-
basic_sr介绍
pytorch基础知识和basicSR中用到的语法
1.Sampler类与4种采样方式
一文弄懂Pytorch的DataLoader, DataSet, Sampler之间的关系
pytorch源码阅读(三)Sampler类与4种采样方式下面代码是自定义的一个采样器:
ratio控制扩充数据集的倍数
num_replicas是进程数,一般是world_size
rank: 当前进程的rank其实目的就是把数据集的索引划分为num_replicas组,供每个进程(process) 处理
至于ratio,是为了使每个epoch训练的数据增多,for saving time when restart the dataloader after each epochimport math import torch from torch.utils.data.sampler import Sampler class EnlargedSampler(Sampler): """Sampler that restricts data loading to a subset of the dataset. Modified from torch.utils.data.distributed.DistributedSampler Support enlarging the dataset for iteration-based training, for saving time when restart the dataloader after each epoch Args: dataset (torch.utils.data.Dataset): Dataset used for sampling. num_replicas (int | None): Number of processes participating in the training. It is usually the world_size. rank (int | None): Rank of the current process within num_replicas. ratio (int): Enlarging ratio. Default: 1. """ def __init__(self, dataset, num_replicas, rank, ratio=1): self.dataset = dataset self.num_replicas = num_replicas self.rank = rank self.epoch = 0 self.num_samples = math.ceil(len(self.dataset) * ratio / self.num_replicas) self.total_size = self.num_samples * self.num_replicas def __iter__(self): # deterministically shuffle based on epoch g = torch.Generator() g.manual_seed(self.epoch) indices = torch.randperm(self.total_size, generator=g).tolist() dataset_size = len(self.dataset) indices = [v % dataset_size for v in indices] # subsample indices = indices[self.rank:self.total_size:self.num_replicas] assert len(indices) == self.num_samples return iter(indices) def __len__(self): return self.num_samples def set_epoch(self, epoch): self.epoch = epoch- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
测试一下:
import numpy as np if __name__ == "__main__": data = np.arange(20).tolist() en_sample = EnlargedSampler(data, 2, 0) en_sample.set_epoch(1) for i in en_sample: print(i) print('\n------------------\n') en_sample = EnlargedSampler(data, 2, 1) en_sample.set_epoch(1) # 设置为同一个epoch . rank=0或者1时生成的index是互补的 # 或者不用设置,默认为0即可。 for i in en_sample: print(i)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
结果:

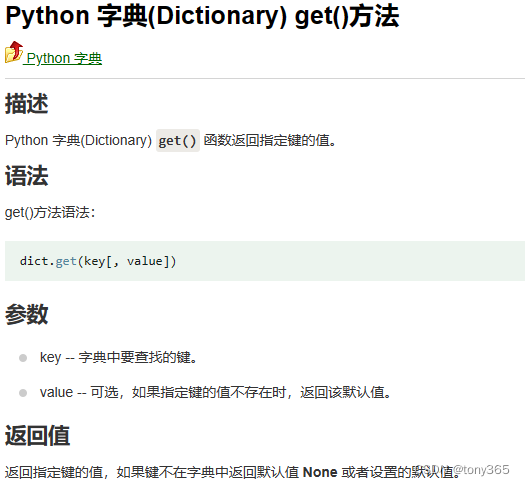
2.python dict的get方法使用
3.prefetch_dataloader.py
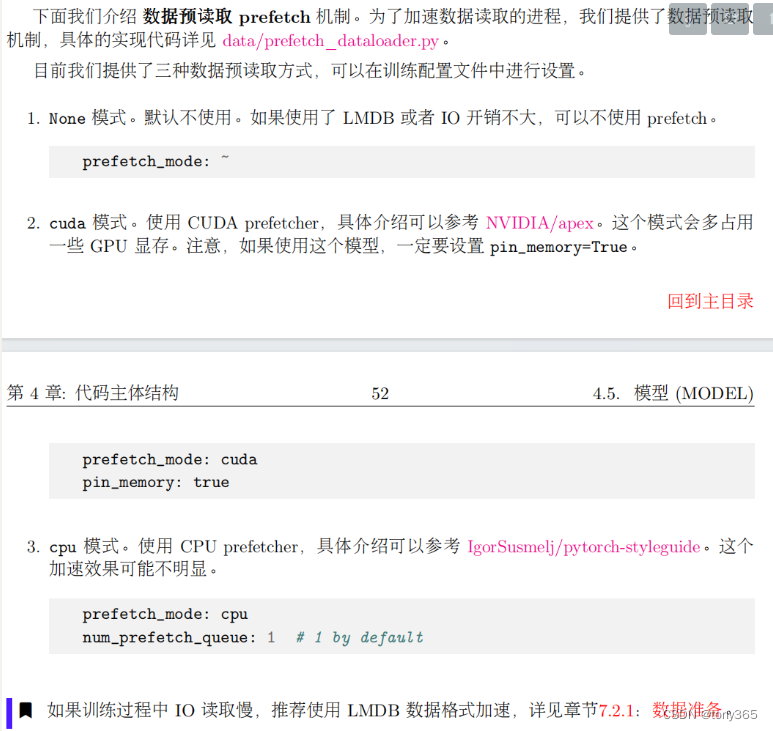
载入本批数据的时候,预先载入下一批数据。主要看next函数
import queue as Queue import threading import torch from torch.utils.data import DataLoader class PrefetchGenerator(threading.Thread): """A general prefetch generator. Reference: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/7323664/python-generator-pre-fetch Args: generator: Python generator. num_prefetch_queue (int): Number of prefetch queue. """ def __init__(self, generator, num_prefetch_queue): threading.Thread.__init__(self) self.queue = Queue.Queue(num_prefetch_queue) self.generator = generator self.daemon = True self.start() def run(self): for item in self.generator: self.queue.put(item) self.queue.put(None) def __next__(self): next_item = self.queue.get() if next_item is None: raise StopIteration return next_item def __iter__(self): return self class PrefetchDataLoader(DataLoader): """Prefetch version of dataloader. Reference: https://github.com/IgorSusmelj/pytorch-styleguide/issues/5# TODO: Need to test on single gpu and ddp (multi-gpu). There is a known issue in ddp. Args: num_prefetch_queue (int): Number of prefetch queue. kwargs (dict): Other arguments for dataloader. """ def __init__(self, num_prefetch_queue, **kwargs): self.num_prefetch_queue = num_prefetch_queue super(PrefetchDataLoader, self).__init__(**kwargs) def __iter__(self): return PrefetchGenerator(super().__iter__(), self.num_prefetch_queue) class CPUPrefetcher(): """CPU prefetcher. Args: loader: Dataloader. """ def __init__(self, loader): self.ori_loader = loader self.loader = iter(loader) def next(self): try: return next(self.loader) except StopIteration: return None def reset(self): self.loader = iter(self.ori_loader) class CUDAPrefetcher(): """CUDA prefetcher. Reference: https://github.com/NVIDIA/apex/issues/304# It may consume more GPU memory. Args: loader: Dataloader. opt (dict): Options. """ def __init__(self, loader, opt): self.ori_loader = loader self.loader = iter(loader) self.opt = opt self.stream = torch.cuda.Stream() self.device = torch.device('cuda' if opt['num_gpu'] != 0 else 'cpu') self.preload() def preload(self): try: self.batch = next(self.loader) # self.batch is a dict except StopIteration: self.batch = None return None # put tensors to gpu with torch.cuda.stream(self.stream): for k, v in self.batch.items(): if torch.is_tensor(v): self.batch[k] = self.batch[k].to(device=self.device, non_blocking=True) def next(self): torch.cuda.current_stream().wait_stream(self.stream) # 等待下一批处理完毕 batch = self.batch # 赋值 self.preload() # 预先载入下一批 return batch def reset(self): self.loader = iter(self.ori_loader) self.preload()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
4. pytorch 并行和分布式训练
4.1 选择要使用的cuda
当我们的服务器上有多个GPU,我们应该指明我们使用的GPU是哪一块,如果我们不设置的话,tensor.cuda()方法会默认将tensor保存到第一块GPU上,等价于tensor.cuda(0),这将会导致爆出out of memory的错误。我们可以通过以下两种方式继续设置。
- 在文件最开始部分
#设置在文件最开始部分 import os os.environ["CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICE"] = "0,1,2" # 设置默认的显卡- 1
- 2
- 3
- 在命令行运行的时候设置
CUDA_VISBLE_DEVICE=0,1 python train.py # 使用0,1两块GPU- 1
4.2 DataParallel使用方法
常规使用方法
model = UNetSeeInDark() model._initialize_weights() gpus = [0,1,2,3] model = nn.DataParallel(model, device_ids=gpus) device = torch.device('cuda:0') model = model.to(device) # 如果不使用并行,只需要注释掉 model = nn.DataParallel(model, device_ids=gpus) # 如果要更改要使用的gpu, 更改gpus,和device中的torch.device('cuda:0')中的number即可- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
保存和载入
保存可以使用
# 因为model被DP wrap了,得先取出模型 save_model_path = os.path.join(save_model_dir, f'checkpoint_{epoch:05d}.pth') # torch.save(model.state_dict(), save_model_path) torch.save(model.module.state_dict(), save_model_path)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
然后载入模型:
model_copy.load_state_dict(torch.load(m_path, map_location=device))- 1
如果没有提出model.module进行保存
在载入的时候可能需要如下方式:checkpoint = torch.load(m_path) model_copy.load_state_dict({k.replace('module.', ''): v for k, v in checkpoint.items()})- 1
- 2
4.3 DistributedDataParallel
首先DataParallel是单进程多线程的方法,并且仅能工作在单机多卡的情况。而DistributedDataParallel方法是多进程,多线程的,并且适用与单机多卡和多机多卡的情况。即使在在单机多卡的情况下DistributedDataParallell也比DataParallel的速度更快。
目前还未深入理解:
深入理解Pytorch中的分布式训练
pytorch分布式训练
Pytorch中多GPU并行计算教程
PyTorch 并行训练极简 Demo5.wangdb 入门
直接参看:https://docs.wandb.ai/quickstart
最详细的介绍和入门5.1 sign up(https://wandb.ai/site)

5.2 安装和login
pip install wandb
wandb.login() 然后复制API key5.3 demo
import wandb import random # start a new wandb run to track this script wandb.init( # set the wandb project where this run will be logged project="my-awesome-project", # track hyperparameters and run metadata config={ "learning_rate": 0.02, "architecture": "CNN", "dataset": "CIFAR-100", "epochs": 10, } ) # simulate training epochs = 10 offset = random.random() / 5 for epoch in range(2, epochs): acc = 1 - 2 ** -epoch - random.random() / epoch - offset loss = 2 ** -epoch + random.random() / epoch + offset # log metrics to wandb wandb.log({"acc": acc, "loss": loss}) # [optional] finish the wandb run, necessary in notebooks5b1bb8a27da51a7375b4b52c24a82fe1807877f1 wandb.finish()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
运行之后:
wandb: Currently logged in as: wangty537. Use `wandb login --relogin` to force relogin wandb: Tracking run with wandb version 0.15.10 wandb: Run data is saved locally in D:\code\denoise\noise-synthesis-main\wandb\run-20230921_103737-j9ezjcqo wandb: Run `wandb offline` to turn off syncing. wandb: Syncing run wobbly-jazz-1 wandb: View project at https://wandb.ai/wangty537/my-awesome-project wandb: View run at https://wandb.ai/wangty537/my-awesome-project/runs/j9ezjcqo wandb: Waiting for W&B process to finish... (success). wandb: wandb: Run history: wandb: acc ▁▆▇██▇▇█ wandb: loss █▄█▁▅▁▄▁ wandb: wandb: Run summary: wandb: acc 0.88762 wandb: loss 0.12236 wandb: wandb: View run wobbly-jazz-1 at: https://wandb.ai/wangty537/my-awesome-project/runs/j9ezjcqo wandb: Synced 5 W&B file(s), 0 media file(s), 0 artifact file(s) and 0 other file(s) wandb: Find logs at: .\wandb\run-20230921_103737-j9ezjcqo\logs- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
然后可以在 https://wandb.ai/home 查看相关信息

https://docs.wandb.ai/quickstart 还介绍了更多高阶应用。
5.model and train
5.1 create model
利用注册机制
# create model model = build_model(opt) def build_model(opt): """Build model from options. Args: opt (dict): Configuration. It must contain: model_type (str): Model type. """ opt = deepcopy(opt) model = MODEL_REGISTRY.get(opt['model_type'])(opt) logger = get_root_logger() logger.info(f'Model [{model.__class__.__name__}] is created.') return model- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
5.2 opt中设置
model_type: SRModel scale: 2- 1
- 2
5.2 SRModel 类
BaseModel是基类
@MODEL_REGISTRY.register() class SRModel(BaseModel): xxx- 1
- 2
- 3
-
相关阅读:
三、C#—变量,表达式,运算符(3)
Java异常处理
idea中父工程Project创建
小白必看!上位机控制单片机原理
Coze入门指南:创建Bot时,如何写好人设与回复逻辑(Persona & Prompt)
使用cpolar发布群晖NAS博客网站 1(7.X版)
Swift中运算符相关内容
【Linux】apt update和apt upgrade
qt 画多边形,可以拖拽
第二章:人工智能深度学习教程-深度学习简介
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/tywwwww/article/details/133906794
