-
Linux 64位 C++协程池原理分析及代码实现
导语
本文介绍了协程的作用、结构、原理,并使用C++和汇编实现了64位系统下的协程池。文章内容避免了协程晦涩难懂的部分,用大量图文来分析原理,适合新手阅读学习。
1. Web服务器问题
现代分布式Web后台服务逻辑通常由一系列RPC请求组成,若串行则耗时比较长。

此时一般都会使用线程池并行运行RPC请求,如图中GetData函数

假设请求数据包不大,那么可假设GetData耗时组成如下图所示。在非阻塞读情况下,CPU将在Wait环节空转浪费资源(不断地read,得到返回码-1)。

2. 协程的引入
有没有办法只用一个线程并行执行GetData呢?答案是:可以!我们假设有3个并行的GetData任务,下图线程1通过跳转控制流,减少CPU资源浪费。执行流为①~⑦,在Wait阶段则跳到其他任务如①~⑤。运行结束后也跳到其他任务如⑥~⑦。通过这种方式,3个GetData能用一个线程以52ms的耗时并行执行。

如果GetData任务可以被这样分配,则可以减少线程切换的消耗。因为协程的调度是线程内用户态执行的,CPU消耗非常小。

相关视频推荐
需要C/C++ Linux服务器架构师学习资料加qun812855908获取(资料包括C/C++,Linux,golang技术,Nginx,ZeroMQ,MySQL,Redis,fastdfs,MongoDB,ZK,流媒体,CDN,P2P,K8S,Docker,TCP/IP,协程,DPDK,ffmpeg等),免费分享

3. 协程的原理
从上文可知,协程之间的切换本质是函数的跳转,即如何让正在执行的函数跳转到另一个新的函数上,以及下次如何又跳转回来。如下面代码所示:
- void func1() {
- printf("① 跳转到func2");
- Coroutine::CoYield(); // 通过该函数跳到func2
- printf("③ func2跳转回func1");
- }
- void func2() {
- printf("② func2执行完毕");
- }
要实现这种能力,需要结合汇编知识。首先研究如下简单函数的汇编语言
- #include <iostream>
- using namespace std;
- class Object {
- public:
- int val[12];
- };
- int func(Object *pObj1, Object *pObj2) {
- pObj1->val[0] = 1;
- pObj1->val[11] = 11;
- pObj2->val[0] = 2;
- pObj2->val[11] = 12;
- int arr[100];
- arr[0] = 3;
- arr[99] = 99;
- return pObj1->val[0];
- }
- int main() {
- Object obj, obj2;
- int a = func(&obj, &obj2);
- return a;
- }
下面看看在64位系统汇编中,func函数是如何执行的。
push %rbp是进入func函数执行的第一个指令,作用是把rbp的地址压到栈顶。因为rsp始终指向栈顶,所以压栈后,rsp的地址下移8字节。rdi和rsi相差48个字节,该空间被class Object内的int val[12]占用。
前两个指令让rbp指向rsp往下296字节的位置。后面两个指令把rdi和rsi地址保存在最下面。
 为什么rsp下移296字节?首先,上述代码使用了临时变量int arr[100],需要有400个字节的栈空间;其次,x64系统存有128字节的红色区域可使用;最后,rdi和rsi地址共占16字节。因此,rbp到红色区域底部的空间一共是 288 + 8 + 104 + 8 + 8 = 416字节。
为什么rsp下移296字节?首先,上述代码使用了临时变量int arr[100],需要有400个字节的栈空间;其次,x64系统存有128字节的红色区域可使用;最后,rdi和rsi地址共占16字节。因此,rbp到红色区域底部的空间一共是 288 + 8 + 104 + 8 + 8 = 416字节。
接下来才开始执行func函数第一行代码,给val[0]赋值。
然后分别给pObj1和pObj2的成员变量赋值

接下来给临时变量arr赋值

最后让eax指向返回值,恢复函数栈的栈底和栈顶。

4. 协程的结构
从前面我们知道,每个函数在内存中都有栈顶rsp和栈底rbp。这两个值决定了函数可操作的内存范围,如下图所示
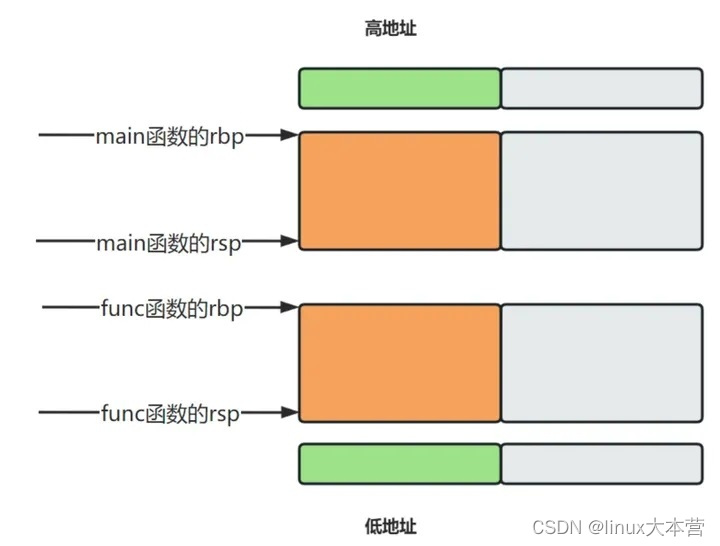
既然协程切换是从一个函数切换到另一个函数,那么就需要知道两个函数的rbp和rsp。然而,函数的rbp和rsp是执行时设定的,代码层面难以获得。
既然如此,我们可以实现腾出空间,让函数在预期的rbp和rsp内。定义一个类如下:- class Coroutine {
- void* m_pRegister[14];
- char m_pStack[1024];
- std::function<void()> m_func;
- };
那么在内存模型中,该类的布局如下所示

这样的协程在能被使用前需要做初始化,如下图所示

在其他协程切换过来时,cpu寄存器可按m_pRegister预设的地址赋值,开始执行DoWork函数,函数代码如下:
- static void Coroutine::DoWork(Coroutine *pThis) {
- pThis->m_func();
- pThis->Yield(); // 转让控制流给同线程的其他协程
- }
由于是静态函数,需令参数pThis为协程地址。所以,初始化时需要设置m_pRegister中的rdi为this。上述第二行代码执行时,rbp会设为this。所以执行m_func时,如下图所示:

5. 协程间的切换
下面以Coroutine1切换到Coroutine2为例。主要分为两步:
1. 保存Coroutine1的上下文
2. 加载Coroutine2的上下文

切换代码可见源代码Coroutine::Switch
6. 协程池的实现
本文实现协程池比较简单,初始化创建线程并设置thread_local变量以保存协程队列状态。并且,每个线程额外创建一个main协程用作Guard。
在执行时,每个线程通过轮询的方式切换协程,若协程无任务则尝试CAS获取Job,否则直接执行已有Job。当Job执行完或主动CoYield时,切换到下一个协程。
为了避免CAS空转,在没有任务时会阻塞休眠。当任务来临时则Notify所有线程的协程。
7. 源代码
example.cpp- /**
- * @file example.cpp
- * @author souma
- * @brief 使用协程池的示例,编译命令如下
- * g++ example.cpp coroutine.cpp -lpthread -O3
- * @version 0.1
- * @date 2023-06-06
- *
- * @copyright Copyright (c) 2023
- *
- */
- #include <iostream>
- #include <array>
- #include "coroutine.h"
- using namespace std;
- using namespace comm;
- void func(const string &sTaskName, uint32_t uWaitSeconds) {
- printf("[%ld] [%s start], wait seconds[%u]\n", time(nullptr), sTaskName.c_str(), uWaitSeconds);
- time_t iStartSec = time(nullptr);
- // 默认可用65535字节的栈内存,具体可看CO_STACK_SIZE
- uint32_t uArrSize = 65535/4;
- int arr[uArrSize];
- while (time(nullptr) - iStartSec < uWaitSeconds) {
- // 操作栈内存
- for (int i = 0; i < uArrSize; ++i) {
- arr[i] = i;
- }
- // 切换控制流
- printf("[%ld] [%s] -> [协程池]\n", time(nullptr), sTaskName.c_str());
- usleep(100);
- Coroutine::CoYield(); // 只需这一个函数即可切换控制流
- printf("[%ld] [协程池] -> [%s]\n", time(nullptr), sTaskName.c_str());
- }
- // 检查栈内存是否正确
- for (int i = 0; i < uArrSize; ++i) {
- if (arr[i] != i) {
- printf("栈内存错误\n");
- exit(-1);
- }
- }
- printf("[%ld] [%s end], expect_timecost[%d], real_timecost[%ld]\n", time(nullptr), sTaskName.c_str(), uWaitSeconds, time(nullptr) - iStartSec);
- }
- int main() {
- // 如果想当线程池用,可以令第一个参数为线程数,第二个参数为1。
- // 在该场景下,使用小线程大协程不仅CPU消耗低,整体耗时也很低,可以自行测试。
- CoroutinePool oPool(2, 300);
- oPool.Run();
- time_t iStartTime = time(nullptr);
- const int iTaskCnt = 400;
- vector<shared_ptr<Future>> vecFuture;
- for (int i = 0; i < iTaskCnt; ++i) {
- // 模拟GetData中的Wait环节, 1 ~ 5秒等待
- shared_ptr<Future> pFuture = oPool.Submit([i](){func("Task" + to_string(i), random() % 5 + 1);});
- if (pFuture != nullptr) {
- vecFuture.emplace_back(pFuture);
- }
- }
- // 阻塞等待所有Task完成
- for (auto it = vecFuture.begin(); it != vecFuture.end(); ++it) {
- (*it)->Get();
- }
- printf("demo's finished, time cost[%ld]\n", time(nullptr) - iStartTime);
- return 0;
- }
coroutine.h- /**
- * @file coroutine.h
- * @author souma
- * @brief 多线程无栈式协程池,请不要用-O0编译否则会产生coredump
- * @version 0.1
- * @date 2023-06-06
- *
- * @copyright Copyright (c) 2023
- *
- */
- #pragma once
- #include <functional>
- #include <memory>
- #include <vector>
- #include <queue>
- #include <thread>
- #include <mutex>
- #include <signal.h>
- #include <pthread.h>
- #include <condition_variable>
- #include <unistd.h>
- namespace comm {
- class Future;
- class CoroutinePool;
- class Coroutine;
- struct CoroutinePoolCtx;
- struct CoroutineTaskCtx;
- struct CoroutinePoolCtx {
- std::vector<std::shared_ptr<Coroutine>> m_vecCoroutine;
- std::shared_ptr<Coroutine> m_pMainCoroutine;
- uint32_t m_uCursor;
- uint32_t m_uWorkCnt;
- };
- struct CoroutineTaskCtx {
- std::function<void()> m_userFunc;
- std::shared_ptr<Future> m_pFuture;
- };
- // class ArraySyncQueue start
- template <class T>
- class ArraySyncQueue {
- public:
- ArraySyncQueue(uint32_t uCapacity, uint32_t uSleepUs = 100, uint32_t uRetryTimes = 3);
- bool Push(T *pObj);
- T* Pop();
- inline bool IsFull() const { return m_uPushCursor == m_uPopCursor - 1 || (m_uPopCursor == 0 && m_uPushCursor == m_vecQueue.size() - 1); }
- bool IsEmpty() const { return m_uPopCursor == m_uPushCursor; }
- ~ArraySyncQueue();
- private:
- uint32_t GetNextCursor(uint32_t uCursor);
- private:
- std::vector<T*> m_vecQueue;
- uint32_t m_uPushCursor = 0;
- uint32_t m_uPopCursor = 0;
- uint32_t m_uSleepUs;
- uint32_t m_uRetryTimes;
- };
- // class ArraySyncQueue end
- // class Coroutine start
- class Coroutine {
- public:
- friend class CoroutinePool;
- /**
- * @brief 调用该函数将执行流交给其他协程,仅在协程池环境下有效
- *
- * @return true:协程切换成功, false:不在协程池环境中运行
- */
- static bool CoYield();
- Coroutine(const Coroutine &) = delete;
- Coroutine(Coroutine &&) = delete;
- Coroutine & operator=(const Coroutine &) = delete;
- Coroutine & operator=(Coroutine &&) = delete;
- private:
- // 4096是预留给库使用的栈内存大小,后者是留给用户使用的栈内存大小
- constexpr static uint32_t CO_STACK_SIZE = 4096 + 65535;
- Coroutine();
- /**
- * @brief 当前协程是否绑定了任务
- *
- * @return true:是
- */
- inline bool HasTask() const { return m_pTaskCtx != nullptr; }
- /**
- * @brief 两个协程切换,从pPrev切换到pNext
- */
- static void Switch(Coroutine *pPrev, Coroutine *pNext);
- /**
- * @brief 将控制流转给同线程的其他协程
- */
- void Yield();
- /**
- * @brief 这个是给main协程用的
- */
- void Register();
- /**
- * @brief 这个是给执行用户任务的协程用的
- */
- void Register(std::shared_ptr<CoroutineTaskCtx> pTaskCtx);
- /**
- * @return CoroutinePoolCtx& 当前线程的协程上下文
- */
- static CoroutinePoolCtx & GetCtx();
- /**
- * @brief 让当前线程的cursor往后移,轮询协程
- */
- static void MoveCursor();
- /**
- * @brief 协程包一层的函数
- */
- static void DoWork(Coroutine *pThis);
- /**
- *
- * @return void* 获得自建rsp地址
- */
- void* GetRsp();
- /**
- * 保存寄存器的值到m_pStack中
- */
- void SaveReg();
- private:
- void* m_pRegister[14];
- char m_pStack[CO_STACK_SIZE];
- std::shared_ptr<CoroutineTaskCtx> m_pTaskCtx;
- };
- // class Coroutine end
- // class CoroutinePool start
- class CoroutinePool {
- public:
- friend class Coroutine;
- /**
- * @brief 建立一个多线程协程池,即创建uThreadCnt个线程,每个线程含有uCoroutineCnt个协程
- 调用Run开始运行,调用Stop或直接析构结束
- * @param uThreadCnt 线程数,小于1则为1
- * @param uCoroutineCnt 每个线程的协程数,小于1则为1
- * @param uJobQueueSize 总任务队列大小,小于1则为1
- */
- CoroutinePool(uint32_t uThreadCnt, uint32_t uCoroutineCnt, uint32_t uJobQueueSize = 1024000);
- /**
- * @brief 线程安全,可重入
- * @return true:正常
- */
- bool Run();
- /**
- * @brief 停止协程池 (会先保证池中任务完成再停止),线程安全可重入
- *
- */
- void Stop();
- /**
- * @param userFunc 用户函数
- * @return std::shared_ptr<Future> nullptr:协程池队列满了,提交不了
- */
- std::shared_ptr<Future> Submit(const std::function<void()> &userFunc);
- ~CoroutinePool();
- CoroutinePool(const CoroutinePool &) = delete;
- CoroutinePool(CoroutinePool &&) = delete;
- CoroutinePool & operator=(const CoroutinePool &) = delete;
- CoroutinePool & operator=(CoroutinePool &&) = delete;
- private:
- static void LoopWork(CoroutinePool &oPool);
- private:
- bool m_bStarted;
- uint32_t m_uThreadCnt;
- uint32_t m_uRoutineCnt;
- ArraySyncQueue<CoroutineTaskCtx> m_queueJob;
- std::vector<std::shared_ptr<std::thread>> m_vecThread;
- std::mutex m_oMutex;
- std::condition_variable m_oCondition;
- };
- // class CoroutinePool end
- // class Future start
- class Future {
- public:
- /**
- * @brief 阻塞获得结果
- *
- * @param uTimeoutMs 超时时间
- * @return true:成功, false:超时
- */
- bool Get(uint32_t uTimeoutMs = -1);
- /**
- * @brief 设置状态为完成
- */
- void SetFinished();
- Future();
- Future(const Future&) = delete;
- Future(Future&&) = delete;
- Future & operator=(const Future&) = delete;
- Future & operator=(Future&&) = delete;
- private:
- std::mutex m_oMutex;
- std::condition_variable m_oCondition;
- bool m_bFinished;
- };
- // class Future end
- }
coroutine.cpp- /**
- * @file coroutine.cpp
- * @author souma
- * @brief 协程池的具体实现
- * @version 0.1
- * @date 2023-06-06
- *
- * @copyright Copyright (c) 2023
- *
- */
- #include "coroutine.h"
- #include <cstring>
- using namespace std;
- namespace comm {
- // class Coroutine start
- Coroutine::Coroutine() {
- m_pTaskCtx = nullptr;
- }
- void Coroutine::Register() {
- m_pTaskCtx = make_shared<CoroutineTaskCtx>();
- m_pTaskCtx->m_userFunc = [](){};
- m_pTaskCtx->m_pFuture = nullptr;
- SaveReg();
- }
- void Coroutine::Register(shared_ptr<CoroutineTaskCtx> pTaskCtx) {
- m_pTaskCtx = pTaskCtx;
- SaveReg();
- }
- inline void Coroutine::Yield() {
- Coroutine::Switch(this, Coroutine::GetCtx().m_pMainCoroutine.get());
- }
- bool Coroutine::CoYield() {
- if (GetCtx().m_vecCoroutine.size() == 0) {
- return false;
- }
- GetCtx().m_vecCoroutine[GetCtx().m_uCursor]->Yield();
- return true;
- }
- CoroutinePoolCtx & Coroutine::GetCtx() {
- thread_local CoroutinePoolCtx coroutinePoolCtx;
- return coroutinePoolCtx;
- }
- void Coroutine::MoveCursor() {
- GetCtx().m_uCursor = GetCtx().m_uCursor == GetCtx().m_vecCoroutine.size() - 1 ? 0 : GetCtx().m_uCursor + 1;
- }
- extern "C" __attribute__((noinline, weak))
- void Coroutine::Switch(Coroutine *pPrev, Coroutine *pNext) {
- // 1.保存pPrev协程的上下文, rdi和pPrev同指向
- // 2.加载pNext协程的上下文, rsi和pNext同指向
- asm volatile(R"(
- movq %rsp, %rax
- movq %rbp, 104(%rdi)
- movq %rax, 96(%rdi)
- movq %rbx, 88(%rdi)
- movq %rcx, 80(%rdi)
- movq %rdx, 72(%rdi)
- movq 0(%rax), %rax
- movq %rax, 64(%rdi)
- movq %rsi, 56(%rdi)
- movq %rdi, 48(%rdi)
- movq %r8, 40(%rdi)
- movq %r9, 32(%rdi)
- movq %r12, 24(%rdi)
- movq %r13, 16(%rdi)
- movq %r14, 8(%rdi)
- movq %r15, (%rdi)
- movq (%rsi), %r15
- movq 8(%rsi), %r14
- movq 16(%rsi), %r13
- movq 24(%rsi), %r12
- movq 32(%rsi), %r9
- movq 40(%rsi), %r8
- movq 48(%rsi), %rdi
- movq 64(%rsi), %rax
- movq 72(%rsi), %rdx
- movq 80(%rsi), %rcx
- movq 88(%rsi), %rbx
- movq 96(%rsi), %rsp
- movq 104(%rsi), %rbp
- movq 56(%rsi), %rsi
- movq %rax, (%rsp)
- xorq %rax, %rax
- )");
- }
- void Coroutine::DoWork(Coroutine *pThis) {
- pThis->m_pTaskCtx->m_userFunc();
- pThis->m_pTaskCtx->m_pFuture->SetFinished();
- pThis->m_pTaskCtx.reset();
- Coroutine::GetCtx().m_uWorkCnt--;
- pThis->Yield();
- }
- void* Coroutine::GetRsp() {
- // m_pRegister和m_pStack中间预留一个指针空间
- auto sp = std::end(m_pStack) - sizeof(void*);
- // 预定Rsp的地址保证能够整除8字节
- sp = decltype(sp)(reinterpret_cast<size_t>(sp) & (~0xF));
- return sp;
- }
- void Coroutine::SaveReg() {
- void *pStack = GetRsp();
- memset(m_pRegister, 0, sizeof m_pRegister);
- void **pRax = (void**)pStack;
- *pRax = (void*) DoWork;
- // rsp
- m_pRegister[12] = pStack;
- // rax
- m_pRegister[8] = *pRax;
- // rdi
- m_pRegister[6] = this;
- }
- // class Coroutine end
- // class CoroutinePool start
- CoroutinePool::CoroutinePool(uint32_t uThreadCnt, uint32_t uCoroutineCnt, uint32_t uJobQueueSize) : m_queueJob(uJobQueueSize) {
- m_bStarted = false;
- m_uThreadCnt = max(uThreadCnt, 1u);
- m_uRoutineCnt = max(uCoroutineCnt, 1u);
- }
- bool CoroutinePool::Run() {
- if (!__sync_bool_compare_and_swap(&m_bStarted, false, true)) {
- return false;
- }
- for (decltype(m_uThreadCnt) i = 0; i < m_uThreadCnt; ++i) {
- m_vecThread.emplace_back(make_shared<thread>(CoroutinePool::LoopWork, ref(*this)));
- }
- return true;
- }
- void CoroutinePool::Stop() {
- if (!__sync_bool_compare_and_swap(&m_bStarted, true, false)) {
- return;
- }
- m_oCondition.notify_all();
- for (auto it = m_vecThread.begin(); it != m_vecThread.end(); ++it) {
- (*it)->join();
- }
- m_vecThread.clear();
- }
- shared_ptr<Future> CoroutinePool::Submit(const function<void()> &userFunc) {
- shared_ptr<Future> pNewFuture = make_shared<Future>();
- CoroutineTaskCtx *pTaskCtx = new CoroutineTaskCtx;
- pTaskCtx->m_pFuture = pNewFuture;
- pTaskCtx->m_userFunc = userFunc;
- if (!m_queueJob.Push(pTaskCtx)) {
- delete pTaskCtx, pTaskCtx = nullptr;
- return nullptr;
- }
- m_oCondition.notify_all();
- return pNewFuture;
- }
- CoroutinePool::~CoroutinePool() {
- Stop();
- }
- void CoroutinePool::LoopWork(CoroutinePool &oPool) {
- Coroutine::GetCtx().m_uCursor = 0;
- Coroutine::GetCtx().m_uWorkCnt = 0;
- Coroutine::GetCtx().m_pMainCoroutine = shared_ptr<Coroutine>(new Coroutine);
- Coroutine::GetCtx().m_pMainCoroutine->Register();
- Coroutine::GetCtx().m_vecCoroutine.clear();
- for (decltype(oPool.m_uRoutineCnt) i = 0; i < oPool.m_uRoutineCnt; ++i) {
- Coroutine::GetCtx().m_vecCoroutine.emplace_back(shared_ptr<Coroutine>(new Coroutine));
- }
- Coroutine *pMainCoroutine, *pCurCoroutine;
- while (oPool.m_bStarted || Coroutine::GetCtx().m_uWorkCnt > 0 || !oPool.m_queueJob.IsEmpty()) {
- pMainCoroutine = Coroutine::GetCtx().m_pMainCoroutine.get();
- pCurCoroutine = Coroutine::GetCtx().m_vecCoroutine[Coroutine::GetCtx().m_uCursor].get();
- if (pCurCoroutine->HasTask()) {
- Coroutine::Switch(pMainCoroutine, pCurCoroutine);
- Coroutine::MoveCursor();
- continue;
- }
- CoroutineTaskCtx *pTaskCtx = oPool.m_queueJob.Pop();
- if (pTaskCtx == nullptr) {
- if (Coroutine::GetCtx().m_uWorkCnt > 0) {
- Coroutine::MoveCursor();
- continue;
- }
- unique_lock<mutex> oLock(oPool.m_oMutex);
- oPool.m_oCondition.wait(oLock);
- continue;
- }
- pCurCoroutine->Register(shared_ptr<CoroutineTaskCtx>(pTaskCtx));
- ++Coroutine::GetCtx().m_uWorkCnt;
- Coroutine::Switch(pMainCoroutine, pCurCoroutine);
- Coroutine::MoveCursor();
- }
- }
- // class CoroutinePool end
- // class Future start
- Future::Future() {
- m_bFinished = false;
- }
- bool Future::Get(uint32_t uTimeoutMs) {
- unique_lock<mutex> oLock(m_oMutex);
- if (m_bFinished) {
- return true;
- }
- return m_oCondition.wait_for(oLock, chrono::milliseconds(uTimeoutMs)) == cv_status::no_timeout;
- }
- void Future::SetFinished() {
- {
- unique_lock<mutex> oLock(m_oMutex);
- m_bFinished = true;
- }
- m_oCondition.notify_all();
- }
- // class Future end
- // class ArraySyncQueue start
- template <class T>
- ArraySyncQueue<T>::ArraySyncQueue(uint32_t uCapacity, uint32_t uSleepUs, uint32_t uRetryTimes) {
- for (uint32_t i = 0; i < std::max(uCapacity, 1u); ++i) {
- m_vecQueue.emplace_back(nullptr);
- }
- m_uSleepUs = uSleepUs;
- m_uRetryTimes = uRetryTimes;
- }
- template <class T>
- bool ArraySyncQueue<T>::Push(T *pObj) {
- if (pObj == nullptr) {
- return false;
- }
- uint32_t uRetryTimes = 0;
- while (uRetryTimes <= m_uRetryTimes) {
- uint32_t uPushCursor = m_uPushCursor;
- if (uPushCursor == m_uPopCursor - 1 || (m_uPopCursor == 0 && uPushCursor == m_vecQueue.size() - 1)) {
- // 队列满了
- return false;
- }
- if (!__sync_bool_compare_and_swap(&m_vecQueue[uPushCursor], nullptr, pObj)) {
- uRetryTimes++;
- usleep(m_uSleepUs);
- continue;
- }
- m_uPushCursor = GetNextCursor(uPushCursor);
- return true;
- }
- // 竞争失败
- return false;
- }
- template <class T>
- T* ArraySyncQueue
::Pop() { - uint32_t uRetryTimes = 0;
- while (uRetryTimes <= m_uRetryTimes) {
- uint32_t uPopCursor = m_uPopCursor;
- if (uPopCursor == m_uPushCursor) {
- return nullptr;
- }
- T* pToReturn = m_vecQueue[uPopCursor];
- if (pToReturn == nullptr || !__sync_bool_compare_and_swap(&m_vecQueue[uPopCursor], pToReturn, nullptr)) {
- usleep(m_uSleepUs);
- uRetryTimes++;
- continue;
- }
- m_uPopCursor = GetNextCursor(uPopCursor);
- return pToReturn;
- }
- return nullptr;
- }
- template <class T>
- uint32_t ArraySyncQueue<T>::GetNextCursor(uint32_t uCursor) {
- if (uCursor == m_vecQueue.size() - 1) {
- return 0;
- }
- return uCursor + 1;
- }
- template <class T>
- ArraySyncQueue<T>::~ArraySyncQueue() {
- m_uRetryTimes = -1;
- do {
- T *pObj = Pop();
- if (pObj == nullptr) {
- return;
- }
- delete pObj, pObj = nullptr;
- } while (true);
- }
- // class ArraySyncQueue end
- }
8. 补充说明
8.1. 为什么不能-O0编译?
在-O0的情况下,编译器会给函数(coroutine.cpp:57)Coroutine::Switch包一层汇编指令,导致实际执行汇编指令不是期望的。具体可以分别用-O0和-O3在GDB下disassemble看到差异。
8.2. 如果函数使用栈很大怎么办?
源码中定义的协程栈为CO_STACK_SIZE=4096 + 65535KB,若用户函数使用的栈超过该范围会产生coredump。简单可行的解法是:1.尽量使用堆变量;2.改大CO_STACK_SIZE。
-
相关阅读:
跟运维学 Linux - 01
《异常检测——从经典算法到深度学习》27 可执行且可解释的在线服务系统中重复故障定位方法
渔业安全生产综合管理指挥系统-航迹数据优化方案
倒贴5000也要去打工的00后,图什么?
RestTemplate发送http请求
IOC操作Bean管理(基于注解方式)
2024HVV行动-进军蓝中研判(log4j2、fastjson、Struts2、Shiro)
Spring Cache + Caffeine的整合与使用
短链接网站系统设计与实践
信息学奥赛一本通:1309:【例1.6】回文数(Noip1999)
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_40989769/article/details/133827752
