-
hadoop3.x入门到精通-阶段五(图解剖析MapReduce源码分析)
源码分析开始

maptask并行度决定机制
- 数据块是hdfs物理上切分成了一块一块
- 数据切片是逻辑上把整个文件进行逻辑拆分(决定maptask任务数量),注意在切分的时候他会保证数据的完整性,比如一个单词hello如果在切分的地方,他不会切分成hel和lo

上图对应的源码
package org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input;
FileInputFormat的getSplits(JobContext job)
- 得到最小的大小
- long minSize = Math.max(getFormatMinSplitSize(), getMinSplitSize(job));
- protected long getFormatMinSplitSize() {
- return 1;
- }
- public static long getMinSplitSize(JobContext job) {
- return job.getConfiguration().getLong(SPLIT_MINSIZE, 1L);
- }
- public static final String SPLIT_MINSIZE =
- "mapreduce.input.fileinputformat.split.minsize"; 默认没有配置过
- 得到最大的大小
- long maxSize = getMaxSplitSize(job);
- public static long getMaxSplitSize(JobContext context) {
- return context.getConfiguration().getLong(SPLIT_MAXSIZE,
- Long.MAX_VALUE);
- }
- public static final String SPLIT_MAXSIZE =
- "mapreduce.input.fileinputformat.split.maxsize"; 默认没有配置过
- public List<InputSplit> getSplits(JobContext job) throws IOException {
- StopWatch sw = new StopWatch().start();
- //得到最小的大小
- long minSize = Math.max(getFormatMinSplitSize(), getMinSplitSize(job));
- //得到最大的大小
- long maxSize = getMaxSplitSize(job);
- // generate splits
- List<InputSplit> splits = new ArrayList<InputSplit>();
- //得到文件的状态
- List<FileStatus> files = listStatus(job);
- boolean ignoreDirs = !getInputDirRecursive(job)
- && job.getConfiguration().getBoolean(INPUT_DIR_NONRECURSIVE_IGNORE_SUBDIRS, false);
- for (FileStatus file: files) {
- if (ignoreDirs && file.isDirectory()) {
- continue;
- }
- Path path = file.getPath();
- long length = file.getLen();
- if (length != 0) {
- BlockLocation[] blkLocations;
- if (file instanceof LocatedFileStatus) {
- blkLocations = ((LocatedFileStatus) file).getBlockLocations();
- } else {
- FileSystem fs = path.getFileSystem(job.getConfiguration());
- blkLocations = fs.getFileBlockLocations(file, 0, length);
- }
- //判断文件是否可以切分,比如snappy就是不能切分的那么就不能更具切分来提高maptask数量
- if (isSplitable(job, path)) {
- long blockSize = file.getBlockSize();
- //blockSize集群的默认值是128m本地是32m
- long splitSize = computeSplitSize(blockSize, minSize, maxSize);
- long bytesRemaining = length;
- //这里大于1.1的时候才切分
- while (((double) bytesRemaining)/splitSize > SPLIT_SLOP) {
- int blkIndex = getBlockIndex(blkLocations, length-bytesRemaining);
- splits.add(makeSplit(path, length-bytesRemaining, splitSize,
- blkLocations[blkIndex].getHosts(),
- blkLocations[blkIndex].getCachedHosts()));
- bytesRemaining -= splitSize;
- }
- if (bytesRemaining != 0) {
- int blkIndex = getBlockIndex(blkLocations, length-bytesRemaining);
- splits.add(makeSplit(path, length-bytesRemaining, bytesRemaining,
- blkLocations[blkIndex].getHosts(),
- blkLocations[blkIndex].getCachedHosts()));
- }
- } else { // not splitable
- if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) {
- // Log only if the file is big enough to be splitted
- if (length > Math.min(file.getBlockSize(), minSize)) {
- LOG.debug("File is not splittable so no parallelization "
- + "is possible: " + file.getPath());
- }
- }
- splits.add(makeSplit(path, 0, length, blkLocations[0].getHosts(),
- blkLocations[0].getCachedHosts()));
- }
- } else {
- //Create empty hosts array for zero length files
- splits.add(makeSplit(path, 0, length, new String[0]));
- }
- }
- // Save the number of input files for metrics/loadgen
- job.getConfiguration().setLong(NUM_INPUT_FILES, files.size());
- sw.stop();
- if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) {
- LOG.debug("Total # of splits generated by getSplits: " + splits.size()
- + ", TimeTaken: " + sw.now(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS));
- }
- return splits;
- }
上面计算切片大小的公式
- protected long computeSplitSize(long blockSize, long minSize,
- long maxSize) {
- return Math.max(minSize, Math.min(maxSize, blockSize));
- }
也就是他总是取中间值,如果想改变大小,要么最大值比blockSize小,要么minsize比blockSize大
总结:
- 如果maxSize比blockSize小最后的切片大小就是maxSize
- 如果minSize比blockSize大最后的切片大小就是minSize
- 如果不改变两个值那么默认就是blockSize
- 单独的文件单独切分
- 还有切片的时候要切分的文件要大于切片的比例的1.1才切分
InputFormat数据输入
- public abstract class InputFormat<K, V> {
- //获得分片数据
- public abstract
- List<InputSplit> getSplits(JobContext context
- ) throws IOException, InterruptedException;
- //创建RecordReader负责数据的读取
- public abstract
- RecordReader<K,V> createRecordReader(InputSplit split,
- TaskAttemptContext context
- ) throws IOException,
- InterruptedException;
- }
类的继承关系

FileInputFormat的继承图

TextInputFormat对FileInputFormat读取数据进行了实现createRecordReader()

CombineFileInputFormat 重写了getSplits方法,它的作用是解决小文件问题的
- public List<InputSplit> getSplits(JobContext job)
- throws IOException {
- long minSizeNode = 0;
- long minSizeRack = 0;
- long maxSize = 0;
- Configuration conf = job.getConfiguration();
- // the values specified by setxxxSplitSize() takes precedence over the
- // values that might have been specified in the config
- if (minSplitSizeNode != 0) {
- minSizeNode = minSplitSizeNode;
- } else {
- minSizeNode = conf.getLong(SPLIT_MINSIZE_PERNODE, 0);
- }
- if (minSplitSizeRack != 0) {
- minSizeRack = minSplitSizeRack;
- } else {
- minSizeRack = conf.getLong(SPLIT_MINSIZE_PERRACK, 0);
- }
- if (maxSplitSize != 0) {
- maxSize = maxSplitSize;
- } else {
- maxSize = conf.getLong("mapreduce.input.fileinputformat.split.maxsize", 0);
- // If maxSize is not configured, a single split will be generated per
- // node.
- }
- if (minSizeNode != 0 && maxSize != 0 && minSizeNode > maxSize) {
- throw new IOException("Minimum split size pernode " + minSizeNode +
- " cannot be larger than maximum split size " +
- maxSize);
- }
- if (minSizeRack != 0 && maxSize != 0 && minSizeRack > maxSize) {
- throw new IOException("Minimum split size per rack " + minSizeRack +
- " cannot be larger than maximum split size " +
- maxSize);
- }
- if (minSizeRack != 0 && minSizeNode > minSizeRack) {
- throw new IOException("Minimum split size per node " + minSizeNode +
- " cannot be larger than minimum split " +
- "size per rack " + minSizeRack);
- }
- // all the files in input set
- List<FileStatus> stats = listStatus(job);
- List<InputSplit> splits = new ArrayList<InputSplit>();
- if (stats.size() == 0) {
- return splits;
- }
- // In one single iteration, process all the paths in a single pool.
- // Processing one pool at a time ensures that a split contains paths
- // from a single pool only.
- for (MultiPathFilter onepool : pools) {
- ArrayList<FileStatus> myPaths = new ArrayList<FileStatus>();
- // pick one input path. If it matches all the filters in a pool,
- // add it to the output set
- for (Iterator<FileStatus> iter = stats.iterator(); iter.hasNext();) {
- FileStatus p = iter.next();
- if (onepool.accept(p.getPath())) {
- myPaths.add(p); // add it to my output set
- iter.remove();
- }
- }
- // create splits for all files in this pool.
- getMoreSplits(job, myPaths, maxSize, minSizeNode, minSizeRack, splits);
- }
- // create splits for all files that are not in any pool.
- getMoreSplits(job, stats, maxSize, minSizeNode, minSizeRack, splits);
- // free up rackToNodes map
- rackToNodes.clear();
- return splits;
- }
它的切片机制

设置它作为指定的inputformat
- job.setInputFormatClass(CombineTextInputFormat.class);
- CombineTextInputFormat.setMaxInputSplitSize(job,4194304);
总结:
- inputformat的作用就是读取文件还有更具文件制定切片规则
- TextInputFormat使用的是默认的分片规则,也就是FileInputFormat的.
- CombineTextInputFormat重写了分片规则,它有一个虚拟存储的概念,更具虚拟存储计算最终的分片大小
Shuffle机制
map方法之后reduce方法之前这个过程为shuffle
MapTask
在run方法里面
- if (isMapTask()) {
- // If there are no reducers then there won't be any sort. Hence the map
- // phase will govern the entire attempt's progress.
- //如果reducetask的个数为零那么就不进行排序
- if (conf.getNumReduceTasks() == 0) {
- mapPhase = getProgress().addPhase("map", 1.0f);
- } else {
- // If there are reducers then the entire attempt's progress will be
- // split between the map phase (67%) and the sort phase (33%).
- //有reducetask的时候先map后排序
- mapPhase = getProgress().addPhase("map", 0.667f);
- sortPhase = getProgress().addPhase("sort", 0.333f);
- }
- }
ReduceTask
在run方法里面,有复制,排序阶段
- if (isMapOrReduce()) {
- copyPhase = getProgress().addPhase("copy");
- sortPhase = getProgress().addPhase("sort");
- reducePhase = getProgress().addPhase("reduce");
- }
总结:也就是如果没有reducetask那么就只是执行map方法,如果有reduce那么会执行 Shuffle
map-sort-copy-sort-reduce
图解Shuffle机制
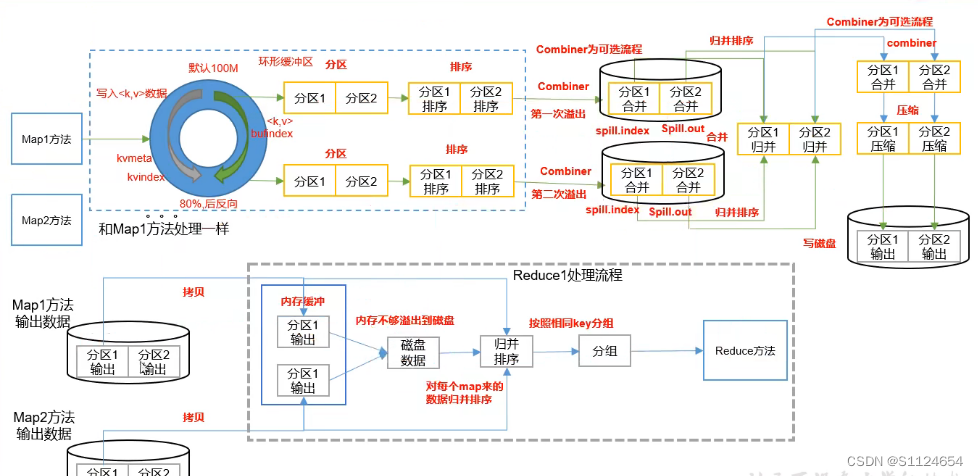
- 先map处理数据得到<k,v>数据,然后进入环形缓冲区,环形缓冲区处理的过程中会使用默认的分区(如果没有自定义的话),更具hash取模的方式得到分区编号当到80%的时候发生文件溢出
- 溢出以后对于分区数据进行key的排序(默认是字符排序规则),排序的时候只会排序索引,不移动数据
- 如果添加了Combiner操作的话,先执行一直预合并
- 为了减少reducetask的压力,多个溢出文件会在maptask合并,也就是多个溢出文件,合并成一个大文件,里面包含了分区分界,合并的过程也会排序,最终合并的文件写入磁盘(因为当时的技术原因,数据量如果太大不写入磁盘就会出现内存溢出)
- 然后到了reduceTask阶段,先copy文件,如果文件太大先溢出到磁盘,然后更具磁盘的分区数据进行再次排序操作,(注意map过来的数据先分区内排序,比如分区1过来的数据,然后先一块排序,reduce还会有一个分组的过程,按照相同的key进行分组)
重点:也就是说数据到达reduce以后分组的过程是可以自定义的,后面讲解
Partitioner

分区器的分区数是和reduceTask的多少有关
默认的分区器为,更具hash取模numReduceTasks
- public class HashPartitioner<K2, V2> implements Partitioner<K2, V2> {
- public void configure(JobConf job) {}
- /** Use {@link Object#hashCode()} to partition. */
- public int getPartition(K2 key, V2 value,
- int numReduceTasks) {
- //Integer.MAX_VALUE 二进制是01111...因为key.hashCode()可能为负数,与操作以后就是正数了
- return (key.hashCode() & Integer.MAX_VALUE) % numReduceTasks;
- }
- }
Partitioner原理MapTask时序图分析

分区器的代码剖析
- NewOutputCollector(org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.JobContext jobContext,
- JobConf job,
- TaskUmbilicalProtocol umbilical,
- TaskReporter reporter
- ) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
- collector = createSortingCollector(job, reporter);
- // public int getNumReduceTasks() { return getInt(JobContext.NUM_REDUCES, 1); }
- //如果不配置那么默认的reduceTask是1个mapreduce.job.reduces
- partitions = jobContext.getNumReduceTasks();
- if (partitions > 1) {
- //如果大于一个reducetask,默认使用 HashPartitioner.class
- //如果自定义那么就使用mapreduce.job.partitioner.class,进入这个方法,
- //jobContext.getPartitionerClass()可以知道
- partitioner = (org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Partitioner<K,V>)
- ReflectionUtils.newInstance(jobContext.getPartitionerClass(), job);
- } else {
- //如果分区器就是默认一个那么就默认进入partitions - 1=0号分区
- partitioner = new org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Partitioner<K,V>() {
- @Override
- public int getPartition(K key, V value, int numPartitions) {
- return partitions - 1;
- }
- };
- }
- }
自定义分区器
- //<Student, IntWritable> 表示map方法得到的<K,V>
- public class MyPartition extends Partitioner<Student, IntWritable> {
- @Override
- public int getPartition(Student student, IntWritable intWritable, int numPartitions) {
- return student.getId()%2;
- }
- }
job.setPartitionerClass(MyPartition.class);设置的原理
- public void setPartitionerClass(Class<? extends Partitioner> cls
- ) throws IllegalStateException {
- ensureState(JobState.DEFINE);
- //PARTITIONER_CLASS_ATTR为mapreduce.job.partitioner.class
- conf.setClass(PARTITIONER_CLASS_ATTR, cls,
- Partitioner.class);
- }
分区器的注意事项:
- 分区号必须是从0开始,逐一累加.
- 如果reduce的个数设置为1,那么会走默认的partition-1的分区器(就是不会走自己的分区器)
- reducetask的个数不能少于自定义分区的数目,比如reduce设置的是2那么只有0,1两个reduceTask处理,如果自定义的partitions返回了一个3,那么就会报错,因为没有一个reduceTask为3的去处理
- 如果reduceTask>分区数,那么就会有空的文件出现
总结:
也就是如果分区器返回的分区序号是0那么就是又reduce为零的处理,如果返回的为2如果没有设置reduceTask的数目为3的话,就会报错,reduceTask为3对应的分区序号是0,1,2,所以分区器返回的序号要包含0,1,2才能执行。如果分区序号返回了比如0,1,2,3,那么3的分区序号就没有reduceTask处理就会报错,如果分区序号返回了比如0,1,那么reduceTask为2的就处理不到数据就会是空文件
WritableComparable排序(Shuffle机制排序关键)
hadoop默认的排序是字典排序,默认的排序方法是快速排序
字典排序 根据单词的前后顺序排序
排序涉及到的地方

排序分类
- 部分排序:就是reduce分区内有序
- 全排序:就是只有一个reduce一个文件的时候排序操作
- 负载排序:就是reduce分组的时候的key的比较操作
hadoop排序比较的类和接口
-
WritableComparable:排序的接口(支持序列化和比较功能)
-
WritableComparator:比较器
hadoop如何实现比较的?
使用的是比较器WritableComparator
自定义比较器的例子
Student
- public class Student implements WritableComparable<Student> {
- private int id;
- private String name;
- private int sore;
- public Integer getId() {
- return id;
- }
- public void setId(Integer id) {
- this.id = id;
- }
- public String getName() {
- return name;
- }
- public void setName(String name) {
- this.name = name;
- }
- public Integer getSore() {
- return sore;
- }
- public void setSore(Integer sore) {
- this.sore = sore;
- }
- public Student() {
- super();
- }
- @Override
- public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException {
- out.writeInt(id);
- out.writeUTF(name);
- out.writeInt(sore);
- }
- @Override
- public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException {
- this.id = in.readInt();
- this.name = in.readUTF();
- this.sore = in.readInt();
- }
- @Override
- public String toString() {
- return this.id+"\t"+this.name +"\t"+this.sore;
- }
- @Override
- public int compareTo(Student o) {
- // int thisValue = this.sore;
- // int thatValue = o.sore;
- // return (thisValue < thatValue ? 1 : (thisValue==thatValue ? 0 : -1));
- return 0;
- }
- }
MyWritableComparator
- public class MyWritableComparator extends WritableComparator {
- public MyWritableComparator() {
- super(Student.class, true);
- }
- @Override
- public int compare(WritableComparable a, WritableComparable b) {
- Student aStudent=(Student) a;
- Student bStudent = (Student) b;
- return -aStudent.getId().compareTo(bStudent.getId());
- }
- }
设置比较器
job.setSortComparatorClass(MyWritableComparator.class);自定义比较接口实现排序
- /**
- * 因为mapper是根据key来比较的所以这时候就实现WritableComparable
- */
- public class Student implements WritableComparable<Student> {
- private int id;
- private String name;
- private int sore;
- public Integer getId() {
- return id;
- }
- public void setId(Integer id) {
- this.id = id;
- }
- public String getName() {
- return name;
- }
- public void setName(String name) {
- this.name = name;
- }
- public Integer getSore() {
- return sore;
- }
- public void setSore(Integer sore) {
- this.sore = sore;
- }
- public Student() {
- super();
- }
- @Override
- public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException {
- out.writeInt(id);
- out.writeUTF(name);
- out.writeInt(sore);
- }
- @Override
- public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException {
- this.id = in.readInt();
- this.name = in.readUTF();
- this.sore = in.readInt();
- }
- @Override
- public String toString() {
- return this.id+"\t"+this.name +"\t"+this.sore;
- }
- @Override
- public int compareTo(Student o) {
- int thisValue = this.sore;
- int thatValue = o.sore;
- return (thisValue < thatValue ? 1 : (thisValue==thatValue ? 0 : -1));
- // return 0;
- }
- }
hadoop比较的原理
maptask里面的方法调用流程
run->runNewMapper->NewOutputCollector->createSortingCollector->collector.init(context);
->// k/v serialization comparator = job.getOutputKeyComparator();

- // k/v serialization
- comparator = job.getOutputKeyComparator();
上面就是比较器的源代码的关键
- public RawComparator getOutputKeyComparator() {
- //public static final String KEY_COMPARATOR = "mapreduce.job.output.key.comparator.class";
- //mapreduce.job.output.key.comparator.class默认没有设置
- Class<? extends RawComparator> theClass = getClass(
- JobContext.KEY_COMPARATOR, null, RawComparator.class);
- if (theClass != null)
- //设置了比较器就走这里
- return ReflectionUtils.newInstance(theClass, this);
- //默认走这里(WritableComparable)如果继承了比较接口就会得到对应的比较处理器
- return WritableComparator.get(getMapOutputKeyClass().asSubclass(WritableComparable.class), this);
- }
- //getMapOutputKeyClass()得到的是job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Student.class);
- public static WritableComparator get(
- Class<? extends WritableComparable> c, Configuration conf) {
- //从comparators的map里面根据c得到key的比较器对象,这里如果是默认的比如IntWritable他们有默认的比较器,那么就会返回,comparator 就不为空,反之就为空
- WritableComparator comparator = comparators.get(c);
- if (comparator == null) {
- // force the static initializers to run
- //如果没有,强制类加载
- forceInit(c);
- // look to see if it is defined now
- comparator = comparators.get(c);
- // if not, use the generic one
- //如果还是没有那么就创建一个比较器
- if (comparator == null) {
- comparator = new WritableComparator(c, conf, true);
- }
- }
- // Newly passed Configuration objects should be used.
- ReflectionUtils.setConf(comparator, conf);
- return comparator;
- }
- =========================
- 下面是创建WritableComparator
- protected WritableComparator(Class<? extends WritableComparable> keyClass,
- Configuration conf,
- boolean createInstances) {
- this.keyClass = keyClass;
- this.conf = (conf != null) ? conf : new Configuration();
- //createInstances这里注意要传入true才能比较
- if (createInstances) {
- key1 = newKey();
- key2 = newKey();
- buffer = new DataInputBuffer();
- } else {
- key1 = key2 = null;
- buffer = null;
- }
- }
- ============由于是比较器那么我们查看下他的比较方法=========
- public int compare(WritableComparable a, WritableComparable b) {
- return a.compareTo(b);
- }
- @Override
- public int compare(Object a, Object b) {
- return compare((WritableComparable)a, (WritableComparable)b);
- }
- 总结:
- 在mapreduce比较key的时候最终会执行的比较方法,
- public int compare(WritableComparable a, WritableComparable b) {
- return a.compareTo(b);
- }
- @Override
- public int compare(Object a, Object b) {
- return compare((WritableComparable)a, (WritableComparable)b);
- }
- 所以要么实现WritableComparable 接口,要么自定义一个比较器
- public class MyWritableComparator extends WritableComparator {
- public MyWritableComparator() {
- //true设置的是createInstances
- super(Student.class, true);
- }
- //这里重写WritableComparator 的比较方法,低层调用的时候会使用这个比较器方法比较
- @Override
- public int compare(WritableComparable a, WritableComparable b) {
- Student aStudent=(Student) a;
- Student bStudent = (Student) b;
- return -aStudent.getId().compareTo(bStudent.getId());
- }
- }
- 然后设置
- job.setSortComparatorClass(MyWritableComparator.class);
下面说明IntWritable的比较器实现(下面的代码也能说明上面代码的原因),hadoop自身的数据类型都实现了自己的比较器
- public static class Comparator extends WritableComparator {
- public Comparator() {
- super(IntWritable.class);
- }
- @Override
- public int compare(byte[] b1, int s1, int l1,
- byte[] b2, int s2, int l2) {
- int thisValue = readInt(b1, s1);
- int thatValue = readInt(b2, s2);
- return (thisValue<thatValue ? -1 : (thisValue==thatValue ? 0 : 1));
- }
- }
- static {
- //这里注册了自己的类对应的比较器 // register this comparator
- WritableComparator.define(IntWritable.class, new Comparator());
- }
总结:
mapreduce的排序有两种方式,一种是自定义WritableComparator,一种是实现WritableComparable,当时最终使用的还是WritableComparator,只不过实现WritableComparable接口的时候,系统默认的根据接口创建一个WritableComparator
- if (comparator == null) {
- comparator = new WritableComparator(c, conf, true);
- }
Combiner合并

- Combiner是MR程序中Mapper和Reducer之外的一种组件。
- Combiner组件的父关就是Reducer。.
- Combiner是在每一个MapTask所在的节点运行;Reducer是接收全局所有Mapper的输出结果.
- Combiner的意义就是对每一个MapTask的输出进行局部汇总,以减小网络传输量。
那么如果只是汇总的话Combiner可以直接使用Reducer的代码
job.setCombinerClass(StudentReduce.class);效果图

ReduceTask分组比较器(辅助比较器)
说明:
reduce分组,对于key相同的一组<key,value>数据分配到一组
job.setGroupingComparatorClass(MyWritableComparator.class);作用的地方

分组比较器源代码追踪

ReduceTask方法调用过程
run->RawComparator comparator = job.getOutputValueGroupingComparator();
- public RawComparator getOutputValueGroupingComparator() {
- //GROUP_COMPARATOR_CLASS = "mapreduce.job.output.group.comparator.class"
- //默认是为空
- Class<? extends RawComparator> theClass = getClass(
- JobContext.GROUP_COMPARATOR_CLASS, null, RawComparator.class);
- if (theClass == null) {
- //如果为空那么就是根据WritableComparable生成默认的比较器
- return getOutputKeyComparator();
- }
- return ReflectionUtils.newInstance(theClass, this);
- }
- ================这个方法和上面的排序方法分析一样可以参考上面的mapreduce比较器============
- public RawComparator getOutputKeyComparator() {
- Class<? extends RawComparator> theClass = getClass(
- JobContext.KEY_COMPARATOR, null, RawComparator.class);
- if (theClass != null)
- return ReflectionUtils.newInstance(theClass, this);
- return WritableComparator.get(getMapOutputKeyClass().asSubclass(WritableComparable.class), this);
- }
使用排序和辅助排序的例子

需求:
- 根据id,还有金额排序
- 然后id一样的分到一个组里面
这个时候我们就可以用id,还有金额实现 WritableComparable进行排序,然后自定义WritableComparator根据id进行分组(key一样的在一个分组)
job.setGroupingComparatorClass(MyWritableComparator.class);原理:
分组的原理,对于排好的数据,分组他是更具上面的一条数据和下面的一条数据进行比较,如果相同表示在一个组里面,如果不相同那么就是一个新的组开始,所以分组必须先排序,分组不是真正的分开,他是根据上一条数据和下一条数据的比较决定是否要新开始一个组
读取key的时候一直是一个的原理

OrderBean key 就是一个引用,hadoop在数据改变的时候会让这个引用指向堆里面的新数据
在没有东西要写的时候可以使用NullWritable.get()
OutputFormat
- public interface OutputFormat<K, V> {
- //负责数据的写出
- RecordWriter<K, V> getRecordWriter(FileSystem ignored, JobConf job,
- String name, Progressable progress)
- throws IOException;
- //检查路径是否存在
- void checkOutputSpecs(FileSystem ignored, JobConf job) throws IOException;
- }
默认子类抽象FileOutputFormat
- public void checkOutputSpecs(FileSystem ignored, JobConf job)
- throws FileAlreadyExistsException,
- InvalidJobConfException, IOException {
- // Ensure that the output directory is set and not already there
- Path outDir = getOutputPath(job);
- if (outDir == null && job.getNumReduceTasks() != 0) {
- throw new InvalidJobConfException("Output directory not set in JobConf.");
- }
- if (outDir != null) {
- FileSystem fs = outDir.getFileSystem(job);
- // normalize the output directory
- outDir = fs.makeQualified(outDir);
- setOutputPath(job, outDir);
- // get delegation token for the outDir's file system
- TokenCache.obtainTokensForNamenodes(job.getCredentials(),
- new Path[] {outDir}, job);
- // check its existence
- //如果文件存在报的错误
- if (fs.exists(outDir)) {
- throw new FileAlreadyExistsException("Output directory " + outDir +
- " already exists");
- }
- }
- }
默认的子类实现TextOutputFormat
计数器
介绍
计数器就是每调用一次,就会加上相应的数值,然后如下图打印到控制台
- context.getCounter("mycount","mymapcount").increment(1);
- 表示每执行一次计数器加一

Job提交流程源码图解
https://www.aliyundrive.com/s/HDBhGwM1zEV
job.waitForCompletion(true)源码开始



Job提交然后执行另外一个job线程流程图解
https://www.aliyundrive.com/s/gaDEn28iRgb

MapTask源码爆肝图解
https://www.aliyundrive.com/s/3FTs5ZLMAge

ReductTask源码爆肝图解
https://www.aliyundrive.com/s/WFKqi3yzx8C

源码图解百度网盘下载
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/184FKNuk3ryUDTyqg7auQVg
提取码:yyds -
相关阅读:
图解算法,原理逐步揭开「GitHub 热点速览」
【JQuery_Ajax_方法使用】Ajax的JQuery函数/方法
开发家政小程序的优点
【To .NET】C#数据模型,从Entity Framework Core到LINQ
c/c++面试题
第6章 数据库事务 & 第7章 DAO及相关实现类
网络安全(黑客技术)自学内容
leetcode刷题 (6.1) 字符串
MySQL安装TokuDB引擎
c++ primer中文版第五版作业第十一章
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/S1124654/article/details/125534276
