-
C++类与对象二
目录
一、类的嵌套

- #include
- using namespace std;
- class CC1
- {
- public:
- int x;
- void Func();
- class CC2
- {
- public:
- int x;
- void Func();
- }obc;
- };
- void CC1::Func()
- {
- x = 3000;
- cout << "x=" << x << endl;
- }
- void CC1 :: CC2::Func()
- {
- x = 4000;
- cout << "x=" << x << endl;
- }
- int main()
- {
- CC1 obj;
- obj.Func();
- obj.obc.Func();
- cout << endl;
- cout << "2:x=" << obj.x << endl;
- cout << "2:x=" << obj.obc.x << endl;
- return 0;
- }

二、对象引用私有数据成员
通过公有函数为私有成员赋值
- #include
- using namespace std;
- //通过仅有函数为私有数据成员赋值
- class CTest {
- int x, y;
- public:
- void setxy(int a, int b)
- {
- x = a;
- y = b;
- }
- void dispxy()
- {
- cout << "x=" << x << ",y=" << y << endl;
- }
- };
- int main()
- {
- CTest obj1;
- obj1.setxy(1, 2);
- obj1.dispxy();
- }

利用指针访问私有数据成员
- #include
- using namespace std;
- //利用指针访问私有数据成员
- class CTest {
- int x, y;
- public:
- void setxy(int a, int b){
- x = a;
- y = b;
- }
- void printxy() {
- cout << "x=" << x << ",y=" << y << endl;
- }
- void getxy(int* px, int* py) { //提取x y的值
- *px = x;
- *py = y;
- }
- };
- int main()
- {
- CTest obj;
- obj.setxy(100, 200);
- obj.printxy();
- int m, n;
- obj.getxy(&m, &n);
- cout << "m=" << m << ",n=" << n << endl;
- }

利用函数访问私有数据成员
- #include
- using namespace std;
- //利用函数访问私有数据成员
- class CTest {
- int x, y;
- public:
- void setxy(int a, int b){
- x = a;
- y = b;
- }
- void printxy() {
- cout << "x=" << x << ",y=" << y << endl;
- }
- int getx() { return x; }
- int gety() { return y; }
- };
- int main()
- {
- CTest obj;
- obj.setxy(100, 200);
- obj.printxy();
- cout << "x=" << obj.getx() << endl;
- cout << "y=" << obj.gety() << endl;
- }

利用引用访问私有数据成员
- #include
- using namespace std;
- //利用引用访问私有数据成员
- class CTest {
- int x, y;
- public:
- void setxy(int a, int b){
- x = a;
- y = b;
- }
- void printxy() {
- cout << "x=" << x << ",y=" << y << endl;
- }
- void getxy(int& px, int& py) {
- px = x;
- py = y;
- }
- };
- int main()
- {
- CTest obj;
- obj.setxy(100, 200);
- obj.printxy();
- int m, n;
- obj.getxy(m, n);
- cout << "m=" << m << endl;
- cout << "n=" << n << endl;
- }

三、成员函数重载

- #include
- using namespace std;
- class CTest
- {
- int x, y;
- int m, n;
- public:
- void setxy(int a, int b) {
- x = a;
- y = b;
- }
- void setxy(int a, int b, int c, int d) {
- x = a;
- y = b;
- m = c;
- n = d;
- }
- void dispxy(int x) {
- cout << x << "," << y << endl;
- }
- void dispxymn() {
- cout << x << "," << y << "," << m << "," << n << endl;
- }
- };
- int main()
- {
- CTest obj1, obj2;
- obj1.setxy(10, 20);
- obj2.setxy(10, 20, 30, 40);
- obj1.dispxy(666);
- obj2.dispxymn();
- return 0;
- }

- #include
- using namespace std;
- class CTest
- {
- int x, y;
- public:
- void setxy(int a, int b) {
- x = a;
- y = b;
- }
- void dispxy()
- {
- cout << "x=" << x << "y=" <}int sum(){return x + y;}};int main(){CTest obj1, obj2;//定义对象CTest* pobj; //对象类的指针(对象指针)pobj = &obj1;pobj->setxy(3, 4);pobj->dispxy();cout << "x+y=" << pobj->sum() << endl;return 0;}
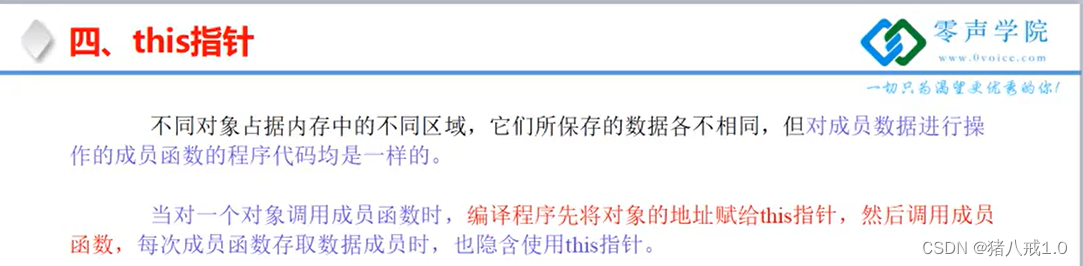
四、this指针
- #include
- using namespace std;
- class CTest
- {
- private:
- int x;
- public:
- int getx() const {
- return x;
- }
- void setx(int x) {
- this->x=x;
- cout << "this指针存储的内存地址为:" << this << endl;
- }
- };
- int main()
- {
- CTest obj;
- obj.setx(888);
- cout << "对象obj在内存的地址为:" << &obj << endl;
- cout << "对象obj所保存的值为:" << obj.getx() << endl;
- return 0;
- }
- 相关阅读:
抽象工厂模式:构建复杂的对象族
自动化测试的生命周期是什么?
小白零基础自学Java,究竟如何才能学的透彻!
odoo javascript参考(七)
java 并发执行批量异步任务(Future、 CompletableFuture 实现)
HTTPS的加密方式超详细解读
【关于Linux中----进程优先级、环境变量和进程地址空间】
HelloWorld显示Go语言交叉编译的强大20230926
MQ系列6:消息的消费
查看目录和文件大小: du -sh
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_58631644/article/details/136724260