-
数学知识总结
素数
质数/素数定义
在大于1的整数中,如果只包含1和本身这两个约数,就被称为质数,或者叫素数
判断素数(试除法)
约数有一个重要的性质:
假设n代表数字,d代表n的一个约数
即d能整除n(d|n)
那么n/d为n的另外一个约数
即n/d能整除d(n/d | n)
简单思路:

模板:
- bool is_prime(int n)
- {
- if (n <= 1) return false;
- for (int i = 2; i <= n / i; i ++ )
- if (n % i == 0) return false;
- return true;
- }
866. 试除法判定质数

- #include
- #include
- #include
- using namespace std;
- bool is_prime(int n)
- {
- if (n <= 1) return false;
- for (int i = 2; i <= n / i; i ++ )
- if (n % i == 0) return false;
- return true;
- }
- int main()
- {
- int n;
- cin >> n;
- while (n --)
- {
- int a;
- cin >> a;
- if (is_prime(a)) puts("Yes");
- else puts("No");
- }
- return 0;
- }
分解质因数(试除法)
从小到大枚举所有的数
为什么不需要判断是否为质因子?
因为i是n的因子,即n是i的倍数,当枚举的到i时,n中已经不包含有2~i-1的因子,即i中也不包含,2~i-1的因子,所以i是质数
n中最多只包括一个大于sqrt(n)的质因子
如果最后剩下一个大于1的数,那就是大于sqrt(n)的质因子
模板:
-
- void divide(int n)
- {
- for (int i = 2; i <= n / i; i ++ )
- {
- if (n % i == 0)
- {
- int cnt = 0;
- while (n % i == 0)
- {
- cnt ++;
- n /= i;
- }
- printf("%d %d\n", i, cnt);
- }
- }
- if (n > 1) printf("%d %d\n", n, 1);
- printf("\n");
- }
-
acwing 867. 分解质因数

- #include
- #include
- using namespace std;
- void divide(int n)
- {
- for (int i = 2; i <= n / i; i ++ )
- {
- if (n % i == 0)
- {
- int cnt = 0;
- while (n % i == 0)
- {
- cnt ++;
- n /= i;
- }
- printf("%d %d\n", i, cnt);
- }
- }
- if (n > 1) printf("%d %d\n", n, 1);
- printf("\n");
- }
- int main()
- {
- int n;
- scanf("%d", &n);
- while (n --)
- {
- int a;
- scanf("%d", &a);
- divide(a);
- }
- return 0;
- }
埃氏筛法
算法思路:

模板:
- void gets_prime(int n)
- {
- for (int i = 2; i <= n; i ++ )
- {
- if (!st[i])
- {
- cnt ++;
- for (int j = i * 2; j <= n; j += i) st[j] = true;
- }
- }
- }
868. 筛质数

- #include
- #include
- #include
- using namespace std;
- const int N = 1000010;
- bool st[N];
- int cnt;
- void gets_prime(int n)
- {
- for (int i = 2; i <= n; i ++ )
- {
- if (!st[i])
- {
- cnt ++;
- for (int j = i * 2; j <= n; j += i) st[j] = true;
- }
- }
- }
- int main()
- {
- int n;
- cin >> n;
- gets_prime(n);
- cout << cnt << endl;
- }
线性筛(欧拉筛法)
算法思路:


模板:
- void oula(int n)
- {
- for (int i = 2; i <= n; i ++ )
- {
- if (!st[i]) primes[cnt ++] = i;
- for (int j = 0; primes[j] <= n / i; j ++ )
- {
- st[i * primes[j]] = true;
- if (i % primes[j] == 0) break;
- }
- }
- }
868. 筛质数

- #include
- #include
- #include
- using namespace std;
- const int N = 1000010;
- int primes[N];
- bool st[N];
- int cnt;
- void oula(int n)
- {
- for (int i = 2; i <= n; i ++ )
- {
- if (!st[i]) primes[cnt ++] = i;
- for (int j = 0; primes[j] <= n / i; j ++ )
- {
- st[i * primes[j]] = true;
- if (i % primes[j] == 0) break;
- }
- }
- }
- int main()
- {
- int n;
- cin >> n;
- oula(n);
- cout << cnt << endl;
- }
约数
试除法
思路:

模板:
- int res = 0;
- for (int i = 1; i <= n / i; i ++ )
- {
- if (n % i == 0)
- {
- if (i == n / i) res += 2;
- else res += 1;
- }
- }
—————————————这就是纯暴力解法,时间复杂度高——————————————
通过算数基本定理来求约数个数
思路:

模板:
- unordered_map<int, int> prime;//prime[质因子] = 次方
- for (int i = 2; i <= x / i; i ++ )//分解质因数
- {
- if (x % i == 0)
- {
- while (x % i == 0)
- {
- x /= i;
- prime[i] ++;
- }
- }
- }
- if (x > 1) prime[x] ++;
- long long res = 1;
- for (auto it = prime.begin(); it != prime.end(); it ++)
- {
- res = res * (prime->second + 1);
- }
870. 约数个数

输入样例:
- 3
- 2
- 6
- 8
代码展示:
- #include
- #include
- #include
- #include
- using namespace std;
- typedef long long LL;
- const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
- int main()
- {
- int n;
- scanf("%d",&n);
- unordered_map<int, int> prime;
- while (n --)
- {
- int x;
- cin >> x;
- for (int i = 2; i <= x / i; i ++ )
- {
- while (x % i == 0)
- {
- x /= i;
- prime[i] ++;
- }
- }
- if (x > 1) prime[x] ++;
- }
- LL res = 1;
- for (auto p : prime) res = res * (p.second + 1) % mod;
- printf("%lld\n",res);
- }
————————————————————next—————————————————————
通过算术基本定理求约数之和
思路:

模板:
- unordered_map<int, int> prime;//prime[质因子] = 次方
- for (int i = 2; i <= x / i; i ++ )//分解质因数
- {
- if (x % i == 0)
- {
- while (x % i == 0)
- {
- x /= i;
- prime[i] ++;
- }
- }
- }
- if (x > 1) prime[x] ++;
- long long res = 1;
- for (auto it = prime.begin(); it != prime.end(); it ++)
- {
- int a = it->first, b = it->second;
- long long t = 1;
- for (int i = 0; i < b; i ++) t = t * a + 1;
- res = res * t;
- }
871. 约数之和
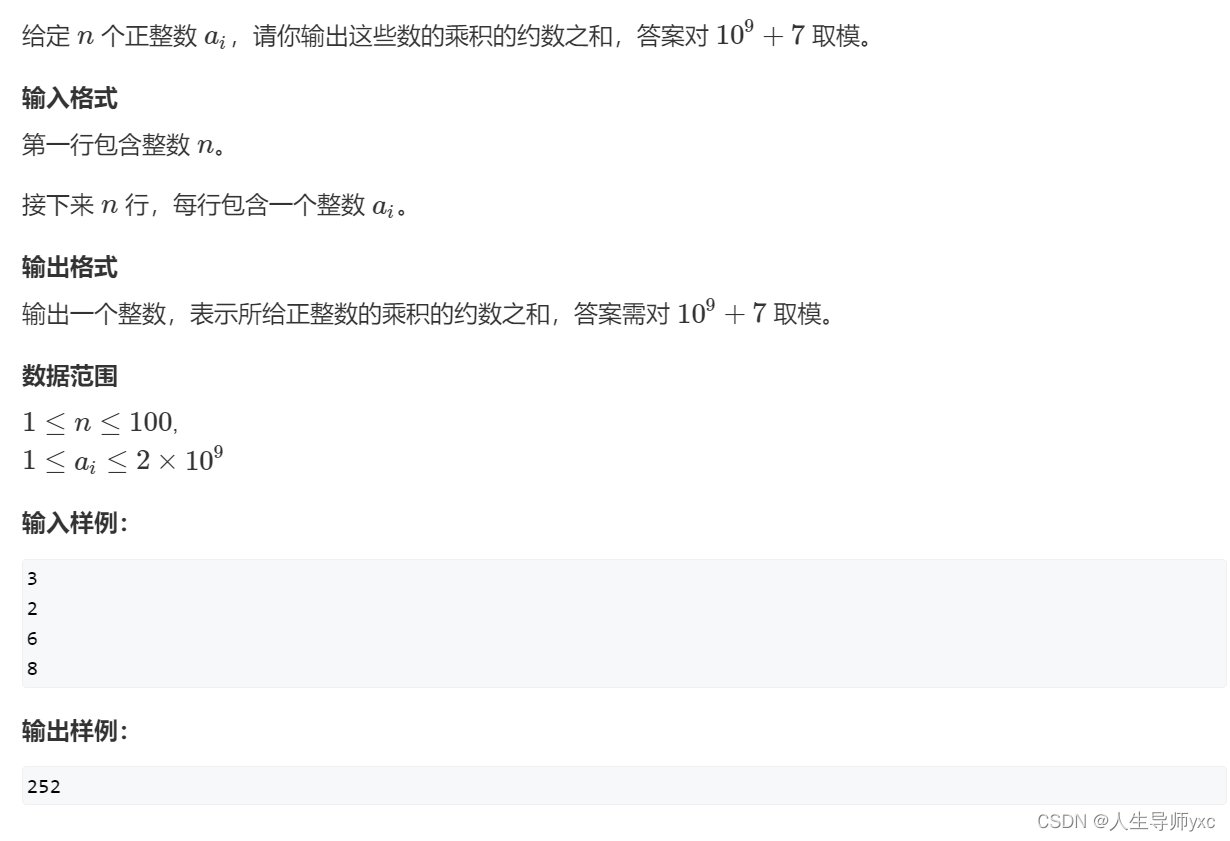
输入样例:
- 3
- 2
- 6
- 8
代码展示:
- #include
- #include
- #include
- #include
- using namespace std;
- typedef long long LL;
- const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
- int main()
- {
- int n;
- scanf("%d",&n);
- unordered_map<int, int> prime;
- while (n --)
- {
- int x;
- cin >> x;
- for (int i = 2; i <= x / i; i ++ )
- {
- while (x % i == 0)
- {
- prime[i] ++;
- x /= i;
- }
- }
- if (x > 1) prime[x] ++;
- }
- LL res = 1;
- for (auto p : prime)
- {
- int a = p.first, b = p.second;
- LL t = 1;
- for (int i = 0; i < b; i ++ ) t = (t * a + 1) % mod;
- res = res * t % mod;
- }
- cout << res << endl;
- }
———————————————————next—————————————————————
求最大公约数
思路:

模板:
- int gcd(int a, int b)
- {
- return b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a;
- }
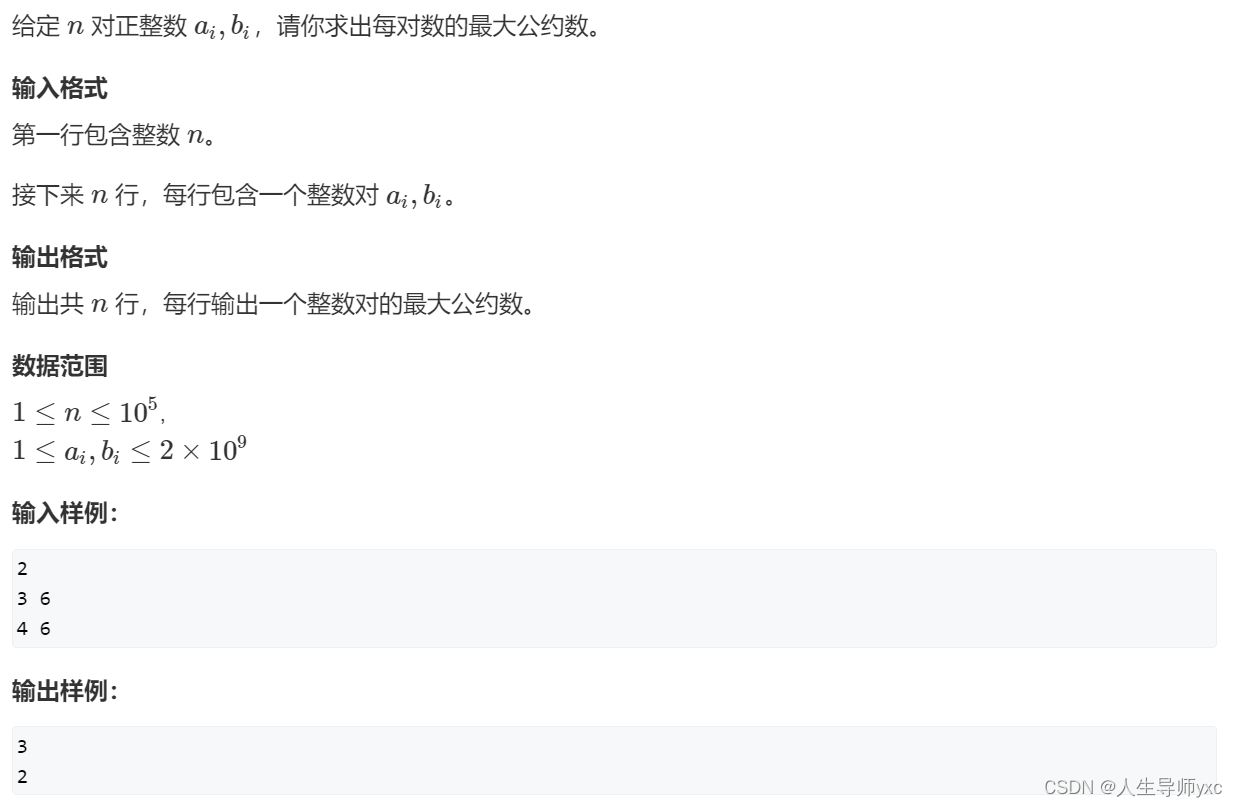
输入样例:
- 2
- 3 6
- 4 6
AcWing 872. 最大公约数
代码展示:
- #include
- #include
- #include
- using namespace std;
- int gcd(int a, int b)
- {
- return b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a;
- }
- int main()
- {
- int n;
- cin >> n;
- while (n --)
- {
- int a, b;
- cin >> a >> b;
- int ans = gcd(a, b);
- cout << ans << endl;
- }
- return 0;
- }
欧拉函数
基本思路:



模板(暴力):
- long long res = x;
- for (int i = 2; i <= x / i; i ++ )
- {
- if (x % i == 0)
- {
- while (x % i == 0) x /= i;
- res = res * (i - 1) / i;
- }
- }
- if (x > 1) res = res * (x - 1) / x;
Acwing873. 欧拉函数

- #include
- #include
- using namespace std;
- int main()
- {
- int n;
- cin >> n;
- while (n --)
- {
- int x;
- cin >> x;
- long long res = x;
- for (int i = 2; i <= x / i; i ++ )
- {
- if (x % i == 0)
- {
- while (x % i == 0) x /= i;
- res = res * (i - 1) / i;
- }
- }
- if (x > 1) res = res * (x - 1) / x;
- cout << res << endl;
- }
- }
模板(线性筛法):
- const int N = 1e6 + 10;
- int primes[N], cnt;
- bool st[N];
- int phi[N];
- void oula(int x)
- {
- phi[1] = 1;
- for (int i = 2; i <= x; i ++)
- {
- if (!st[i])
- {
- primes[cnt ++] = i;
- phi[i] = i - 1;
- }
- for (int j = 0; primes[j] <= x / i; j ++)
- {
- st[i * primes[j]] = true;
- phi[i * primes[j]] = primes[j] * phi[i] * (primes[j] - 1) / primes[j];
- if (i % primes[j] == 0)
- {
- phi[i * primes[j]] = primes[j] * phi[i];
- break;
- }
- }
- }
- }
运用线性筛算欧拉函数思路:

Acwing874. 筛法求欧拉函数

- #include
- #include
- using namespace std;
- const int N = 1e6 + 10;
- int primes[N], cnt;
- bool st[N];
- int phi[N];
- void oula(int x)
- {
- phi[1] = 1;
- for (int i = 2; i <= x; i ++)
- {
- if (!st[i])
- {
- primes[cnt ++] = i;
- phi[i] = i - 1;
- }
- for (int j = 0; primes[j] <= x / i; j ++)
- {
- st[i * primes[j]] = true;
- phi[i * primes[j]] = primes[j] * phi[i] * (primes[j] - 1) / primes[j];
- if (i % primes[j] == 0)
- {
- phi[i * primes[j]] = primes[j] * phi[i];
- break;
- }
- }
- }
- }
- int main()
- {
- int n;
- cin >> n;
- oula(n);
- long long res = 0;
- for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) res += phi[i];
- cout << res << endl;
- }
快速幂
基本思路:

模板:
- typedef long long LL;
- LL qmi(int a, int k, int p)
- {
- LL res = 1;
- while (k)
- {
- if (k & 1) res = res * a % p;
- k >>= 1;
- a = (LL)a * a % p;
- }
- return res;
- }
AcWing 875. 快速幂

- #include
- #include
- #include
- using namespace std;
- typedef long long LL;
- LL qmi(int a, int k, int p)
- {
- LL res = 1;
- while (k)
- {
- if (k & 1) res = res * a % p;
- k >>= 1;
- a = (LL)a * a % p;
- }
- return res;
- }
- int main()
- {
- int n;
- cin >> n;
- while (n --)
- {
- int a, k, p;
- cin >> a >> k >> p;
- cout << qmi(a, k, p) << endl;
- }
- }
快速幂求逆元思路:

 AcWing 876. 快速幂求逆元
AcWing 876. 快速幂求逆元 
- #include
- #include
- using namespace std;
- typedef long long LL;
- LL qmi(int a, int k, int p)
- {
- LL res = 1;
- while (k)
- {
- if (k & 1) res = res * a % p;
- k >>= 1;
- a = (LL) a * a % p;
- }
- return res;
- }
- int main()
- {
- int n;
- cin >> n;
- while (n --)
- {
- int a, p;
- cin >> a >> p;
- if (a % p) cout << qmi(a, p - 2, p) << endl;
- else puts("impossible");
- }
- }
扩展欧几里得
基本思路:

模板:
- int exgcd(int a, int b, int &x, int &y)
- {
- if (b == 0)
- {
- x = 1, y = 0;
- return a;
- }
- int d = exgcd(b, a % b, y, x);
- y = y - a / b * x;
- return d;
- }
Acwing877. 扩展欧几里得算法

- #include
- #include
- using namespace std;
- int exgcd(int a, int b, int &x, int &y)
- {
- if (b == 0)
- {
- x = 1, y = 0;
- return a;
- }
- int d = exgcd(b, a % b, y, x);
- y = y - a / b * x;
- return d;
- }
- int main()
- {
- int n;
- cin >> n;
- while (n --)
- {
- int a, b, x, y;
- cin >> a >> b;
- exgcd(a, b, x, y);
- cout << x << ' ' << y << endl;
- }
- }
裴蜀定理:
对任何整数a、b和它们的最大公约数d,关于未知数x和y的线性不定方程(称为裴蜀等式):若a,b是整数,且gcd(a,b)=d,那么对于任意的整数x,y,ax+by都一定是d的倍数,特别地,一定存在整数x,y,使ax+by=d成立。
 Acwing878. 线性同余方程
Acwing878. 线性同余方程
- #include
- #include
- using namespace std;
- typedef long long LL;
- int exgcd(int a, int b, int &x, int &y)
- {
- if (b == 0)
- {
- x = 1, y = 0;
- return a;
- }
- int d = exgcd(b, a % b, y, x);
- y = y - a / b * x;
- return d;
- }
- int main()
- {
- int n;
- cin >> n;
- while (n --)
- {
- int a, b, m, x, y;
- cin >> a >> b >> m;
- int d = exgcd(a, m, x, y);
- if (b % d) puts("impossible");
- else cout << (LL)x * (b / d) % m << endl;
- }
- }
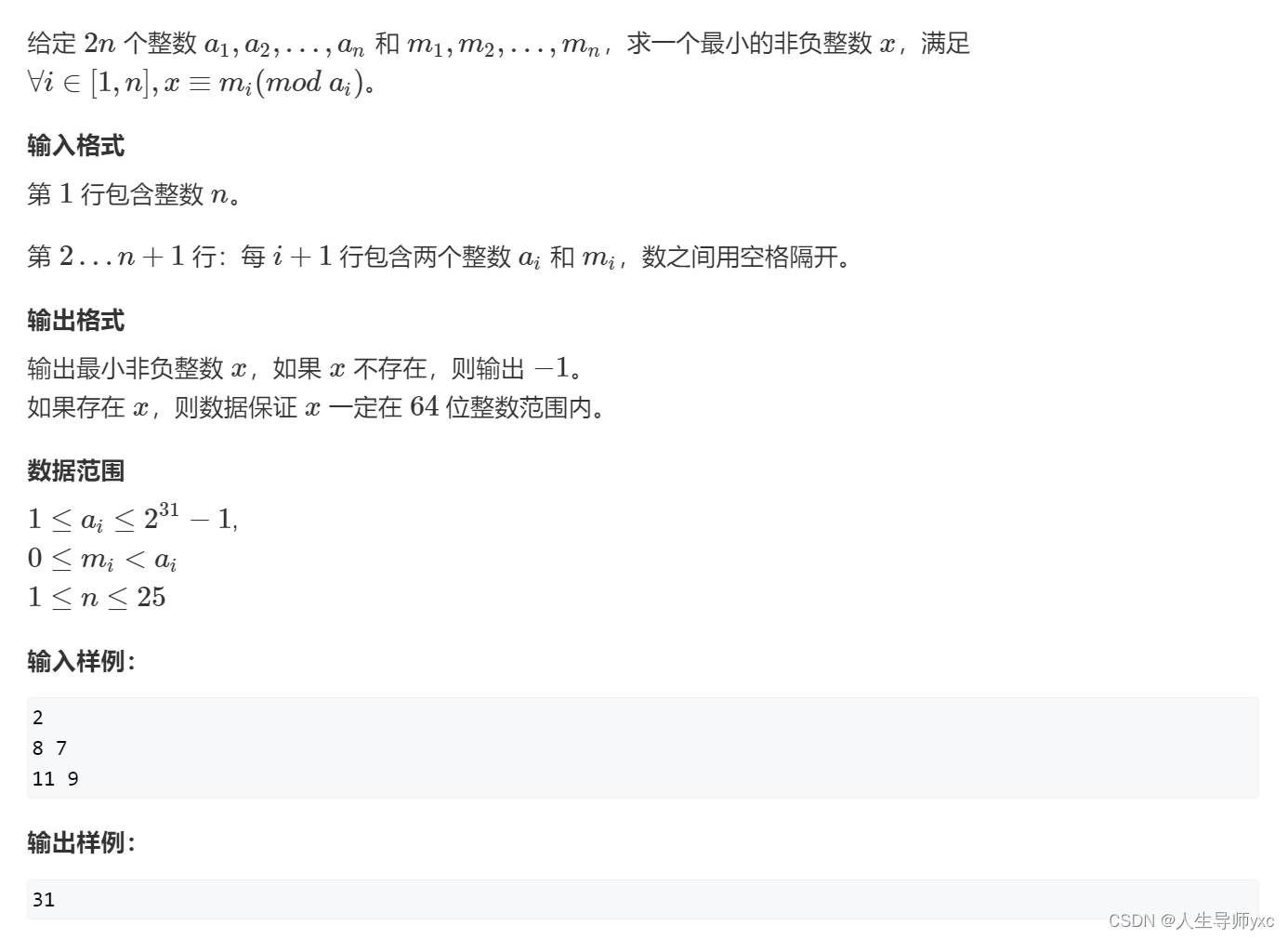
中国剩余定理
定义(来自百度百科):

AcWing 204. 表达整数的奇怪方式
基本思路:

- #include
- #include
- using namespace std;
- typedef long long LL;
- LL exgcd(LL a, LL b, LL &x, LL &y)
- {
- if (b == 0)
- {
- x = 1, y = 0;
- return a;
- }
- LL d = exgcd(b, a % b, y, x);
- y -= a / b * x;
- return d;
- }
- int main()
- {
- int n;
- cin >> n;
- LL a1, m1, x;
- cin >> a1 >> m1;
- for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i ++ )
- {
- LL a2, m2;
- cin >> a2 >> m2;
- LL k1, k2;
- LL d = exgcd(a1, a2, k1, k2);
- if ((m2 - m1) % d)
- {
- x = -1;
- break;
- }
- k1 = k1 * ((m2 - m1) / d);
- LL t = a2 / d;
- k1 = (k1 % t + t) % t;
- x = k1 * a1 + m1;
- m1 = k1 * a1 + m1;
- a1 = abs(a1 / d * a2);
- }
- if (x != -1) x = (m1 % a1 + a1) % a1;
- cout << x << endl;
- }
求组合数
方法:

1. 递推
动态规划思想:

AcWing 885. 求组合数 I

- #include
- #include
- using namespace std;
- const int N = 2010, mod = 1e9 + 7;
- int C[N][N];
- void dp()
- {
- for (int i = 0; i < N; i ++ )
- {
- for (int j = 0; j <= i; j ++ )
- {
- if (!j) C[i][j] = 1; //从i件物品中选取0件的方案数为1
- else C[i][j] = (C[i - 1][j] + C[i - 1][j - 1]) % mod; //状态转移方程
- }
- }
- }
- int main()
- {
- int n;
- cin >> n;
- dp();
- while (n --)
- {
- int a, b;
- cin >> a >> b;
- cout << C[a][b] << endl;
- }
- return 0;
- }
2.预处理
思路:
 模板:
模板: - //快速幂
- int qmi(int a, int k, int p)
- {
- int res = 1;
- while (k)
- {
- if (k & 1) res = (LL)res * a % p;
- a = (LL)a * a % p;
- k >>= 1;
- }
- return res;
- }
- //预处理
- void initial()
- {
- fact[0] = 1;
- infact[0] = 1;
- for (int i = 1; i < N; i ++)
- {
- fact[i] = (LL)fact[i - 1] * i % mod;
- infact[i] = (LL)infact[i - 1] * qmi(i, mod - 2, mod) % mod;
- }
- }
AcWing 886. 求组合数 II

- #include
- #include
- using namespace std;
- typedef long long LL;
- const int N = 1e5 + 10, mod = 1e9 + 7;
- int fact[N], infact[N];
- //快速幂
- int qmi(int a, int k, int p)
- {
- int res = 1;
- while (k)
- {
- if (k & 1) res = (LL)res * a % p;
- a = (LL)a * a % p;
- k >>= 1;
- }
- return res;
- }
- //预处理
- void initial()
- {
- fact[0] = 1;
- infact[0] = 1;
- for (int i = 1; i < N; i ++)
- {
- fact[i] = (LL)fact[i - 1] * i % mod;
- infact[i] = (LL)infact[i - 1] * qmi(i, mod - 2, mod) % mod;
- }
- }
- int main()
- {
- int n;
- cin >> n;
- initial();
- while (n --)
- {
- int a, b;
- cin >> a >> b;
- int res = (LL)fact[a] * infact[b] % mod * infact[a - b] % mod;
- cout << res << endl;
- }
- }
3.卢卡斯(lucas)
定义:
Lucas定理是用来求 c(n,m) mod p,p为素数的值。
公式:
C(n,m)%p=C(n/p,m/p)*C(n%p,m%p)%p
AcWing 887. 求组合数 III

- #include
- #include
- using namespace std;
- typedef long long LL;
- //快速幂
- int qmi(int a, int k, int p)
- {
- int res = 1;
- while (k)
- {
- if (k & 1) res = (LL)res * a % p;
- a = (LL)a * a % p;
- k >>= 1;
- }
- return res;
- }
- //求组合数
- int C(int a, int b, int p)
- {
- if (b > a) return 0;
- int res = 1;
- for (int i = 1, j = a; i <= b; i ++, j --)
- {
- res = (LL) res * j % p;
- res = (LL) res * qmi(i, p - 2, p) % p;
- }
- return res;
- }
- //卢卡斯定理
- int lucas(LL a, LL b, int p)
- {
- if (a < p && b < p) return C(a, b, p);
- return (LL)C(a % p, b % p, p) * lucas(a / p, b / p, p) % p;
- }
- int main()
- {
- int n;
- cin >> n;
- while (n --)
- {
- LL a, b;
- int p;
- cin >> a >> b >> p;
- cout << lucas(a, b, p) << endl;
- }
- }
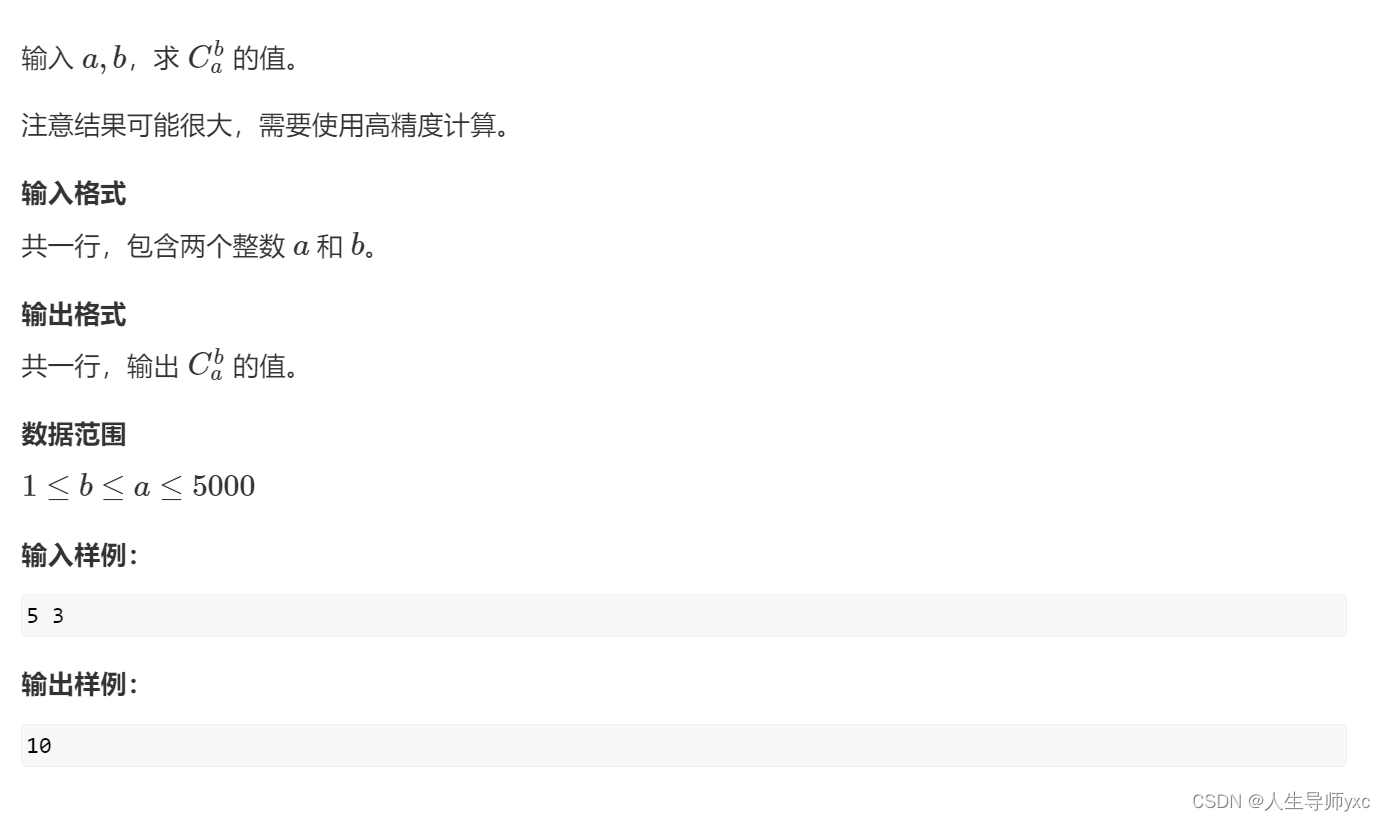
4.高精度
思路:

Acwing888. 求组合数 IV
- #include
- #include
- #include
- using namespace std;
- const int N = 5010;
- int primes[N], cnt;
- bool st[N];
- int sum[N];
- //线性筛(欧拉筛)
- void get_primes(int n)
- {
- for (int i = 2; i <= n; i ++)
- {
- if (!st[i]) primes[cnt ++] = i;
- for (int j = 0; primes[j] <= n / i; j ++)
- {
- st[i * primes[j]] = true;
- if (i % primes[j] == 0) break;
- }
- }
- }
- //求n中p的个数
- int get(int n, int p)
- {
- int res = 0;
- while (n)
- {
- res += n / p;
- n /= p;
- }
- return res;
- }
- //高精度乘法
- vector<int> mul(vector<int> a, int b)
- {
- vector<int> c;
- int t = 0;
- for (int i = 0; i < a.size(); i ++)
- {
- t += a[i] * b;
- c.push_back(t % 10);
- t /= 10;
- }
- while (t)
- {
- c.push_back(t % 10);
- t /= 10;
- }
- return c;
- }
- int main()
- {
- int a, b;
- cin >> a >> b;
- get_primes(a);
- for (int i = 0; i < cnt; i ++)
- {
- int p = primes[i];
- sum[i] = get(a, p) - get(b, p) - get(a - b, p);
- }
- vector<int> res;
- res.push_back(1);
- for (int i = 0; i < cnt; i ++)
- for (int j = 0; j < sum[i]; j ++)
- res = mul(res, primes[i]);
- for (int i = res.size() - 1; i >= 0; i --) cout << res[i];
- cout << endl;
- return 0;
- }
容斥原理
基本思路:

 AcWing 890. 能被整除的数
AcWing 890. 能被整除的数
思路分析:
1.用二进制表示每种选法:1表示选当前集合,0表示不选当前集合
2.|Sp|集合p表示1~n中p的倍数的个数,通过观察发现,|Sp| = [n | p]
4.通过当前选中集合个数确定每一项前面的符号,再由容斥原理可以求出最终答案
样例模拟:

- #include
- #include
- using namespace std;
- typedef long long LL;
- const int N = 20;
- int primes[N];
- int main()
- {
- int n, m;
- cin >> n >> m;
- for (int i = 0; i < m; i ++ ) cin >> primes[i];
- int res = 0;
- for (int i = 1; i < 1 << m; i ++)
- {
- int cnt = 0; // 记录当前集合的个数,奇数个为正,偶数个为负
- int t = 1; //当前选法的所有数相乘
- for (int j = 0; j < m; j ++ ) // 枚举每一位数, 为1则选该质数
- {
- if (i >> j & 1) //为1
- {
- if ((LL)t * primes[j] > n)
- {
- t = -1;
- break;
- }
- t *= primes[j]; //当前选法质数相乘
- cnt ++; //当前选法的质数个数
- }
- }
- if (t != -1)
- {
- if (cnt % 2) res += n / t; //奇数
- else res -= n / t; //偶数
- }
- }
- cout << res << endl;
- return 0;
- }
博弈论
Nim游戏
公平组合游戏ICG
(来自算法进阶指南的摘抄)
若一个游戏满足:
1. 由两名玩家交替行动;
2. 在游戏进程的任意时刻,可以执行的合法行动与轮到哪名玩家无关;
3. 不能行动的玩家判负;
则称该游戏为一个公平组合游戏。
NIM博弈属于公平组合游戏,但城建的棋类游戏,比如围棋,就不是公平组合游戏。因为围棋交战双方分别只能落黑子和白子,胜负判定也比较复杂,不满足条件2和条件3。先手必胜状态
可以走到某个必败状态
先手必败状态
走不到任何一个必败状态
基本思路及结论:
关于位运算中异或的相关知识参考:基础算法总结_人生导师yxc的博客-CSDN博客
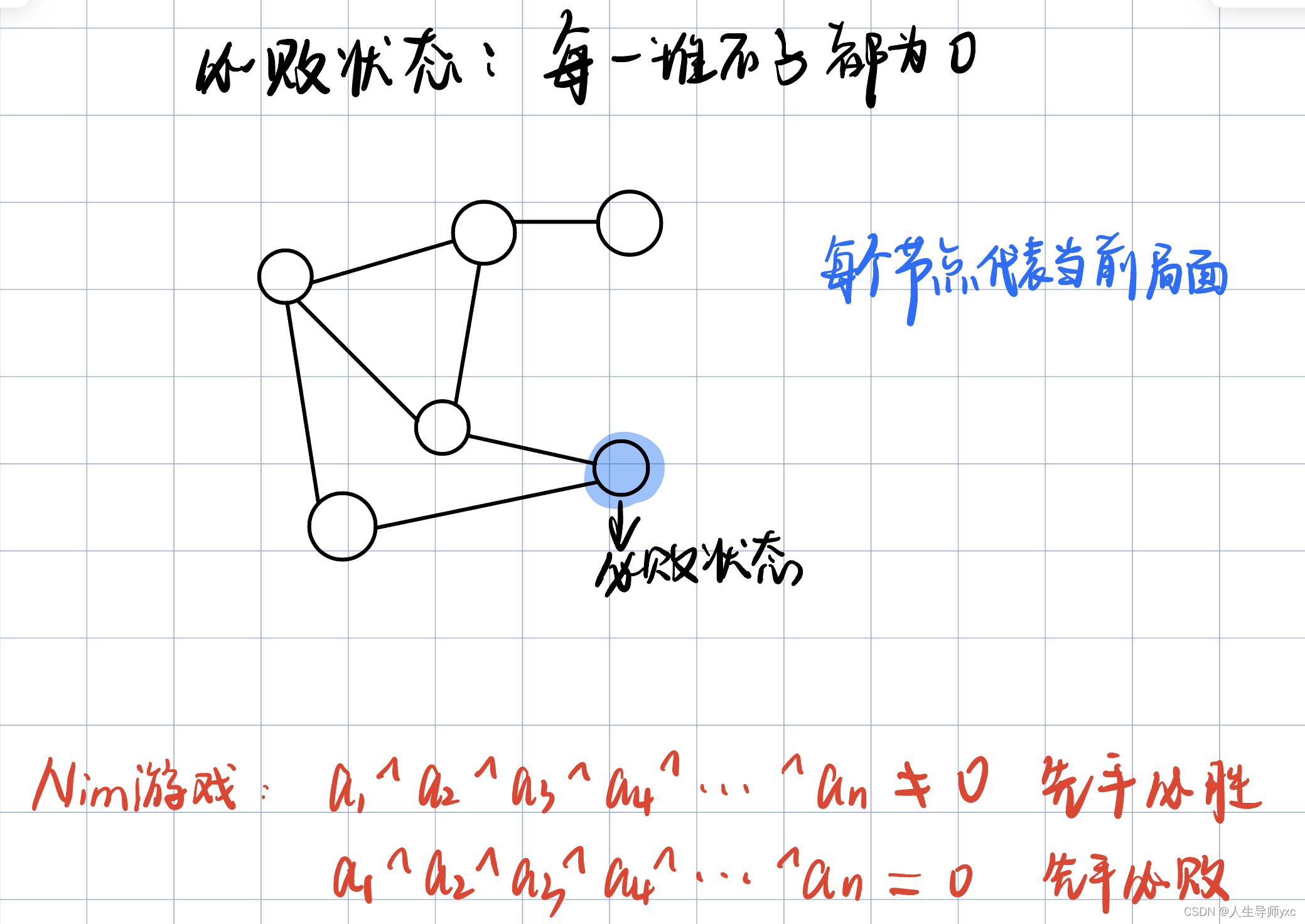
证明:

AcWing 891. Nim游戏

- #include
- #include
- using namespace std;
- int main()
- {
- int n;
- cin >> n;
- int res = 0;
- while (n --)
- {
- int x;
- cin >> x;
- res ^= x;
- }
- if (res) puts("Yes");
- else puts("No");
- return 0;
- }
SG函数
mex运算:
设S表示一个非负整数集合。定义mex(S)为求出不属于集合S的最小非负整数的运算,即:
mex(S) = min{x}, x属于自然数,且x不属于S定义:
(来自算法进阶指南)
在有向图游戏中,对于每个节点x,设从x出发共有k条有向边,分别到达节点y1, y2, ..., yk,定义SG(x)为x的后继节点y1, y2, ..., yk 的SG函数值构成的集合再执行mex(S)运算的结果,即:
SG(x) = mex(SG(y1), SG(y2), ..., SG(yk))
特别地,整个有向图游戏G的SG函数值被定义为有向图游戏起点s的SG函数值,即SG(G) = SG(s)。AcWing 893. 集合-Nim游戏

- #include
- #include
- #include
- #include
- using namespace std;
- const int N = 10010;
- int s[N], f[N];
- int k, n;
- int sg(int x)
- {
- if (f[x] != -1) return f[x];
- unordered_set<int> S;
- for (int i = 0; i < k; i ++)
- {
- int sum = s[i];
- if (x >= sum) S.insert(sg(x - sum));
- }
- for (int i = 0; ; i ++)
- {
- if (!S.count(i))
- {
- f[x] = i;
- return f[x];
- }
- }
- }
- int main()
- {
- cin >> k;
- for (int i = 0; i < k; i ++) cin >> s[i];
- memset(f, -1, sizeof f);
- cin >> n;
- int res = 0;
- for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++)
- {
- int x;
- cin >> x;
- res ^= sg(x);
- }
- if (res) puts("Yes");
- else puts("No");
- }
-
相关阅读:
八、【Vue-Router】编程式路由导航
代谢组学以冬虫夏草多糖的益生机制为例研究和发现关键肠道菌群
云原生之旅 - 13)基于 Github Action 的自动化流水线
【SpringBoot】实现引入登录时的验证码功能
第二十七讲.动态设置相关参数(replication为2和blocksize为10字节)
led灯珠型号及使用参数
Linux分区指南
MAUI+MASA Blazor 兼容性测试报告及分析
cubeIDE开发, stm32的ADC(模数转换器) 开发要点
SHELL中的循环语句
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_73569492/article/details/133841389
