-
双链表实现,增 删 改 查(基础详细版)
0.在开始之前建议先跟着思路,走一遍,调试部分我就不放了主要写的是实现思路。当然最后也会把源码附上。
1. 带头双向循环链表(简称:双向链表)

- 双向循环带头链表:
- 红色的指向正的 最后一个节点指向头结点
- 绿色的指向反的 从最后一个开始遍历,直到头结点
- 头结点里存储着指向尾节点的和头结点的
- 比如:phead->next = pcur ; phead->prev = ptail;
- 每个节点的当前节点都保存着指向下一个节点的地址和指向上一个节点的地址
- 代码的基本结构
- typedef int LTDataType;
- typedef struct ListNode
- {
- struct ListNode* next; //指针保存下⼀个节点的地址
- struct ListNode* prev; //指针保存前⼀个节点的地
- LTDataType data;
- }LTNode;
- 单链表和双链表为NULL时的两种不一样的情况
- 单链表:第一个直接置为NULL
- 双链表: 只有一个带头链表,里面不存储任何有效的数据,双向链表不能置为NULL,要让他指向自己实现自循环
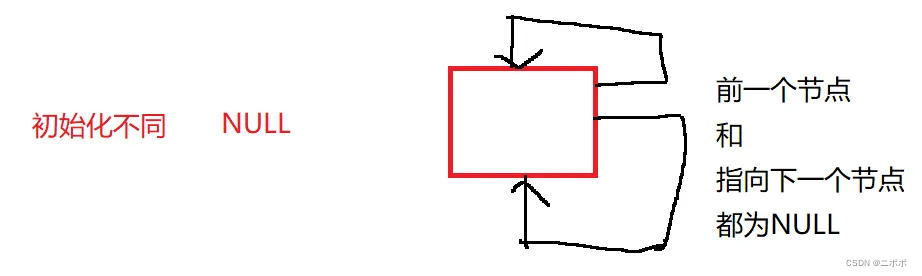
1.1. 单链表和双链表与指针的关系

- 双链表的本质,就是不会对头节点改变,而单链表头插对头节点改变了,所以要二级指针
- 区别就是要不要对(单链表和双链表)的头指针改变
- 举个例子:对于单链表的头指针,有些地方也可以不用传二级指针
就比如尾插时不用对头指针改变,而头插就需要对头指针改变了
- 已知传过去的是创建好有空间的节点,此时尾插不需要二级指针
- 总结概括:改变单链表头指针指向就要传二级地址。双链表不要改变头节点
2. 代码实现
- 在双链表中不用改变头结点,要改变的是结构体内前后指针的指向。和改变头结点的指向完全是两个概念
- 在实现也是要分三个文件的,DouList.c DouList.h test.c 。功能的实现,函数和类型的声明,测试文件
- 这里讲的是核心部分,也就是功能的实现
2.1. 双链表基本结构
- prev指向上一个节点,next指向下一个节点
- typedef int DLDataType;
- typedef struct ListNode
- {
- DLDataType data;
- struct ListNode* prev;//指向上一个节点
- struct ListNode* next;//指向下一个节点
- }DLNode;//链表节点
2.1.1. 初始化
- //第二种初始化方法为了保证接口的一致性,让传递的值都是一级指针
- DLNode* DLInit()
- {
- DLNode* node = DLBuyNode(-1);
- return node;
- }
- DLNode* DLInit()
- {
- DLNode* node = DLBuyNode(-1);
- return node;
- }
- //test.c 通过接收返回值的方式
- void DListTest1()
- {
- DLNode* plist = NULL;//哨兵位
- plist = DLInit();
- }
2.1.2. 空间申请
- 空间申请部分很简单,就是创建新的节点,然后赋值上需要插入的值
- 接着让新创建的节点实现自循环,因为这个是双链表
- //新空间
- DLNode* DLBuyNode(DLDataType x)
- {
- DLNode* newnode = (DLNode*)malloc(sizeof(DLNode));
- if (newnode == NULL)
- {
- perror("malloc nwe");
- exit(-1);//推出整个程序
- }
- newnode->data = x;
- newnode->next = newnode->prev = newnode;//申请新节点,需要自循环
- return newnode;
- }
2.2. 尾插
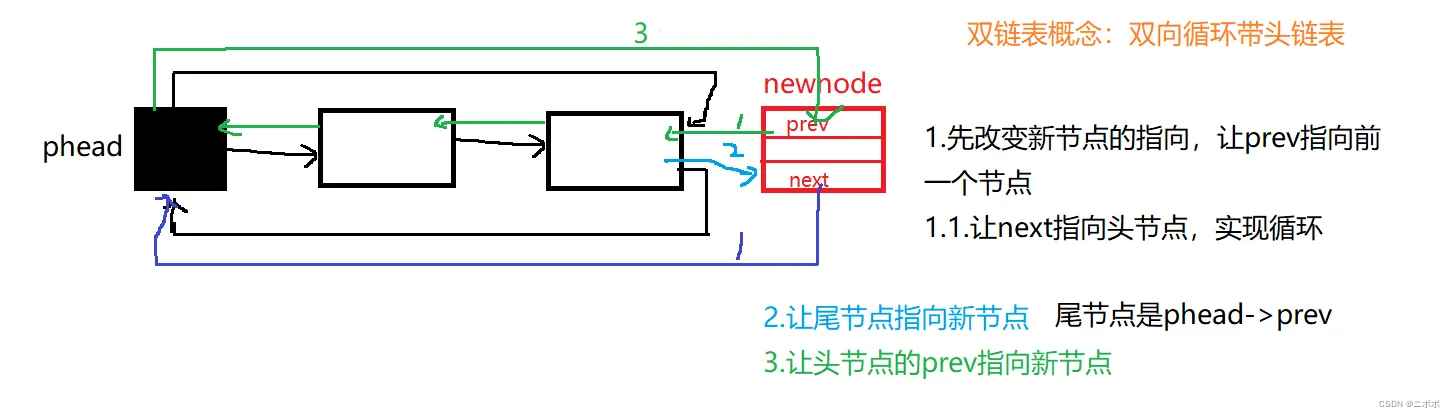

- 不管是头插还是尾插都不需要改变头节点的位置
- 头节点既不能删除也不能改变,没必要传二级指针
- 头节点不能为NULL,因为这是双链表
- phead->prev->next = newnode;必须写在前面,不然会找不到尾节点
- void DLPushBack(DLNode* phead, DLDataType x)
- {
- assert(phead);
- DLNode* newnode = DLBuyNode(x);
- //phead phead->prev newnode
- newnode->prev = phead->prev;//phead->prev 是头节点指向的上一个节点也就是尾节点
- newnode->next = phead;
- phead->prev->next = newnode;//尾节点指向的下一个节点
- phead->prev = newnode;
- }
2.2.1. 空间申请
- 空间申请部分很简单,就是创建新的节点,然后赋值上需要插入的值
- 接着让新创建的节点实现自循环,因为这个是双链表
- //新空间
- DLNode* DLBuyNode(DLDataType x)
- {
- DLNode* newnode = (DLNode*)malloc(sizeof(DLNode));
- if (newnode == NULL)
- {
- perror("malloc nwe");
- exit(-1);//推出整个程序
- }
- newnode->data = x;
- newnode->next = newnode->prev = newnode;//申请新节点,需要自循环
- return newnode;
- }
-
这张图是什么意思呢?意思是在头节点左边插入其实也是尾插,你可以想象一下,把链表想成环形

2.3. 打印链表
- 打印链表需要有两个注意的点,这个不同于单链表,结束条件不能为pcur != NULL;也不可以是pcur->next != NULL,打印到尾节点时会停下循环不进尾节点
- 而是pcur != phead; 头节点不存储有效数据,也就不用打印,拿这个作为结束条件再好不过
- void DLPrint(DLNode* phead)
- {
- DLNode* pcur = phead->next;//头节点指向下一个节点,也就是第一个有效节点
- while (pcur != phead)
- {
- printf("%d->", pcur->data);
- pcur = pcur->next;//遍历指向下一个节点
- }
- printf("\n");
- }
2.4. 头插

- 尾插:在头节点的前面尾插,看上面的图newnode的位置意思是一样的
- 头插:在头节点的后面头插
- 方法的先后顺序是一定不能改变的
- void DLPushFront(DLNode* phead,DLDataType x)
- {
- assert(phead);//头节点不能为NULL
- DLNode* newnode = DLBuyNode(x);
- newnode->next = phead->next;
- newnode->prev = phead;
- //方法1
- //phead->next->prev = newnode;//第一个有效节点指向newnode
- //phead->next = newnode;//指向下一个节点
- //方法2
- phead->next = newnode;
- newnode->next->prev = newnode;
- }
- 注意:要搞清楚头插和尾插时候的前后顺序
2.5. 尾删

- 如果不保存del节点会导致内存泄露
- 尾删和头删可以发现,不用在乎谁先指向谁
- 只要不满足phead为非NULL 和 phead->next != phead就会报错
- void DLDelBack(DLNode* phead)
- {
- //当phead->next != phead就正常执行
- assert(phead && phead->next != phead);//链表都为NULL你删什么?,如果是只剩一个头结点当然也不行
- DLNode* del = phead->prev;
- del->prev->next = phead;//删除的前一个节点指向phead
- phead->prev = del->prev;//头结点的前一个节点指向del->prev
- free(del);
- del = NULL;
- }
2.6. 头删
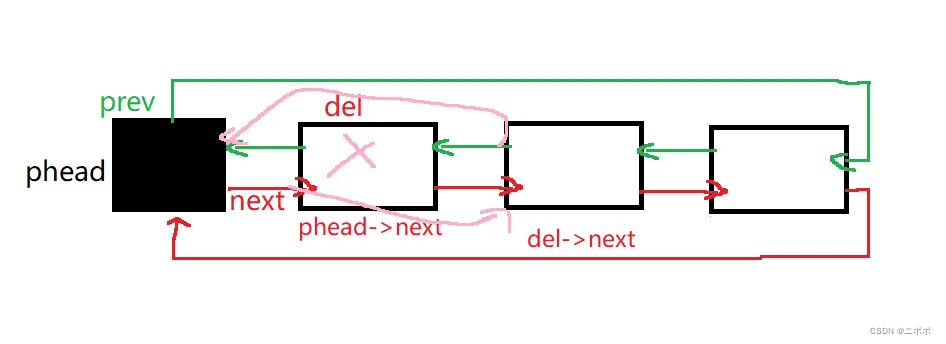
- 头删很简单,就是先保存del节点
- 让phead->next指向del->next ,然后让del->next->prev= phead;
- void DLDelFront(DLNode* phead)
- {
- assert(phead && phead->next != phead);//如果保错就说明,要么为NULL,要么只有一个头结点
- DLNode* del = phead->next;//第一个有效节点
- phead->next = del->next;
- del->next->prev = phead;
- free(del);
- del = NULL;
- }
2.7. 查找
- 查找很简单啦,这就不讲了,唯一和单链表不同的是结束条件,pcur != phead,当遍历到头节点的时候就结束
- //查找
- DLNode* DLFind(DLNode* phead, DLDataType x)
- {
- assert(phead);
- DLNode* pcur = phead->next;//可能存在多次查找,其次记得是第一个有效节点
- while (pcur != phead)
- {
- if (pcur->data == x)
- {
- return pcur;
- }
- pcur = pcur->next;
- }
- return NULL;
- }
- //test.c部分
- DLNode* find = DLFind(plist, 22);
- if (find == NULL)
- printf("没找到");
- else
- printf("找到了");
2.8. 在指定位置之前插入
- 两种情况


- //在指定位置插入
- void DLInsert(DLNode* pos, DLDataType x)
- {
- assert(pos);//防止phead == NULL链表
- DLNode* newnode = DLBuyNode(x);
- //pos newnode pos->next
- newnode->next = pos->next;
- newnode->prev = pos;
- // 2,3点
- pos->next->prev = newnode;
- pos->next = newnode;
- }
2.9. pos位置删除
- pos位置删除,pos左右两边的节点手拉手就行
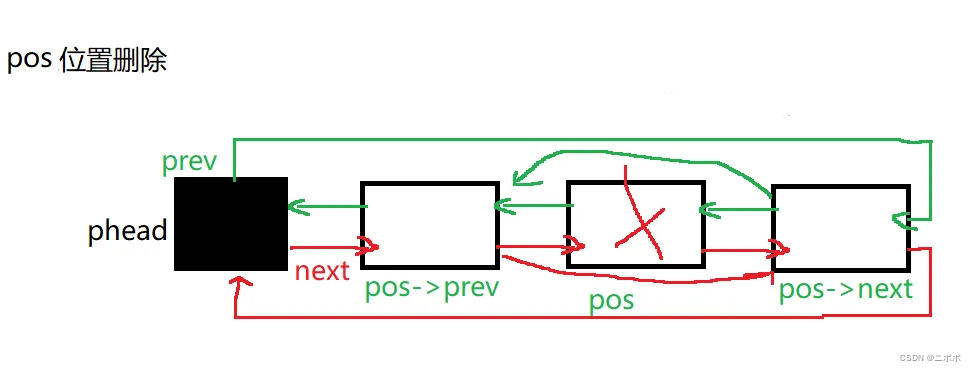
- //在指定位置删除
- void DLErase(DLNode* pos)
- {
- assert(pos);//可能会缺少phead的检查
- //pos->prev pos pos->next
- pos->next->prev = pos->prev;
- pos->prev->next = pos->next;
- free(pos);//pos置为NULL并不影响find
- pos = NULL;
- }
3. 初始化的方式
- 为了保证接口的一致性
- 假如说这些方法,这个方法要传一级指针,那个方法要穿二级指针,总是不能统一,在后续开发中不会大大增加你的开发难度吗?
- //新空间
- DLNode* DLBuyNode(DLDataType x)
- {
- DLNode* newnode = (DLNode*)malloc(sizeof(DLNode));
- if (newnode == NULL)
- {
- perror("malloc nwe");
- exit(-1);//推出整个程序
- }
- newnode->data = x;
- newnode->next = newnode->prev = newnode;//申请新节点,需要自循环
- return newnode;
- }
- //第一种,双链表的初始化
- //void DLInit(DLNode** pphead)//只传参不返回值,因为可以对实参直接改变
- //{
- // *pphead = DLBuyNode(-1);
- //}
- //第二种初始化方法为了保证接口的一致性,让传递的值都是一级指针
- DLNode* DLInit()
- {
- DLNode* node = DLBuyNode(-1);
- return node;
- }
- void DListTest1()
- {
- //第一种
- //DLNode* plist = NULL;//哨兵位
- //DLInit(&plist);//对头节点改变需要二级指针
- //第二种初始化方式
- DLNode* plist = DLInit();
- }
4. 链表的销毁
- 形参是一级指针,传参的时候也是一级指针,这是传值调用了。但是free这个函数只管释放掉动态开辟的空间
- 假如用第一点的方式free掉头节点,并置为NULL,会导致实参这边指针变量没有置为NULL,为什么呢?
- 因为形参的改变并没有影响实参(这个传的是一级指针),而有了两个变量名,虽然空间释放了,但是实参没受影响,所以也要置为NULL。
- 为什么不传二级指针直接改变实参头指针的指向呢,因为要保持接口的一致性
- //销毁链表
- void DLDesTroy(DLNode* phead)
- {
- assert(phead);//此时链表可以为NULL
- DLNode* pcur = phead->next;
- while (pcur != phead)
- {
- DLNode* node = pcur->next;//保存后一个节点
- free(pcur);
- pcur = node;//把后一个节点给到pcur
- }
- free(phead);
- phead = NULL;//两个名字都有访问这块空间的权限,但是这个函数里的名字,并不会影响传过来之前的变量名
- }
- free,原本意思对动态开辟的内存进行释放,函数内和实参这边的函数都有访问权限
- 可以理解为,两个地方都可以对这个块空间释放,但是有两个变量名所以,实参函数这边的指针就变成了野指针
- 而且是传值调用,如果想对实参函数这边的指针改变就需要二级指针了,而free只管free掉动态开辟的空间
- //test.c
- void DListTest1()
- {
- DLNode* plist = NULL;//哨兵位
- DLInit(&plist);//对头节点改变需要二级指针
- //测试尾插
- DLPushBack(plist, 1);
- DLPushBack(plist, 2);
- DLPushBack(plist, 3);
- //DLPushFront(plist, 11);
- //DLPushFront(plist, 22);
- //DLPushFront(plist, 33);
- DLPrint(plist);
- //链表销毁
- DLDesTroy(plist);//销毁完后是需要置为NULL的
- plist = NULL;
- }
- 当然也是可以到实参这边free掉函数的,可以看下边两个例子

- 再举个例子
- 这边我们创建一个单独销毁的函数叫des,如果传二级指针是可以直接对plist这个头节点释放并且置为NULL的,确确实实可以影响到plist这个实参
- 下面是函数调试图,可以发现函数调用传的二级指针,拿到了plist的地址确确实实对plist实参进行了空间的释放

- void des(DLNode** del)
- {
- free(*del);//拿到了plist的地址,对plist的指向改变
- *del = NULL;
- }
- void DListTest1()
- {
- DLNode* plist = NULL;//哨兵位
- DLInit(&plist);//对头节点改变需要二级指针
- //测试尾插
- DLPushBack(plist, 1);
- DLPushBack(plist, 2);
- DLPushBack(plist, 3);
- DLPrint(plist);
- //链表销毁
- DLDesTroy(plist);
- des(&plist);//这边我们创建一个单独销毁的函数
- }
- int main()
- {
- DListTest1();
- return 0;
- }
5.源码
5.1调试部分test.c
- #include "DList.h"
- void DListTest1()
- {
- //DLNode* plist = NULL;//哨兵位
- //DLInit(&plist);//对头节点改变需要二级指针
- //第二种初始化方式
- DLNode* plist = DLInit();
- 测试尾插
- //DLPushBack(plist, 1);
- //DLPushBack(plist, 2);
- //DLPushBack(plist, 3);
- //测试头插
- DLPushFront(plist, 11);
- DLPrint(plist);
- DLPushFront(plist, 22);
- DLPrint(plist);
- DLPushFront(plist, 33);
- DLPrint(plist);
- //测试尾删
- //DLDelBack(plist);
- //DLPrint(plist);
- //DLDelBack(plist);
- //DLPrint(plist);
- //DLDelBack(plist);
- //DLPrint(plist);
- //DLDelBack(plist);
- //DLPrint(plist);
- //测试头删
- //DLDelFront(plist);
- //DLPrint(plist);
- //DLDelFront(plist);
- //DLPrint(plist);
- //DLDelFront(plist);
- //DLPrint(plist);
- DLNode* find = DLFind(plist, 11);// 33 22 11
- if (find == NULL)
- printf("没找到\n");
- else
- printf("找到了\n");
- //在pos节点后插入
- DLInsert(find, 99);// 33 22 11 99
- DLPrint(plist);
- //删除pos节点
- DLErase(find);
- find = NULL;
- DLPrint(plist);
- }
- int main()
- {
- DListTest1();
- return 0;
- }
5.2方法实现 DList.c
- #include "DList.h"
- //新空间
- DLNode* DLBuyNode(DLDataType x)
- {
- DLNode* newnode = (DLNode*)malloc(sizeof(DLNode));
- if (newnode == NULL)
- {
- perror("malloc nwe");
- exit(-1);//推出整个程序
- }
- newnode->data = x;
- newnode->next = newnode->prev = newnode;//申请新节点,需要自循环
- return newnode;
- }
- //双链表的初始化
- //void DLInit(DLNode** pphead)//只传参不返回值,因为可以对实参直接改变
- //{
- // *pphead = DLBuyNode(-1);
- //}
- //第二种初始化方法为了保证接口的一致性,让传递的值都是一级指针
- DLNode* DLInit()
- {
- DLNode* node = DLBuyNode(-1);
- return node;
- }
- //打印链表
- void DLPrint(DLNode* phead)
- {
- DLNode* pcur = phead->next;//头节点指向下一个节点,也就是第一个有效节点
- while (pcur != phead)
- {
- printf("%d->", pcur->data);
- pcur = pcur->next;
- }
- printf("\n");
- }
- //尾插
- void DLPushBack(DLNode* phead, DLDataType x)
- {
- assert(phead);
- DLNode* newnode = DLBuyNode(x);
- //phead phead->prev newnode
- newnode->prev = phead->prev;//phead->prev 是头节点指向的上一个节点也就是尾节点
- newnode->next = phead;
- phead->prev->next = newnode;//尾节点指向下一个节点
- phead->prev = newnode;
- }
- //头插
- void DLPushFront(DLNode* phead, DLDataType x)
- {
- assert(phead);//头节点不能为NULL
- DLNode* newnode = DLBuyNode(x);
- newnode->next = phead->next;
- newnode->prev = phead;
- //方法1
- //phead->next->prev = newnode;//第一个有效节点指向newnode
- //phead->next = newnode;//指向下一个节点
- //方法2
- phead->next = newnode;
- newnode->next->prev = newnode;
- }
- //尾删
- void DLDelBack(DLNode* phead)
- {
- //当phead->next != phead就正常执行
- assert(phead && phead->next != phead);//链表都为NULL你删什么?,如果是只剩一个头结点当然也不行
- DLNode* del = phead->prev;
- del->prev->next = phead;//删除的前一个节点指向phead
- phead->prev = del->prev;//头结点的前一个节点指向del->prev
- free(del);
- del = NULL;
- }
- //头删
- void DLDelFront(DLNode* phead)
- {
- assert(phead && phead->next != phead);//如果保错就说明,要么为NULL,要么只有一个头结点
- DLNode* del = phead->next;//第一个有效节点
- phead->next = del->next;
- del->next->prev = phead;
- free(del);
- del = NULL;
- }
- //查找
- DLNode* DLFind(DLNode* phead, DLDataType x)
- {
- assert(phead);
- DLNode* pcur = phead->next;//可能存在多次查找,其次记得是第一个有效节点
- while (pcur != phead)
- {
- if (pcur->data == x)
- {
- return pcur;
- }
- pcur = pcur->next;
- }
- return NULL;
- }
- //在指定位置插入
- void DLInsert(DLNode* pos, DLDataType x)
- {
- assert(pos);//防止phead == NULL链表
- DLNode* newnode = DLBuyNode(x);
- //pos newnode pos->next
- newnode->next = pos->next;
- newnode->prev = pos;
- pos->next->prev = newnode;
- pos->next = newnode;
- }
- //在指定位置删除
- void DLErase(DLNode* pos)
- {
- assert(pos);//可能会缺少phead的检查
- //pos->prev pos pos->next
- pos->next->prev = pos->prev;
- pos->prev->next = pos->next;
- free(pos);//pos置为NULL并不影响find
- pos = NULL;
- }
5.3声明函数和类型的部分 DList.h
- #pragma once
- #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
- #include
- #include
- #include
- typedef int DLDataType;
- typedef struct ListNode
- {
- DLDataType data;
- struct ListNode* prev;//指向前一个节点
- struct ListNode* next;//指向下一个节点
- }DLNode;//链表节点
- //双链表初始化
- //void DLInit(DLNode** pphead);
- //第二种初始化方式
- DLNode* DLInit();
- //尾插
- void DLPushBack(DLNode* phead, DLDataType x);
- //头插
- void DLPushFront(DLNode* phead, DLDataType x);
- //尾删
- void DLDelBack(DLNode* phead);
- //头删
- void DLDelFront(DLNode* phead);
- //查找
- DLNode* DLFind(DLNode* phead, DLDataType x);
- //在指定位置插入
- void DLInsert(DLNode* pos, DLDataType x);
- //指定位置删除
- void DLErase(DLNode* pos);
总结:
这里只算是基础部分,当然最主要的是学会如何使用手里的工具
- 双向循环带头链表:
-
相关阅读:
【python】爬虫系列之lxml库介绍和xpath提取网页数据
git clone:SSL: no alternative certificate subject name matches target host name
2022.11.9 英语背诵
分类问题和回归问题的区别是什么?
经典动态规划问题的递归实现方法——LeetCode39 组合总和
【PNR#2 Div1 C】图同构(图论)
【概率论与数理统计】【线性代数】计算机保研复习
《进阶篇第9章》学习vuex知识点后练习:求和案例_纯vue版代码
数据结构学习:链表
OpenSSL ca证书命令操作详解
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_70873145/article/details/138057934
