-
【设计模式】策略模式
引例

方案一

说明:- 不满足OCP,添加新的排序算法或修改某个已有排序算法需要重新编译整个类
- 可复用性差,Sorting类不可被直接复用
方案二
将客户类和算法类分开

说明:Sorting类可复用,但Sorting类仍不满足OCP
方案三
分离变化点:排序算法内部逻辑可能变化,排序算法个数可能变化,于是做成层次类,实现一个抽象的Sort接口

说明:满足开闭原则、依赖倒置原则
Client类和算法实现类都依赖Sort抽象接口
具体使用而言,在 Client 中的 Sort 对象实例化某个具体的子类即可
还有一个问题:Client使用不同的Sort方法时可能需要进行重复的初始化、计算排序时间等与Sort层次类提供功能无关的工作
方案四
在Client和Sort层次类之间加上一个负责初始化/全局控制的类,用以协调Client和Sort层次类,即环境类Context

代码实现// Sort抽象接口 public interface Sort { int[] sort(int[] num); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
// 具体排序类实现 public class BubbleSort implements Sort{ @Override public int[] sort(int[] num) { int n = num.length; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < n - i - 1; j++) { if (num[j] > num[j + 1]) { int temp = num[j]; num[j] = num[j + 1]; num[j + 1] = temp; } } } return num; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
// Context环境类的实现 public class Context { private Sort s; private long startTime; private long endTime; public Context(Sort s) { this.s = s; } public void startExc() { startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); } public void endExc() { endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); } public long getExcTime() { long exeTime = 0; exeTime = endTime - startTime; return exeTime; } public int[] sortIntArray(int[] a) { return s.sort(a); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
// Client客户端代码实现 public class Client { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr = {64, 34, 25, 12, 22, 11, 90}; Sort s = new BubbleSort(); Context con = new Context(s); con.startExc(); arr = con.sortIntArray(arr); con.endExc(); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr)); System.out.println(con.getExcTime()); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
说明:这个设计模式仍有修改空间,应该通过在Sort具体类的sort方法中直接调用con.startExc()和con.endExc() 方法,这样得到的运行时间更加准确
方案五
在Sort层次类和Context环境类之间增加一条反向依赖

理论
定义
通过将一系列实现相同功能的算法封装起来,形成层次类,是得它们可以相互替换,且算法的变化不会影响使用算法的客户
说明
对象行为模式通用结构

使用场景
- 一个系统需要动态地在几种算法中选择一种时,可将每个算法封装到策略类中
- 一个类中以条件语句并列起来的多种行为,每个条件分支可被封装到策略类中
课后练习
练习一

设计思路一:使用策略工厂的思路,DiscountStrategy作为抽象接口下接具体的discount策略做成一个打折策略层次类,DiscountStrategyFactory作为环境类,OrderService作为Client调用对应DiscountStrategyFactory再使用对应的打折策略

DiscountStrategyFactory实现代码:public class DiscountStrategyFactory { private static final Map<OrderType, DiscountStrategy> strategies = new HashMap<OrderType, DiscountStrategy>(); static { strategies.put(OrderType.NORMAL, new NormalDiscountStrateg()); strategies.put(OrderType.GROUPON, new GrouponDiscountStrategy()); strategies.put(OrderType.PROMOTION, new PromotionDiscountStrategy()); } public static DiscountStrategy getDiscountStrategy(OrderType type) { return strategies.get(type); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
练习二

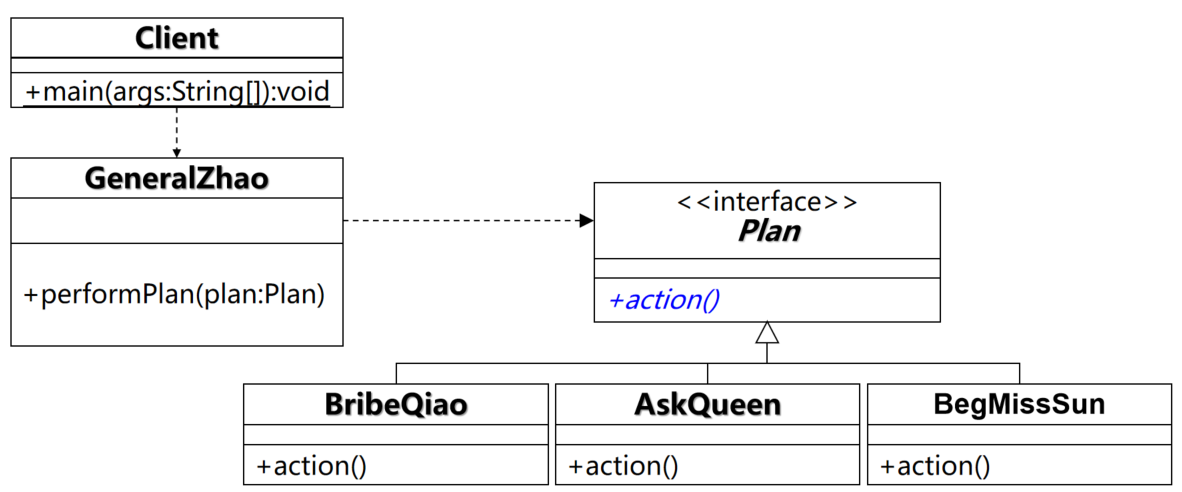
-
相关阅读:
Netty笔记
骨传导耳机怎么听到声音?骨传导耳机是否会对听力造成损害?
Unity减少发布打包文件的体积——获取精灵图片的信息限制它的大小
Nginx (6):nginx防盗链配置
ETL实现实时文件监听
Vue2 和 Vue3 的区别
Springboot集成ORM框架开发(保姆级)
田口实验法
day02 springmvc
【计算机网络实验】TCP和UDP传输过程仿真与分析
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_61819793/article/details/134382246
