-
【mmdetection代码解读 3.x版本】以Fcos+FasterRcnn为例
前言
因为之前一直在搞DOTA数据集的旋转框检测,所以一直在用mmrotate作为主要工具。现在回来重新搞mmdetection框架发现有了不小的变化,出了3.x版本的新内容。相比于之前的版本变化比较大,因此正好做一个代码解读与之前发布的2.x版本进行对照。
新版本最让我惊喜的是可以将单阶段检测器作为 RPN进行两阶段的检测,官方文档如下
https://mmdetection.readthedocs.io/zh_CN/latest/user_guides/single_stage_as_rpn.html按照官方文档的要求我们将Fcos作为RPN的提取网络,为ROI提取proposal,具体配置文件如下
_base_ = [ '../_base_/models/faster-rcnn_r50_fpn.py', '../_base_/datasets/coco_detection.py', '../_base_/schedules/schedule_1x.py', '../_base_/default_runtime.py' ] model = dict( # 从 configs/fcos/fcos_r50-caffe_fpn_gn-head_1x_coco.py 复制 neck=dict( start_level=1, add_extra_convs='on_output', # 使用 P5 relu_before_extra_convs=True), rpn_head=dict( _delete_=True, # 忽略未使用的旧设置 type='FCOSHead', num_classes=1, # 对于 rpn, num_classes = 1,如果 num_classes > 1,它将在 TwoStageDetector 中自动设置为1 in_channels=256, stacked_convs=4, feat_channels=256, strides=[8, 16, 32, 64, 128], loss_cls=dict( type='FocalLoss', use_sigmoid=True, gamma=2.0, alpha=0.25, loss_weight=1.0), loss_bbox=dict(type='IoULoss', loss_weight=1.0), loss_centerness=dict( type='CrossEntropyLoss', use_sigmoid=True, loss_weight=1.0)), roi_head=dict( # featmap_strides 的更新取决于于颈部的步伐 bbox_roi_extractor=dict(featmap_strides=[8, 16, 32, 64, 128]))) # 学习率 param_scheduler = [ dict( type='LinearLR', start_factor=0.001, by_epoch=False, begin=0, end=1000), # 慢慢增加 lr,否则损失变成 NAN dict( type='MultiStepLR', begin=0, end=12, by_epoch=True, milestones=[8, 11], gamma=0.1) ]- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
和之前2.x版本的代码分析一样,跳过Resnet和FPN的部分,我们直接从RPN开始
RPN部分的代码
我们首先找到FasterRCNN这主类,可以看到继承了TwoStageDetector,所以我们接下来的重点是TwoStageDetector这个类
1. loss函数(two_stage.py)
不知道为什么3.x版本的two_stage函数没有了forward函数反而多了几个loss,predict函数。因为不知道运行顺序所以直接每一个类都打上了断点,最后发现是进入了loss函数里。
def loss(self, batch_inputs: Tensor, batch_data_samples: SampleList) -> dict:- 1
- 2

x = self.extract_feat(batch_inputs) 其中extract_feat的内容是 x = self.backbone(batch_inputs) if self.with_neck: x = self.neck(x) return x- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7

losses = dict() if self.with_rpn: proposal_cfg = self.train_cfg.get('rpn_proposal', self.test_cfg.rpn) rpn_data_samples = copy.deepcopy(batch_data_samples)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6

for data_sample in rpn_data_samples: data_sample.gt_instances.labels = \ torch.zeros_like(data_sample.gt_instances.labels) 将每个 data_sample 中的目标实例的标签信息都设置为零,因为作为rpn网络只要进行二分类任务- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5

rpn_losses, rpn_results_list = self.rpn_head.loss_and_predict( x, rpn_data_samples, proposal_cfg=proposal_cfg) 详见1.1.1 计算 RPN 模型的损失并生成建议框的预测结果- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4

keys = rpn_losses.keys() for key in list(keys): if 'loss' in key and 'rpn' not in key: rpn_losses[f'rpn_{key}'] = rpn_losses.pop(key) losses.update(rpn_losses)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5

roi_losses = self.roi_head.loss(x, rpn_results_list, batch_data_samples) losses.update(roi_losses)- 1
- 2
- 3

1.1 loss_and_predict函数(base_dense_head.py)
def loss_and_predict( self, x: Tuple[Tensor], batch_data_samples: SampleList, proposal_cfg: Optional[ConfigDict] = None ) -> Tuple[dict, InstanceList]:- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
outputs = unpack_gt_instances(batch_data_samples) (batch_gt_instances, batch_gt_instances_ignore, batch_img_metas) = outputs 将批量数据中的目标实例信息和图像元信息提取出来,以便后续的处理和分析- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5


outs = self(x) 输入预测网络预测cls_score, bbox_pred, centerness三个属性- 1
- 2
- 3
loss_inputs = outs + (batch_gt_instances, batch_img_metas, batch_gt_instances_ignore) loss_inputs 元组将用于计算损失函数,其中包括模型的输出 outs、目标实例信息 batch_gt_instances、 图像元信息 batch_img_metas 以及忽略的目标实例信息 batch_gt_instances_ignore- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5

losses = self.loss_by_feat(*loss_inputs) 详见1.1.1 计算损失值- 1
- 2
- 3

predictions = self.predict_by_feat( *outs, batch_img_metas=batch_img_metas, cfg=proposal_cfg) 详见1.1.2 生成目标检测的预测成果- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
1.1.1 loss_by_feat函数(fcos_head.py)
def loss_by_feat( self, cls_scores: List[Tensor], bbox_preds: List[Tensor], centernesses: List[Tensor], batch_gt_instances: InstanceList, batch_img_metas: List[dict], batch_gt_instances_ignore: OptInstanceList = None ) -> Dict[str, Tensor]:- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9

assert len(cls_scores) == len(bbox_preds) == len(centernesses) featmap_sizes = [featmap.size()[-2:] for featmap in cls_scores] 获取每一个特征图的尺寸- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4

all_level_points = self.prior_generator.grid_priors( featmap_sizes, dtype=bbox_preds[0].dtype, device=bbox_preds[0].device) 组成先验框的点- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
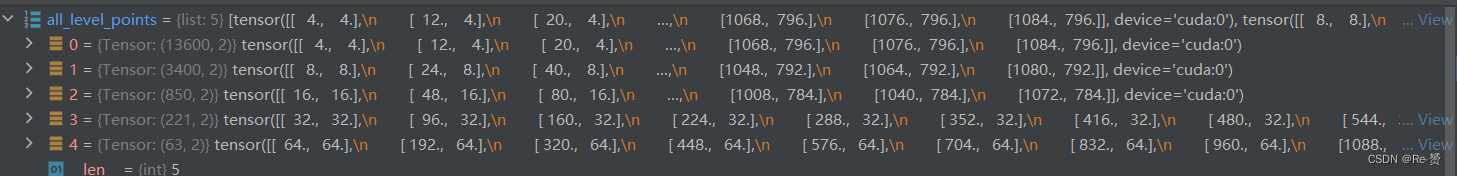
labels, bbox_targets = self.get_targets(all_level_points, batch_gt_instances) 详见1.1.1.1- 1
- 2


flatten_cls_scores = [ cls_score.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).reshape(-1, self.cls_out_channels) for cls_score in cls_scores ] flatten_bbox_preds = [ bbox_pred.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).reshape(-1, 4) for bbox_pred in bbox_preds ] flatten_centerness = [ centerness.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).reshape(-1) for centerness in centernesses ] flatten_cls_scores = torch.cat(flatten_cls_scores) flatten_bbox_preds = torch.cat(flatten_bbox_preds) flatten_centerness = torch.cat(flatten_centerness)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15

flatten_labels = torch.cat(labels) flatten_bbox_targets = torch.cat(bbox_targets) # repeat points to align with bbox_preds flatten_points = torch.cat( [points.repeat(num_imgs, 1) for points in all_level_points])- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5


bg_class_ind = self.num_classes pos_inds = ((flatten_labels >= 0) & (flatten_labels < bg_class_ind)).nonzero().reshape(-1) 将背景类的索引设置为 num_classes 用于获取正样本的索引- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6

num_pos = torch.tensor( len(pos_inds), dtype=torch.float, device=bbox_preds[0].device) num_pos = max(reduce_mean(num_pos), 1.0) 计算了正样本的数量,并且将其转换为张量 num_pos,后使用 reduce_mean 函数来计算正样本数量的平均值,并使用 max 函数确保这个平均值至少为1.0。- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5

loss_cls = self.loss_cls( flatten_cls_scores, flatten_labels, avg_factor=num_pos) 使用分类损失函数 self.loss_cls 来计算分类损失- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
pos_bbox_preds = flatten_bbox_preds[pos_inds] pos_centerness = flatten_centerness[pos_inds] pos_bbox_targets = flatten_bbox_targets[pos_inds] pos_centerness_targets = self.centerness_target(pos_bbox_targets) # centerness weighted iou loss centerness_denorm = max( reduce_mean(pos_centerness_targets.sum().detach()), 1e-6) 通过索引 pos_inds 从之前展平的张量中提取了正样本对应的 边界框预测、中心度预测、边界框目标和中心度目标- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10

if len(pos_inds) > 0: pos_points = flatten_points[pos_inds] pos_decoded_bbox_preds = self.bbox_coder.decode( pos_points, pos_bbox_preds) pos_decoded_target_preds = self.bbox_coder.decode( pos_points, pos_bbox_targets) loss_bbox = self.loss_bbox( pos_decoded_bbox_preds, pos_decoded_target_preds, weight=pos_centerness_targets, avg_factor=centerness_denorm) loss_centerness = self.loss_centerness( pos_centerness, pos_centerness_targets, avg_factor=num_pos) 如果存在正样本 所有点坐标中提取正样本的点坐标 使用边界框编码器解码正样本的边界框预测和目标 计算边界框损失,使用解码后的边界框预测和目标值 计算中心度损失- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19


return dict( loss_cls=loss_cls, loss_bbox=loss_bbox, loss_centerness=loss_centerness)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
1.1.1.1 get_targets函数
def get_targets( self, points: List[Tensor], batch_gt_instances: InstanceList ) -> Tuple[List[Tensor], List[Tensor]]:- 1
- 2
- 3

assert len(points) == len(self.regress_ranges) num_levels = len(points) # expand regress ranges to align with points expanded_regress_ranges = [ points[i].new_tensor(self.regress_ranges[i])[None].expand_as( points[i]) for i in range(num_levels) ] 将回归范围扩展以与点对齐- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9

concat_regress_ranges = torch.cat(expanded_regress_ranges, dim=0) concat_points = torch.cat(points, dim=0) num_points = [center.size(0) for center in points] 连接所有级别的点和回归范围 存储每个级别中的点的数量- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6


labels_list, bbox_targets_list = multi_apply( 详见1.1.1.2 self._get_targets_single, batch_gt_instances, points=concat_points, regress_ranges=concat_regress_ranges, num_points_per_lvl=num_points) 将 _get_target_single 方法应用到多个图像上,以计算每个图像中的回归、分类和角度目标- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8


labels_list = [labels.split(num_points, 0) for labels in labels_list] bbox_targets_list = [ bbox_targets.split(num_points, 0) for bbox_targets in bbox_targets_list ] 将目标分割为每个图像的每个级别- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7


concat_lvl_labels = [] concat_lvl_bbox_targets = [] for i in range(num_levels): concat_lvl_labels.append( torch.cat([labels[i] for labels in labels_list])) bbox_targets = torch.cat( [bbox_targets[i] for bbox_targets in bbox_targets_list]) if self.norm_on_bbox: bbox_targets = bbox_targets / self.strides[i] concat_lvl_bbox_targets.append(bbox_targets) return concat_lvl_labels, concat_lvl_bbox_targets 连接每个级别中每个图像的目标 返回包含连接后的每个级别的分类标签、回归目标- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14

1.1.1.2 _get_targets_single函数
def _get_targets_single( self, gt_instances: InstanceData, points: Tensor, regress_ranges: Tensor, num_points_per_lvl: List[int]) -> Tuple[Tensor, Tensor]:- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4

num_points = points.size(0) num_gts = len(gt_instances) gt_bboxes = gt_instances.bboxes gt_labels = gt_instances.labels- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4

if num_gts == 0: return gt_labels.new_full((num_points,), self.num_classes), \ gt_bboxes.new_zeros((num_points, 4))- 1
- 2
- 3
areas = (gt_bboxes[:, 2] - gt_bboxes[:, 0]) * ( gt_bboxes[:, 3] - gt_bboxes[:, 1]) areas = areas[None].repeat(num_points, 1)- 1
- 2
- 3

regress_ranges = regress_ranges[:, None, :].expand( num_points, num_gts, 2) gt_bboxes = gt_bboxes[None].expand(num_points, num_gts, 4) xs, ys = points[:, 0], points[:, 1] xs = xs[:, None].expand(num_points, num_gts) ys = ys[:, None].expand(num_points, num_gts) 对参数进行扩展- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8



left = xs - gt_bboxes[..., 0] right = gt_bboxes[..., 2] - xs top = ys - gt_bboxes[..., 1] bottom = gt_bboxes[..., 3] - ys bbox_targets = torch.stack((left, top, right, bottom), -1)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5



if self.center_sampling: # condition1: inside a `center bbox` radius = self.center_sample_radius center_xs = (gt_bboxes[..., 0] + gt_bboxes[..., 2]) / 2 center_ys = (gt_bboxes[..., 1] + gt_bboxes[..., 3]) / 2 center_gts = torch.zeros_like(gt_bboxes) stride = center_xs.new_zeros(center_xs.shape) lvl_begin = 0 for lvl_idx, num_points_lvl in enumerate(num_points_per_lvl): lvl_end = lvl_begin + num_points_lvl stride[lvl_begin:lvl_end] = self.strides[lvl_idx] * radius lvl_begin = lvl_end x_mins = center_xs - stride y_mins = center_ys - stride x_maxs = center_xs + stride y_maxs = center_ys + stride center_gts[..., 0] = torch.where(x_mins > gt_bboxes[..., 0], x_mins, gt_bboxes[..., 0]) center_gts[..., 1] = torch.where(y_mins > gt_bboxes[..., 1], y_mins, gt_bboxes[..., 1]) center_gts[..., 2] = torch.where(x_maxs > gt_bboxes[..., 2], gt_bboxes[..., 2], x_maxs) center_gts[..., 3] = torch.where(y_maxs > gt_bboxes[..., 3], gt_bboxes[..., 3], y_maxs) cb_dist_left = xs - center_gts[..., 0] cb_dist_right = center_gts[..., 2] - xs cb_dist_top = ys - center_gts[..., 1] cb_dist_bottom = center_gts[..., 3] - ys center_bbox = torch.stack( (cb_dist_left, cb_dist_top, cb_dist_right, cb_dist_bottom), -1) inside_gt_bbox_mask = center_bbox.min(-1)[0] > 0 else: # condition1: inside a gt bbox inside_gt_bbox_mask = bbox_targets.min(-1)[0] > 0- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37





max_regress_distance = bbox_targets.max(-1)[0] inside_regress_range = ( (max_regress_distance >= regress_ranges[..., 0]) & (max_regress_distance <= regress_ranges[..., 1]))- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4


areas[inside_gt_bbox_mask == 0] = INF areas[inside_regress_range == 0] = INF min_area, min_area_inds = areas.min(dim=1)- 1
- 2
- 3


labels = gt_labels[min_area_inds] labels[min_area == INF] = self.num_classes # set as BG bbox_targets = bbox_targets[range(num_points), min_area_inds] return labels, bbox_targets- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5


1.1.2 predict_by_feat函数(base_dense_head.py)
def predict_by_feat(self, cls_scores: List[Tensor], bbox_preds: List[Tensor], score_factors: Optional[List[Tensor]] = None, batch_img_metas: Optional[List[dict]] = None, cfg: Optional[ConfigDict] = None, rescale: bool = False, with_nms: bool = True) -> InstanceList:- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8

assert len(cls_scores) == len(bbox_preds) if score_factors is None: # e.g. Retina, FreeAnchor, Foveabox, etc. with_score_factors = False else: # e.g. FCOS, PAA, ATSS, AutoAssign, etc. with_score_factors = True assert len(cls_scores) == len(score_factors) num_levels = len(cls_scores)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11

featmap_sizes = [cls_scores[i].shape[-2:] for i in range(num_levels)] mlvl_priors = self.prior_generator.grid_priors( featmap_sizes, dtype=cls_scores[0].dtype, device=cls_scores[0].device) 获取每个尺度层级的特征图大小 生成每个尺度层级上的先验框坐标- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8

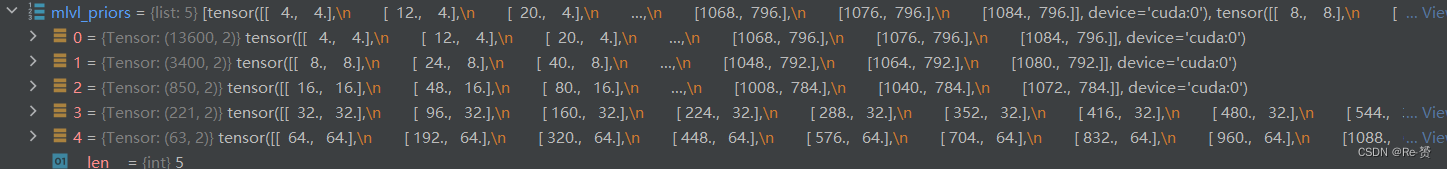
result_list = [] for img_id in range(len(batch_img_metas)): img_meta = batch_img_metas[img_id] cls_score_list = select_single_mlvl( cls_scores, img_id, detach=True) bbox_pred_list = select_single_mlvl( bbox_preds, img_id, detach=True) if with_score_factors: score_factor_list = select_single_mlvl( score_factors, img_id, detach=True) else: score_factor_list = [None for _ in range(num_levels)] 提取当前图片的类别得分、边界框预测、和中心度预测- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15



results = self._predict_by_feat_single( cls_score_list=cls_score_list, bbox_pred_list=bbox_pred_list, score_factor_list=score_factor_list, mlvl_priors=mlvl_priors, img_meta=img_meta, cfg=cfg, rescale=rescale, with_nms=with_nms) result_list.append(results) 通过单张图片的特征和预测,获取边界框信息 详见1.1.2.1- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
return result_list- 1

1.1.2.1 _predict_by_feat_single函数(base_dense_head.py)
def _predict_by_feat_single(self, cls_score_list: List[Tensor], bbox_pred_list: List[Tensor], score_factor_list: List[Tensor], mlvl_priors: List[Tensor], img_meta: dict, cfg: ConfigDict, rescale: bool = False, with_nms: bool = True) -> InstanceData:- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9

if score_factor_list[0] is None: # e.g. Retina, FreeAnchor, etc. with_score_factors = False else: # e.g. FCOS, PAA, ATSS, etc. with_score_factors = True- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
cfg = self.test_cfg if cfg is None else cfg cfg = copy.deepcopy(cfg) img_shape = img_meta['img_shape'] nms_pre = cfg.get('nms_pre', -1) mlvl_bbox_preds = [] mlvl_valid_priors = [] mlvl_scores = [] mlvl_labels = [] if with_score_factors: mlvl_score_factors = [] else: mlvl_score_factors = None- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13


for level_idx, (cls_score, bbox_pred, score_factor, priors) in \ enumerate(zip(cls_score_list, bbox_pred_list, score_factor_list, mlvl_priors)): assert cls_score.size()[-2:] == bbox_pred.size()[-2:] dim = self.bbox_coder.encode_size bbox_pred = bbox_pred.permute(1, 2, 0).reshape(-1, dim) if with_score_factors: score_factor = score_factor.permute(1, 2, 0).reshape(-1).sigmoid() cls_score = cls_score.permute(1, 2, 0).reshape(-1, self.cls_out_channels) if self.use_sigmoid_cls: scores = cls_score.sigmoid() else: # remind that we set FG labels to [0, num_class-1] # since mmdet v2.0 # BG cat_id: num_class scores = cls_score.softmax(-1)[:, :-1] 对每一层特征做处理,这里以第一层100 * 136 作为演示- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22



score_thr = cfg.get('score_thr', 0) results = filter_scores_and_topk( scores, score_thr, nms_pre, dict(bbox_pred=bbox_pred, priors=priors)) 使用score_thr和topk过滤结果- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7

scores, labels, keep_idxs, filtered_results = results- 1




bbox_pred = filtered_results['bbox_pred'] priors = filtered_results['priors']- 1
- 2


if with_score_factors: score_factor = score_factor[keep_idxs] mlvl_bbox_preds.append(bbox_pred) mlvl_valid_priors.append(priors) mlvl_scores.append(scores) mlvl_labels.append(labels)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7

至此循环结束 bbox_pred = torch.cat(mlvl_bbox_preds) priors = cat_boxes(mlvl_valid_priors) bboxes = self.bbox_coder.decode(priors, bbox_pred, max_shape=img_shape)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5


results = InstanceData() results.bboxes = bboxes results.scores = torch.cat(mlvl_scores) results.labels = torch.cat(mlvl_labels) if with_score_factors: results.score_factors = torch.cat(mlvl_score_factors) 使用InstanceData类进行封装- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8

return self._bbox_post_process( results=results, cfg=cfg, rescale=rescale, with_nms=with_nms, img_meta=img_meta) 详见1.1.2.2- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
1.1.2.2 _bbox_post_process函数(base_dense_head.py)
def _bbox_post_process(self, results: InstanceData, cfg: ConfigDict, rescale: bool = False, with_nms: bool = True, img_meta: Optional[dict] = None) -> InstanceData:- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6

if rescale: assert img_meta.get('scale_factor') is not None scale_factor = [1 / s for s in img_meta['scale_factor']] results.bboxes = scale_boxes(results.bboxes, scale_factor) if hasattr(results, 'score_factors'): # TODO: Add sqrt operation in order to be consistent with # the paper. score_factors = results.pop('score_factors') results.scores = results.scores * score_factors- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
if cfg.get('min_bbox_size', -1) >= 0: w, h = get_box_wh(results.bboxes) valid_mask = (w > cfg.min_bbox_size) & (h > cfg.min_bbox_size) if not valid_mask.all(): results = results[valid_mask] 检测允许的最小边界框的尺寸- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7


if with_nms and results.bboxes.numel() > 0: bboxes = get_box_tensor(results.bboxes) det_bboxes, keep_idxs = batched_nms(bboxes, results.scores, results.labels, cfg.nms) results = results[keep_idxs] # some nms would reweight the score, such as softnms results.scores = det_bboxes[:, -1] results = results[:cfg.max_per_img] return results 进行NMS操作并且返回结果- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12




ROI部分代码
2.1 loss函数(standard_roi_head.py)
def loss(self, x: Tuple[Tensor], rpn_results_list: InstanceList, batch_data_samples: List[DetDataSample]) -> dict:- 1
- 2

assert len(rpn_results_list) == len(batch_data_samples) outputs = unpack_gt_instances(batch_data_samples) batch_gt_instances, batch_gt_instances_ignore, _ = outputs- 1
- 2
- 3

num_imgs = len(batch_data_samples) sampling_results = [] for i in range(num_imgs): # rename rpn_results.bboxes to rpn_results.priors rpn_results = rpn_results_list[i] rpn_results.priors = rpn_results.pop('bboxes') assign_result = self.bbox_assigner.assign( rpn_results, batch_gt_instances[i], batch_gt_instances_ignore[i]) sampling_result = self.bbox_sampler.sample( assign_result, rpn_results, batch_gt_instances[i], feats=[lvl_feat[i][None] for lvl_feat in x]) sampling_results.append(sampling_result) 计算 batch_data_samples 列表的长度,即批次中包含的图像数量。 遍历批次中的每张图像: 获取第 i 张图像的 RPN RPN 检测结果中的 'bboxes' 键的值赋给 'priors' 键 使用一个 bbox_assigner(通常是负责分配正负样本的组件)来执行分配操作 使用 bbox_sampler(通常是负责采样正负样本的组件)来执行采样操作- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23



losses = dict() # bbox head loss if self.with_bbox: bbox_results = self.bbox_loss(x, sampling_results) 详见2.1.1 losses.update(bbox_results['loss_bbox']) 计算 bbox 损失- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
if self.with_mask: mask_results = self.mask_loss(x, sampling_results, bbox_results['bbox_feats'], batch_gt_instances) losses.update(mask_results['loss_mask']) return losses- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
2.1.1 bbox_loss函数(standard_roi_head.py)
def bbox_loss(self, x: Tuple[Tensor], sampling_results: List[SamplingResult]) -> dict:- 1
- 2
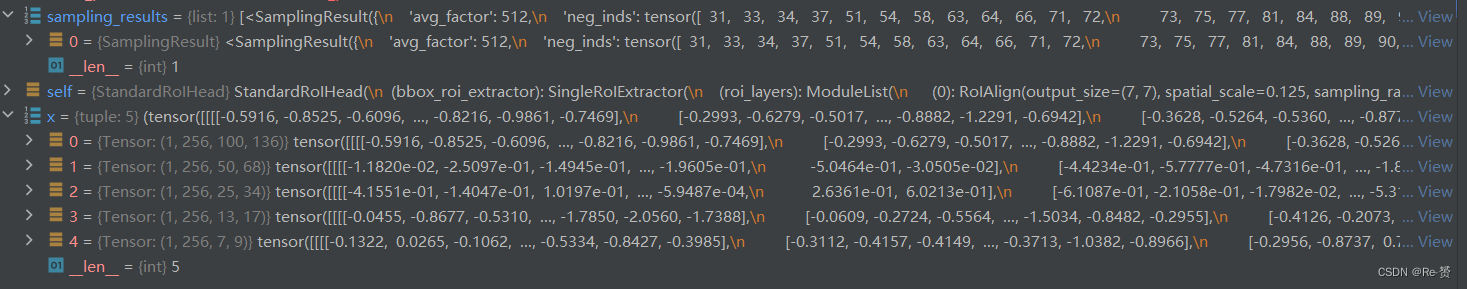
rois = bbox2roi([res.priors for res in sampling_results])- 1

bbox_results = self._bbox_forward(x, rois)- 1

bbox_loss_and_target = self.bbox_head.loss_and_target( cls_score=bbox_results['cls_score'], bbox_pred=bbox_results['bbox_pred'], rois=rois, sampling_results=sampling_results, rcnn_train_cfg=self.train_cfg) 详见2.1.3 bbox_results.update(loss_bbox=bbox_loss_and_target['loss_bbox']) return bbox_results- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9

2.1.2 _bbox_forward函数(standard_roi_head.py)
def _bbox_forward(self, x: Tuple[Tensor], rois: Tensor) -> dict:- 1

bbox_feats = self.bbox_roi_extractor( x[:self.bbox_roi_extractor.num_inputs], rois)- 1
- 2

if self.with_shared_head: bbox_feats = self.shared_head(bbox_feats) cls_score, bbox_pred = self.bbox_head(bbox_feats)- 1
- 2
- 3

bbox_results = dict( cls_score=cls_score, bbox_pred=bbox_pred, bbox_feats=bbox_feats) return bbox_results- 1
- 2
- 3

2.1.2.1 bbox_roi_extractor函数(single_level_roi_extractor.py)
def forward(self, feats: Tuple[Tensor], rois: Tensor, roi_scale_factor: Optional[float] = None):- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4

rois = rois.type_as(feats[0]) out_size = self.roi_layers[0].output_size num_levels = len(feats) roi_feats = feats[0].new_zeros( rois.size(0), self.out_channels, *out_size) 将 RoIs 的数据类型转换为与 feats[0](即特征图)相同的数据类型 获取感兴趣区域 (RoI) 操作的输出尺寸 out_size 获取特征金字塔的级别数 创建一个全零的特征张量 roi_feats- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10

if torch.__version__ == 'parrots': roi_feats.requires_grad = True if num_levels == 1: if len(rois) == 0: return roi_feats return self.roi_layers[0](feats[0], rois)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
target_lvls = self.map_roi_levels(rois, num_levels) if roi_scale_factor is not None: rois = self.roi_rescale(rois, roi_scale_factor)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4

for i in range(num_levels): mask = target_lvls == i inds = mask.nonzero(as_tuple=False).squeeze(1) if inds.numel() > 0: rois_ = rois[inds] roi_feats_t = self.roi_layers[i](feats[i], rois_) roi_feats[inds] = roi_feats_t else: # Sometimes some pyramid levels will not be used for RoI # feature extraction and this will cause an incomplete # computation graph in one GPU, which is different from those # in other GPUs and will cause a hanging error. # Therefore, we add it to ensure each feature pyramid is # included in the computation graph to avoid runtime bugs. roi_feats += sum( x.view(-1)[0] for x in self.parameters()) * 0. + feats[i].sum() * 0. return roi_feats 遍历特征金字塔中的不同级别的特征图: 创建一个布尔掩码 mask,用于筛选出与当前级别 i 相匹配的 RoIs 通过 nonzero 方法找到满足 mask 的 RoIs 的索引 检查当前级别是否有与之相关的 RoIs: 从原始 RoIs rois 中提取当前级别 i 的 RoIs 将当前级别 i 的特征图 feats[i] 和相应的 RoIs rois_ 传递给 RoI 池化层 将获得的 RoIs 特征 roi_feats_t 存储到总体 RoI 特征张量 roi_feats 中- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26





2.1.2.2 map_roi_levels函数(single_level_roi_extractor.py)
def map_roi_levels(self, rois: Tensor, num_levels: int) -> Tensor: """Map rois to corresponding feature levels by scales. - scale < finest_scale * 2: level 0 - finest_scale * 2 <= scale < finest_scale * 4: level 1 - finest_scale * 4 <= scale < finest_scale * 8: level 2 - scale >= finest_scale * 8: level 3 Args: rois (Tensor): Input RoIs, shape (k, 5). num_levels (int): Total level number. Returns: Tensor: Level index (0-based) of each RoI, shape (k, ) """ scale = torch.sqrt( (rois[:, 3] - rois[:, 1]) * (rois[:, 4] - rois[:, 2])) target_lvls = torch.floor(torch.log2(scale / self.finest_scale + 1e-6)) target_lvls = target_lvls.clamp(min=0, max=num_levels - 1).long() return target_lvls 计算每个 RoI 的尺度。这里的尺度计算是通过 RoI 的高度和宽度相乘来获得的 通过对 RoI 的尺度进行对数计算,然后除以 self.finest_scale 并取下限,得到一个表示 RoIs 所在级别的浮点数 target_lvls 对 target_lvls 进行裁剪,确保它在合适的级别范围内。最小值为 0,最大值为 num_levels - 1 返回一个包含每个 RoI 所在级别索引的张量,该索引是从 0 到 num_levels - 1 的整数,用于指示每个 RoI 应映射到哪个特征金字塔级别- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25



2.1.3 loss_and_target函数(bbox_head.py)
def loss_and_target(self, cls_score: Tensor, bbox_pred: Tensor, rois: Tensor, sampling_results: List[SamplingResult], rcnn_train_cfg: ConfigDict, concat: bool = True, reduction_override: Optional[str] = None) -> dict:- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8

cls_reg_targets = self.get_targets( sampling_results, rcnn_train_cfg, concat=concat)- 1
- 2

losses = self.loss( cls_score, bbox_pred, rois, *cls_reg_targets, reduction_override=reduction_override) return dict(loss_bbox=losses, bbox_targets=cls_reg_targets)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
2.1.3.1 loss函数(bbox_head.py)
def loss(self, cls_score: Tensor, bbox_pred: Tensor, rois: Tensor, labels: Tensor, label_weights: Tensor, bbox_targets: Tensor, bbox_weights: Tensor, reduction_override: Optional[str] = None) -> dict:- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9

losses = dict() if cls_score is not None: avg_factor = max(torch.sum(label_weights > 0).float().item(), 1.) if cls_score.numel() > 0: loss_cls_ = self.loss_cls( cls_score, labels, label_weights, avg_factor=avg_factor, reduction_override=reduction_override) if isinstance(loss_cls_, dict): losses.update(loss_cls_) else: losses['loss_cls'] = loss_cls_ if self.custom_activation: acc_ = self.loss_cls.get_accuracy(cls_score, labels) losses.update(acc_) else: losses['acc'] = accuracy(cls_score, labels) 计算分类损失和精度- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
if bbox_pred is not None: bg_class_ind = self.num_classes # 0~self.num_classes-1 are FG, self.num_classes is BG pos_inds = (labels >= 0) & (labels < bg_class_ind) # do not perform bounding box regression for BG anymore. if pos_inds.any(): if self.reg_decoded_bbox: # When the regression loss (e.g. `IouLoss`, # `GIouLoss`, `DIouLoss`) is applied directly on # the decoded bounding boxes, it decodes the # already encoded coordinates to absolute format. bbox_pred = self.bbox_coder.decode(rois[:, 1:], bbox_pred) bbox_pred = get_box_tensor(bbox_pred) if self.reg_class_agnostic: pos_bbox_pred = bbox_pred.view( bbox_pred.size(0), -1)[pos_inds.type(torch.bool)] else: pos_bbox_pred = bbox_pred.view( bbox_pred.size(0), self.num_classes, -1)[pos_inds.type(torch.bool), labels[pos_inds.type(torch.bool)]] losses['loss_bbox'] = self.loss_bbox( pos_bbox_pred, bbox_targets[pos_inds.type(torch.bool)], bbox_weights[pos_inds.type(torch.bool)], avg_factor=bbox_targets.size(0), reduction_override=reduction_override) else: losses['loss_bbox'] = bbox_pred[pos_inds].sum() return losses 计算出正样本的索引 如果存在正样本: 是否应在已编码的边界框上应用回归损失。如果为真,将已编码的坐标解码为绝对格式 根据是否是类别无关的回归 计算边界框回归损失 loss_bbox- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37


-
相关阅读:
为什么要用std::function
Es 拼音搜索无法高亮
Spring使用注解开发
C++提高:03STL- 常用容器_1
python 图像处理(一阶梯度图像和角度图像)
19 C++设计模式之中介者(Mediator)模式
一套极简的MQTT使用接口EasyMqttClient
最大似然函数 损失函数 逻辑回归与线性回归的比较
卡尔曼滤波器第 2 部分 - 贝叶斯滤波器
MyBatisPlus的使用【详细】
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_45935290/article/details/133706185
