Ajax 实战(一)
简介
AJAX(Asynchronous Javascript And XML)翻译成中文就是“异步Javascript和XML”。即使用Javascript语言与服务器进行异步交互,传输的数据为XML(当然,传输的数据不只是XML,现在更多使用json数据)
- 同步交互:客户端发出一个请求后,需要等待服务器响应结束后,才能发出第二个请求;
- 异步交互:客户端发出一个请求后,无需等待服务器响应结束,就可以发出第二个请求;
优点
- 异步
- 局部刷新:不需要刷新整个页面,节省了资源的消耗,给用户的体验极佳
入门案例
'''
需求:
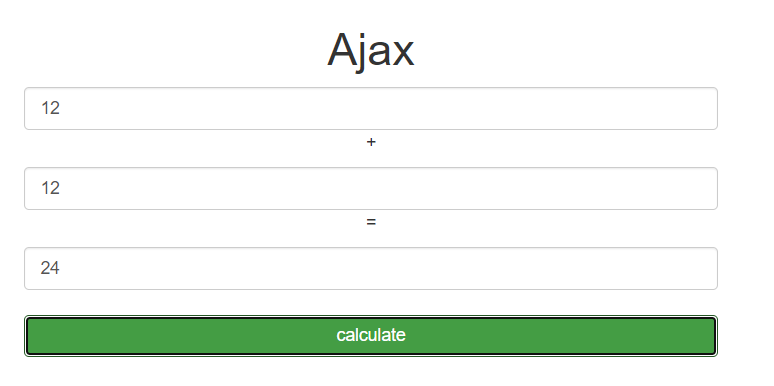
实现简单的计算器,加法举例
通过Ajax,实现前端输入两个数字,服务器做加法,返回到前端页面
'''
'''urls.py'''
path('', views.test_Ajax)
'''views.py'''
from django.shortcuts import render, HttpResponse
def test_Ajax(request):
if request.method == 'POST':
num1 = int(request.POST.get('num1')) # 获取前端提交的数据
num2 = int(request.POST.get('num2'))
print(num1, num2)
return HttpResponse(num1 + num2) # 返回给前端
return render(request, 'sum.html')
'''sum.html'''
'''html结构'''
<div class="container">
<div class="row">
<h1 class="text-center">Ajax</h1>
<div class="col-md-6 col-lg-offset-3 ">
<input type="text" id="d1" class="active form-control">
<p class="text-center">+</p>
<input type="text" id="d2" class="sucess form-control">
<p class="text-center">=</p>
<input type="text" id="d3" class="info form-control">
<br>
<button id='btn' class="btn btn-success btn-block">calculate</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
'''js实现'''
<script>
{#绑定点击事件#}
$('#btn').click(function () {
{#获取input元素内输入的值#}
var num1 = $('#d1').val()
var num2 = $('#d2').val()
$.ajax({
url: '', //ajax请求的地址
method: 'post', //请求方式
data: {num1: num1, num2: num2}, //携带参数
success: function (data) { //服务端成功返回会回调,执行匿名函数
console.log(data)
$('#d3').val(data)
}
})
})
</script>
注意:
使用Ajax的时候,在视图函数中使用request对象方法判断什么类型的请求,如果是Ajax,不管本质是post还是get等,写request.is_ajax()即可
基于Ajax进行登录验证
需求:
1.前端登录页面
2.后端数据库验证前端提交的信息
'''urls.py'''
path('login/', views.login),
'''views.py'''
from django.shortcuts import render,redirect,HttpResponse
from app01 import models
from django.http import JsonResponse
import json
def login(request):
if request.method == 'GET':
return render(request,'login.html')
# elif request.method=="POST":
elif request.is_ajax():
response = {'status':200,'msg':None}
username = request.POST.get('username')
password = request.POST.get('password')
# 数据库校验
res = models.User.objects.filter(username=username,password=password).first()
if res:
# 登录成功
# return redirect('http://www.baidu.com') # ajax使用重定向出错
response['msg']='登录成功'
else:
response['msg']='登录失败,用户名或密码错误'
response['status']=404
# return HttpResponse(json.dumps(response))
return JsonResponse(response,safe=False,json_dumps_params={'ensure_ascii':False})
'''models.py'''
from django.db import models
class User(models.Model):
name=models.CharField(max_length=32)
password=models.CharField(max_length=32)
<body>
{#<form action="" method="post">#}
<div class="container">
<h1 class="text-center">Ajax登录认证</h1>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-8 col-lg-offset-2">
<p>Username: <input type="text" class="form-control" name="username" id="user_id"></p>
<p>Password: <input type="password" class="form-control" name="password" id="pwd_id"></p>
<p><button type="submit" class="btn btn-block btn-primary">提交</button> <span class="error" style="color: tomato"></span></p>
</div>
</div>
</div>
{#</form>#}
</body>
<script>
$('.btn').click(function (){
$.ajax(
{
url:'/login/',
method:'post',
data:{username:$('#user_id').val(),password:$('#pwd_id').val()}, //返回给后端的数据
success:function (data){
console.log(data)
//data是对象类型
if(data.status == 200){
//登录成功,前端重定向
location.href='http://www.baidu.com'
}else{
//登录失败
$('.error').html(data.msg)
}
},
error:function (data){
console.log(data)
alert('请求错误')
}
}
)
})
</script>
注意
-
如果使用Ajax,form表单提交完数据会自己刷新,所有在使用button元素提交的时候会刷两次,可以讲form元素去掉;
-
如果使用Ajax,form元素也可以不去掉,那么就不能使用button元素,可以使用
input元素,type=‘button’ -
在Ajax中,如果使用json模块序列化数据,前端返回的是字符串不是对象,响应头中是
text/html格式,需要自己在html页面通过JSON.parse(data)反序列化,ajax接收到数据后需要自己转成对象 -
在Ajax中,如果使用
JsonResponse模块序列化数据,返回的就是一个对象,响应头中是application/json格式,不需要自己手动反序列化,ajax接收到数据后会自动转成对象 -
如果使用Ajax,能不能解析返回的数据,取决于响应的类型,如果是json类型,那么就自动解析,不是需要自己手动解析
-
如果使用了ajax,后端就不要返回rediret,render,HttpResponse,直接返回JsonResponse,因为返回json前端才能处理
-
总结:后端返回数据,统一都用JsonResponse
HTTP请求编码格式和报文
我们知道请求和响应都有数据格式,请求格式常用得比如:urlencoded、form-data、json····响应格式常用得有:text/html、json····
- application/x-www-form-urlencoded:窗体数据被编码为名称/值对。(默认)。空格转换为 “+” 加号,但不对特殊字符编码。
- multipart/form-data:窗体数据被编码为一条消息,页上的每个控件对应消息中的一个部分。
- text/plain:窗体数据以纯文本形式进行编码,其中不含任何控件或格式字符。
- JSON:以纯文本形式进行编码,其格式为JSON
现有HTML代码如下:用属性enctype的值来区分Content-Type
<form action="http://localhost:8080" method="post" enctype="application/x-www-form-urlencoded">
<input type="text" name="userName" value="zhan gsan"/>
<input type="text" name="password" value="password"/>
<input type="file" name="resultFile" />
<input type="submit" value="submit"/>
</form>
当Content-Type为不同值时,报文结果分别为下:
Content-Type=application/x-www-form-urlencoded#
浏览器用x-www-form-urlencoded的编码方式把form数据转换成一个字串(name1=value1&name2=value2…),然后把这个字串append到url后面,用?分割,加载这个新的url。 当action为post时候,浏览器把form数据封装到http body中,然后发送到server。
POST / HTTP/1.1
Host: localhost:8080
Connection: keep-alive
Content-Length: 62
Cache-Control: max-age=0
Upgrade-Insecure-Requests: 1
Origin: null
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/63.0.3239.132 Safari/537.36
Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/webp,image/apng,*/*;q=0.8
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate, br
Accept-Language: zh-CN,zh;q=0.9
userName=zhan+gsan&password=password&resultFile=dddddddddd.vlx
Content-Type=multipart/form-data#
浏览器会把整个表单以控件为单位分割,并为每个部分加上Content-Disposition(form-data或者file),name(控件name)等信息,并加上分割符(boundary)。
此报文分割符为:boundary=—-WebKitFormBoundarys70zFPQBqcgHeMy9
POST / HTTP/1.1
Host: localhost:8080
Connection: keep-alive
Content-Length: 659
Cache-Control: max-age=0
Upgrade-Insecure-Requests: 1
Origin: null
Content-Type: multipart/form-data; boundary=----WebKitFormBoundarys70zFPQBqcgHeMy9
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/63.0.3239.132 Safari/537.36
Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/webp,image/apng,*/*;q=0.8
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate, br
Accept-Language: zh-CN,zh;q=0.9
------WebKitFormBoundarys70zFPQBqcgHeMy9
Content-Disposition: form-data; name="userName"
zhan gsan
------WebKitFormBoundarys70zFPQBqcgHeMy9
Content-Disposition: form-data; name="password"
password
------WebKitFormBoundarys70zFPQBqcgHeMy9
Content-Disposition: form-data; name="resultFile"; filename="dddddddddd.vlx"
Content-Type: application/octet-stream
{"nodes":[{"name":"11111","image":"theme/gast/ren.png","entityId":"1000001"},{"name":"5555","image":"theme/gast/ren.png","entityId":"1000001"}],"edges":[{"source":"11111","target":"5555","relation":"ssss","count":"1","currentExtDepth":"1"}]}
------WebKitFormBoundarys70zFPQBqcgHeMy9--
Content-Type=text/plain#
POST / HTTP/1.1
Host: localhost:8080
Connection: keep-alive
Content-Length: 66
Cache-Control: max-age=0
Upgrade-Insecure-Requests: 1
Origin: null
Content-Type: text/plain
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/63.0.3239.132 Safari/537.36
Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/webp,image/apng,*/*;q=0.8
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate, br
Accept-Language: zh-CN,zh;q=0.9
userName=zhan gsan
password=password
resultFile=dddddddddd.vlx
参考:请求头编码格式
总结#
1 http --post--请求,有编码格式,主流有三种
-urlencoded :默认的----》从request.POST取提交的数据
-form-data :上传文件的----》从request.POST取提交的数据,request.FILES中取文件
-json :ajax发送json格式数据-----》request.POST取不出数据了,需要request.body
2 使用ajax和form表单,默认都是urlencoded格式
3 如果上传文件:form表单指定格式,ajax要使用Formdata对象
4 如果编码方式是urlencoded格式,放到body体中数据格式如下
username=Hammer&password=123 # post请求,Ajax预处理后得数据格式,urlencoded数据格式
5 如果是formdata编码格式,body体中是:两部分,数据和文件
6 如果是json格式,body体中的格式是:就是json格式字符串
-注意:注意:注意:如果这种格式,request.POST取不到值了
上传文件
前面我们介绍到上传文件可以通过form表单来上传文件,通过input元素修改type=file就上传单个文件,如果加multiple参数就可以上传多个文件等····
form表单上传文件
<h1>form表单上传文件</h1>
<form action="" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
<p>用户名:<input type="text" name="name"></p>
<p>文件:<input type="file" name="myfile"></p>
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
def file_upload(request):
if request.method=='GET':
return render(request,'file_upload.html')
else:
myfile=request.FILES.get('myfile')
with open(myfile.name,'wb') as f:
for line in myfile:
f.write(line)
return HttpResponse('ok')
现在我们可以使用ajax上传文件,那么格式和编码有什么要求?实例如下:
<h1>ajax上传文件</h1>
<p>用户名:<input type="text" id="id_name"></p>
<p>文件:<input type="file" id="id_myfile"></p>
<button id="id_btn">提交</button>
<script>
$('#id_btn').click(function () {
//如果要上传文件,需要借助于一个js的FormData对象
var formdata = new FormData() //实例化得到一个FormData对象
formdata.append('name', $('#id_name').val()) //追加了一个name对应填入的值
//追加文件
var file = $('#id_myfile')[0].files[0]
formdata.append('myfile', file)
$.ajax({
url: 'file_upload',
method: 'post',
//上传文件,一定要注意如下两行
processData: false, //不预处理数据,
contentType: false, //不指定编码格式,使用formdata对象的默认编码就是formdata格式
data: formdata,
success: function (data) {
console.log(data)
}
})
})
</script>
def file_upload(request):
if request.method=='GET':
return render(request,'file_upload.html')
else:
name=request.POST.get('name')
myfile=request.FILES.get('myfile')
print(type(myfile)) # 查看类型
from django.core.files.uploadedfile import InMemoryUploadedFile
with open(myfile.name,'wb') as f:
for line in myfile:
f.write(line)
return HttpResponse('上传成功')
先拿到input元素:
$(‘#id_myfile’)[0]再拿到所有文件:
$(‘#id_myfile’)[0].files再通过索引取出要取得文件:
$(‘#id_myfile’)[0].files[0]
总结
- 如果要上传文件,需要借助于一个js的FormData对象
- Ajax上传局部刷新
- Ajax上传文件如果不想使用urlencoded默认处理,可以通过
processData: false不预处理,contentType: false不指定编码格式
Ajax上传json格式
注意:json模块在3.5版本之前不可以直接loads二进制格式(bytes),在3.6版本以后可以
Ajax传json格式只需指定编码格式和序列化数据就能上传
后端需要注意得是post请求得从body体里取数据,然后反序列化即可
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="https://cdn.bootcdn.net/ajax/libs/jquery/3.4.1/jquery.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<h1>ajax提交json格式</h1>
<p>用户名: <input type="text" id="id_name"></p>
<p>密码: <input type="password" id="id_password"></p>
<button id="id_button">提交</button>
</body>
<script>
$('#id_button').click(function () {
$.ajax({
url: '/ajax_json/',
method: 'post',
contentType: 'application/json', //指定编码格式
data: JSON.stringify({name:$('#id_name').val(),password:$('#id_password').val()}), //json格式字符串,序列化数据
success: function (data) {
console.log(data)
}
})
})
</script>
</html>
后端
def ajax_json(request):
if request.method=='GET':
return render(request,'ajax_json.html')
else:
# json格式,从POST中取不出来
name=request.POST.get('name')
print(type(request.POST)) # 返回QueryDict对象,不允许修改
# from django.http.request import QueryDict
print(name) # None
# 在body体中,bytes格式
# django默认只处理两种格式数据urlencode和form-data,json格式需要自己处理
import json
request.data=json.loads(request.body) # 反序列化,从前端获取数据
name=request.data.get('name')
password=request.data.get('password')
print(name)
print(password)
return HttpResponse('ok')
django内置序列化
django提供了一个模块可以将对象直接序列化,然后返回给前端,但是可扩展性低,字段不能控制,返回得是一个整体
from django.core import serializers
def user_list(request):
user_list = models.User.objects.all() # queryset对象
res = serializers.serialize('json', user_list)
return HttpResponse(res)
现在想要字段可控,可以采用for循环列表套字典得格式,然后序列化
def user_list(request):
user_list = models.User.objects.all() # queryset对象
l = []
for user in user_list:
l.append({'name':user.name,'password':user.password})
return JsonResponse(l,safe=False) # 返回给前端
# 如果使用json模块不需要加safe参数
ps:可以通过json.cn将序列化的数据转成对象
【待续】