-
Pytorch之SwinTransformer图像分类
- 💂 个人主页:风间琉璃
- 🤟 版权: 本文由【风间琉璃】原创、在CSDN首发、需要转载请联系博主
- 💬 如果文章对你有
帮助、欢迎关注、点赞、收藏(一键三连)和订阅专栏哦
前言
Swin Transformer(Liu et al., 2021) 是一种基于视觉Transformer的层次化模型。与之前的Vision Transformer相比,Swin Transformer采用了层次化构建方法,使用不同倍数的下采样来构建特征图,并在每个窗口内使用Windows Multi-Head Self-Attention(W-MSA)进行注意力计算。这种方法既减少了计算量,尤其是在浅层特征图较大时,又能在相邻窗口之间传递信息。此外,Swin Transformer在目标检测、实例分割等任务上也具有较好的表现,Swin Transformers 已经被用作当今许多视觉模型架构的主干。
在看本篇之前,建议你有Vision Transformer的相关基础,Transformer和Vision Transformer参考连接:ViT
一、Swin Transformer
1.Swin Transformer概览
将 Transformer 从语言应用到视觉方面主要有两大挑战:
⋆ \star ⋆ 视觉实体变化大,在不同场景下视觉Transformer性能未必很好
⋆ \star ⋆ 图像分辨率高,像素点多,Transformer基于全局自注意力的计算导致计算量较大Swin Transformer 引入了两个关键的概念来解决原始 ViT 所面临的问题:
分层特征图(hierarchical feature maps)和转移窗口注意力(shifted window attention)。Swin Transformer 的名字来源于“Shifted window Transformer”。Swin Transformer和Vision Transformer对比:

在上图左边是Swin Transformer,右边Vision Transformer,这张图它想表达Swin Transformer的两个核心点:
①Swin Transformer使用层次化构建方法(Hierarchical feature maps),特征图尺寸中有对图像下采样4倍的,8倍的以及16倍的,抽取不同层次的视觉特征,使其更适合分割检测等任务。而ViT中是一直16倍下采样。Swin Transformer通过从小尺寸 patch开始,逐渐在更深的 Transformer 层中合并相邻 patch,从而构造出一个
层次化表示 (hierarchical representation)。通过这些层次化特征图,Swin Transformer 模型可方便地利用先进技术进行密集预测,例如特征金字塔网络 (FPN) 或 U-Net。②Swin Transformer中使用了
Windows Multi-Head Self-Attention(W-MSA),在上图的4倍下采样和8倍下采样中,将特征图划分成了多个不相交的区域(Window),并且Multi-Head Self-Attention只在每个窗口(Window)内进行。上图两边红框代表在红框内进行transformer,右边ViT的红框是整张图,而左边Swin Transformer的红框是在小窗口上进行的。相对于ViT中直接对整个特征图进行Multi-Head Self-Attention,这样做的目的是能够减少计算量的,尤其是在浅层特征图很大的时候。
这样做虽然减少了计算量但也会隔绝不同窗口之间的信息传递,所以在论文中作者又提出了
Shifted Windows Multi-Head Self-Attention(SW-MSA),通过此方法能够让信息在相邻的窗口中进行传递。

为了解决采用W-MSA模块时,只会在每个窗口内进行自注意力计算,窗口与窗口之间是无法进行信息传递的,Swin Transformer引入了一个关键设计元素是它在连续自注意力层之间的窗口分区的移位 (shift),即Shifted Windows Multi-Head Self-Attention(SW-MSA),如上图所示。每一个小块叫做一个patch,每一个深色方块框起来的叫一个local window,在每一个local window中计算self-attention。如果是只计算一次self-attention,每个local window之间是孤立的,会隔绝不同窗口之间的信息传递。但是实际上所有的local window组成一张图片,他们之间是有关联的,所以引入了shifted-window进行了第二次self-attention,使用这个滑动窗口多头注意力机制的目的是为了实现不同windows之间的信息交互。
在Swin Transformer网络结构中一般是先使用
W-MSA模块,然后紧跟着使用SW-MSA模块的。在使用完W-MSA模块后再对特征进行分块可以理解为在上一层的基础上将每个windows分别向下后再向右移动了两个像素,经过这样处理后每个窗口都具有了特征图不同块的信息。2.Patch Partition
对于图像数据,其数据格式为[H, W, C],不满足Transformer输入要求。所以需要
先通过Patch Partition来对图像数据处理,将图像划分为固定大小的patch。然后将每个块沿着通道维度展开,可以用作后续任务的输入。如下图所示,具体细节可以参考前面给的链接文章。

3.Patch Merging
在 ResNet 等卷积神经网络中,特征图的下采样是使用卷积操作完成的,在Swin Transformer 中使用的无卷积下采样技术称为
Patch Merging。在每个Stage(Stage1除外)开始前通过一个Patch Merging层进行
下采样,用于缩小分辨率,调整通道数 进而形成层次化的设计,同时也能节省一定运算量。在CNN中,则是在每个Stage开始前用stride=2的卷积/池化层来降低分辨率。每次降采样是两倍,因此在行方向和列方向上,间隔2选取元素。然后拼接在一起作为一整个张量,最后展开。此时通道维度会变成原先的4倍(因为H,W各缩小2倍),此时再通过一个全连接层再调整通道维度为原来的两倍。

如上图所示,假设输入Patch Merging的是一个8x8大小的单通道特征图(feature map),Patch Merging会将每个4x4的相邻像素划分为一个patch,然后将每个patch中相同位置像素给拼在一起得到4个feature map, 并将这四个feature map在深度方向进行concat拼接。然后在通过一个LayerNorm层和全连接层在feature map的深度方向做线性变化,将feature map的深度由C变成C/2,即减半(上图中不包含最后的全连接层调整)。该模块主要存在于Stage2-4,
作用主要为下采样,即高和宽减半、通道翻倍。4.W-MSA
引入
Windows Multi-head Self-Attention(W-MSA)模块是为了减少计算量。如下图所示,左侧使用的是普通的Multi-head Self-Attention(MSA)模块,对于feature map中的每个patch,在Self-Attention计算过程中需要和所有的patch去计算。这导致Patch 数量平方复杂度,使其不适合高分辨率图像。为了解决这个问题,Swin Transformer 使用了Windows Multi-head Self-Attention(W-MSA)。 一个 Window 只是一个 patch 的集合,注意力计算只在每个 Window 内进行。 例如,下图右侧使用 2 x 2 块的 Window 大小,然后单独对每个Windows内部进行Self-Attention。。

对于普通的MSA模块来说,会对每一个patch去求解它的q,k,v的值,对任意一个patch所求得的q会对特征图中其他像素的k进行一个相似度的匹配,然后再进行一系列的操作,具体细节参考前面ViT的文章。
在W-MSA模块当中,首先会将特征图分成多个Windows后再进行处理,然后再对每个窗口的内部执行多头注意力机制的计算,但是这种方法窗口与窗口之间是无法进行信息交互的,这种缺点也会使得感受野变小,无法看到全局的感受野。
5.SW-MSA(滑动窗口多头注意力机制)
采用W-MSA模块时,
只会在每个窗口内进行自注意力计算,导致窗口与窗口之间是无法进行信息传递的。为了解决这个问题,Swin Transformer 在 W-MSA 模块之后使用了Shifted Windows Multi-Head Self-Attention(SW-MSA)模块,即进行偏移的W-MSA。

左侧使用W-MSA(假设是第L层),一般W-MSA和SW-MSA是成对使用的,那么第L+1层使用是SW-MSA(右侧图)。根据左右两幅图对比能够发现窗口(Windows)发生了偏移,可以看成窗口从左上角分别向右侧和下方各偏移了 M 2 \cfrac{M}{2} 2M个patch。在L层时每个窗口里的patch只能和同一个窗口里的patch相互学习。在偏移后的窗口(右侧图),由于窗口的移动,导致某些patch进入新的窗口,这些带有上一层窗口信息的patch可以和别的带有上一层前窗口信息的patch相互学习。解决了不同窗口之间无法进行信息交流的问题。
比如对于第一行第2列的2x4的窗口,它能够使第L层的第一排的两个窗口信息进行交流;第二行第二列的4x4的窗口,他能够使第L层的四个窗口信息进行交流。以上解决了不同窗口之间无法进行信息交流的问题。
在SW-MSA方法中,将特征划分为多个不规则的块,则增加了计算量,因为W-MSA模块将模型划分为4个等大小的块,而SW-MSA将模型分为9个块,因此模型计算量加大。为了解决这个麻烦,作者又提出而了
Efficient batch computation for shifted configuration,一种更加高效的计算方法。下面是原论文给的示意图: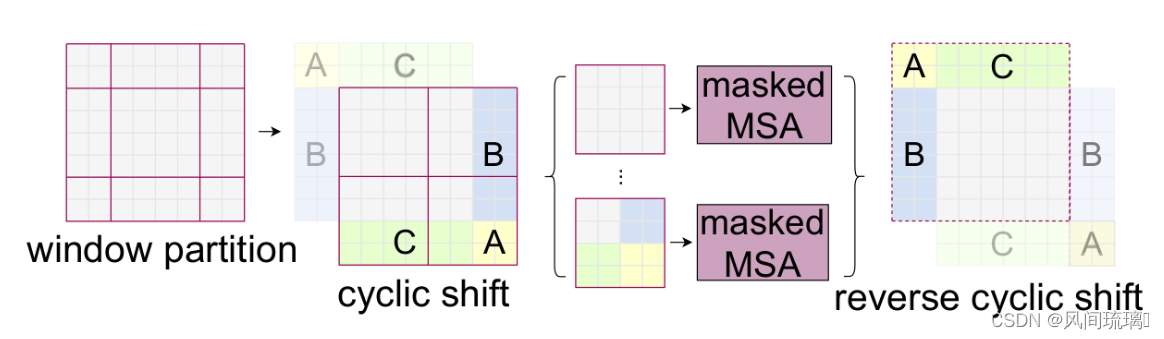
通过对特征图移位,并给 Attention 设置Mask来间接实现 Shift Window Attention (SW-MSA)。从而,在保持原 Window 数不变的情况下,使最后的计算结果等价。

将上图中的区域对应着进行标号,每个块进行了0-8的编号。为了减少计算量,首先将区域第一行移至第三行,然后再将新的的第一列移至第三列。网上另一种移动方式是:首先将1和2两块移到最下方7和8的下面,然后,将3和6移动到右边5和8的右边,最后,将0移动到最右下角。这两种最后得到到的特征图都是一样的。移动完后,4是一个窗口;将5和3合并成一个窗口;7和1合并成一个窗口;8、6、2和0合并成一个窗口。这样可以间接的划分为新得4x4窗口,所以能够保证计算量是一样的。
但是把不同的区域合并在一起进行MSA,会造成信息错乱,需要设计一种新的计算方式。为了防止这个问题,在实际计算中使用的是masked MSA即带蒙板mask的MSA,可以通过设置蒙板来隔绝不同区域的信息。
关于mask如何使用,可以看下下面这幅图,下图是以上面的区域5和区域3为例。

对于该窗口内的每一个patch在进行MSA计算时,都要先生成对应的query(q),key(k),value(v)。假设对于上图的像素0而言,得到 q 0 q^0 q0后要与每一个像素的k进行匹配(match),假设 α 0 , 0 \alpha _{0,0} α0,0代表 q 0 q^0 q0与像素0对应的 k 0 k^0 k0进行匹配的结果,同理可以得到 α 0 , 0 \alpha _{0,0} α0,0至 α 0 , 15 \alpha _{0,15} α0,15。按照普通的MSA计算,接下来进行
SoftMax操作。但对于这里的masked MSA,像素0是属于区域5的,只想让它和区域5内的像素进行匹配。那么可以将像素0与区域3中的所有像素匹配结果 α \alpha α都减去100(例如 α 0 , 2 \alpha _{0,2} α0,2, α 0 , 3 \alpha _{0,3} α0,3, α 0 , 6 \alpha _{0,6} α0,6, α 0 , 7 \alpha _{0,7} α0,7…)。一般 α \alpha α的值都很小,一般都是零点几,将其中一些数减去100后在通过
SoftMax得到对应的权重基本上为0。所以对于像素0而言实际上还是只和区域5内的像素进行了MSA。对于其他像素也可以采用相同的操作。注意,在计算完后还要把数据给挪回到原来的位置上。在这种Shifted操作之后,一个窗口可能由原始特征图中不相邻的patch组成,因此在计算时使用了
Mask,以限制对相邻 patch 的自注意。6.Relative Position bias(相对位置偏移)
绝对位置编码是在进行self-attention计算之前为每一个token添加一个可学习的参数,相对位置编码如下式所示,是在进行self-attention计算时,在计算过程中添加一个可学习的相对位置参数。
A t t e n t i o n ( Q , K , V ) = s o f t m a x ( Q K T d k + B ) V Attention(Q,K,V) = softmax(\cfrac{QK^T}{\sqrt{d_k}} + B)V Attention(Q,K,V)=softmax(dkQKT+B)V计算流程如下:
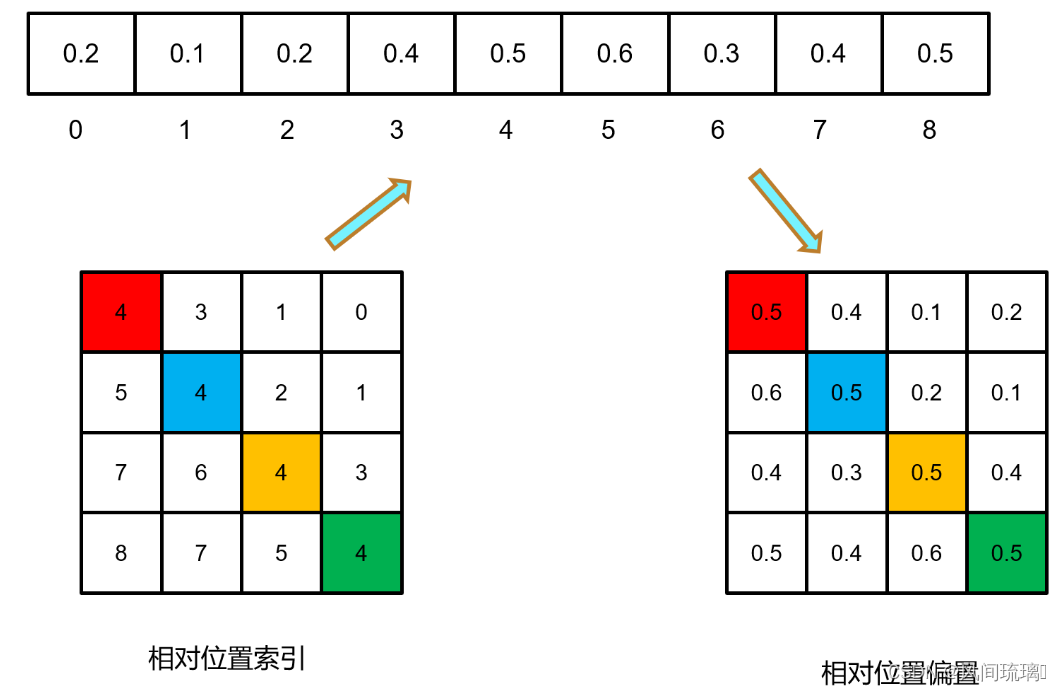
假设输入的feature map高宽为2,首先可以构建出每个像素的绝对位置,如左下方的矩阵所示,对于每个像素的绝对位置是使用行号和列号表示的。
 首先对蓝色像素使用q与所有像素k进行匹配过程中,是以蓝色像素为参考点,使用蓝色像素的绝对位置索引与其他位置索引进行相减,得到其他位置相对蓝色像素的相对位置索引。同理可以得到相对黄色,红色以及绿色像素的相对位置索引矩阵。
首先对蓝色像素使用q与所有像素k进行匹配过程中,是以蓝色像素为参考点,使用蓝色像素的绝对位置索引与其他位置索引进行相减,得到其他位置相对蓝色像素的相对位置索引。同理可以得到相对黄色,红色以及绿色像素的相对位置索引矩阵。接下来将每个
相对位置索引矩阵按行展平,并拼接在一起可以得到下面的4x4矩阵 。作者为了方便把二维索引给转成一维索引,如下图所示。
 首先在原始的相对位置索引上加上M-1(M为窗口的大小,在本示例中M=2)。然后将所有的行标都乘上2M-1。最后将行标和列标进行相加,这样即保证了相对位置关系。
首先在原始的相对位置索引上加上M-1(M为窗口的大小,在本示例中M=2)。然后将所有的行标都乘上2M-1。最后将行标和列标进行相加,这样即保证了相对位置关系。至此相对位置索引计算完毕,但是公式中要的是相对位置偏置参数,可训练参数 B ^ \widehat{B} B 保存在
relative position bias table(相对位置偏置表)里的,由于相对位置索引总共有(2M-1)×(2M-1)种,则表的长度为(2M-1) x (2M-1),上述公式中的相对位置偏执参数B是根据上面的相对位置索引表根据查relative position bias table表得到的,如下图所示。
最后使用对应的相对位置偏置表(Relative position bias table)进行映射即可得到最终的相对位置偏置B。7.网络结构
🥇Swin Transformer Block

上图为Swin Transformer Block结构图,一个 Swin Transformer block 由一个 基于移位窗口的 MSA 模块 构成,且后接一个夹有 GeLU 非线性在中间的 2 层 MLP。LayerNorm (LN) 层被应用于每个 MSA 模块和每个 MLP 前,且一个残差连接被应用于每个模块后。Swin Transformer使用window self-attention降低了计算复杂度,又为了保证不重叠窗口之间有联系,采用了shifted window self-attention的方式重新计算一遍窗口偏移之后的自注意力。所以Swin Transformer Block都是成对出现的 (W-MSA + SW-MSA为一对) ,先使用一个W-MSA结构再使用一个SW-MSA结构。所以堆叠Swin Transformer Block的次数都是偶数,在整体模型里Swin Transformer Blocks下的×2、×6就是因为成对使用的意思。
两个连续 Swin Transformer Blocks 的计算可表示为计算过程如下:

🥈Architecture

上图展示了 Swin Transformer 架构概览 (tiny 版 SwinT)。它首先将图片输入到Patch Partition模块中进行分块,即每4x4相邻的像素为一个Patch,然后在channel方向展平(flatten)。假设输入的是RGB三通道图片,那么每个patch就有4x4=16个像素,然后每个像素有R、G、B三个值所以展平后是16x3=48,所以通过Patch Partition后图像shape由 [H, W, 3]变成了[H/4, W/4, 48]。然后通过Linear Embeding层对每个像素的channel数据做线性变换,由48变成C,即图像shape再由 [H/4, W/4, 48]变成了
[H/4, W/4, C]。在源码中Patch Partition和Linear Embeding直接通过一个卷积层实现的。然后通过四个Stage构建不同大小的特征图,除了Stage1中先通过一个Linear Embeding层外,剩下三个stage都是先通过一个Patch Merging层进行下采样,像 CNN 一样逐层扩大感受野,以便获取到全局的信息。为产生一个
层次化表示 (Hierarchical Representation),随着网络的加深,tokens 数逐渐通过Patch Meraging被减少,其维度扩大。每个 Stage 都会改变张量的维度,从而形成一种层次化的表征。由此,该架构可方便地替换现有的各种视觉任务的主干网络。最后对于分类网络,后面还会接上一个Layer Norm层、全局池化层以及全连接层得到最终输出。如下图所示:

下图给出的关于不同Swin Transformer的配置,T(Tiny),S(Small),B(Base),L(Large):

参数说明:
⋆ \star ⋆win. sz. 7x7表示使用的窗口(Windows)的大小
⋆ \star ⋆dim表示feature map的channel深度(或者说token的向量长度)
⋆ \star ⋆head表示多头注意力模块中head的个数二、网络实现
1.构建Swin Transformers网络
""" Swin Transformer A PyTorch impl of : `Swin Transformer: Hierarchical Vision Transformer using Shifted Windows` - https://arxiv.org/pdf/2103.14030 Code/weights from https://github.com/microsoft/Swin-Transformer """ import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.nn.functional as F import torch.utils.checkpoint as checkpoint import numpy as np from typing import Optional def drop_path_f(x, drop_prob: float = 0., training: bool = False): """Drop paths (Stochastic Depth) per sample (when applied in main path of residual blocks). This is the same as the DropConnect impl I created for EfficientNet, etc networks, however, the original name is misleading as 'Drop Connect' is a different form of dropout in a separate paper... See discussion: https://github.com/tensorflow/tpu/issues/494#issuecomment-532968956 ... I've opted for changing the layer and argument names to 'drop path' rather than mix DropConnect as a layer name and use 'survival rate' as the argument. """ if drop_prob == 0. or not training: return x keep_prob = 1 - drop_prob shape = (x.shape[0],) + (1,) * (x.ndim - 1) # work with diff dim tensors, not just 2D ConvNets random_tensor = keep_prob + torch.rand(shape, dtype=x.dtype, device=x.device) random_tensor.floor_() # binarize output = x.div(keep_prob) * random_tensor return output class DropPath(nn.Module): """Drop paths (Stochastic Depth) per sample (when applied in main path of residual blocks). """ def __init__(self, drop_prob=None): super(DropPath, self).__init__() self.drop_prob = drop_prob def forward(self, x): return drop_path_f(x, self.drop_prob, self.training) def window_partition(x, window_size: int): """ 将feature map按照window_size划分成一个个没有重叠的window Args: x: (B, H, W, C) window_size (int): window size(M) Returns: windows: (num_windows*B, window_size, window_size, C) """ B, H, W, C = x.shape x = x.view(B, H // window_size, window_size, W // window_size, window_size, C) # permute: [B, H//Mh, Mh, W//Mw, Mw, C] -> [B, H//Mh, W//Mh, Mw, Mw, C] # view: [B, H//Mh, W//Mw, Mh, Mw, C] -> [B*num_windows, Mh, Mw, C] windows = x.permute(0, 1, 3, 2, 4, 5).contiguous().view(-1, window_size, window_size, C) return windows def window_reverse(windows, window_size: int, H: int, W: int): """ 将一个个window还原成一个feature map Args: windows: (num_windows*B, window_size, window_size, C) window_size (int): Window size(M) H (int): Height of image W (int): Width of image Returns: x: (B, H, W, C) """ B = int(windows.shape[0] / (H * W / window_size / window_size)) # view: [B*num_windows, Mh, Mw, C] -> [B, H//Mh, W//Mw, Mh, Mw, C] x = windows.view(B, H // window_size, W // window_size, window_size, window_size, -1) # permute: [B, H//Mh, W//Mw, Mh, Mw, C] -> [B, H//Mh, Mh, W//Mw, Mw, C] # view: [B, H//Mh, Mh, W//Mw, Mw, C] -> [B, H, W, C] x = x.permute(0, 1, 3, 2, 4, 5).contiguous().view(B, H, W, -1) return x class PatchEmbed(nn.Module): """ 2D Image to Patch Embedding """ def __init__(self, patch_size=4, in_c=3, embed_dim=96, norm_layer=None): super().__init__() patch_size = (patch_size, patch_size) self.patch_size = patch_size self.in_chans = in_c self.embed_dim = embed_dim self.proj = nn.Conv2d(in_c, embed_dim, kernel_size=patch_size, stride=patch_size) self.norm = norm_layer(embed_dim) if norm_layer else nn.Identity() def forward(self, x): _, _, H, W = x.shape # padding # 如果输入图片的H,W不是patch_size的整数倍,需要进行padding pad_input = (H % self.patch_size[0] != 0) or (W % self.patch_size[1] != 0) if pad_input: # to pad the last 3 dimensions, # (W_left, W_right, H_top,H_bottom, C_front, C_back) x = F.pad(x, (0, self.patch_size[1] - W % self.patch_size[1], 0, self.patch_size[0] - H % self.patch_size[0], 0, 0)) # 下采样patch_size倍 x = self.proj(x) _, _, H, W = x.shape # flatten: [B, C, H, W] -> [B, C, HW] # transpose: [B, C, HW] -> [B, HW, C] x = x.flatten(2).transpose(1, 2) x = self.norm(x) return x, H, W class PatchMerging(nn.Module): r""" Patch Merging Layer. Args: dim (int): Number of input channels. norm_layer (nn.Module, optional): Normalization layer. Default: nn.LayerNorm """ def __init__(self, dim, norm_layer=nn.LayerNorm): super().__init__() self.dim = dim self.reduction = nn.Linear(4 * dim, 2 * dim, bias=False) self.norm = norm_layer(4 * dim) def forward(self, x, H, W): """ x: B, H*W, C """ B, L, C = x.shape assert L == H * W, "input feature has wrong size" x = x.view(B, H, W, C) # padding # 如果输入feature map的H,W不是2的整数倍,需要进行padding pad_input = (H % 2 == 1) or (W % 2 == 1) if pad_input: # to pad the last 3 dimensions, starting from the last dimension and moving forward. # (C_front, C_back, W_left, W_right, H_top, H_bottom) # 注意这里的Tensor通道是[B, H, W, C],所以会和官方文档有些不同 x = F.pad(x, (0, 0, 0, W % 2, 0, H % 2)) x0 = x[:, 0::2, 0::2, :] # [B, H/2, W/2, C] x1 = x[:, 1::2, 0::2, :] # [B, H/2, W/2, C] x2 = x[:, 0::2, 1::2, :] # [B, H/2, W/2, C] x3 = x[:, 1::2, 1::2, :] # [B, H/2, W/2, C] x = torch.cat([x0, x1, x2, x3], -1) # [B, H/2, W/2, 4*C] x = x.view(B, -1, 4 * C) # [B, H/2*W/2, 4*C] x = self.norm(x) x = self.reduction(x) # [B, H/2*W/2, 2*C] return x class Mlp(nn.Module): """ MLP as used in Vision Transformer, MLP-Mixer and related networks """ def __init__(self, in_features, hidden_features=None, out_features=None, act_layer=nn.GELU, drop=0.): super().__init__() out_features = out_features or in_features hidden_features = hidden_features or in_features self.fc1 = nn.Linear(in_features, hidden_features) self.act = act_layer() self.drop1 = nn.Dropout(drop) self.fc2 = nn.Linear(hidden_features, out_features) self.drop2 = nn.Dropout(drop) def forward(self, x): x = self.fc1(x) x = self.act(x) x = self.drop1(x) x = self.fc2(x) x = self.drop2(x) return x class WindowAttention(nn.Module): r""" Window based multi-head self attention (W-MSA) module with relative position bias. It supports both of shifted and non-shifted window. Args: dim (int): Number of input channels. window_size (tuple[int]): The height and width of the window. num_heads (int): Number of attention heads. qkv_bias (bool, optional): If True, add a learnable bias to query, key, value. Default: True attn_drop (float, optional): Dropout ratio of attention weight. Default: 0.0 proj_drop (float, optional): Dropout ratio of output. Default: 0.0 """ def __init__(self, dim, window_size, num_heads, qkv_bias=True, attn_drop=0., proj_drop=0.): super().__init__() self.dim = dim self.window_size = window_size # [Mh, Mw] self.num_heads = num_heads head_dim = dim // num_heads self.scale = head_dim ** -0.5 # define a parameter table of relative position bias self.relative_position_bias_table = nn.Parameter( torch.zeros((2 * window_size[0] - 1) * (2 * window_size[1] - 1), num_heads)) # [2*Mh-1 * 2*Mw-1, nH] # get pair-wise relative position index for each token inside the window coords_h = torch.arange(self.window_size[0]) coords_w = torch.arange(self.window_size[1]) coords = torch.stack(torch.meshgrid([coords_h, coords_w], indexing="ij")) # [2, Mh, Mw] coords_flatten = torch.flatten(coords, 1) # [2, Mh*Mw] # [2, Mh*Mw, 1] - [2, 1, Mh*Mw] relative_coords = coords_flatten[:, :, None] - coords_flatten[:, None, :] # [2, Mh*Mw, Mh*Mw] relative_coords = relative_coords.permute(1, 2, 0).contiguous() # [Mh*Mw, Mh*Mw, 2] relative_coords[:, :, 0] += self.window_size[0] - 1 # shift to start from 0 relative_coords[:, :, 1] += self.window_size[1] - 1 relative_coords[:, :, 0] *= 2 * self.window_size[1] - 1 relative_position_index = relative_coords.sum(-1) # [Mh*Mw, Mh*Mw] self.register_buffer("relative_position_index", relative_position_index) self.qkv = nn.Linear(dim, dim * 3, bias=qkv_bias) self.attn_drop = nn.Dropout(attn_drop) self.proj = nn.Linear(dim, dim) self.proj_drop = nn.Dropout(proj_drop) nn.init.trunc_normal_(self.relative_position_bias_table, std=.02) self.softmax = nn.Softmax(dim=-1) def forward(self, x, mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None): """ Args: x: input features with shape of (num_windows*B, Mh*Mw, C) mask: (0/-inf) mask with shape of (num_windows, Wh*Ww, Wh*Ww) or None """ # [batch_size*num_windows, Mh*Mw, total_embed_dim] B_, N, C = x.shape # qkv(): -> [batch_size*num_windows, Mh*Mw, 3 * total_embed_dim] # reshape: -> [batch_size*num_windows, Mh*Mw, 3, num_heads, embed_dim_per_head] # permute: -> [3, batch_size*num_windows, num_heads, Mh*Mw, embed_dim_per_head] qkv = self.qkv(x).reshape(B_, N, 3, self.num_heads, C // self.num_heads).permute(2, 0, 3, 1, 4) # [batch_size*num_windows, num_heads, Mh*Mw, embed_dim_per_head] q, k, v = qkv.unbind(0) # make torchscript happy (cannot use tensor as tuple) # transpose: -> [batch_size*num_windows, num_heads, embed_dim_per_head, Mh*Mw] # @: multiply -> [batch_size*num_windows, num_heads, Mh*Mw, Mh*Mw] q = q * self.scale attn = (q @ k.transpose(-2, -1)) # relative_position_bias_table.view: [Mh*Mw*Mh*Mw,nH] -> [Mh*Mw,Mh*Mw,nH] relative_position_bias = self.relative_position_bias_table[self.relative_position_index.view(-1)].view( self.window_size[0] * self.window_size[1], self.window_size[0] * self.window_size[1], -1) relative_position_bias = relative_position_bias.permute(2, 0, 1).contiguous() # [nH, Mh*Mw, Mh*Mw] attn = attn + relative_position_bias.unsqueeze(0) if mask is not None: # mask: [nW, Mh*Mw, Mh*Mw] nW = mask.shape[0] # num_windows # attn.view: [batch_size, num_windows, num_heads, Mh*Mw, Mh*Mw] # mask.unsqueeze: [1, nW, 1, Mh*Mw, Mh*Mw] attn = attn.view(B_ // nW, nW, self.num_heads, N, N) + mask.unsqueeze(1).unsqueeze(0) attn = attn.view(-1, self.num_heads, N, N) attn = self.softmax(attn) else: attn = self.softmax(attn) attn = self.attn_drop(attn) # @: multiply -> [batch_size*num_windows, num_heads, Mh*Mw, embed_dim_per_head] # transpose: -> [batch_size*num_windows, Mh*Mw, num_heads, embed_dim_per_head] # reshape: -> [batch_size*num_windows, Mh*Mw, total_embed_dim] x = (attn @ v).transpose(1, 2).reshape(B_, N, C) x = self.proj(x) x = self.proj_drop(x) return x class SwinTransformerBlock(nn.Module): r""" Swin Transformer Block. Args: dim (int): Number of input channels. num_heads (int): Number of attention heads. window_size (int): Window size. shift_size (int): Shift size for SW-MSA. mlp_ratio (float): Ratio of mlp hidden dim to embedding dim. qkv_bias (bool, optional): If True, add a learnable bias to query, key, value. Default: True drop (float, optional): Dropout rate. Default: 0.0 attn_drop (float, optional): Attention dropout rate. Default: 0.0 drop_path (float, optional): Stochastic depth rate. Default: 0.0 act_layer (nn.Module, optional): Activation layer. Default: nn.GELU norm_layer (nn.Module, optional): Normalization layer. Default: nn.LayerNorm """ def __init__(self, dim, num_heads, window_size=7, shift_size=0, mlp_ratio=4., qkv_bias=True, drop=0., attn_drop=0., drop_path=0., act_layer=nn.GELU, norm_layer=nn.LayerNorm): super().__init__() self.dim = dim self.num_heads = num_heads self.window_size = window_size self.shift_size = shift_size self.mlp_ratio = mlp_ratio assert 0 <= self.shift_size < self.window_size, "shift_size must in 0-window_size" self.norm1 = norm_layer(dim) self.attn = WindowAttention( dim, window_size=(self.window_size, self.window_size), num_heads=num_heads, qkv_bias=qkv_bias, attn_drop=attn_drop, proj_drop=drop) self.drop_path = DropPath(drop_path) if drop_path > 0. else nn.Identity() self.norm2 = norm_layer(dim) mlp_hidden_dim = int(dim * mlp_ratio) self.mlp = Mlp(in_features=dim, hidden_features=mlp_hidden_dim, act_layer=act_layer, drop=drop) def forward(self, x, attn_mask): H, W = self.H, self.W B, L, C = x.shape assert L == H * W, "input feature has wrong size" shortcut = x x = self.norm1(x) x = x.view(B, H, W, C) # pad feature maps to multiples of window size # 把feature map给pad到window size的整数倍 pad_l = pad_t = 0 pad_r = (self.window_size - W % self.window_size) % self.window_size pad_b = (self.window_size - H % self.window_size) % self.window_size x = F.pad(x, (0, 0, pad_l, pad_r, pad_t, pad_b)) _, Hp, Wp, _ = x.shape # cyclic shift if self.shift_size > 0: shifted_x = torch.roll(x, shifts=(-self.shift_size, -self.shift_size), dims=(1, 2)) else: shifted_x = x attn_mask = None # partition windows x_windows = window_partition(shifted_x, self.window_size) # [nW*B, Mh, Mw, C] x_windows = x_windows.view(-1, self.window_size * self.window_size, C) # [nW*B, Mh*Mw, C] # W-MSA/SW-MSA attn_windows = self.attn(x_windows, mask=attn_mask) # [nW*B, Mh*Mw, C] # merge windows attn_windows = attn_windows.view(-1, self.window_size, self.window_size, C) # [nW*B, Mh, Mw, C] shifted_x = window_reverse(attn_windows, self.window_size, Hp, Wp) # [B, H', W', C] # reverse cyclic shift if self.shift_size > 0: x = torch.roll(shifted_x, shifts=(self.shift_size, self.shift_size), dims=(1, 2)) else: x = shifted_x if pad_r > 0 or pad_b > 0: # 把前面pad的数据移除掉 x = x[:, :H, :W, :].contiguous() x = x.view(B, H * W, C) # FFN x = shortcut + self.drop_path(x) x = x + self.drop_path(self.mlp(self.norm2(x))) return x class BasicLayer(nn.Module): """ A basic Swin Transformer layer for one stage. Args: dim (int): Number of input channels. depth (int): Number of blocks. num_heads (int): Number of attention heads. window_size (int): Local window size. mlp_ratio (float): Ratio of mlp hidden dim to embedding dim. qkv_bias (bool, optional): If True, add a learnable bias to query, key, value. Default: True drop (float, optional): Dropout rate. Default: 0.0 attn_drop (float, optional): Attention dropout rate. Default: 0.0 drop_path (float | tuple[float], optional): Stochastic depth rate. Default: 0.0 norm_layer (nn.Module, optional): Normalization layer. Default: nn.LayerNorm downsample (nn.Module | None, optional): Downsample layer at the end of the layer. Default: None use_checkpoint (bool): Whether to use checkpointing to save memory. Default: False. """ def __init__(self, dim, depth, num_heads, window_size, mlp_ratio=4., qkv_bias=True, drop=0., attn_drop=0., drop_path=0., norm_layer=nn.LayerNorm, downsample=None, use_checkpoint=False): super().__init__() self.dim = dim self.depth = depth self.window_size = window_size self.use_checkpoint = use_checkpoint self.shift_size = window_size // 2 # build blocks self.blocks = nn.ModuleList([ SwinTransformerBlock( dim=dim, num_heads=num_heads, window_size=window_size, shift_size=0 if (i % 2 == 0) else self.shift_size, mlp_ratio=mlp_ratio, qkv_bias=qkv_bias, drop=drop, attn_drop=attn_drop, drop_path=drop_path[i] if isinstance(drop_path, list) else drop_path, norm_layer=norm_layer) for i in range(depth)]) # patch merging layer if downsample is not None: self.downsample = downsample(dim=dim, norm_layer=norm_layer) else: self.downsample = None def create_mask(self, x, H, W): # calculate attention mask for SW-MSA # 保证Hp和Wp是window_size的整数倍 Hp = int(np.ceil(H / self.window_size)) * self.window_size Wp = int(np.ceil(W / self.window_size)) * self.window_size # 拥有和feature map一样的通道排列顺序,方便后续window_partition img_mask = torch.zeros((1, Hp, Wp, 1), device=x.device) # [1, Hp, Wp, 1] h_slices = (slice(0, -self.window_size), slice(-self.window_size, -self.shift_size), slice(-self.shift_size, None)) w_slices = (slice(0, -self.window_size), slice(-self.window_size, -self.shift_size), slice(-self.shift_size, None)) cnt = 0 for h in h_slices: for w in w_slices: img_mask[:, h, w, :] = cnt cnt += 1 mask_windows = window_partition(img_mask, self.window_size) # [nW, Mh, Mw, 1] mask_windows = mask_windows.view(-1, self.window_size * self.window_size) # [nW, Mh*Mw] attn_mask = mask_windows.unsqueeze(1) - mask_windows.unsqueeze(2) # [nW, 1, Mh*Mw] - [nW, Mh*Mw, 1] # [nW, Mh*Mw, Mh*Mw] attn_mask = attn_mask.masked_fill(attn_mask != 0, float(-100.0)).masked_fill(attn_mask == 0, float(0.0)) return attn_mask def forward(self, x, H, W): attn_mask = self.create_mask(x, H, W) # [nW, Mh*Mw, Mh*Mw] for blk in self.blocks: blk.H, blk.W = H, W if not torch.jit.is_scripting() and self.use_checkpoint: x = checkpoint.checkpoint(blk, x, attn_mask) else: x = blk(x, attn_mask) if self.downsample is not None: x = self.downsample(x, H, W) H, W = (H + 1) // 2, (W + 1) // 2 return x, H, W class SwinTransformer(nn.Module): r""" Swin Transformer A PyTorch impl of : `Swin Transformer: Hierarchical Vision Transformer using Shifted Windows` - https://arxiv.org/pdf/2103.14030 Args: patch_size (int | tuple(int)): Patch size. Default: 4 in_chans (int): Number of input image channels. Default: 3 num_classes (int): Number of classes for classification head. Default: 1000 embed_dim (int): Patch embedding dimension. Default: 96 depths (tuple(int)): Depth of each Swin Transformer layer. num_heads (tuple(int)): Number of attention heads in different layers. window_size (int): Window size. Default: 7 mlp_ratio (float): Ratio of mlp hidden dim to embedding dim. Default: 4 qkv_bias (bool): If True, add a learnable bias to query, key, value. Default: True drop_rate (float): Dropout rate. Default: 0 attn_drop_rate (float): Attention dropout rate. Default: 0 drop_path_rate (float): Stochastic depth rate. Default: 0.1 norm_layer (nn.Module): Normalization layer. Default: nn.LayerNorm. patch_norm (bool): If True, add normalization after patch embedding. Default: True use_checkpoint (bool): Whether to use checkpointing to save memory. Default: False """ def __init__(self, patch_size=4, in_chans=3, num_classes=1000, embed_dim=96, depths=(2, 2, 6, 2), num_heads=(3, 6, 12, 24), window_size=7, mlp_ratio=4., qkv_bias=True, drop_rate=0., attn_drop_rate=0., drop_path_rate=0.1, norm_layer=nn.LayerNorm, patch_norm=True, use_checkpoint=False, **kwargs): super().__init__() self.num_classes = num_classes self.num_layers = len(depths) self.embed_dim = embed_dim self.patch_norm = patch_norm # stage4输出特征矩阵的channels self.num_features = int(embed_dim * 2 ** (self.num_layers - 1)) self.mlp_ratio = mlp_ratio # split image into non-overlapping patches self.patch_embed = PatchEmbed( patch_size=patch_size, in_c=in_chans, embed_dim=embed_dim, norm_layer=norm_layer if self.patch_norm else None) self.pos_drop = nn.Dropout(p=drop_rate) # stochastic depth dpr = [x.item() for x in torch.linspace(0, drop_path_rate, sum(depths))] # stochastic depth decay rule # build layers self.layers = nn.ModuleList() for i_layer in range(self.num_layers): # 注意这里构建的stage和论文图中有些差异 # 这里的stage不包含该stage的patch_merging层,包含的是下个stage的 layers = BasicLayer(dim=int(embed_dim * 2 ** i_layer), depth=depths[i_layer], num_heads=num_heads[i_layer], window_size=window_size, mlp_ratio=self.mlp_ratio, qkv_bias=qkv_bias, drop=drop_rate, attn_drop=attn_drop_rate, drop_path=dpr[sum(depths[:i_layer]):sum(depths[:i_layer + 1])], norm_layer=norm_layer, downsample=PatchMerging if (i_layer < self.num_layers - 1) else None, use_checkpoint=use_checkpoint) self.layers.append(layers) self.norm = norm_layer(self.num_features) self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool1d(1) self.head = nn.Linear(self.num_features, num_classes) if num_classes > 0 else nn.Identity() self.apply(self._init_weights) def _init_weights(self, m): if isinstance(m, nn.Linear): nn.init.trunc_normal_(m.weight, std=.02) if isinstance(m, nn.Linear) and m.bias is not None: nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0) elif isinstance(m, nn.LayerNorm): nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0) nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1.0) def forward(self, x): # x: [B, L, C] x, H, W = self.patch_embed(x) x = self.pos_drop(x) for layer in self.layers: x, H, W = layer(x, H, W) x = self.norm(x) # [B, L, C] x = self.avgpool(x.transpose(1, 2)) # [B, C, 1] x = torch.flatten(x, 1) x = self.head(x) return x def swin_tiny_patch4_window7_224(num_classes: int = 1000, **kwargs): # trained ImageNet-1K # https://github.com/SwinTransformer/storage/releases/download/v1.0.0/swin_tiny_patch4_window7_224.pth model = SwinTransformer(in_chans=3, patch_size=4, window_size=7, embed_dim=96, depths=(2, 2, 6, 2), num_heads=(3, 6, 12, 24), num_classes=num_classes, **kwargs) return model def swin_small_patch4_window7_224(num_classes: int = 1000, **kwargs): # trained ImageNet-1K # https://github.com/SwinTransformer/storage/releases/download/v1.0.0/swin_small_patch4_window7_224.pth model = SwinTransformer(in_chans=3, patch_size=4, window_size=7, embed_dim=96, depths=(2, 2, 18, 2), num_heads=(3, 6, 12, 24), num_classes=num_classes, **kwargs) return model def swin_base_patch4_window7_224(num_classes: int = 1000, **kwargs): # trained ImageNet-1K # https://github.com/SwinTransformer/storage/releases/download/v1.0.0/swin_base_patch4_window7_224.pth model = SwinTransformer(in_chans=3, patch_size=4, window_size=7, embed_dim=128, depths=(2, 2, 18, 2), num_heads=(4, 8, 16, 32), num_classes=num_classes, **kwargs) return model def swin_base_patch4_window12_384(num_classes: int = 1000, **kwargs): # trained ImageNet-1K # https://github.com/SwinTransformer/storage/releases/download/v1.0.0/swin_base_patch4_window12_384.pth model = SwinTransformer(in_chans=3, patch_size=4, window_size=12, embed_dim=128, depths=(2, 2, 18, 2), num_heads=(4, 8, 16, 32), num_classes=num_classes, **kwargs) return model def swin_base_patch4_window7_224_in22k(num_classes: int = 21841, **kwargs): # trained ImageNet-22K # https://github.com/SwinTransformer/storage/releases/download/v1.0.0/swin_base_patch4_window7_224_22k.pth model = SwinTransformer(in_chans=3, patch_size=4, window_size=7, embed_dim=128, depths=(2, 2, 18, 2), num_heads=(4, 8, 16, 32), num_classes=num_classes, **kwargs) return model def swin_base_patch4_window12_384_in22k(num_classes: int = 21841, **kwargs): # trained ImageNet-22K # https://github.com/SwinTransformer/storage/releases/download/v1.0.0/swin_base_patch4_window12_384_22k.pth model = SwinTransformer(in_chans=3, patch_size=4, window_size=12, embed_dim=128, depths=(2, 2, 18, 2), num_heads=(4, 8, 16, 32), num_classes=num_classes, **kwargs) return model def swin_large_patch4_window7_224_in22k(num_classes: int = 21841, **kwargs): # trained ImageNet-22K # https://github.com/SwinTransformer/storage/releases/download/v1.0.0/swin_large_patch4_window7_224_22k.pth model = SwinTransformer(in_chans=3, patch_size=4, window_size=7, embed_dim=192, depths=(2, 2, 18, 2), num_heads=(6, 12, 24, 48), num_classes=num_classes, **kwargs) return model def swin_large_patch4_window12_384_in22k(num_classes: int = 21841, **kwargs): # trained ImageNet-22K # https://github.com/SwinTransformer/storage/releases/download/v1.0.0/swin_large_patch4_window12_384_22k.pth model = SwinTransformer(in_chans=3, patch_size=4, window_size=12, embed_dim=192, depths=(2, 2, 18, 2), num_heads=(6, 12, 24, 48), num_classes=num_classes, **kwargs) return model- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
- 213
- 214
- 215
- 216
- 217
- 218
- 219
- 220
- 221
- 222
- 223
- 224
- 225
- 226
- 227
- 228
- 229
- 230
- 231
- 232
- 233
- 234
- 235
- 236
- 237
- 238
- 239
- 240
- 241
- 242
- 243
- 244
- 245
- 246
- 247
- 248
- 249
- 250
- 251
- 252
- 253
- 254
- 255
- 256
- 257
- 258
- 259
- 260
- 261
- 262
- 263
- 264
- 265
- 266
- 267
- 268
- 269
- 270
- 271
- 272
- 273
- 274
- 275
- 276
- 277
- 278
- 279
- 280
- 281
- 282
- 283
- 284
- 285
- 286
- 287
- 288
- 289
- 290
- 291
- 292
- 293
- 294
- 295
- 296
- 297
- 298
- 299
- 300
- 301
- 302
- 303
- 304
- 305
- 306
- 307
- 308
- 309
- 310
- 311
- 312
- 313
- 314
- 315
- 316
- 317
- 318
- 319
- 320
- 321
- 322
- 323
- 324
- 325
- 326
- 327
- 328
- 329
- 330
- 331
- 332
- 333
- 334
- 335
- 336
- 337
- 338
- 339
- 340
- 341
- 342
- 343
- 344
- 345
- 346
- 347
- 348
- 349
- 350
- 351
- 352
- 353
- 354
- 355
- 356
- 357
- 358
- 359
- 360
- 361
- 362
- 363
- 364
- 365
- 366
- 367
- 368
- 369
- 370
- 371
- 372
- 373
- 374
- 375
- 376
- 377
- 378
- 379
- 380
- 381
- 382
- 383
- 384
- 385
- 386
- 387
- 388
- 389
- 390
- 391
- 392
- 393
- 394
- 395
- 396
- 397
- 398
- 399
- 400
- 401
- 402
- 403
- 404
- 405
- 406
- 407
- 408
- 409
- 410
- 411
- 412
- 413
- 414
- 415
- 416
- 417
- 418
- 419
- 420
- 421
- 422
- 423
- 424
- 425
- 426
- 427
- 428
- 429
- 430
- 431
- 432
- 433
- 434
- 435
- 436
- 437
- 438
- 439
- 440
- 441
- 442
- 443
- 444
- 445
- 446
- 447
- 448
- 449
- 450
- 451
- 452
- 453
- 454
- 455
- 456
- 457
- 458
- 459
- 460
- 461
- 462
- 463
- 464
- 465
- 466
- 467
- 468
- 469
- 470
- 471
- 472
- 473
- 474
- 475
- 476
- 477
- 478
- 479
- 480
- 481
- 482
- 483
- 484
- 485
- 486
- 487
- 488
- 489
- 490
- 491
- 492
- 493
- 494
- 495
- 496
- 497
- 498
- 499
- 500
- 501
- 502
- 503
- 504
- 505
- 506
- 507
- 508
- 509
- 510
- 511
- 512
- 513
- 514
- 515
- 516
- 517
- 518
- 519
- 520
- 521
- 522
- 523
- 524
- 525
- 526
- 527
- 528
- 529
- 530
- 531
- 532
- 533
- 534
- 535
- 536
- 537
- 538
- 539
- 540
- 541
- 542
- 543
- 544
- 545
- 546
- 547
- 548
- 549
- 550
- 551
- 552
- 553
- 554
- 555
- 556
- 557
- 558
- 559
- 560
- 561
- 562
- 563
- 564
- 565
- 566
- 567
- 568
- 569
- 570
- 571
- 572
- 573
- 574
- 575
- 576
- 577
- 578
- 579
- 580
- 581
- 582
- 583
- 584
- 585
- 586
- 587
- 588
- 589
- 590
- 591
- 592
- 593
- 594
- 595
- 596
- 597
- 598
- 599
- 600
- 601
- 602
- 603
- 604
- 605
- 606
- 607
- 608
- 609
- 610
- 611
- 612
- 613
- 614
- 615
- 616
- 617
- 618
- 619
- 620
- 621
- 622
- 623
- 624
- 625
- 626
- 627
- 628
- 629
- 630
- 631
- 632
- 633
- 634
- 635
- 636
- 637
- 638
- 639
- 640
- 641
- 642
- 643
- 644
- 645
- 646
- 647
- 648
- 649
- 650
- 651
- 652
- 653
- 654
- 655
- 656
- 657
- 658
- 659
- 660
- 661
- 662
- 663
- 664
- 665
- 666
- 667
- 668
- 669
- 670
- 671
- 672
- 673
- 674
- 675
- 676
- 677
2.训练和测试模型
import os import argparse import torch import torch.optim as optim from torch.utils.tensorboard import SummaryWriter from torchvision import transforms from my_dataset import MyDataSet from model import swin_tiny_patch4_window7_224 as create_model from utils import read_split_data, train_one_epoch, evaluate def main(args): device = torch.device(args.device if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu") if os.path.exists("./weights") is False: os.makedirs("./weights") tb_writer = SummaryWriter() train_images_path, train_images_label, val_images_path, val_images_label = read_split_data(args.data_path) img_size = 224 data_transform = { "train": transforms.Compose([transforms.RandomResizedCrop(img_size), transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(), transforms.ToTensor(), transforms.Normalize([0.485, 0.456, 0.406], [0.229, 0.224, 0.225])]), "val": transforms.Compose([transforms.Resize(int(img_size * 1.143)), transforms.CenterCrop(img_size), transforms.ToTensor(), transforms.Normalize([0.485, 0.456, 0.406], [0.229, 0.224, 0.225])])} # 实例化训练数据集 train_dataset = MyDataSet(images_path=train_images_path, images_class=train_images_label, transform=data_transform["train"]) # 实例化验证数据集 val_dataset = MyDataSet(images_path=val_images_path, images_class=val_images_label, transform=data_transform["val"]) batch_size = args.batch_size nw = min([os.cpu_count(), batch_size if batch_size > 1 else 0, 8]) # number of workers print('Using {} dataloader workers every process'.format(nw)) train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True, pin_memory=True, num_workers=nw, collate_fn=train_dataset.collate_fn) val_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(val_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False, pin_memory=True, num_workers=nw, collate_fn=val_dataset.collate_fn) model = create_model(num_classes=args.num_classes).to(device) if args.weights != "": assert os.path.exists(args.weights), "weights file: '{}' not exist.".format(args.weights) weights_dict = torch.load(args.weights, map_location=device)["model"] # 删除有关分类类别的权重 for k in list(weights_dict.keys()): if "head" in k: del weights_dict[k] print(model.load_state_dict(weights_dict, strict=False)) if args.freeze_layers: for name, para in model.named_parameters(): # 除head外,其他权重全部冻结 if "head" not in name: para.requires_grad_(False) else: print("training {}".format(name)) pg = [p for p in model.parameters() if p.requires_grad] optimizer = optim.AdamW(pg, lr=args.lr, weight_decay=5E-2) for epoch in range(args.epochs): # train train_loss, train_acc = train_one_epoch(model=model, optimizer=optimizer, data_loader=train_loader, device=device, epoch=epoch) # validate val_loss, val_acc = evaluate(model=model, data_loader=val_loader, device=device, epoch=epoch) tags = ["train_loss", "train_acc", "val_loss", "val_acc", "learning_rate"] tb_writer.add_scalar(tags[0], train_loss, epoch) tb_writer.add_scalar(tags[1], train_acc, epoch) tb_writer.add_scalar(tags[2], val_loss, epoch) tb_writer.add_scalar(tags[3], val_acc, epoch) tb_writer.add_scalar(tags[4], optimizer.param_groups[0]["lr"], epoch) torch.save(model.state_dict(), "./weights/model-{}.pth".format(epoch)) if __name__ == '__main__': parser = argparse.ArgumentParser() parser.add_argument('--num_classes', type=int, default=5) parser.add_argument('--epochs', type=int, default=10) parser.add_argument('--batch-size', type=int, default=8) parser.add_argument('--lr', type=float, default=0.0001) # 数据集所在根目录 # https://storage.googleapis.com/download.tensorflow.org/example_images/flower_photos.tgz parser.add_argument('--data-path', type=str, default="F:/NN/Learn_Pytorch/flower_photos") # 预训练权重路径,如果不想载入就设置为空字符 parser.add_argument('--weights', type=str, default='./swin_tiny_patch4_window7_224.pth', help='initial weights path') # 是否冻结权重 parser.add_argument('--freeze-layers', type=bool, default=False) parser.add_argument('--device', default='cuda:0', help='device id (i.e. 0 or 0,1 or cpu)') opt = parser.parse_args() main(opt)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
这里使用了预训练权重,在其基础上训练自己的数据集。训练100epoch的准确率能到达96%左右。

三、实现图像分类
这里使用花朵数据集,下载连接:https://storage.googleapis.com/download.tensorflow.org/example_images/flower_photos.tgz
def main(): device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu") # 与训练的预处理一样 data_transform = transforms.Compose([ transforms.Resize(256), transforms.CenterCrop(224), transforms.ToTensor(), transforms.Normalize([0.485, 0.456, 0.406], [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]) ]) # 加载图片 img_path = 'daisy2.jpg' assert os.path.exists(img_path), "file: '{}' does not exist.".format(img_path) image = Image.open(img_path) # image.show() # [N, C, H, W] img = data_transform(image) # 扩展维度 img = torch.unsqueeze(img, dim=0) # 获取标签 json_path = 'class_indices.json' assert os.path.exists(json_path), "file: '{}' does not exist.".format(json_path) with open(json_path, 'r') as f: # 使用json.load()函数加载JSON文件的内容并将其存储在一个Python字典中 class_indict = json.load(f) # create model model = create_model(num_classes=5).to(device) # load model weights model_weight_path = "./weights/model-9.pth" model.load_state_dict(torch.load(model_weight_path, map_location=device)) model.eval() with torch.no_grad(): # 对输入图像进行预测 output = torch.squeeze(model(img.to(device))).cpu() # 对模型的输出进行 softmax 操作,将输出转换为类别概率 predict = torch.softmax(output, dim=0) # 得到高概率的类别的索引 predict_cla = torch.argmax(predict).numpy() res = "class: {} prob: {:.3}".format(class_indict[str(predict_cla)], predict[predict_cla].numpy()) draw = ImageDraw.Draw(image) # 文本的左上角位置 position = (10, 10) # fill 指定文本颜色 draw.text(position, res, fill='green') image.show() for i in range(len(predict)): print("class: {:10} prob: {:.3}".format(class_indict[str(i)], predict[i].numpy()))- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
分类结果:

结束语
感谢阅读吾之文章,今已至此次旅程之终站 🛬。
吾望斯文献能供尔以宝贵之信息与知识也 🎉。
学习者之途,若藏于天际之星辰🍥,吾等皆当努力熠熠生辉,持续前行。
然而,如若斯文献有益于尔,何不以三连为礼?点赞、留言、收藏 - 此等皆以证尔对作者之支持与鼓励也 💞。
-
相关阅读:
iNeuOS工业互联网操作系统,顺利从NetCore3.1升级到Net6的过程汇报
独立站卖家如何借势营销
Go 接口
数据结构(二)顺序表和链表
Java毕业设计基于springboot 美妆化妆品销售购物网站多商家 前后端分离node
opencv+tkinter来在GUI内读取视频或摄像头
要使用API接口获取淘宝电商平台的数据,您需要遵循以下步骤:
python的前缀树(字典树)
解忧云SMS短信服务平台系统 短信发送系统 全解密完美版
C#,动态规划(DP)模拟退火(Simulated Annealing)算法与源代码
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_53144843/article/details/133548227