-
6、函数式编程--高级用法
7. 高级用法
基本数据类型优化
我们之前用到的很多Stream的方法由于都使用了泛型。所以涉及到的参数和返回值都是引用数据类型。
即使我们操作的是整数小数,但是实际用的都是他们的包装类。JDK5中引入的自动装箱和自动拆箱让我们在使用对应的包装类时就好像使用基本数据类型一样方便。但是你一定要知道装箱和拆箱肯定是要消耗时间的。虽然这个时间消耗很下。但是在大量的数据不断的重复装箱拆箱的时候,你就不能无视这个时间损耗了。
所以为了让我们能够对这部分的时间消耗进行优化。Stream还提供了很多专门针对基本数据类型的方法。
例如:mapToInt,mapToLong,mapToDouble,flatMapToInt,flatMapToDouble等。
private static void test27() { List<Author> authors = getAuthors(); authors.stream() .map(author -> author.getAge()) .map(age -> age + 10) .filter(age->age>18) .map(age->age+2) .forEach(System.out::println); authors.stream() .mapToInt(author -> author.getAge()) .map(age -> age + 10) .filter(age->age>18) .map(age->age+2) .forEach(System.out::println); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
分析图:

并行流
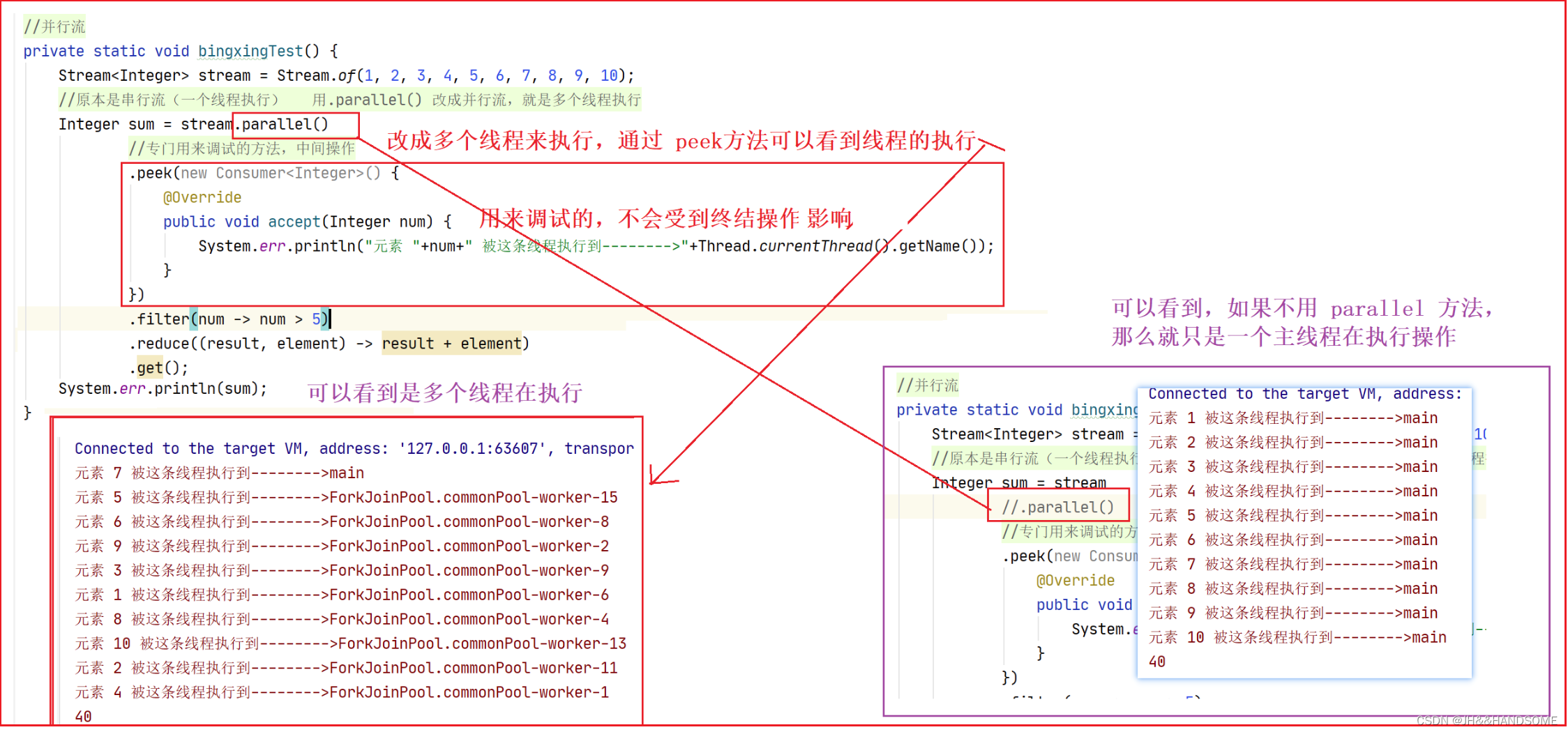
当流中有大量元素时,我们可以使用并行流去提高操作的效率。其实并行流就是把任务分配给多个线程去完全。如果我们自己去用代码实现的话其实会非常的复杂,并且要求你对并发编程有足够的理解和认识。而如果我们使用Stream的话,我们只需要修改一个方法的调用就可以使用并行流来帮我们实现,从而提高效率。
parallel方法可以把串行流转换成并行流。
private static void test28() { Stream<Integer> stream = Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10); Integer sum = stream.parallel() .peek(new Consumer<Integer>() { @Override public void accept(Integer num) { System.out.println(num+Thread.currentThread().getName()); } }) .filter(num -> num > 5) .reduce((result, ele) -> result + ele) .get(); System.out.println(sum); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
也可以通过parallelStream直接获取并行流对象。
List<Author> authors = getAuthors(); authors.parallelStream() .map(author -> author.getAge()) .map(age -> age + 10) .filter(age->age>18) .map(age->age+2) .forEach(System.out::println);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
分析图
parallel()
这个是集合转成stream流之后,stream流再调用parallel()方法变成并行流
parallelStream()
这个是集合转Stream流的时候,直接转成并行流

reduce求和分析图

-
相关阅读:
Python吴恩达深度学习作业21 -- 词向量的基本操作
Swager如何使用
uniapp开发微信小程序-用户授权登录和获取手机号码
SQL注入 Less24(二次注入)
python+nodejs+Vue宠物用品商城系统django源码介绍
2022年0903我的SpringBoot框架入门的第一个程序
时间的api
安装Homebrew安装Git(Mac)
理解并掌握C#的Channel:从使用案例到源码解读(一)
【目标检测】Faster R-CNN论文代码复现过程解读(含源代码)
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44411039/article/details/133880848