一、多线程程序
QThread类提供了管理线程的方法:
- 一个对象管理一个线程
- 一般从QThread继承一个自定义类,重载run函数
1、实现程序

(1)创建项目,基于QDialog
(2)添加类,修改基于QThread

class DiceThread : public QThread
{
Q_OBJECT
private:
int m_seq = 0;
int m_diceValue;
bool m_Paused = true;
bool m_stop = false;
public:
explicit DiceThread();
void diceBegin();
void dicePause();
void stopThread();
protected:
void run() Q_DECL_OVERRIDE;
signals:
void newValued(int seq, int diceValue);
public slots:
};
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
DiceThread::DiceThread()
{
}
void DiceThread::diceBegin()
{
m_Paused = false;
}
void DiceThread::dicePause()
{
m_Paused = true;
}
void DiceThread::stopThread()
{
m_stop = true;
}
void DiceThread::run()
{
m_stop = false;
m_seq = 0;
qsrand(QTime::currentTime().second());
while (!m_stop) {
if(!m_Paused)
{
m_diceValue = qrand()%6+1;
m_seq++;
emit newValued(m_seq, m_diceValue);
}
sleep(1);
}
quit();
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
(3)实现按钮功能
Dialog::Dialog(QWidget *parent) :
QDialog(parent),
ui(new Ui::Dialog)
{
ui->setupUi(this);
ui->btnStartThread->setEnabled(true);
ui->btnStart->setEnabled(false);
ui->btnStop->setEnabled(false);
ui->btnStopThread->setEnabled(false);
connect(&threadA, SIGNAL(started()),
this, SLOT(on_threadAStarted()));
connect(&threadA, SIGNAL(finished()),
this, SLOT(on_threadAFinished()));
connect(&threadA, SIGNAL(newValued(int,int)),
this, SLOT(on_threadAnewValue(int,int)));
}
Dialog::~Dialog()
{
delete ui;
}
void Dialog::closeEvent(QCloseEvent *event)
{
if(threadA.isRunning())
{
threadA.stopThread();
threadA.wait();
}
event->accept();
}
void Dialog::on_btnStartThread_clicked()
{
threadA.start();
}
void Dialog::on_btnStart_clicked()
{
threadA.diceBegin();
}
void Dialog::on_btnStop_clicked()
{
threadA.dicePause();
}
void Dialog::on_btnStopThread_clicked()
{
threadA.stopThread();
}
void Dialog::on_btnClearText_clicked()
{
ui->plainTextEdit->clear();
}
void Dialog::on_threadAnewValue(int seq, int diceValue)
{
ui->plainTextEdit->appendPlainText(QString::asprintf("第%d次投色子: 点数%d", seq, diceValue));
}
void Dialog::on_threadAStarted()
{
ui->labelStatus->setText("Thread状态:started");
ui->btnStartThread->setEnabled(false);
ui->btnStart->setEnabled(true);
ui->btnStop->setEnabled(true);
ui->btnStopThread->setEnabled(true);
}
void Dialog::on_threadAFinished()
{
ui->labelStatus->setText("Thread状态:finished");
ui->btnStartThread->setEnabled(true);
ui->btnStart->setEnabled(false);
ui->btnStop->setEnabled(false);
ui->btnStopThread->setEnabled(false);
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85

二、互斥量
QMutex和QMutexLocker是基于互斥量的线程同步类
- QMutex定义的实力是互斥量,主要提供了三个函数
- lock():锁定互斥量,如果另一个线程锁定了这个互斥量,将阻塞直到另一个解锁
- unlock():解锁一个互斥量
- trylock():尝试锁定一个互斥量,如果成功返回true,失败(其他线程已经锁定这个互斥量)返回false,不阻塞线程。
- QMutexLocker简化了互斥量的处理
- 构造一个函数接受一个互斥量作为参数,并将其锁定
- 析构函数解锁该互斥量
1、实现程序
(1)拷贝上一个项目
(2)修改程序为直接读取
void DiceThread::readValue(int *seq, int *diceValue)
{
*seq = m_seq;
*diceValue = m_diceValue;
}
void DiceThread::run()
{
m_stop = false;
m_seq = 0;
qsrand(QTime::currentTime().second());
while (!m_stop) {
if(!m_Paused)
{
m_diceValue = 50;
msleep(50);
m_diceValue = qrand();
msleep(50);
m_diceValue = m_diceValue%6+1;
msleep(50);
m_seq++;
// emit newValued(m_seq, m_diceValue);
}
sleep(1);
}
quit();
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
void Dialog::on_TimerOut()
{
int seq, diceValue;
threadA.readValue(&seq, &diceValue);
ui->plainTextEdit->appendPlainText(QString::asprintf("第%d次投色子: 点数%d", seq, diceValue));
}

(3)使用QMutex互斥量
void DiceThread::readValue(int *seq, int *diceValue)
{
mMutex.lock();
*seq = m_seq;
*diceValue = m_diceValue;
mMutex.unlock();
}
void DiceThread::run()
{
m_stop = false;
m_seq = 0;
qsrand(QTime::currentTime().second());
while (!m_stop)
{
if(!m_Paused)
{
mMutex.lock();
m_diceValue = 50;
msleep(50);
m_diceValue = qrand();
msleep(50);
m_diceValue = m_diceValue % 6 + 1;
msleep(50);
m_seq++;
// emit newValued(m_seq, m_diceValue);
mMutex.unlock();
}
sleep(1);
}
quit();
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32

(4)使用QMutexLocker
void DiceThread::readValue(int *seq, int *diceValue)
{
QMutexLocker locker(&mMutex);
*seq = m_seq;
*diceValue = m_diceValue;
}
(5)使用QMutex.trylock
bool DiceThread::readValue(int *seq, int *diceValue)
{
// QMutexLocker locker(&mMutex);
if(mMutex.tryLock())
{
*seq = m_seq;
*diceValue = m_diceValue;
mMutex.unlock();
return true;
}
return false;
}
三、读写锁
QReadWriteLock提供了以下主要函数:
- lockForRead():只读方式锁定资源,如果有其他线程以写入方式锁定,这个函数会阻塞
- lockForWrite():以写入方式锁定资源,如果本线程或者其他线程以读取或写入锁定资源,则函数阻塞
- unlock():解锁
- tryLockForRead():是lockForRead非阻塞版本
- tryLockForWrite():是lockForWrite非阻塞版本
- 读写锁同样有QReadLocker和QWriteLocker
四、条件变量QWaitCondition
QWaitCondition用于通知其他线程,如接收数据和处理数据之间通知。提供了一些函数:
- wait(QMutex *lockedMutex):进入等待状态,解锁互斥量lockMutex,被唤醒后锁定lockMutex并退出函数
- wakeAll():唤醒所有处于等待的线程,线程唤醒的顺序不确定,有操作系统调度策略决定
- QakeOne():唤醒一个处于等待状态的线程,唤醒哪个线程不确定,由操作系统调度策略决定
1、实现程序
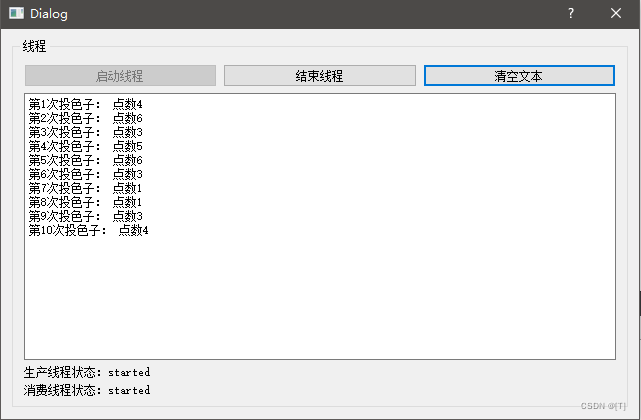
(1)拷贝上一个项目
(2)使用QWaitCondition设置数据更新
int m_seq = 0;
int m_diceValue;
bool m_stop = false;
QMutex m_Mutex;
QWaitCondition waitCondition;
ProducerThread::ProducerThread()
{
}
void ProducerThread::stopThread()
{
m_stop = true;
}
void ProducerThread::run()
{
m_stop = false;
m_seq = 0;
qsrand(QTime::currentTime().second());
while (!m_stop)
{
m_Mutex.lock();
m_diceValue = qrand() % 6 + 1;
m_seq++;
m_Mutex.unlock();
waitCondition.wakeOne();
sleep(1);
}
quit();
}
ConsumerThread::ConsumerThread()
{
}
void ConsumerThread::stopThread()
{
m_stop = true;
waitCondition.wakeOne(); // 需要给wait置信号,否则阻塞无法结束
}
void ConsumerThread::run()
{
m_stop = false;
while (!m_stop)
{
m_Mutex.lock();
waitCondition.wait(&m_Mutex);
emit newValued(m_seq, m_diceValue);
m_Mutex.unlock();
msleep(100);
}
quit();
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62

五、信号量
QSemaphore信号量通常用于保护一定数量的相同的资源。QSemaphore是实现信号量功能的类,提供了以下函数:
- acquire(int n):尝试获得n个资源,如果不够将阻塞线程,直到n个资源可用
- release(int n):释放资源,如果资源已经全部可用,则可扩充资源总数
- int available():返回房前信号量的资源个数
- bool tryAcquire(int n=1):尝试获取n个资源,不成功是,不阻塞线程
1、实现程序

(1)创建项目,基于QDIalog

(2)创建线程类
(3)使用信号量实现功能
const int bufferSize = 8;
int buffer1[bufferSize] = {0};
int buffer2[bufferSize] = {0};
int curBuf = 1; // 当前采集数据使用的缓冲区
QSemaphore semEmptyBufs(2); // 两个资源
QSemaphore semFullBufs;
ThreadDAQ::ThreadDAQ()
{
}
void ThreadDAQ::stopThread()
{
m_stop = true;
}
void ThreadDAQ::run()
{
m_stop = false;
int counter = 0;
while(!m_stop)
{
semEmptyBufs.acquire();
for (int i = 0; i < bufferSize; ++i)
{
if(curBuf == 1)
{
buffer1[i] = counter;
}
else
{
buffer2[i] = counter;
}
counter++;
msleep(50);
}
if(curBuf == 1)
{
curBuf = 2;
}
else
{
curBuf = 1;
}
semFullBufs.release();
}
exit();
}
ThreadShow::ThreadShow()
{
}
void ThreadShow::stopThread()
{
m_stop = true;
}
void ThreadShow::run()
{
m_stop = false;
int seq = 0;
while(!m_stop)
{
semFullBufs.acquire();
int buf[bufferSize] = {0};
if(curBuf == 1)
{
memcpy(buf, buffer2, sizeof(int)*bufferSize);
}
else
{
memcpy(buf, buffer1, sizeof(int)*bufferSize);
}
emit newValue(buf, bufferSize, seq++);
semEmptyBufs.release();
}
exit();
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
Dialog::Dialog(QWidget *parent) :
QDialog(parent),
ui(new Ui::Dialog)
{
ui->setupUi(this);
ui->btnStopThread->setEnabled(false);
connect(&threadConsumer, SIGNAL(newValue(int*, int, int)),
this, SLOT(on_threadNewValue(int*, int, int)));
connect(&threadProducer, SIGNAL(started()),
this, SLOT(on_threadProducer_started()));
connect(&threadProducer, SIGNAL(finished()),
this, SLOT(on_threadProducer_finished()));
connect(&threadConsumer, SIGNAL(started()),
this, SLOT(on_threadConsumer_started()));
connect(&threadConsumer, SIGNAL(finished()),
this, SLOT(on_threadConsumer_finished()));
}
Dialog::~Dialog()
{
delete ui;
}
void Dialog::on_threadNewValue(int *data, int count, int seq)
{
QString str = QString::asprintf("第%03d次,内容:", seq);
for (int var = 0; var < count; ++var)
{
str += QString::asprintf("%03d ,", data[var]);
}
ui->plainTextEdit->appendPlainText(str);
}
void Dialog::on_btnStartThread_clicked()
{
threadConsumer.start();
threadProducer.start();
ui->btnStartThread->setEnabled(false);
ui->btnStopThread->setEnabled(true);
}
void Dialog::on_btnStopThread_clicked()
{
threadProducer.stopThread();
threadConsumer.stopThread();
ui->btnStartThread->setEnabled(true);
ui->btnStopThread->setEnabled(false);
}
void Dialog::on_btnClearText_clicked()
{
ui->plainTextEdit->clear();
}
void Dialog::on_threadProducer_started()
{
ui->labelProducer->setText("Producer线程:started");
}
void Dialog::on_threadProducer_finished()
{
ui->labelProducer->setText("Producer线程:finished");
}
void Dialog::on_threadConsumer_started()
{
ui->labelConsumer->setText("Consumer线程:started");
}
void Dialog::on_threadConsumer_finished()
{
ui->labelConsumer->setText("Consumer线程:finished");
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84










