-
AI项目十七:ResNet50训练部署教程
若该文为原创文章,转载请注明原文出处。
ResNet50训练主要还是想部署到RK3568开发板上,先记录下训练和转成ONNX模型过程。
一、 Resnet50简介
ResNet50网络是2015年由微软实验室的何恺明提出,获得ILSVRC2015图像分类竞赛第一名。在ResNet网络提出之前,传统的卷积神经网络都是将一系列的卷积层和池化层堆叠得到的,但当网络堆叠到一定深度时,就会出现退化问题。 残差网络的特点是容易优化,并且能够通过增加相当的深度来提高准确率。其内部的残差块使用了跳跃连接,缓解了在深度神经网络中增加深度带来的梯度消失问题。

二、数据集下载
本教程以车辆分类算法为例,数据集的百度网盘下载链接为:
https://pan.baidu.com/s/1pkYm9AA3s3WDM7GecShlbQ 提取码:6666解压完成后得到以下两个文件夹:

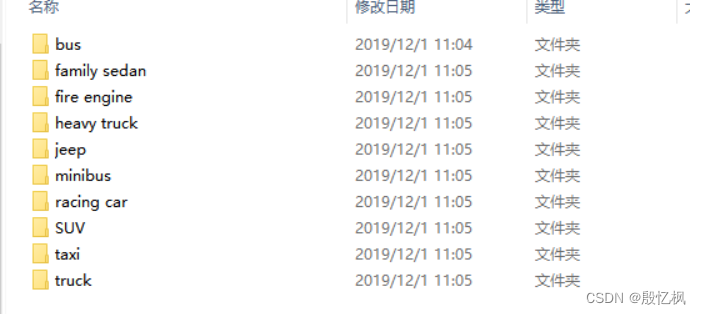
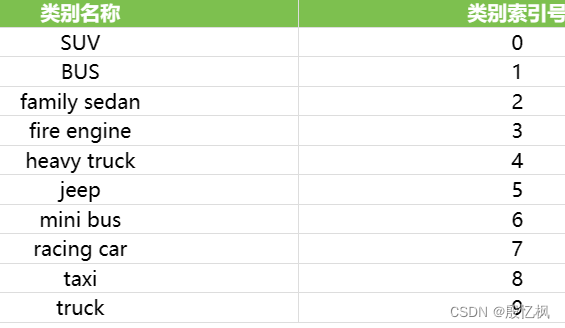
打开可以看到一共10类汽车:
三、环境搭建
1、创建虚拟环境
conda create -n Resnet50_env python=3.8 -y2、激活环境
conda activate Resnet50_env注意:使用的是CPU版本,电脑无GPU
3、安装环境
- pip install numpy
- pip install torch
- pip install torchvision
- pip install matplotlib
至此,环境安装完成,开始训练
四、 ResNet50图像分类训练
直接上源码:train.py
- # -#-coding:utf-8 -*-
- import os
- import numpy as np
- import torch
- import torch.nn as nn
- import torch.nn.functional as F
- import torch.optim as optim
- import torchvision
- from torch.autograd.variable import Variable
- from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
- from torchvision import datasets, transforms
- import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
- from PIL import ImageFile
- ImageFile.LOAD_TRUNCATED_IMAGES = True
- # 2.定义超参数
- BATCH_SIZE = 16 # 每批处理的数据
- DEVICE = torch.device('cuda:0' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu') # 放在cuda或者cpu上训练
- EPOCHS = 15 # 训练数据集的轮次
- modellr = 1e-3
- # 3.构建pipeline,对图像做处理
- pipeline = transforms.Compose([
- # 分辨率重置为256
- transforms.Resize(256),
- # 对加载的图像作归一化处理, 并裁剪为[224x224x3]大小的图像(因为这图片像素不一致直接统一)
- transforms.CenterCrop(224),
- # 将图片转成tensor
- transforms.ToTensor(),
- # 正则化,模型出现过拟合现象时,降低模型复杂度
- transforms.Normalize(mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406], std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
- ])
- # 图片路径(训练图片和测试图片的)
- base_dir_train = 'G:/enpei_Project_Code/22_Resnet50_bus/1.data/datasets/train'
- base_dir_val = 'G:/enpei_Project_Code/22_Resnet50_bus/1.data/datasets/val'
- # 4. 加载数据集
- train_dataset = datasets.ImageFolder(root=base_dir_train, transform=pipeline)
- print("train_dataset=" + repr(train_dataset[1][0].size()))
- print("train_dataset.class_to_idx=" + repr(train_dataset.class_to_idx))
- # 创建训练集的可迭代对象,一个batch_size地读取数据,shuffle设为True表示随机打乱顺序读取
- train_loader = DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, shuffle=True)
- # 测试集
- val_dataset = datasets.ImageFolder(root=base_dir_val, transform=pipeline)
- print(val_dataset)
- print("val_dataset=" + repr(val_dataset[1][0].size()))
- print("val_dataset.class_to_idx=" + repr(val_dataset.class_to_idx))
- # 创建测试集的可迭代对象,一个batch_size地读取数据
- val_loader = DataLoader(val_dataset, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, shuffle=True)
- # 获得一批测试集的数据
- images, labels = next(iter(val_loader))
- print(images.shape)
- print(labels.shape)
- # 损失函数,交叉熵损失函数
- criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
- # 使用预训练模型
- resnet_model = torchvision.models.resnet50(pretrained=True)
- num_ftrs = resnet_model.fc.in_features
- resnet_model.fc = nn.Linear(num_ftrs, 10)
- resnet_model.to(DEVICE)
- # 选择简单暴力的Adam优化器,学习率调低
- optimizer = optim.Adam(resnet_model.parameters(), lr=modellr)
- #optimizer = optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr = 0.01)
- train_loss_list = []
- train_accuracy_list = []
- test_loss_list = []
- test_accuracy_list = []
- train_iteration_list = []
- test_iteration_list = []
- best_val_acc = 0
- # 定义训练方法
- def train(model, device, train_loader, optimizer, epoch):
- iteration = 0
- train_correct = 0.0
- model.train()
- sum_loss = 0.0
- total_num = len(train_loader.dataset)
- print(total_num, len(train_loader))
- for batch_idx, (data, target) in enumerate(train_loader):
- # 获取数据与标签
- data, target = Variable(data).to(device), Variable(target).to(device)
- # 梯度清零
- optimizer.zero_grad()
- # 计算损失
- output = model(data)
- loss = criterion(output, target)
- #反向传播
- loss.backward()
- #更新参数
- optimizer.step()
- print_loss = loss.data.item()
- sum_loss += print_loss
- _, train_predict = torch.max(output.data, 1)
- if torch.cuda.is_available():
- train_correct += (train_predict.cuda() == target.cuda()).sum()
- else:
- train_correct += (train_predict == target).sum()
- accuracy = (train_correct / total_num) * 100
- print("Epoch: %d , Batch: %3d , Loss : %.8f,train_correct:%d , train_total:%d , accuracy:%.6f" % (
- epoch + 1, batch_idx + 1, loss.item(), train_correct, total_num, accuracy))
- # 存在集合画图
- if (epoch + 1) == EPOCHS: # 只画出最后一个epoch时候的准确度变化曲线
- iteration += 1
- train_loss_list.append(loss.item())
- train_iteration_list.append(iteration)
- train_accuracy_list.append(accuracy)
- # 定义验证方法
- def val(model, device, val_loader, epoch):
- print("=====================预测开始=================================")
- iteration = 0
- model.eval()
- test_loss = 0.0
- correct = 0.0
- total_num = len(val_loader.dataset)
- print(total_num, len(val_loader))
- with torch.no_grad():
- for data, target in val_loader:
- data, target = Variable(data).to(device), Variable(target).to(device)
- output = model(data)
- loss = criterion(output, target)
- _, pred = torch.max(output.data, 1)
- if torch.cuda.is_available():
- correct += torch.sum(pred.cuda() == target.cuda())
- else:
- correct += torch.sum(pred == target)
- print_loss = loss.data.item()
- test_loss += print_loss
- acc = correct / total_num * 100
- avg_loss = test_loss / len(val_loader)
- """
- 因为调用这个方法的时候就是每次结束训练一次之后调用
- """
- # iteration += 1
- # 存入集合准备画图
- test_loss_list.append(avg_loss)
- test_accuracy_list.append(acc)
- test_iteration_list.append(epoch)
- print('\nVal set: Average loss: {:.4f}, Accuracy: {}/{} ({:.6f}%)\n'.format(
- avg_loss, correct, len(val_loader.dataset), acc))
- global best_val_acc
- if acc > best_val_acc:
- best_val_acc = acc
- print("Best Accuracy:{:.6f}%".format(best_val_acc))
- torch.save(resnet_model.state_dict(), 'best-{:.6f}.model.pth'.format(best_val_acc)) # 保存模型
- # 训练
- for epoch in range(EPOCHS):
- train(resnet_model, DEVICE, train_loader, optimizer, epoch)
- val(resnet_model, DEVICE, val_loader, epoch)
- #torch.save(resnet_model, 'model.pth') # 保存模型
- # 可视化测试机的loss和accuracy
- plt.figure(1)
- plt.plot(test_iteration_list, test_loss_list)
- plt.title("ResNet50 test loss")
- plt.ylabel("loss")
- plt.xlabel("Number of test iteration")
- plt.show()
- plt.figure(2)
- plt.plot(test_iteration_list, test_accuracy_list)
- plt.title("ResNet50 test accuracy")
- plt.xlabel("Number of test iteration")
- plt.ylabel("accuracy")
- plt.show()
- # 可视化训练集loss和accuracy
- plt.figure(3)
- plt.plot(train_iteration_list, train_loss_list)
- plt.title("ResNet50 train loss")
- plt.xlabel("Number of train iteration")
- plt.ylabel("accuracy")
- plt.show()
- plt.figure(4)
- plt.plot(train_iteration_list, train_accuracy_list)
- plt.title("ResNet50 train accuracy")
- plt.xlabel("Number of train iteration")
- plt.ylabel("accuracy")
- plt.show()
代码需要注意的是数据集路径,用的是绝对路径,自行修改。
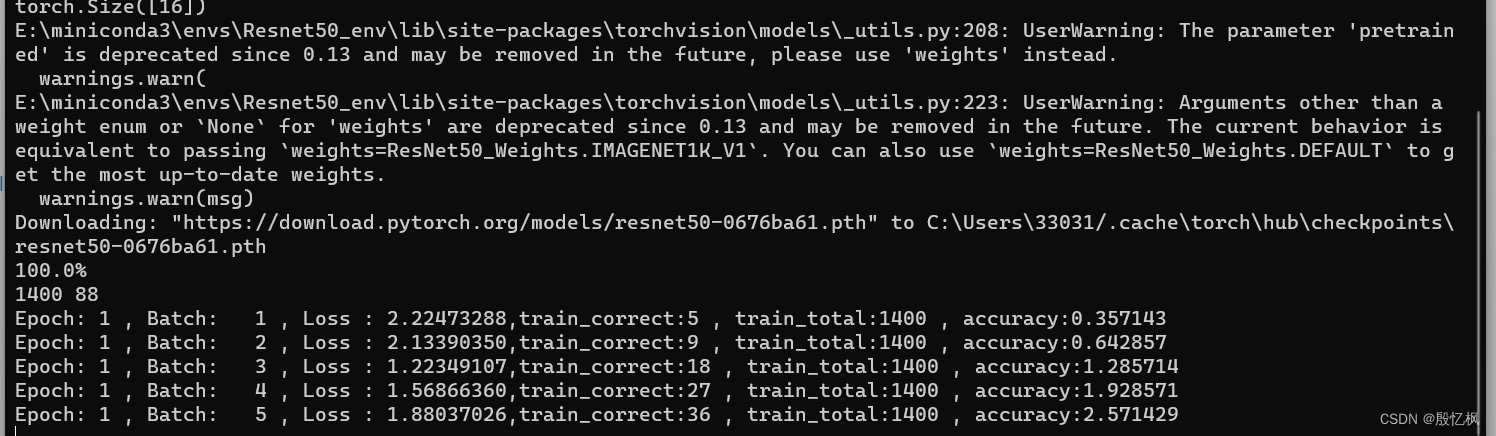
代码训练的epoch是15,等待一段时间吧!
五、测试模型
测试模型脚本predict.py
- import os
- from PIL import Image
- import cv2
- import torch
- import torch.nn as nn
- from torch.autograd.variable import Variable
- import torchvision
- from torchvision import transforms
- # 0-SUV, 1-BUS, 2-family sedan, 3-fire engine, 4-heavy truck,
- # 5-jeep, 6-mini bus, 7-racing car, 8-taxi, 9-truck
- def predict_single_image():
- MODEL_SAVE_FILE = 'best-82.000000.model.pth'
- device = torch.device('cuda:0' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
- model = torchvision.models.resnet50()
- num_ftrs = model.fc.in_features
- model.fc = nn.Linear(num_ftrs, 10)
- model.to(device)
- model.load_state_dict(torch.load(MODEL_SAVE_FILE,map_location='cpu'))
- model = torch.nn.DataParallel(model,device_ids=[0])
- model.eval()
- img = cv2.imread("test.jpg")
- img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
- image = Image.fromarray(img)
- pipeline = transforms.Compose([
- # 分辨率重置为256
- transforms.Resize(256),
- # 对加载的图像作归一化处理, 并裁剪为[224x224x3]大小的图像(因为这图片像素不一致直接统一)
- transforms.CenterCrop(224),
- # 将图片转成tensor
- transforms.ToTensor(),
- # 正则化,模型出现过拟合现象时,降低模型复杂度
- transforms.Normalize(mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406], std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
- ])
- image = pipeline(image)
- image = image.unsqueeze(0)
- print(image.shape)
- input_var = Variable(image).float().to(device)
- output = model(input_var)
- print("output:", output)
- print("output.shape:", output.shape)
- soft_output = torch.softmax(output, dim=-1)
- print("soft_output:", soft_output)
- percent, predicted = torch.max(soft_output.data, 1)
- print("percent:", percent)
- print("predicted:", predicted)
- '''
- USE_GPU = torch.cuda.is_available()
- if USE_GPU:
- inputs = inputs.cuda()
- if not os.path.exists(MODEL_SAVE_FILE):
- print('can not find model save file.')
- exit()
- else:
- if USE_GPU:
- model.load_state_dict(torch.load(MODEL_SAVE_FILE))
- else:
- model.load_state_dict(torch.load(MODEL_SAVE_FILE, map_location=lambda storage, loc: storage))
- outputs = model(inputs)
- _, prediction_tensor = torch.max(outputs.data, 1)
- if USE_GPU:
- prediction = prediction_tensor.cpu().numpy()[0][0]
- print('predict: ', prediction)
- print('this is {}'.format(classes_name[prediction]))
- else:
- prediction = prediction_tensor.numpy()[0][0]
- print('predict: ', prediction)
- print('this is {}'.format(classes_name[prediction]))
- '''
- predict_single_image()
运行
python predict.py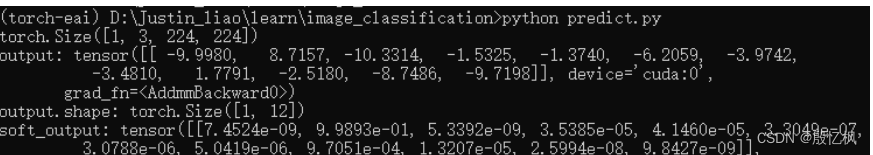
六、模型转换
1、转成onnx模型
pth_to_onnx.py
- import torch
- import torch.nn as nn
- import torchvision
- from torch.autograd.variable import Variable
- MODEL_SAVE_FILE = 'best-82.000000.model.pth'
- device = torch.device('cuda:0' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
- model = torchvision.models.resnet50()
- num_ftrs = model.fc.in_features
- model.fc = nn.Linear(num_ftrs, 10)
- model.to(device)
- model.load_state_dict(torch.load(MODEL_SAVE_FILE,map_location='cpu'))
- batch_size = 1 #批处理大小
- # #set the model to inference mode
- model.eval()
- d_input = Variable(torch.randn(1, 3, 224, 224))
- export_onnx_file = "10class_ResNet50.onnx" # 目的ONNX文件名
- torch.onnx.export(model, d_input, export_onnx_file, opset_version=12,verbose=True)
这里需要注意的 是opset_version算子,rk3568用12
python pth_to_onnx.py
onnx模型是我需要的,打算部署到rk3568,需要把onnx模型转成rknn模型,后续测试
2、转成pt模型
pth_to_pt.py
- import torch
- import torch.nn as nn
- import torchvision
- MODEL_SAVE_FILE = 'best-82.000000.model.pth'
- device = torch.device('cuda:0' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
- model = torchvision.models.resnet50()
- num_ftrs = model.fc.in_features
- model.fc = nn.Linear(num_ftrs, 10)
- model.to(device)
- model.load_state_dict(torch.load(MODEL_SAVE_FILE,map_location='cpu'))
- model.eval()
- example = torch.rand(1,3,224,224).to(device)
- traced_script_module = torch.jit.trace(model, example)
- traced_script_module.save('./10class_ResNet50.pt')
运行转换:
python pth_to_pt.py如有侵权,或需要完整代码,请及时联系博主。
-
相关阅读:
【Qt】Unicode编码作用 ,以及在Qt中的理解
java毕业设计民宿管理平台mybatis+源码+调试部署+系统+数据库+lw
第30章 市场营销
R语言实战应用案例:论文篇(二)-特殊盒须图绘制
spring框架漏洞整理(Spring Data漏洞)
Redis整理
SpringBoot集成Mybatis-Plus
TCP协议
日更【系统架构设计师知识总结2】指令系统(结合真题)
使用Python进行钻石价格分析
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_38807927/article/details/133915602
