-
【论文解读】QLORA: Efficient Finetuning of Quantized LLMs
一.介绍
1.1 创新点
-
(1)4位NormalFloat,一种信息理论上最优的正态分布数据量化数据类型,比4位整数和4位浮点数产生更好的经验结果。
-
(2)双量化。
-
(3)Paged Optimizers,使用NVIDIA统一内存,以避免处理具有长序列长度的小批量时发生的梯度检查点内存峰值。
1.2 原理
将预训练模型量化为4位,然后添加一组可学习的Low-rank Adapter权重[28],这些权重通过量化权重的反向传播梯度进行调整

1.3 前置知识
1.3.1 逐块k位量化

为了防止异常值问题,一种常见的方法是将输入张量分成独立量化的块,每个块都有自己的量化常数c。避免因为离群值导致量化效果不佳
1.3.2 LoRA
- 是一种通过使用一小组可训练参数(通常称为适配器)来降低内存需求的方法,同时不更新保持固定的完整模型参数。
- 随机梯度下降过程中的梯度通过固定的预训练模型权值传递给适配器,适配器进行更新以优化损失函数。LoRA通过一个额外的因式投影来增强一个线性投影

二.QLORA
2.1 4位NormalFloat量化
NormalFloat (NF)数据类型建立在Quantile Quantization的基础上,这是一种信息理论上最优的数据类型,可确保每个量化bin具有从输入张量分配的相同数量的值。
(1)估计理论的
 分位数N(0, 1)获得k位分布为正态分布分位数量化数据类型,
分位数N(0, 1)获得k位分布为正态分布分位数量化数据类型,(2)把这个数据类型和其数值正则化到(−1,1)范围内,
(3)量化输入权重张量通过改变绝对最大尺度范围来实现正则化(−1,1)。
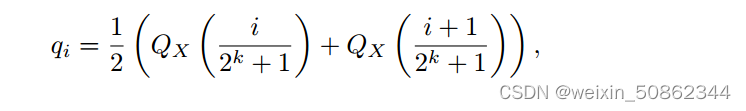 其中
其中 是标准正态分布N(0,1)的分位数函数。对称k位量化的一个问题是,这种方法没有零的精确表示,这是量化填充和其他零值元素而没有错误的重要性质。
是标准正态分布N(0,1)的分位数函数。对称k位量化的一个问题是,这种方法没有零的精确表示,这是量化填充和其他零值元素而没有错误的重要性质。解决对称量化问题:
负部分为
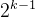 ,正部分为
,正部分为 ,然后我们统一这些qi集合并删除两个集合中出现的两个零中的一个。我们将结果数据类型命名为在每个量化中具有相同预期值的k位NormalFloat (NFk),因为该数据类型对于零中心正态分布数据在信息理论上是最优的
,然后我们统一这些qi集合并删除两个集合中出现的两个零中的一个。我们将结果数据类型命名为在每个量化中具有相同预期值的k位NormalFloat (NFk),因为该数据类型对于零中心正态分布数据在信息理论上是最优的2.2 双量化 Double Quantization
2.2.1 为什么需要双量化:内存开销大
虽然精确的4位量化需要很小的块大小,但它也有相当大的内存开销。
e.g. 使用32位常量,W的块大小为64,量化常量平均为每个参数添加32/64 = 0.5位。
2.2.2 实现过程
- 双量化将第一次量化的量化常数
 作为第二次量化的输入。
作为第二次量化的输入。 - 使用块大小为256的8位浮点数进行第二次量化,因为8位量化没有观察到性能下降。 在量化之前从c2中减去平均值,使值在零附近居中,并利用对称量化。
这第二步产生量子化的量化常数
 和第二级量化常数
和第二级量化常数 。
。2.3 分页优化器 Paged Optimizers
在GPU偶尔内存不足的情况下,在CPU和GPU之间进行自动页对页传输,以实现无错误的GPU处理。
2.4 QLoRA
使用单个LoRA适配器在量化基本模型中定义单个线性层的QLORA如下
 其中doubleDequant(·)定义为:
其中doubleDequant(·)定义为:
三.QLoRA代码实现
3.1 NF4类型和双量化
冗长的代码中其中这么几句便可以在transforms中使用NF4类型和双量化

3.1.1 在transforms中使用
- from transformers import BitsAndBytesConfig
- import torch
- model_name =""
- nf4_config = BitsAndBytesConfig(
- load_in_4bit=True,
- bnb_4bit_quant_type="nf4",
- bnb_4bit_use_double_quant=True,
- bnb_4bit_compute_dtype=torch.bfloat16
- )
- model_nf4 = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_name, quantization_config=nf4_config)
3.1.2 底层实现过程
在transformers\utils\bitsandbytes.py的_replace_with_bnb_linear中

在bitsandbytes这个库中
- class LinearNF4(Linear4bit):
- ''' Implements the NF4 data type.
- Constructs a quantization data type where each bin has equal area under a standard normal distribution N(0, 1) that
- is normalized into the range [-1, 1].
- For more information read the paper: QLoRA: Efficient Finetuning of Quantized LLMs (https://arxiv.org/abs/2305.14314)
- Implementation of the NF4 data type in bitsandbytes can be found in the `create_normal_map` function in
- the `functional.py` file: https://github.com/TimDettmers/bitsandbytes/blob/main/bitsandbytes/functional.py#L236.
- '''
- def __init__(self, input_features, output_features, bias=True, compute_dtype=None, compress_statistics=True,device=None):
- super().__init__(input_features, output_features, bias, compute_dtype, compress_statistics, 'nf4', device)
调用了父类的构造方法
- class Linear4bit(nn.Linear):
- def __init__(self, input_features, output_features, bias=True, compute_dtype=None, compress_statistics=True, quant_type='fp4',device=None):
- super().__init__(input_features, output_features, bias, device)
- self.weight = Params4bit(self.weight.data, requires_grad=False, compress_statistics=compress_statistics, quant_type=quant_type)
- self.compute_dtype = compute_dtype
- self.compute_type_is_set = False
权重通过Params4bit进行压缩
- class Params4bit(torch.nn.Parameter):
- def __new__(cls, data=None, requires_grad=True, quant_state=None, blocksize=64, compress_statistics=True, quant_type='fp4'):
- if data is None:
- data = torch.empty(0)
- self = torch.Tensor._make_subclass(cls, data, requires_grad)
- self.blocksize = blocksize
- self.compress_statistics = compress_statistics
- self.quant_type = quant_type
- self.quant_state = quant_state
- self.data = data
- return self
- def cuda(self, device):
- w = self.data.contiguous().half().cuda(device)
- w_4bit, quant_state = bnb.functional.quantize_4bit(w, blocksize=self.blocksize, compress_statistics=self.compress_statistics, quant_type=self.quant_type)
- self.data = w_4bit
- self.quant_state = quant_state
- return self
quantize_4bit最终也是通过调取二进制文件实现若干不同类型之间的变化
-
-
相关阅读:
数据结构与算法知识点总结(5)查找树
使用 Win2D 实现融合效果
动态规划求 x 轴上相距最远的两个相邻点 java 代码实现
一文教你如何快速备考云计算HCIE 3.0 !
Ubuntu系统之管理文件权限一
YII项目在Docker中运行缓慢
CMake Tutorial 巡礼(7)_打包一个安装文件
SSM+基于SSM的智慧社区宠物医院 毕业设计-附源码211621
【自然语言处理】关系抽取 —— CoIn 讲解
java中常用的集合
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_50862344/article/details/133917723