阶段4—实现BeanPostProcessor机制
1.文件目录
2.初始化方法实现
1.编写初始化接口InitializingBean.java
package com.sun.spring.processor;
public interface InitializingBean {
void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception;
}
2.MonsterService.java实现初始化接口
package com.sun.spring.component;
import com.sun.spring.annotation.Autowired;
import com.sun.spring.annotation.Component;
import com.sun.spring.annotation.Scope;
import com.sun.spring.processor.InitializingBean;
@Scope(value = "prototype")
@Component(value = "monsterService")
public class MonsterService implements InitializingBean{
@Autowired
private MonsterDao monsterDao;
public void m1() {
monsterDao.hi();
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("MonsterService 的初始化方法被调用!");
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
3.容器中的createBean方法增加初始化逻辑,判断对象类型是否是InitializingBean的子类型,如果是,则转换成初始化接口类型执行初始化方法
3.后置处理器实现
1.编写后置处理器接口BeanPostProcessor.java
package com.sun.spring.processor;
public interface BeanPostProcessor {
default Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName){
return bean;
}
default Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName){
return bean;
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
2.在组件文件夹下编写后置处理器实现类SunBeanPostProcessor.java会被容器扫描
package com.sun.spring.component;
import com.sun.spring.annotation.Component;
import com.sun.spring.processor.BeanPostProcessor;
@Component
public class SunBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {
System.out.println("\n后置处理器postProcessBeforeInitialization被调用 bean类型=" + bean.getClass() + "bean名字=" + beanName);
if (bean instanceof Car) {
System.out.println("后置处理器发现这个类型是Car类型");
}
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {
System.out.println("后置处理器postProcessAfterInitialization被调用 bean类型=" + bean.getClass() + "bean名字=" + beanName);
return bean;
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
3.容器类完整代码SunSpringApplicationContext.java
package com.sun.spring.ioc;
import com.sun.spring.annotation.Autowired;
import com.sun.spring.annotation.Component;
import com.sun.spring.annotation.ComponentScan;
import com.sun.spring.annotation.Scope;
import com.sun.spring.processor.BeanPostProcessor;
import com.sun.spring.processor.InitializingBean;
import org.apache.commons.lang.StringUtils;
import java.io.File;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
public class SunSpringApplicationContext {
private Class configClass;
private ConcurrentHashMap<String, BeanDefinition> beanDefinitionMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private ConcurrentHashMap<String, Object> singletonObjects = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private List<BeanPostProcessor> beanPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
public SunSpringApplicationContext(Class configClass) throws ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
this.beanDefinitionScan(configClass);
Enumeration<String> keys = beanDefinitionMap.keys();
while (keys.hasMoreElements()) {
String beanName = keys.nextElement();
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = beanDefinitionMap.get(beanName);
if (beanDefinition.getScope().equals("singleton")) {
Object bean = createBean(beanDefinition, beanName);
singletonObjects.put(beanName, bean);
}
}
}
public void beanDefinitionScan(Class configClass) throws ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
this.configClass = configClass;
ComponentScan componentScan = (ComponentScan) this.configClass.getDeclaredAnnotation(ComponentScan.class);
String path = componentScan.value();
System.out.println("要扫描的包=" + path);
ClassLoader classLoader = SunSpringApplicationContext.class.getClassLoader();
path = path.replace(".", "/");
URL resource = classLoader.getResource(path);
File file = new File(resource.getFile());
if (file.isDirectory()) {
File[] files = file.listFiles();
System.out.println("==================================扫描所有组件==================================");
for (File f : files) {
String absolutePath = f.getAbsolutePath();
if (absolutePath.endsWith(".class")) {
String className = absolutePath.substring(absolutePath.lastIndexOf("\\") + 1,
absolutePath.indexOf("."));
String fullPath = path.replace("/", ".") + "." + className;
Class<?> aClass = classLoader.loadClass(fullPath);
if (aClass.isAnnotationPresent(Component.class)) {
if (BeanPostProcessor.class.isAssignableFrom(aClass)) {
BeanPostProcessor beanPostProcessor = (BeanPostProcessor) aClass.newInstance();
beanPostProcessors.add(beanPostProcessor);
continue;
}
System.out.println("这是一个Spring bean=" + aClass);
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = new BeanDefinition();
Scope scopeAnnotation = aClass.getDeclaredAnnotation(Scope.class);
String scope = scopeAnnotation == null || scopeAnnotation.value().equals("") ?
"singleton" : scopeAnnotation.value();
beanDefinition.setScope(scope);
beanDefinition.setClazz(aClass);
Component componentAnnotation = aClass.getDeclaredAnnotation(Component.class);
String beanName = componentAnnotation.value().equals("") ?
StringUtils.uncapitalize(className) : componentAnnotation.value();
beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
} else {
System.out.println("这不是一个Spring bean=" + aClass);
}
}
}
}
}
private Object createBean(BeanDefinition beanDefinition, String beanName) {
Class clazz = beanDefinition.getClazz();
try {
Object instance = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance();
for (Field field : clazz.getDeclaredFields()) {
if (field.isAnnotationPresent(Autowired.class)) {
String name = field.getName();
Object bean = getBean(name);
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(instance, bean);
System.out.println(instance + "依赖注入完毕!");
}
}
Object result = instance;
if (instance instanceof InitializingBean) {
for (BeanPostProcessor beanPostProcessor : beanPostProcessors) {
instance = beanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization(instance, beanName);
}
((InitializingBean) instance).afterPropertiesSet();
for (BeanPostProcessor beanPostProcessor : beanPostProcessors) {
instance = beanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization(instance, beanName);
}
}
if (instance == null) {
return result;
}
return instance;
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public Object getBean(String name) {
if (beanDefinitionMap.containsKey(name)) {
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = beanDefinitionMap.get(name);
if ("singleton".equals(beanDefinition.getScope())) {
return singletonObjects.get(name);
} else {
return createBean(beanDefinition, name);
}
} else {
throw new NullPointerException("没有该bean");
}
}
}

- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
- 213
- 214
- 215
- 216
- 217
- 218
- 219
- 220
- 221
- 222
- 223
- 224
- 225
4.结果展示

4.该阶段完成的任务
- 实现初始化方法
- 编写初始化接口,里面有一个default的初始化方法
- 编写初始化实现类,重写这个初始化方法
- 在容器的依赖注入后添加初始化逻辑,当这个对象的类型是初始化接口的子类型的时候,就将其转换成接口类型并且调用初始化方法
- 后置处理器实现
- 编写一个后置处理器接口,里面有两个方法一个在初始化前调用,一个在初始化后调用
- 在组件文件夹下编写后置处理器实现类
- 在容器中beanDefinitionScan方法的扫描组件时添加后置处理器逻辑,如果该组件实现了后置处理器接口,则转换成后置处理器类型,并且放到ArrayList中方便查找
- 在容器中的createBean方法增加后置处理器逻辑,在初始化方法之前和之后遍历存储后置处理器的ArrayList并分别执行方法
阶段5—实现AOP机制&Spring底层机制总结
1.实现AOP机制
1.原理分析
2.代码实现
1.文件目录

2.编写接口SmartAnimalable.java
package com.sun.spring.component;
public interface SmartAnimalable {
float getSum(float i, float j);
float getSub(float i, float j);
}
2.编写实现类SmartDog.java
package com.sun.spring.component;
import com.sun.spring.annotation.Component;
import com.sun.spring.processor.InitializingBean;
@Component(value = "smartDog")
public class SmartDog implements SmartAnimalable, InitializingBean {
public float getSum(float i, float j) {
float res = i + j;
System.out.println("SmartDog-getSum=" + res);
return res;
}
public float getSub(float i, float j) {
float res = i - j;
System.out.println("SmartDog-getSub=" + res);
return res;
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("smartDog 被初始化!");
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
3.编写切面类SmartAnimalAspect.java
package com.sun.spring.component;
public class SmartAnimalAspect {
public static void showBeginLog() {
System.out.println("前置通知");
}
public static void showSuccessLog() {
System.out.println("返回通知");
}
}
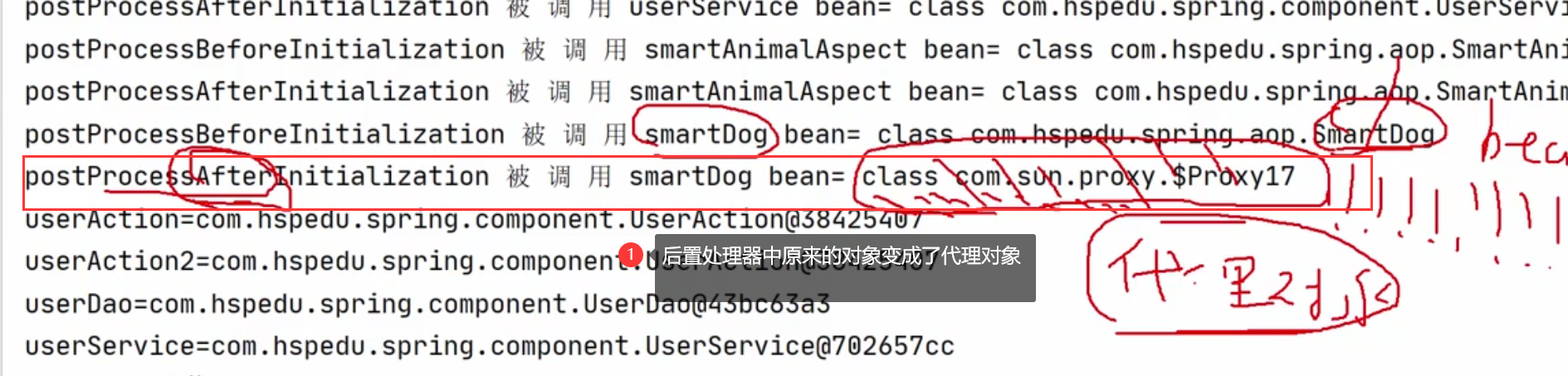
4.修改SunBeanPostProcessor.java对SmartDog的getSum方法进行动态代理
package com.sun.spring.component;
import com.sun.spring.annotation.Component;
import com.sun.spring.processor.BeanPostProcessor;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
@Component
public class SunBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {
System.out.println("\n后置处理器postProcessBeforeInitialization被调用 bean类型=" + bean.getClass() + "bean名字=" + beanName);
if (bean instanceof Car) {
System.out.println("后置处理器发现这个类型是Car类型");
}
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {
System.out.println("后置处理器postProcessAfterInitialization被调用 bean类型=" + bean.getClass() + "bean名字=" + beanName);
if ("smartDog".equals(beanName)) {
ClassLoader classLoader = bean.getClass().getClassLoader();
Class<?>[] interfaces = bean.getClass().getInterfaces();
InvocationHandler invocationHandler = new InvocationHandler() {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
Object result = null;
if ("getSum".equals(method.getName())) {
SmartAnimalAspect.showBeginLog();
result = method.invoke(bean, args);
SmartAnimalAspect.showSuccessLog();
} else {
result = method.invoke(bean, args);
}
return result;
}
};
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(classLoader, interfaces, invocationHandler);
}
return bean;
}
}

- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
5.启动类
package com.sun.spring;
import com.sun.spring.component.MonsterService;
import com.sun.spring.component.SmartAnimalable;
import com.sun.spring.ioc.SunSpringApplicationContext;
import com.sun.spring.ioc.SunSpringConfig;
public class AppMain {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
SunSpringApplicationContext ioc = new SunSpringApplicationContext(SunSpringConfig.class);
Object bean01 = ioc.getBean("monsterDao");
MonsterService bean = (MonsterService) ioc.getBean("monsterService");
System.out.println("==================================测试依赖注入调用方法==================================");
bean.m1();
System.out.println("==================================测试AOP==================================");
SmartAnimalable proxy = (SmartAnimalable) ioc.getBean("smartDog");
proxy.getSub(4,1);
proxy.getSum(2,4);
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
6.结果展示

3.该阶段完成的任务
- 编写接口,编写实现类并将实例交给Spring容器管理,编写切面类
- 后置处理器中进行动态代理操作,这里是对SmartDog类型的getSum方法进行动态代理
- 首先判断beanName是不是smartDog
- 如果是则进行动态代理,invoke方法中先判断当前执行的方法是不是getSum
- 如果是getSum则插入前置通知和返回通知,如果不是则正常执行这个方法
2.Spring底层机制总结
1.bean的生命周期
- 反射创建bean对象
- 依赖注入
- 初始化bean
- getBean
- 销毁bean
2.Spring容器的执行流程
- 获取容器对象
- 读取配置文件,得到要扫描的包
- 扫描包下的组件,将bean定义信息放到Map中
- 如果是单例
- 反射创建bean对象,放到单例池中
- 依赖注入(调用getBean)
- 初始化bean
- 初始化容器前调用后置处理器的before方法
- 初始化容器之后调用后置处理器的after方法
- 如果是多例
- getBean阶段
- 如果是单例
- 如果是多例
- 反射创建bean对象
- 依赖注入(调用getBean)
- 初始化bean
- 初始化容器前调用后置处理器的before方法
- 初始化容器之后调用后置处理器的after方法
- 得到bean对象
- 销毁bean
3.动态代理和AOP的区别
- 动态代理:针对的是某个对象的所有方法
- AOP:针对的是某些类型的所有对象的具体方法
4.关于后置处理器 + 动态代理的理解
- 后置处理器作用于Spring容器中所有类型,所有对象的初始化方法
- getBean得到的就是后置处理器返回的bean
- 当进入到后置处理器的时候
- 获取切面类的所有信息
- 将切入表达式与当前bean对象进行对比,只要类型匹配就进行动态代理
- 使用动态代理进一步筛选要代理的方法,并根据不同的通知执行不同的操作,返回动态代理对象
- 如果是不需要代理的方法,就不进行额外操作
5.AOP的使用方式
- 编写接口,接口对象(注解)(用于展示AOP的效果,因为没有对象)
- 编写切面类(注解),切面对象(注解)
- 通知 + 切点
- 配置beans.xnl
- 具体使用
- 获取针对接口类型的代理对象(通过id或者接口类型获取)
- 使用代理对象调用接口的方法
- 四种通知





