-
【数据结构】线性表(八)队列:顺序队列及其基本操作(初始化、判空、判满、入队、出队、存取队首元素)
堆栈Stack 和 队列Queue是两种非常重要的数据结构,两者都是特殊的线性表:
- 对于堆栈,所有的插入和删除(以至几乎所有的存取)都是在表的同一端进行;
- 对于队列,所有的插入都是在表的一端进行,所有的删除(以至几乎所有的存取)都是在表的另一端进行。
一、队列
1. 定义
队列是一种操作受限的线性表,对于它的所有插入都在表的一端进行,所有的删除(以至几乎所有的存取)都在表的另一端进行,且这些操作又都是按照先进先出(FIFO)的原则进行的。进行删除的一端称为队头(front),进行插入的一端称为队尾(rear)。没有元素的队列称为空队列(简称空队)。
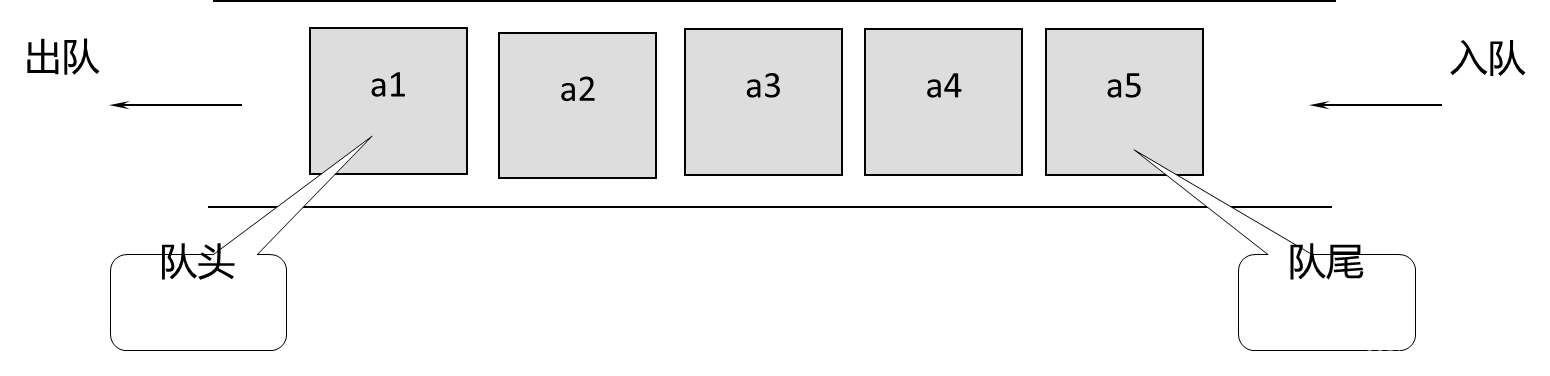
队列就像生活中排队购物,新来的人只能加入队尾(假设不允许插队),购物结束后先离开的总是队头(假设无人中途离队)。也就是说,先加入队列的成员总是先离开队列,因此队列被称为先进先出(First In First Out)的线性表,简称为FIFO表。如图,在空队列中依次加入元素a1,a2,a3,a4,a5,出队次序仍然是a1,a2,a3,a4,a5 .2. 基本操作
-
队列是受限的线性表,其基本操作包括
IsEmpty(): 判断队列是否为空;isFull():判断队列是否为满;enqueue():向队尾添加元素(入队);dequeue():删除队首元素(出队);peek():获取队首的元素值(存取);
-
同普通线性表一样,队列也可以用顺序存储和链接存储两种方式来实现:
二、顺序队列
用顺序存储方式实现的堆栈称为顺序队列。
0. 顺序表
参考前文:顺序表及其基本操作
1. 头文件和常量
#include#define MAX_SIZE 100 - 1
- 2
-
头文件
stdio.h用于输入输出操作 -
通过
#define指令定义了一个常量MAX_SIZE,它表示顺序队列中数组的最大容量为100。
2. 队列结构体
typedef struct { int data[MAX_SIZE]; // 存储队列元素的数组 int front; // 队头指针 int rear; // 队尾指针 } SequentialQueue;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 整型数组
data,用于存储队列元素; front和rear分别表示队头指针和队尾指针。
3. 队列的初始化
void initSequentialQueue(SequentialQueue* queue) { queue->front = -1; queue->rear = -1; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
initSequentialQueue函数:初始化顺序队列,它将队头指针和队尾指针都设置为 -1,表示队列为空。4. 判断队列是否为空
int isSequentialQueueEmpty(SequentialQueue* queue) { return queue->front == -1; }- 1
- 2
- 3
isSequentialQueueEmpty函数用于判断顺序队列是否为空:如果队头指针为 -1,表示队列为空,返回 1;否则返回 0。5. 判断队列是否已满
int isSequentialQueueFull(SequentialQueue* queue) { return (queue->rear + 1) % MAX_SIZE == queue->front; }- 1
- 2
- 3
isSequentialQueueFull函数用于判断顺序队列是否已满。6. 入队
void enqueueSequentialQueue(SequentialQueue* queue, int data) { if (isSequentialQueueFull(queue)) { printf("Error: Queue is full\n"); return; } if (isSequentialQueueEmpty(queue)) { queue->front = 0; queue->rear = 0; } else { queue->rear = (queue->rear + 1) % MAX_SIZE; } queue->data[queue->rear] = data; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 判断队列是否已满
- 如果已满则打印错误信息并返回;
- 否则,根据队列是否为空进行不同的处理:
- 如果队列为空,将队头指针和队尾指针都设置为 0;
- 否则,将队尾指针移动到下一个位置,并将元素存储到队尾指针所指向的位置。
7. 出队
int dequeueSequentialQueue(SequentialQueue* queue) { if (isSequentialQueueEmpty(queue)) { printf("Error: Queue is empty\n"); return -1; } int data = queue->data[queue->front]; if (queue->front == queue->rear) { queue->front = -1; queue->rear = -1; } else { queue->front = (queue->front + 1) % MAX_SIZE; } return data; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 判断队列是否为空
- 如果为空则打印错误信息并返回 -1;
- 否则,取出队头元素,并根据队头指针是否等于队尾指针来判断队列是否为空:
- 如果队列为空,将队头指针和队尾指针都设置为 -1;
- 否则,将队头指针移动到下一个位置。
8. 存取队首元素
int peekSequentialQueue(SequentialQueue* queue) { if (isSequentialQueueEmpty(queue)) { printf("Error: Queue is empty\n"); return -1; } return queue->data[queue->front]; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
peekSequentialQueue函数用于获取队首元素,即返回队列中队头指针所指向的元素的值。首先判断队列是否为空,如果为空则打印错误信息并返回 -1。9. 主函数
int main() { SequentialQueue queue; initSequentialQueue(&queue); enqueueSequentialQueue(&queue, 10); enqueueSequentialQueue(&queue, 20); enqueueSequentialQueue(&queue, 30); printf("Peek: %d\n", peekSequentialQueue(&queue)); printf("Dequeued: %d\n", dequeueSequentialQueue(&queue)); printf("Dequeued: %d\n", dequeueSequentialQueue(&queue)); printf("Peek: %d\n", peekSequentialQueue(&queue)); enqueueSequentialQueue(&queue, 40); printf("Peek: %d\n", peekSequentialQueue(&queue)); return 0; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 声明了一个
SequentialQueue类型的变量queue - 调用
initSequentialQueue函数对其进行初始化 - 调用
enqueueSequentialQueue函数三次,依次将元素 10、20、30 入队 - 使用
peekSequentialQueue函数获取队首元素并打印 - 调用
dequeueSequentialQueue函数两次,依次将队列中的元素出队并打印 - 再次使用
peekSequentialQueue函数获取队首元素并打印 - 调用
enqueueSequentialQueue函数将元素 40 入队,并使用peekSequentialQueue函数获取队首元素并打印

10. 代码整合
#include#define MAX_SIZE 100 // 定义顺序队列 typedef struct { int data[MAX_SIZE]; // 存储队列元素的数组 int front; // 队头指针 int rear; // 队尾指针 } SequentialQueue; // 初始化顺序队列 void initSequentialQueue(SequentialQueue* queue) { queue->front = -1; queue->rear = -1; } // 判断顺序队列是否为空 int isSequentialQueueEmpty(SequentialQueue* queue) { return queue->front == -1; } // 判断顺序队列是否已满 int isSequentialQueueFull(SequentialQueue* queue) { return (queue->rear + 1) % MAX_SIZE == queue->front; } // 入队 void enqueueSequentialQueue(SequentialQueue* queue, int data) { if (isSequentialQueueFull(queue)) { printf("Error: Queue is full\n"); return; } if (isSequentialQueueEmpty(queue)) { queue->front = 0; queue->rear = 0; } else { queue->rear = (queue->rear + 1) % MAX_SIZE; } queue->data[queue->rear] = data; } // 出队 int dequeueSequentialQueue(SequentialQueue* queue) { if (isSequentialQueueEmpty(queue)) { printf("Error: Queue is empty\n"); return -1; } int data = queue->data[queue->front]; if (queue->front == queue->rear) { queue->front = -1; queue->rear = -1; } else { queue->front = (queue->front + 1) % MAX_SIZE; } return data; } // 获取队首元素 int peekSequentialQueue(SequentialQueue* queue) { if (isSequentialQueueEmpty(queue)) { printf("Error: Queue is empty\n"); return -1; } return queue->data[queue->front]; } // 示例代码的主函数 int main() { SequentialQueue queue; initSequentialQueue(&queue); enqueueSequentialQueue(&queue, 10); enqueueSequentialQueue(&queue, 20); enqueueSequentialQueue(&queue, 30); printf("Peek: %d\n", peekSequentialQueue(&queue)); printf("Dequeued: %d\n", dequeueSequentialQueue(&queue)); printf("Dequeued: %d\n", dequeueSequentialQueue(&queue)); printf("Peek: %d\n", peekSequentialQueue(&queue)); enqueueSequentialQueue(&queue, 40); printf("Peek: %d\n", peekSequentialQueue(&queue)); return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
-
相关阅读:
Spark
56. 合并区间
ElementUI增删改的实现及表单验证
创建springboot(五)文章发表项目
Autosar实践——诊断配置(DaVinci Configuration)
高阶导数简介
Vue.js 框架源码与进阶 - Virtual DOM 的实现原理
判断二叉树是否相等
神经网络控制simulink仿真,神经网络控制系统仿真
git学习笔记之用命令行解决冲突
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_63834988/article/details/133944246
