-
V-REP和Python的联合仿真
机器人仿真软件 各类免费的的机器人仿真软件优缺点汇总_robot 仿真 软件收费么_dyannacon的博客-CSDN博客
课程地址 https://class.guyuehome.com/p/t_pc/course_pc_detail/column/p_605af87be4b007b4183a42e7
课程资料 guyueclass: 古月学院课程代码
旋转变换 旋转的左乘与右乘 - 知乎
四足机器人站立控制原理 【基础知识】四足机器人的站立姿态控制原理 - 知乎
单腿逆解参考 https://github.com/richardbloemenkamp/Robotdog
Vrep文档
Vrep放大object

Vrep 导入模型步骤:
1. plugins-->urdf import导入机器人URDF文件
2. 删除机器人对象中的world_joint和world_link_visual
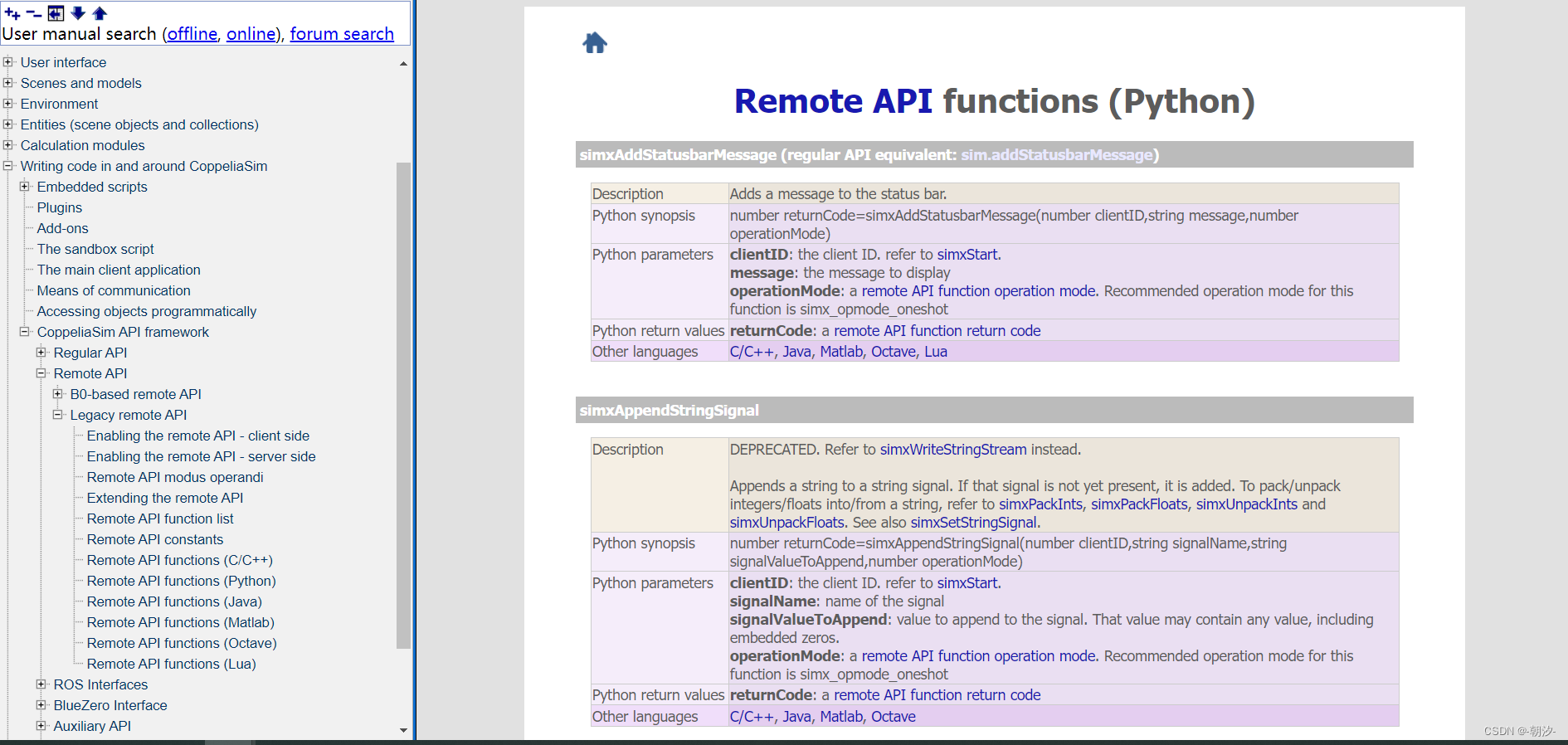
3. 双击设置机器人参数
碰撞参数设置:body参数设置,自身碰撞勾选前四个勾,leg参数设置,自身碰撞勾选后四个勾,即不计算与自身的碰撞关系

设置关节参数
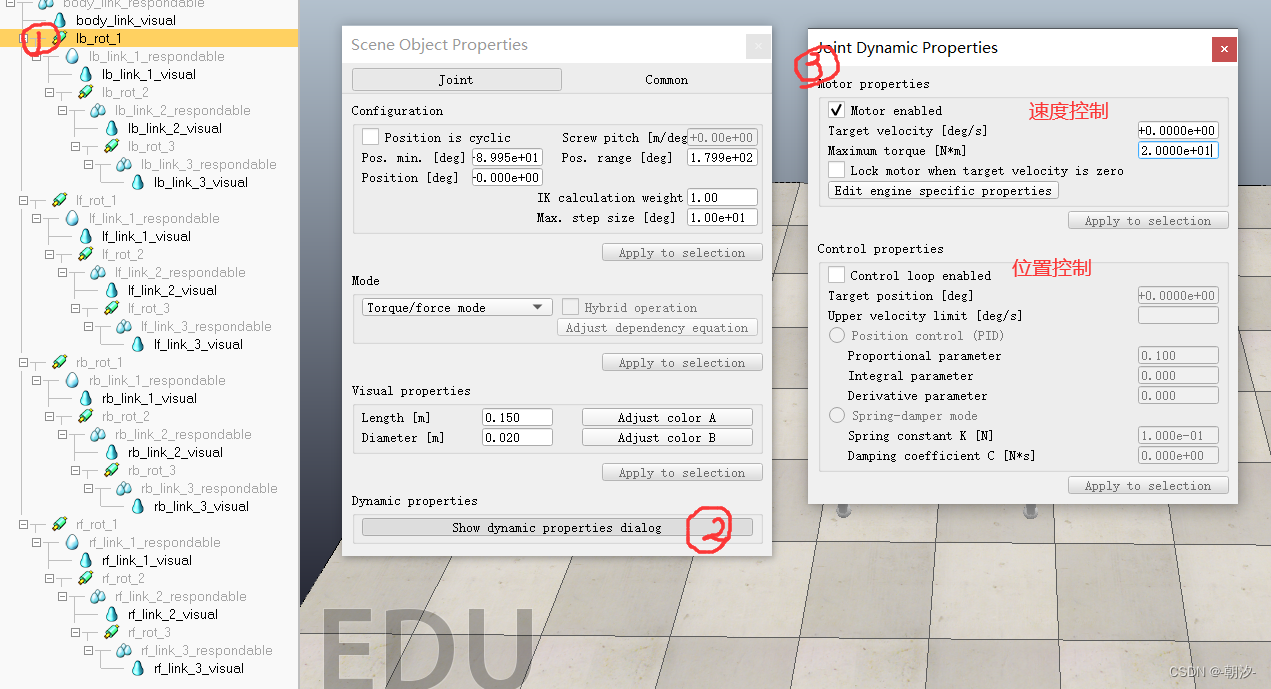

调节颜色

python联合仿真
remote API路径:C:\Program Files\CoppeliaRobotics\CoppeliaSimEdu\programming\remoteApiBindings
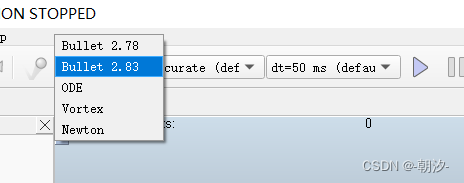
1. 选择仿真器
2. 创建Vrep脚本用于远程连接

3. 绑定脚本到机器人
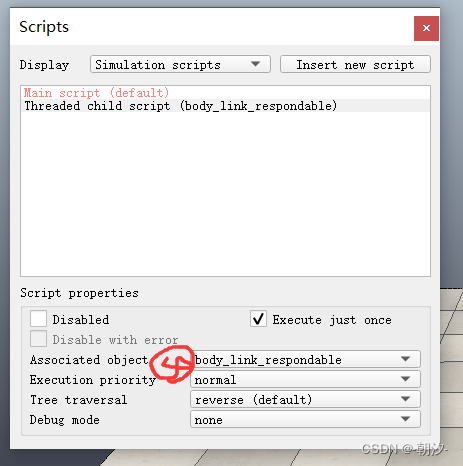
4. 编辑脚本,添加远程连接代码
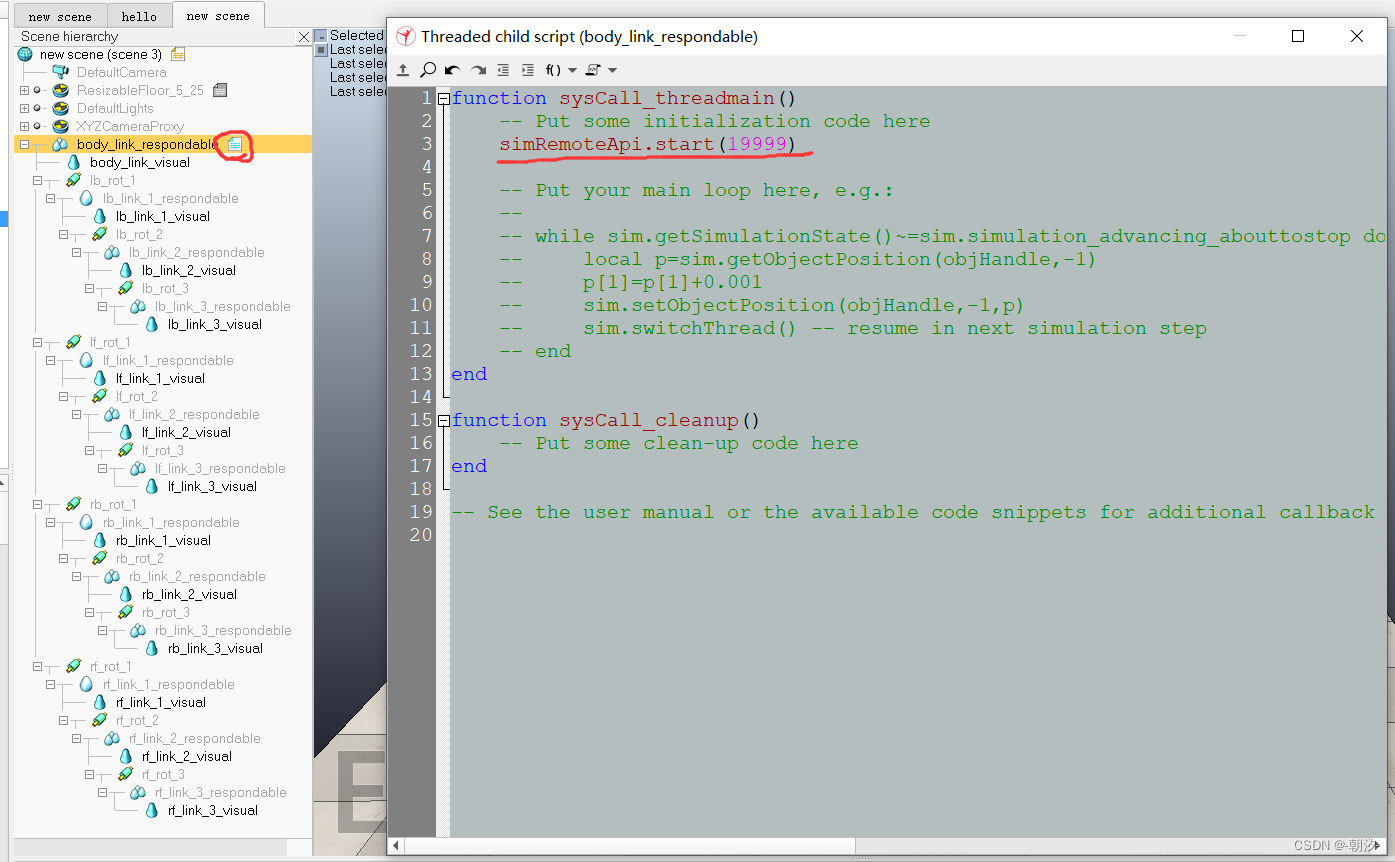
4. 编写python脚本并测试(将腿部足端位置转换为关节的角度)
连接V-REP需要从remote API路径拷贝相关文件
- """
- 连接VREP Server并测试控制四足机器人
- """
- try:
- import sim
- except ImportError:
- print('--------------------------------------------------------------')
- print('"sim.py" could not be imported. This means very probably that')
- print('either "sim.py" or the remoteApi library could not be found.')
- print('Make sure both are in the same folder as this file,')
- print('or appropriately adjust the file "sim.py"')
- print('--------------------------------------------------------------')
- print('')
- sim = None
- import time
- import numpy as np
- def start_simulation():
- sim.simxFinish(-1)
- # 开启套接字与server进行通信
- clientID = sim.simxStart('127.0.0.1', 19999, True, True, 5000, 5)
- if clientID != -1:
- print('Connected to remote API server with ClientID ', clientID)
- # 开始模拟
- sim.simxStartSimulation(clientID, sim.simx_opmode_oneshot)
- return clientID
- else:
- return -1
- def get_joints(client_id):
- # 机器人电机力矩参数
- rotation_forces = [
- # RB
- [500, 500, 500],
- # RF
- [500, 500, 500],
- # LB
- [500, 500, 500],
- # LF
- [500, 500, 500]
- ]
- # 获取机器人关节对象句柄
- rec, rb_rot_1 = sim.simxGetObjectHandle(client_id, 'rb_rot_1', sim.simx_opmode_blocking)
- rec, rb_rot_2 = sim.simxGetObjectHandle(client_id, 'rb_rot_2', sim.simx_opmode_blocking)
- rec, rb_rot_3 = sim.simxGetObjectHandle(client_id, 'rb_rot_3', sim.simx_opmode_blocking)
- rec, rf_rot_1 = sim.simxGetObjectHandle(client_id, 'rf_rot_1', sim.simx_opmode_blocking)
- rec, rf_rot_2 = sim.simxGetObjectHandle(client_id, 'rf_rot_2', sim.simx_opmode_blocking)
- rec, rf_rot_3 = sim.simxGetObjectHandle(client_id, 'rf_rot_3', sim.simx_opmode_blocking)
- rec, lb_rot_1 = sim.simxGetObjectHandle(client_id, 'lb_rot_1', sim.simx_opmode_blocking)
- rec, lb_rot_2 = sim.simxGetObjectHandle(client_id, 'lb_rot_2', sim.simx_opmode_blocking)
- rec, lb_rot_3 = sim.simxGetObjectHandle(client_id, 'lb_rot_3', sim.simx_opmode_blocking)
- rec, lf_rot_1 = sim.simxGetObjectHandle(client_id, 'lf_rot_1', sim.simx_opmode_blocking)
- rec, lf_rot_2 = sim.simxGetObjectHandle(client_id, 'lf_rot_2', sim.simx_opmode_blocking)
- rec, lf_rot_3 = sim.simxGetObjectHandle(client_id, 'lf_rot_3', sim.simx_opmode_blocking)
- # 设置电机力矩
- rec = sim.simxSetJointForce(client_id, rb_rot_1, rotation_forces[0][0], sim.simx_opmode_blocking)
- rec = sim.simxSetJointForce(client_id, rb_rot_2, rotation_forces[0][1], sim.simx_opmode_blocking)
- rec = sim.simxSetJointForce(client_id, rb_rot_3, rotation_forces[0][2], sim.simx_opmode_blocking)
- rec = sim.simxSetJointForce(client_id, rf_rot_1, rotation_forces[1][0], sim.simx_opmode_blocking)
- rec = sim.simxSetJointForce(client_id, rf_rot_2, rotation_forces[1][1], sim.simx_opmode_blocking)
- rec = sim.simxSetJointForce(client_id, rf_rot_3, rotation_forces[1][2], sim.simx_opmode_blocking)
- rec = sim.simxSetJointForce(client_id, lb_rot_1, rotation_forces[2][0], sim.simx_opmode_blocking)
- rec = sim.simxSetJointForce(client_id, lb_rot_2, rotation_forces[2][1], sim.simx_opmode_blocking)
- rec = sim.simxSetJointForce(client_id, lb_rot_3, rotation_forces[2][2], sim.simx_opmode_blocking)
- rec = sim.simxSetJointForce(client_id, lf_rot_1, rotation_forces[3][0], sim.simx_opmode_blocking)
- rec = sim.simxSetJointForce(client_id, lf_rot_2, rotation_forces[3][1], sim.simx_opmode_blocking)
- rec = sim.simxSetJointForce(client_id, lf_rot_3, rotation_forces[3][2], sim.simx_opmode_blocking)
- return [rb_rot_1, rb_rot_2, rb_rot_3], \
- [rf_rot_1, rf_rot_2, rf_rot_3], \
- [lb_rot_1, lb_rot_2, lb_rot_3], \
- [lf_rot_1, lf_rot_2, lf_rot_3]
- def leg_inverse_kine(x, y, z):
- # h,hu和hl分别是单条腿杆件的长度
- h = 0.15
- hu = 0.35
- hl = 0.382
- dyz = np.sqrt(y**2 + z**2)
- lyz = np.sqrt(dyz**2 - h**2)
- gamma_yz = -np.arctan(y/z)
- gamma_h_offset = -np.arctan(h/lyz)
- gamma = gamma_yz - gamma_h_offset
- lxzp = np.sqrt(lyz**2 + x**2)
- n = (lxzp**2 - hl**2 - hu**2) / (2 * hu)
- beta = -np.arccos(n / hl)
- alfa_xzp = -np.arctan(x/lyz)
- alfa_off = np.arccos((hu + n) / lxzp)
- alfa = alfa_xzp + alfa_off
- return gamma, alfa, beta
- if __name__ == '__main__':
- # 机器人电机角度参数
- rb_poses = [40*np.pi/180, 0, 0]
- rf_poses = [0, 0, 0]
- lb_poses = [0, 0, 0]
- lf_poses = [0, 0, 0]
- client_id = start_simulation()
- if client_id != -1:
- joints = get_joints(client_id)
- rb_joints = joints[0]
- rf_joints = joints[1]
- lb_joints = joints[2]
- lf_joints = joints[3]
- time.sleep(1)
- timeout = 60
- start_time = time.time()
- curr_time = time.time()
- # 初始关节角度
- rb_poses = leg_inverse_kine(0, -0.3, -0.632)
- rf_poses = leg_inverse_kine(0, -0.3, -0.632)
- lb_poses = leg_inverse_kine(0, -0.3, -0.632)
- lf_poses = leg_inverse_kine(0, -0.3, -0.632)
- while curr_time - start_time < timeout:
- # 设置关节角度
- rec = sim.simxSetJointTargetPosition(client_id, rb_joints[0], -rb_poses[0], sim.simx_opmode_oneshot)
- rec = sim.simxSetJointTargetPosition(client_id, rb_joints[1], rb_poses[1], sim.simx_opmode_oneshot)
- rec = sim.simxSetJointTargetPosition(client_id, rb_joints[2], rb_poses[2], sim.simx_opmode_oneshot)
- rec = sim.simxSetJointTargetPosition(client_id, rf_joints[0], rf_poses[0], sim.simx_opmode_oneshot)
- rec = sim.simxSetJointTargetPosition(client_id, rf_joints[1], rf_poses[1], sim.simx_opmode_oneshot)
- rec = sim.simxSetJointTargetPosition(client_id, rf_joints[2], rf_poses[2], sim.simx_opmode_oneshot)
- rec = sim.simxSetJointTargetPosition(client_id, lb_joints[0], -lb_poses[0], sim.simx_opmode_oneshot)
- rec = sim.simxSetJointTargetPosition(client_id, lb_joints[1], lb_poses[1], sim.simx_opmode_oneshot)
- rec = sim.simxSetJointTargetPosition(client_id, lb_joints[2], lb_poses[2], sim.simx_opmode_oneshot)
- rec = sim.simxSetJointTargetPosition(client_id, lf_joints[0], lf_poses[0], sim.simx_opmode_oneshot)
- rec = sim.simxSetJointTargetPosition(client_id, lf_joints[1], lf_poses[1], sim.simx_opmode_oneshot)
- rec = sim.simxSetJointTargetPosition(client_id, lf_joints[2], lf_poses[2], sim.simx_opmode_oneshot)
- curr_time = time.time()
- # print("curr time :", curr_time - start_time)
- # 完成模拟
- sim.simxStopSimulation(client_id, sim.simx_opmode_blocking)
- sim.simxFinish(client_id)
- else:
- print('Failed connecting to remote API server')
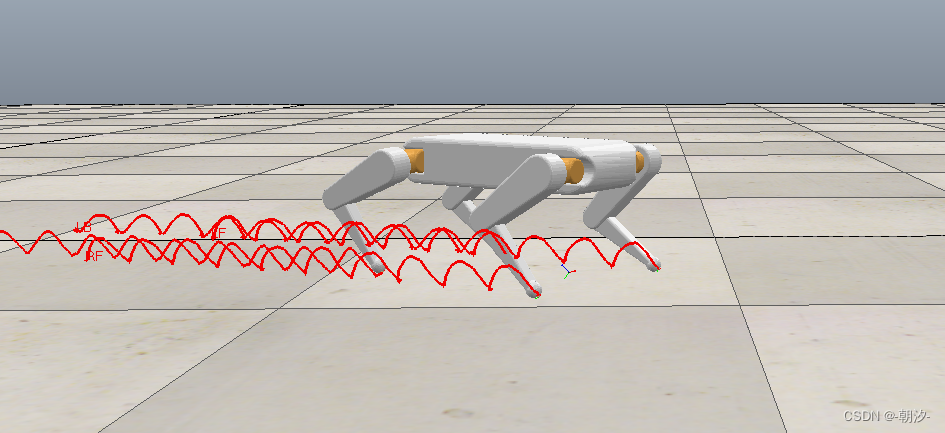
显示足端轨迹
1. 打开shape编辑模式,并在vertex编辑模式下选择节点,在添加dummy

将dummy移动到腿部object下
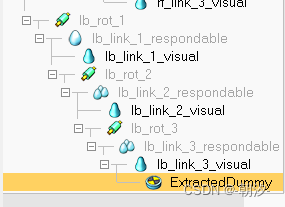
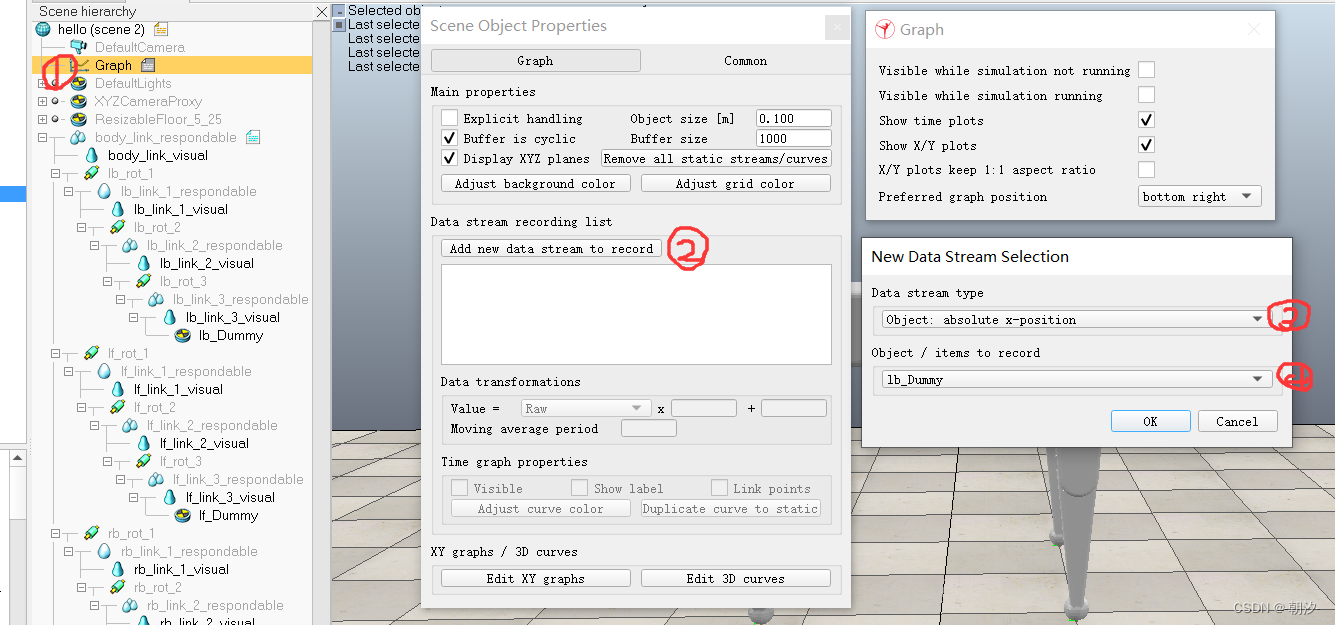
2. 添加图用于创建curve

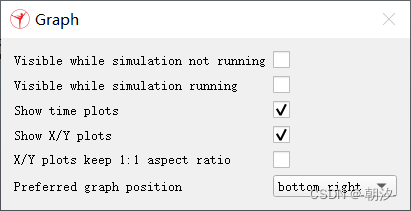
3. 设置3D Curve


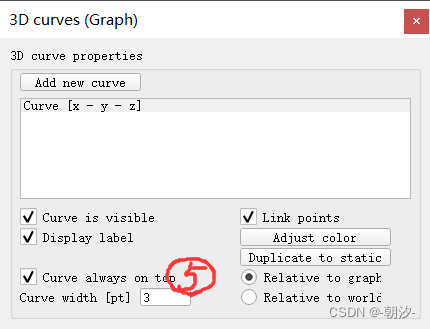


4. 修改位置控制速度上限(将速度上限修改为500)

步态控制
utils.py
- import sim
- import numpy as np
- def start_simulation():
- sim.simxFinish(-1)
- # 开启套接字与server进行通信
- clientID = sim.simxStart('127.0.0.1', 19999, True, True, 5000, 5)
- if clientID != -1:
- print('Connected to remote API server with ClientID ', clientID)
- # 开始模拟
- sim.simxStartSimulation(clientID, sim.simx_opmode_oneshot)
- return clientID
- else:
- return -1
- def get_joints(client_id):
- # 机器人电机力矩参数
- rotation_forces = [
- # RB
- [500, 500, 500],
- # RF
- [500, 500, 500],
- # LB
- [500, 500, 500],
- # LF
- [500, 500, 500]
- ]
- # 获取机器人关节对象句柄
- rec, rb_rot_1 = sim.simxGetObjectHandle(client_id, 'rb_rot_1', sim.simx_opmode_blocking)
- rec, rb_rot_2 = sim.simxGetObjectHandle(client_id, 'rb_rot_2', sim.simx_opmode_blocking)
- rec, rb_rot_3 = sim.simxGetObjectHandle(client_id, 'rb_rot_3', sim.simx_opmode_blocking)
- rec, rf_rot_1 = sim.simxGetObjectHandle(client_id, 'rf_rot_1', sim.simx_opmode_blocking)
- rec, rf_rot_2 = sim.simxGetObjectHandle(client_id, 'rf_rot_2', sim.simx_opmode_blocking)
- rec, rf_rot_3 = sim.simxGetObjectHandle(client_id, 'rf_rot_3', sim.simx_opmode_blocking)
- rec, lb_rot_1 = sim.simxGetObjectHandle(client_id, 'lb_rot_1', sim.simx_opmode_blocking)
- rec, lb_rot_2 = sim.simxGetObjectHandle(client_id, 'lb_rot_2', sim.simx_opmode_blocking)
- rec, lb_rot_3 = sim.simxGetObjectHandle(client_id, 'lb_rot_3', sim.simx_opmode_blocking)
- rec, lf_rot_1 = sim.simxGetObjectHandle(client_id, 'lf_rot_1', sim.simx_opmode_blocking)
- rec, lf_rot_2 = sim.simxGetObjectHandle(client_id, 'lf_rot_2', sim.simx_opmode_blocking)
- rec, lf_rot_3 = sim.simxGetObjectHandle(client_id, 'lf_rot_3', sim.simx_opmode_blocking)
- # 设置电机力矩
- rec = sim.simxSetJointForce(client_id, rb_rot_1, rotation_forces[0][0], sim.simx_opmode_blocking)
- rec = sim.simxSetJointForce(client_id, rb_rot_2, rotation_forces[0][1], sim.simx_opmode_blocking)
- rec = sim.simxSetJointForce(client_id, rb_rot_3, rotation_forces[0][2], sim.simx_opmode_blocking)
- rec = sim.simxSetJointForce(client_id, rf_rot_1, rotation_forces[1][0], sim.simx_opmode_blocking)
- rec = sim.simxSetJointForce(client_id, rf_rot_2, rotation_forces[1][1], sim.simx_opmode_blocking)
- rec = sim.simxSetJointForce(client_id, rf_rot_3, rotation_forces[1][2], sim.simx_opmode_blocking)
- rec = sim.simxSetJointForce(client_id, lb_rot_1, rotation_forces[2][0], sim.simx_opmode_blocking)
- rec = sim.simxSetJointForce(client_id, lb_rot_2, rotation_forces[2][1], sim.simx_opmode_blocking)
- rec = sim.simxSetJointForce(client_id, lb_rot_3, rotation_forces[2][2], sim.simx_opmode_blocking)
- rec = sim.simxSetJointForce(client_id, lf_rot_1, rotation_forces[3][0], sim.simx_opmode_blocking)
- rec = sim.simxSetJointForce(client_id, lf_rot_2, rotation_forces[3][1], sim.simx_opmode_blocking)
- rec = sim.simxSetJointForce(client_id, lf_rot_3, rotation_forces[3][2], sim.simx_opmode_blocking)
- return [rb_rot_1, rb_rot_2, rb_rot_3], \
- [rf_rot_1, rf_rot_2, rf_rot_3], \
- [lb_rot_1, lb_rot_2, lb_rot_3], \
- [lf_rot_1, lf_rot_2, lf_rot_3]
- def leg_inverse_kine(x, y, z):
- """
- 求四足机器人单条腿的逆运动学,输入足端位置,返回单腿关节的旋转的角度
- """
- # h,hu和hl分别是单条腿杆件的长度
- h = 0.15
- hu = 0.35
- hl = 0.382
- dyz = np.sqrt(y ** 2 + z ** 2)
- lyz = np.sqrt(dyz ** 2 - h ** 2)
- gamma_yz = -np.arctan(y / z)
- gamma_h_offset = -np.arctan(h / lyz)
- gamma = gamma_yz - gamma_h_offset
- lxzp = np.sqrt(lyz ** 2 + x ** 2)
- n = (lxzp ** 2 - hl ** 2 - hu ** 2) / (2 * hu)
- beta = -np.arccos(n / hl)
- alfa_xzp = -np.arctan(x / lyz)
- alfa_off = np.arccos((hu + n) / lxzp)
- alfa = alfa_xzp + alfa_off
- return gamma, alfa, beta
- def pose_control(roll, pitch, yaw, pos_x, pos_y, pos_z):
- """
- 输入
- """
- b = 0.4
- l = 0.8
- w = 0.7
- # 基座的高度
- h = 0.732
- # 转换角度
- R = roll * np.pi / 180
- P = pitch * np.pi / 180
- Y = yaw * np.pi / 180
- pos = np.mat([pos_x, pos_y, pos_z]).T
- # 定义旋转矩阵
- rotx = np.mat([[1, 0, 0],
- [0, np.cos(R), -np.sin(R)],
- [0, np.sin(R), np.cos(R)]])
- roty = np.mat([[np.cos(P), 0, -np.sin(P)],
- [0, 1, 0],
- [np.sin(P), 0, np.cos(P)]])
- rotz = np.mat([[np.cos(Y), -np.sin(Y), 0],
- [np.sin(Y), np.cos(Y), 0],
- [0, 0, 1]])
- rot_mat = rotx * roty * rotz
- # 基座位置
- body_struct = np.mat([[l / 2, b / 2, h],
- [l / 2, -b / 2, h],
- [-l / 2, b / 2, h],
- [-l / 2, -b / 2, h]]).T
- # 足端位置
- footpoint_struct = np.mat([[l / 2, w / 2, 0],
- [l / 2, -w / 2, 0],
- [-l / 2, w / 2, 0],
- [-l / 2, -w / 2, 0]]).T
- leg_pose = np.mat(np.zeros((3, 4)))
- for i in range(4):
- leg_pose[:, i] = -pos - rot_mat * body_struct[:, i] + footpoint_struct[:, i]
- return np.squeeze(np.array(leg_pose[:, 3])), np.squeeze(np.array(leg_pose[:, 0])), \
- np.squeeze(np.array(leg_pose[:, 1])), np.squeeze(np.array(leg_pose[:, 2]))
- def cycloid(dt: float, period: float = 1.0, xs: float = -0.1, xf: float = 0.1, zs: float = -0.582, h: float = 0.1):
- """
- 计算摆线上在给定时间t处的坐标。
- 参数:
- t (float): 当前时间点
- Ts (float): 摆线运动总时间,默认为1.0
- xs (float): 起始x坐标,默认为-0.1
- xf (float): 终点x坐标,默认为0.1
- zs (float): 起始z坐标,默认为-0.582
- h (float): 摆线垂直位移,默认为0.1
- 返回:
- tuple[float, float]: xep和zep的坐标值
- """
- sigma = 2 * np.pi * dt / period
- x_p = (xf - xs) * ((sigma - np.sin(sigma)) / (2 * np.pi)) + xs
- y_p = h * (1 - np.cos(sigma)) / 2 + zs
- return x_p, y_p
- if __name__ == '__main__':
- for pos in pose_control(30, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0.732):
- print(pos)
main.py
- import time
- from utils import *
- walk_period = 1.0
- trot_period = 0.4
- gait = 1
- def cal_phase(dt, T, factor, zs = -0.482, h = 0.15):
- if dt < T * factor:
- return cycloid(dt, period=T * factor, zs=zs, h=h)
- else:
- return 0.1 - 0.2 / (T * (1 - factor)) * (dt - T * factor), zs
- def walk_gait(dt):
- zs = -0.482
- h = 0.15
- lb_dt = dt % walk_period
- rf_dt = (dt + 0.25) % walk_period
- rb_dt = (dt + 0.5) % walk_period
- lf_dt = (dt + 0.75) % walk_period
- lb_pos = cal_phase(lb_dt, T=walk_period, factor=0.25, zs=zs, h=h)
- rf_pos = cal_phase(rf_dt, T=walk_period, factor=0.25, zs=zs, h=h)
- rb_pos = cal_phase(rb_dt, T=walk_period, factor=0.25, zs=zs, h=h)
- lf_pos = cal_phase(lf_dt, T=walk_period, factor=0.25, zs=zs, h=h)
- return lb_pos, rf_pos, rb_pos, lf_pos
- def trot_gait(dt):
- zs = -0.482
- h = 0.1
- dt_1 = dt % trot_period
- dt_2 = (dt + 0.2) % trot_period
- pos_1 = cal_phase(dt_1, T=trot_period, factor=0.5, zs=zs, h=h)
- pos_2 = cal_phase(dt_2, T=trot_period, factor=0.5, zs=zs, h=h)
- return pos_1, pos_2
- if __name__ == '__main__':
- # 连接到V-REP服务器
- clientID = start_simulation()
- # 检查连接是否成功
- if clientID != -1:
- joints = get_joints(clientID)
- rb_joints = joints[0]
- rf_joints = joints[1]
- lb_joints = joints[2]
- lf_joints = joints[3]
- timeout = 60
- start_time = time.time()
- curr_time = start_time
- sim_start_time, sim_curr_time = None, None
- lb_pos, rf_pos, rb_pos, lf_pos = None, None, None, None
- # 获取仿真时间
- while curr_time - start_time < timeout:
- res, sim_curr_time = sim.simxGetFloatSignal(clientID, 'time', sim.simx_opmode_oneshot)
- if res == sim.simx_return_ok:
- if sim_start_time is None:
- sim_start_time = sim_curr_time
- print("time ", sim_curr_time - sim_start_time)
- if sim_start_time:
- dt = sim_curr_time - sim_start_time
- if gait == 0:
- # dt = (sim_curr_time - sim_start_time) % walk_period
- lb_pos, rf_pos, rb_pos, lf_pos = walk_gait(dt)
- elif gait == 1:
- # dt = (sim_curr_time - sim_start_time) % trot_period
- pos_1, pos_2 = trot_gait(dt)
- lb_pos = pos_1
- rf_pos = pos_1
- rb_pos = pos_2
- lf_pos = pos_2
- # 从足端位置求解关节角度
- rb_pose = leg_inverse_kine(rb_pos[0], -0.15, rb_pos[1])
- rf_pose = leg_inverse_kine(rf_pos[0], -0.15, rf_pos[1])
- lb_pose = leg_inverse_kine(lb_pos[0], -0.15, lb_pos[1])
- lf_pose = leg_inverse_kine(lf_pos[0], -0.15, lf_pos[1])
- rec = sim.simxSetJointTargetPosition(clientID, rb_joints[0], -rb_pose[0], sim.simx_opmode_oneshot)
- rec = sim.simxSetJointTargetPosition(clientID, rb_joints[1], rb_pose[1], sim.simx_opmode_oneshot)
- rec = sim.simxSetJointTargetPosition(clientID, rb_joints[2], rb_pose[2], sim.simx_opmode_oneshot)
- rec = sim.simxSetJointTargetPosition(clientID, rf_joints[0], rf_pose[0], sim.simx_opmode_oneshot)
- rec = sim.simxSetJointTargetPosition(clientID, rf_joints[1], rf_pose[1], sim.simx_opmode_oneshot)
- rec = sim.simxSetJointTargetPosition(clientID, rf_joints[2], rf_pose[2], sim.simx_opmode_oneshot)
- rec = sim.simxSetJointTargetPosition(clientID, lb_joints[0], -lb_pose[0], sim.simx_opmode_oneshot)
- rec = sim.simxSetJointTargetPosition(clientID, lb_joints[1], lb_pose[1], sim.simx_opmode_oneshot)
- rec = sim.simxSetJointTargetPosition(clientID, lb_joints[2], lb_pose[2], sim.simx_opmode_oneshot)
- rec = sim.simxSetJointTargetPosition(clientID, lf_joints[0], lf_pose[0], sim.simx_opmode_oneshot)
- rec = sim.simxSetJointTargetPosition(clientID, lf_joints[1], lf_pose[1], sim.simx_opmode_oneshot)
- rec = sim.simxSetJointTargetPosition(clientID, lf_joints[2], lf_pose[2], sim.simx_opmode_oneshot)
- # 停止仿真并断开与V-REP的连接
- sim.simxStopSimulation(clientID, sim.simx_opmode_oneshot)
- sim.simxFinish(clientID)
- else:
- print("无法连接到V-REP")
walk步态
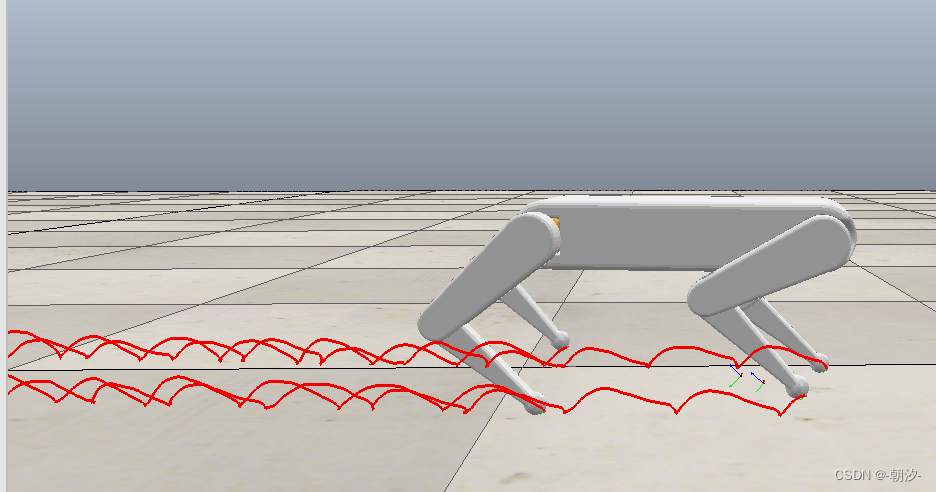
trot步态
-
相关阅读:
Qt国际化
2024年 Flutter 面试题大全(持续更新中)
linux卸载jdk方法
Web3.0与区块链有何不同?现在处于哪个阶段?
table的基本用法
C++学习记录1
对比Python,PySpark 大数据处理其实更香
docker-compose部署mysql
Taichi 加速 Python 中图像处理
【C++】之内存管理 - new/delete
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_40679158/article/details/134252751
