, "name": global_mname}) # 向前端传递所有查找到的书籍信息的集合
- def reduce_book(request):#减少书籍的馆藏数量
- if request.method == "GET":
- ISBN = request.GET.get("book_ISBN2")
- result = Book.objects.filter(ISBN=ISBN).first()
- number = result.book_number - 1 #让该书本的馆藏数量和可借数--
- rest = result.book_rest -1
- Book.objects.filter(ISBN=ISBN).update(book_number = number,book_rest = rest)
- books = Book.objects.all()
- types = Type.objects.all()
- return render(request, 'manager/manage_book.html',context={"books": books, "types": types, "name": global_mname}) # 向前端传递所有查找到的书籍信息的集合
- def delete_book(request):#清空该书籍
- if request.method == "GET":
- ISBN = request.GET.get("ISBN")
- print(ISBN)
- Book.objects.filter(ISBN = ISBN).delete()#在book表里删除该条记录
- books = Book.objects.all()
- types = Type.objects.all()
- return render(request, 'manager/manage_book.html',context={"books": books, "types": types, "name": global_mname}) # 向前端传递所有查找到的书籍信息的集合
- def alter_book(request):#修改书本详情
- types = Type.objects.all()
- if request.method == "GET":#此部分是当用户在manage_book.html页面中点击修改书籍是执行,目的是显示当前书本的信息
- ISBN = request.GET.get("book_ISBN3")
- result = Book.objects.filter(ISBN=ISBN).first()
- context={
- "ISBN": result.ISBN,
- "book_name": result.book_name,
- "book_author": result.book_author,
- "book_publisher": result.book_publisher,
- "book_version": result.book_version,
- "book_price": result.book_price,
- "book_number": result.book_number,
- "book_rest": result.book_rest,
- "book_place": result.book_place,
- "type_name": result.book_type.type_name,
- "name": global_sname,
- "types": types
- }
- return render(request, 'manager/alter_book.html',context) # 向前端传递该书籍的所有信息
- else:#此部分是当用户在alter_book.html页面中点击保存按钮后重新更新用户修改后的信息
- ISBN = request.POST.get("ISBN")
- book_name = request.POST.get("book_name")
- book_author = request.POST.get("book_author")
- book_publisher = request.POST.get("book_publisher")
- book_version = request.POST.get("book_version")
- book_price = request.POST.get("book_price")
- book_number = request.POST.get("book_number")
- book_rest = request.POST.get("book_rest")
- book_place = request.POST.get("book_place")
- type_name = request.POST.get("type_name")
- if book_number.isdigit() and book_rest.isdigit(): # 判断输入的馆藏数和可借数是否为数字
- type = Type.objects.filter(type_name=type_name).first() # 书籍类型是外键
- Book.objects.filter(ISBN=ISBN).update( book_name=book_name, book_author=book_author, book_publisher=book_publisher,
- book_version = book_version,
- book_price = book_price, book_number=book_number, book_rest=book_rest,
- book_place = book_place, book_type=type) # 在book表里更新刚才修改的书本信息
- context = { #把修改后的内容显示出来
- "ISBN": ISBN,
- "book_name": book_name,
- "book_author": book_author,
- "book_publisher": book_publisher,
- "book_version": book_version,
- "book_price": book_price,
- "book_number": book_number,
- "book_rest": book_rest,
- "book_place": book_place,
- "type_name": type_name,
- "name": global_sname,
- "types": types
- }
- return render(request, 'manager/alter_book.html',context) # 重新向前端传递该书籍的所有信息
- else:
- result = Book.objects.filter(ISBN=ISBN).first()
- context = {
- "ISBN": result.ISBN,
- "book_name": result.book_name,
- "book_author": result.book_author,
- "book_publisher": result.book_publisher,
- "book_version": result.book_version,
- "book_price": result.book_price,
- "book_number": result.book_number,
- "book_rest": result.book_rest,
- "book_place": result.book_place,
- "type_name": result.book_type.type_name,
- "name": global_sname,
- "types": types
- }
- return render(request, 'manager/alter_book.html', context) # 向前端传递该书籍的所有信息
- def add_new_book(request):#添加新书籍
- types = Type.objects.all()
- if request.method == "GET":#此部分是当每次点击侧边导航栏的“采购书籍”选项时,显示该界面
- return render(request, 'manager/add_new_book.html', context={ "name": global_mname,"types":types})
- else:#此部分是在add_new_book.html页面中点击确认按钮后完成的添加书籍操作
- ISBN = request.POST.get("ISBN")#获取用户在前端输入框中的数据
- book_name = request.POST.get("book_name")
- book_author = request.POST.get("book_author")
- book_publisher = request.POST.get("book_publisher")
- book_version = request.POST.get("book_version")
- book_price = request.POST.get("book_price")
- book_number = request.POST.get("book_number")
- book_rest = request.POST.get("book_rest")
- book_place = request.POST.get("book_place")
- type_name = request.POST.get("type_name")
- if book_number.isdigit() and book_rest.isdigit():#判断输入的馆藏数和可借数是否为数字
- type = Type.objects.filter(type_name = type_name).first()#书籍类型是外键
- Book.objects.create(ISBN=ISBN,book_name=book_name,book_author=book_author,book_publisher=book_publisher,book_version=book_version,
- book_price=book_price,book_number=book_number,book_rest=book_rest,book_place=book_place,book_type=type)#在book表里添加新记录
- return render(request, 'manager/add_new_book.html', context={ "name": global_mname,"types":types})
- else:
- return render(request, 'manager/add_new_book.html', context={ "name": global_mname,"types":types})
3、数据管理模块
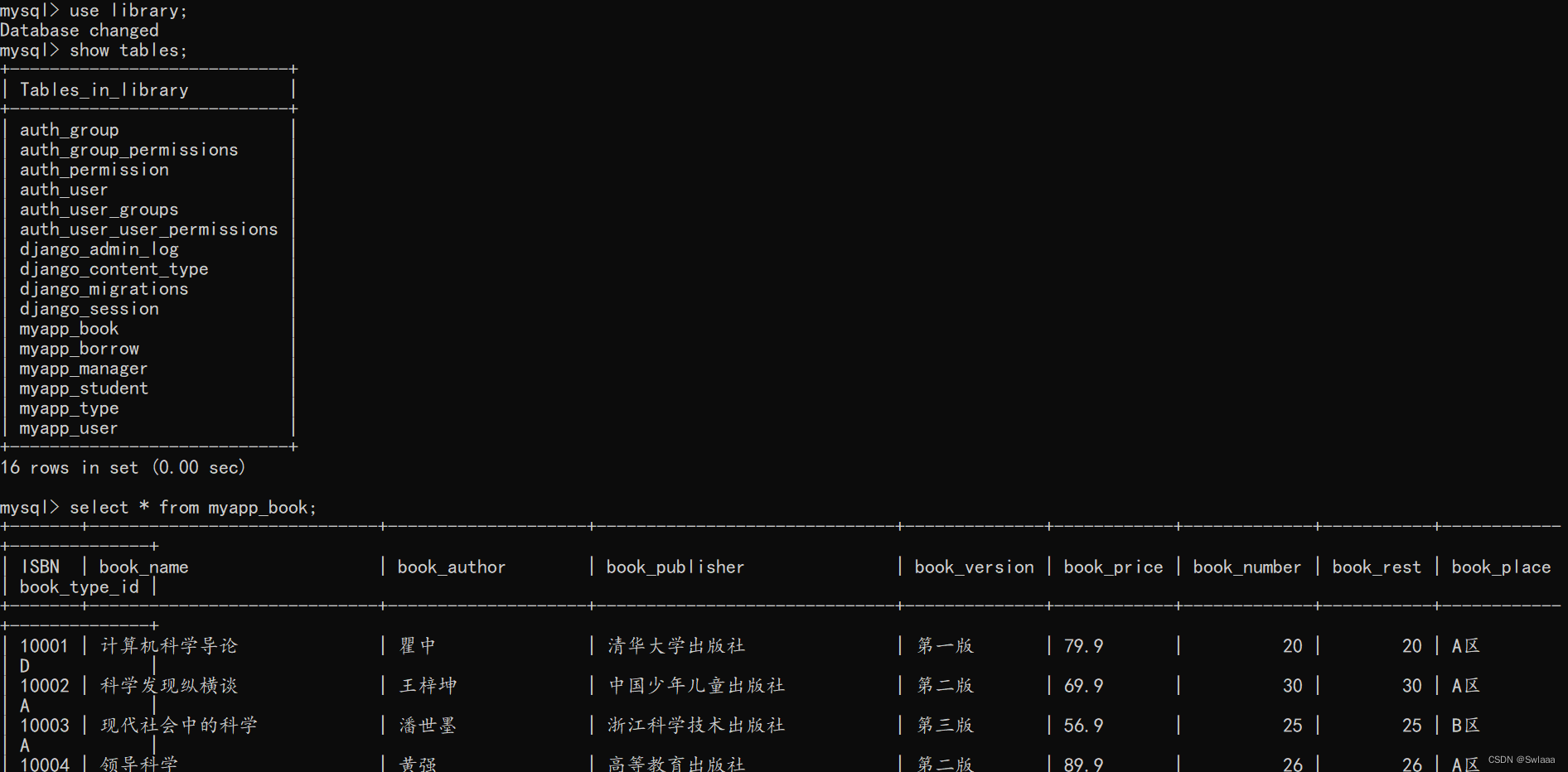
数据管理模块主要是设计数据库的存储和操作,django的ROM机制可以让用户在models上面编写要创建的数据表类型,通过执行迁移,直接在数据库创建数据库表
models.py代码段
- from django.db import models
- class User(models.Model): #用户表
- account=models.CharField(max_length = 20,primary_key=True)#账号
- user_password=models.CharField(max_length = 20)#用户密码
- user_identity=models.CharField(max_length = 20)#用户身份
- class Student(models.Model): #学生信息表
- student_id=models.CharField(max_length = 20,primary_key=True)#学号 主键
- student_name=models.CharField(max_length=20)#姓名
- student_tel=models.CharField(max_length = 20)#电话
- student_major=models.CharField(max_length = 20)#院系
- student_email=models.CharField(max_length = 50)#邮箱
- class Manager(models.Model): #图书管理员信息表
- manager_id=models.CharField(max_length = 20,primary_key=True)#工号 主键
- manager_name=models.CharField(max_length=20)#姓名
- manager_tel=models.CharField(max_length = 20)#电话
- manager_email=models.CharField(max_length = 50)#邮箱
- manager_stack=models.CharField(max_length = 20)#管理书库
- class Type(models.Model):#书籍类型表
- type_id= models.CharField(max_length=20,primary_key=True) # 类型编号,主键
- type_name = models.CharField(max_length=20) # 类型名称
- class Book(models.Model):#书本信息表
- ISBN= models.CharField(max_length = 20,primary_key=True) # 国际标准书号 主键
- book_name = models.CharField(max_length=20) # 书名
- book_author = models.CharField(max_length=20) # 作者
- book_publisher = models.CharField(max_length=20) # 出版社
- book_version = models.CharField(max_length=20) # 版本
- book_price = models.CharField(max_length=20) # 价格
- book_number = models.IntegerField() # 总库存数(馆藏数)
- book_rest = models.IntegerField() # 可借数
- book_place = models.CharField(max_length=20) # 所属书库
- book_type = models.ForeignKey(Type, on_delete=models.CASCADE)#书籍类型
- class Borrow(models.Model):#借阅表
- student_id= models.CharField(max_length=20) # 借书人学号
- student_name = models.CharField(max_length=20) # 借书人姓名
- student_tel = models.CharField(max_length=20) # 借书人联系方式
- book_id = models.CharField(max_length=20) # 书籍编号
- book_name = models.CharField(max_length=20) # 书名
- borrow_time = models.CharField(max_length=20) # 借书时间
- rest_time = models.IntegerField() # 剩余天数
settings.py关于数据库的相关设定
- DATABASES = {
- 'default': {
- 'ENGINE': 'django.db.backends.mysql',
- 'NAME': 'Library', #数据库名字
- 'USER': 'xxxx', #用户名
- 'PASSWORD': 'xxxx',#密码
- 'HOST': 'localhost', #本地主机
- 'PORT': '3306' #端口号
- }
- }
4、前端模块
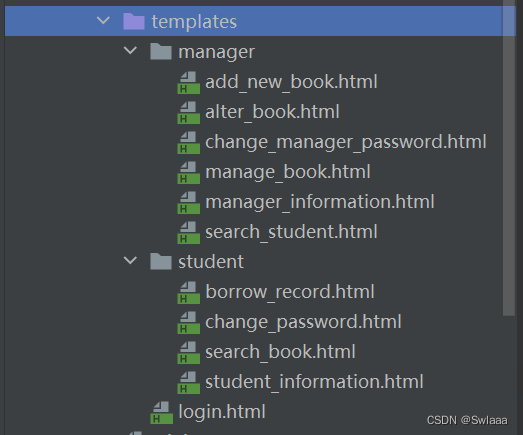
前端模块是向用户展示的用户界面,通常保存在templates文件夹下,后端通过与前端的数据进行交互,通过路由返回具体的页面实现渲染。
templates文件夹目录
urls.py路由路径
- from django.contrib import admin
- from django.urls import path,include
- from MyApp import views as App_views
- urlpatterns = [
- path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
- path('MyApp/',include('MyApp.urls')),
- path('login/',App_views.login),
- path('student_register/',App_views.student_register),
- path('manager_register/',App_views.manager_register),
- path('login_judge/', App_views.login_judge),
- path('student_information/',App_views.student_information),
- path('search_book/',App_views.search_book),
- path('borrow_record/',App_views.borrow_record),
- path('change_password/',App_views.change_password),
- path('borrow_book/',App_views.borrow_book),
- path('return_book/',App_views.return_book),
- path('manager_information/', App_views.manager_information),
- path('manage_book/', App_views.manage_book),
- path('delete_book/', App_views.delete_book),
- path('add_book/', App_views.add_book),
- path('reduce_book/', App_views.reduce_book),
- path('change_manager_password/', App_views.change_manager_password),
- path('add_new_book/', App_views.add_new_book),
- path('alter_book/', App_views.alter_book),
- path('',App_views.login),
- ]
通过django创建的数据库表
视频演示链接:
源代码获取可私信或+QQ:1834661953
-
相关阅读:
面向对象设计模式之工厂方法模式
mac M3芯片 goland 2022.1 断点调试失败(frames are not available)问题,亲测有效
Redis(10)----AOF持久化
ctfshow 反序列化篇(下)
docker容器和宿主机相互拷贝文件方法
C和C++关键字
51单片机的篮球计分器液晶LCD1602显示( proteus仿真+程序+原理图+PCB+设计报告+讲解视频)
文件外发怎么保证安全
【原创】常用元器件(数码管)选型之引脚和极性识别-cayden20221029
[清华大学]漏洞挖掘之状态敏感的模糊测试StateFuzz
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/Gefangen/article/details/125544793
