-
BFS专题8 中国象棋-马-无障碍
题目:
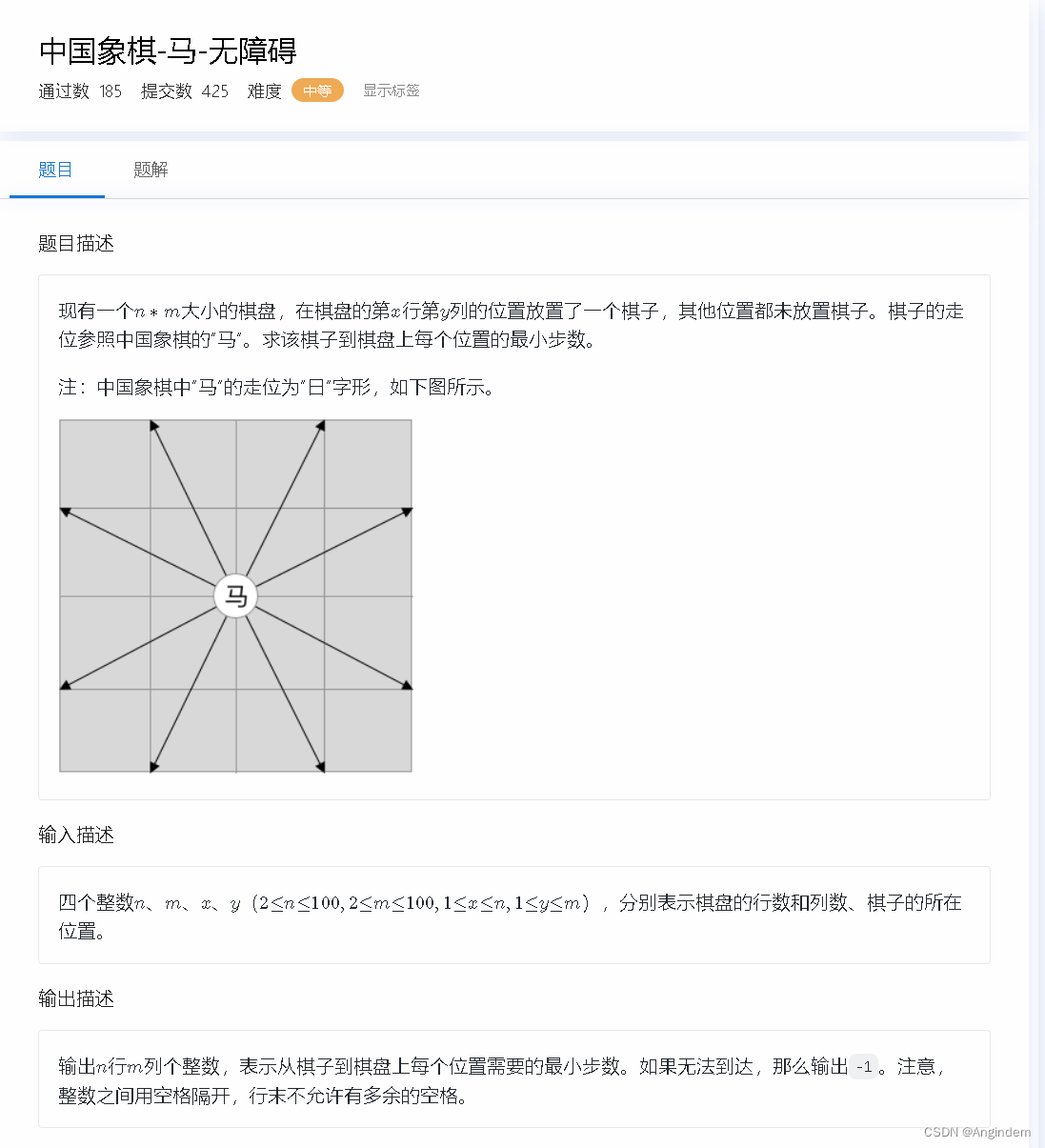
样例:
输入 3 3 2 1输出 - 3 2 1
- 0 -1 4
- 3 2 1

思路:
单纯的BFS走一遍即可,只是方向坐标的移动变化,需要变化一下。
代码详解如下:
- #include
- #include
- #include
- #include
- #include
- #include
- #define endl '\n'
- #define x first
- #define y second
- #define mk make_pair
- #define YES puts("YES")
- #define NO puts("NO")
- #define umap unordered_map
- #define All(x) x.begin(),x.end()
- #pragma GCC optimize(3,"Ofast","inline")
- #define IOS std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0)
- using namespace std;
- const int N = 500;
- using PII = pair<int,int>;
- // 象棋走动的方向
- int dx[8] = {2,2,-2,-2,1,-1,1,-1};
- int dy[8] = {1,-1,1,-1,2,2,-2,-2};
- int g[N][N],n,m; // 象棋棋盘以及大小
- bool st[N][N]; // 标记是否走过当前坐标
- PII now; // 当前象棋坐标
- inline bool isRun(int &x,int &y)
- {
- return (x > 0 && x <= n && y > 0 && y <= m && !st[x][y]);
- }
- inline void BFS()
- {
- // 初始化坐标所对应的最少步数
- memset(g,-1,sizeof g);
- g[now.x][now.y] = 0; // 初始化起点步数为 0
- int step = 0;
- queue
q; - q.emplace(now);
- while(q.size())
- {
- int sz = q.size();
- while(sz--)
- {
- PII tem = q.front();
- q.pop(); // 取出当前坐标
- st[tem.x][tem.y] = true; // 标记当前坐标
- g[tem.x][tem.y] = step; // 存储当前坐标所对应的最少步数
- // 尝试往各个方向坐标走动
- for(int i = 0;i < 8;++i)
- {
- int bx = tem.x + dx[i];
- int by = tem.y + dy[i];
- if(isRun(bx,by))
- {
- // 如果符合走动条件
- // 存储下一个走动的坐标,并标记
- q.emplace(mk(bx,by));
- st[bx][by] = true;
- }
- }
- }
- ++step;
- }
- }
- // 打印棋盘各个坐标所对应的最少步数
- inline void PrintG()
- {
- for(int i = 1;i <= n;++i)
- {
- for(int j = 1;j <= m;++j)
- {
- if(j > 1) cout << ' '; // 控制输入格式
- cout << g[i][j];
- }
- cout << endl;
- }
- }
- inline void solve()
- {
- cin >> n >> m >> now.x >> now.y; // 输入所对应的信息
- BFS(); // BFS 搜索各个坐标所对应的最少步数
- PrintG(); // 输出答案
- }
- int main()
- {
- // freopen("a.txt", "r", stdin);
- IOS;
- int _t = 1;
- // cin >> _t;
- while (_t--)
- {
- solve();
- }
- return 0;
- }
最后提交:
-
相关阅读:
maven集成nexus伺服服务实现项目快速自动化构建与发布
uwb人员定位系统:人员轨迹实时定位
如何防止服务器网站被黑
Opencv项目实战:06 文档扫描仪
林业数据可视化新篇章:山海鲸软件看板设计心得
产品经理需要熟悉的网站
LCD屏硬件调光的几种方式
Games104现代游戏引擎入门-lecture13游戏引擎的引擎工具链基础
青岛大学数据结构与算法——第2章
关于AD9777芯片的说明以及FPGA控制实现 I
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/hacker_51/article/details/133942254