-
JDBC 【SQL注入】
一、SQL注入🍓
(一)、SQL注入问题🥝
1.向jdbc_user表中 插入两条数据
# 插入2条数据 INSERT INTO jdbc_user VALUES(NULL,'jack','123456','2020/2/24'); INSERT INTO jdbc_user VALUES(NULL,'tom','123456','2020/2/24');- 1
- 2
- 3
2.SQL注入演示
# SQL注入演示 -- 填写一个错误的密码 SELECT * FROM jdbc_user WHERE username = 'tom' AND PASSWORD = '123' OR '1' = '1';- 1
- 2
- 3
如果这是一个登陆操作,那么用户就登陆成功了.显然这不是我们想要看到的结果
(二)、注入案例:用户登陆🥝
需求:
用户在控制台上输入用户名和密码, 然后使用 Statement 字符串拼接的方式 实现用户的登录步骤
- 得到用户从控制台上输入的用户名和密码来查询数据库
- 写一个登录的方法
a) 通过工具类得到连接
b) 创建语句对象,使用拼接字符串的方式生成 SQL 语句
c) 查询数据库,如果有记录则表示登录成功,否则登录失败
d) 释放资源
Sql注入方式: 123' or '1'='1- 1
代码示例
public class TestLogin01 { /** * 用户登录案例 * 使用 Statement字符串拼接的方式完成查询 * @param args */ public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException { //1.获取连接 Connection connection = JDBCUtils.getConnection(); //2.获取Statement Statement statement = connection.createStatement(); //3.获取用户输入的用户名和密码 Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("请输入用户名: "); String name = sc.nextLine(); System.out.println("请输入密码: "); String pass = sc.nextLine(); System.out.println(pass); //4.拼接Sql,执行查询 // String pass = "xxx' or '1'='1"; xxx' or '1' = '1 String sql = "select * from jdbc_user " + "where username = " + " '" + name +"' " +" and password = " +" '" + pass +"'"; System.out.println(sql); ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql); //5.处理结果集,判断结果集是否为空 if(resultSet.next()){ System.out.println("登录成功! 欢迎您: " + name); }else { System.out.println("登录失败!"); } //释放资源 JDBCUtils.close(connection,statement,resultSet); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
问题分析:
- 什么是SQL注入?
我们让用户输入的密码和 SQL 语句进行字符串拼接。用户输入的内容作为了 SQL 语句语法的一部分,改变了 原有SQL 真正的意义,以上问题称为 SQL 注入 . - 如何实现的注入
根据用户输入的数据,拼接处的字符串
select * from jdbc_user where username = 'abc' and password = 'abc' or '1'='1' name='abc' and password='abc' 为假 '1'='1' 真 相当于 select * from user where true=true; 查询了所有记录- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
如何解决
要解决 SQL 注入就不能让用户输入的密码和我们的 SQL 语句进行简单的字符串拼接(三)、 预处理对象🥝
-
PreparedStatement 接口介绍
PreparedStatement 是 Statement 接口的子接口,继承于父接口中所有的方法。它是一个预编译的 SQL 语句对象.
预编译: 是指SQL 语句被预编译,并存储在 PreparedStatement 对象中。然后可以使用此对象多次高效地执行该语句。 -
PreparedStatement 特点
因为有预先编译的功能,提高 SQL 的执行效率。
可以有效的防止 SQL 注入的问题,安全性更高 -
获取PreparedStatement对象
通过Connection创建PreparedStatement对象

-
PreparedStatement接口常用方法
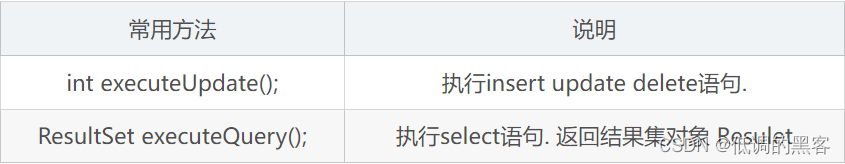
-
使用PreparedStatement的步骤
- 编写 SQL 语句,未知内容使用?占位:
"SELECT * FROM jdbc_user WHERE username=? AND password=?";- 1
- 获得 PreparedStatement 对象
- 设置实际参数:setXxx( 占位符的位置, 真实的值)
- 执行参数化 SQL 语句
- 关闭资源

二、使用PreparedStatement完成登录案例🍓
使用 PreparedStatement 预处理对象,可以有效的避免SQL注入
步骤:
1.获取数据库连接对象
2.编写SQL 使用? 占位符方式
3.获取预处理对象 (预编译对象会将Sql发送给数据库 进行预编译)
4.提示用户输入用户名 & 密码
5.设置实际参数:setXxx(占位符的位置, 真实的值)
6.执行查询获取结果集
7.判断是否查询到数据
8.关闭资源/*** 使用预编译对象 PrepareStatement 完成登录案例 * @param args * @throws SQLException */ public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException { //1.获取连接 Connection connection = JDBCUtils.getConnection(); //2.获取Statement Statement statement = connection.createStatement(); //3.获取用户输入的用户名和密码 Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("请输入用户名: "); String name = sc.nextLine(); System.out.println("请输入密码: "); String pass = sc.nextLine(); System.out.println(pass); //4.获取 PrepareStatement 预编译对象 //4.1 编写SQL 使用 ? 占位符方式 String sql = "select * from jdbc_user where username = ? and password = ?"; PreparedStatement ps = connection.prepareStatement(sql); //4.2 设置占位符参数 ps.setString(1,name); ps.setString(2,pass); //5. 执行查询 处理结果集 ResultSet resultSet = ps.executeQuery(); if(resultSet.next()){ System.out.println("登录成功! 欢迎您: " + name); }else{ System.out.println("登录失败!"); } //6.释放资源 JDBCUtils.close(connection,statement,resultSet); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
(一)、PreparedStatement的执行原理🥝
分别使用 Statement对象 和 PreparedStatement对象进行插入操作
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException { Connection con = JDBCUtils.getConnection(); //获取 Sql语句执行对象 Statement st = con.createStatement(); //插入两条数据 st.executeUpdate("insert into jdbc_user values(null,'张三','123','1992/12/26')"); st.executeUpdate("insert into jdbc_user values(null,'李四','123','1992/12/26')"); //获取预处理对象 PreparedStatement ps = con.prepareStatement("insert into jdbc_user values(?,?,?,?)"); //第一条数 设置占位符对应的参数 ps.setString(1,null); ps.setString(2,"hd"); ps.setString(3,"qwer"); ps.setString(4,"2000/1/10"); //执行插入 ps.executeUpdate(); //第二条数据 ps.setString(1,null); ps.setString(2,"jc"); ps.setString(3,"1122"); ps.setString(4,"2000/1/10"); //执行插入 ps.executeUpdate(); //释放资源 st.close(); ps.close(); con.close(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29

(二)、 Statement 与 PreparedStatement的区别?🥝
- Statement用于执行静态SQL语句,在执行时,必须指定一个事先准备好的SQL语句。
- PrepareStatement是预编译的SQL语句对象,语句中可以包含动态参数“?”,在执行时可以为“?”动态设置参数值。
- PrepareStatement可以减少编译次数提高数据库性能。
三、JDBC 控制事务🍓
之前我们是使用 MySQL 的命令来操作事务。接下来我们使用 JDBC 来操作银行转账的事务。
(一)、数据准备🥝
-- 创建账户表 CREATE TABLE account( -- 主键 id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT, -- 姓名 NAME VARCHAR(10), -- 转账金额 money DOUBLE ); -- 添加两个用户 INSERT INTO account (NAME, money) VALUES ('tom', 1000), ('jack', 1000);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
(二)、事务相关API🥝

(三)、 开发步骤🥝
- 获取连接
- 开启事务
- 获取到 PreparedStatement , 执行两次更新操作
- 正常情况下提交事务
- 出现异常回滚事务
- 最后关闭资源
//JDBC 操作事务 public static void main(String[] args) { Connection con = null; PreparedStatement ps = null; try { //1. 获取连接 con = JDBCUtils.getConnection(); //2. 开启事务 con.setAutoCommit(false); //3. 获取到 PreparedStatement 执行两次更新操作 //3.1 tom 账户 -500 ps = con.prepareStatement("update account set money = money - ? where name = ? "); ps.setDouble(1,500.0); ps.setString(2,"tom"); ps.executeUpdate(); //模拟tom转账后 出现异常 System.out.println(1 / 0); //3.2 jack 账户 +500 ps = con.prepareStatement("update account set money = money + ? where name = ? "); ps.setDouble(1,500.0); ps.setString(2,"jack"); ps.executeUpdate(); //4. 正常情况下提交事务 con.commit(); System.out.println("转账成功!"); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); try { //5. 出现异常回滚事务 con.rollback(); } catch (SQLException ex) { ex.printStackTrace(); } } finally { //6. 最后关闭资源 JDBCUtils.close(con,ps); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
四、数据库连接池🍓
连接池介绍
什么是连接池
实际开发中“获得连接”或“释放资源”是非常消耗系统资源的两个过程,为了解决此类性能问题,通常情况我们 采用连接池技术,来共享连接Connection。这样我们就不需要每次都创建连接、释放连接了,这些操作都交给了连接池.
连接池的好处
用池来管理Connection,这样可以重复使用Connection。 当使用完Connection后,调用Connection的close()方法也不会真的关闭Connection,而是把Connection“归还”给池。Java为数据库连接池提供了公共的接口:javax.sql.DataSource,各个厂商需要让自己的连接池实现这个接口。这样应用程序可以方便的切换不同厂商的连接池!
常见的连接池有 DBCP连接池, C3P0连接池, Druid连接池, 接下里我们就详细学习一下
(一)、 数据准备🥝
#创建数据库 CREATE DATABASE db5 CHARACTER SET utf8; #使用数据库 USE db5; #创建员工表 CREATE TABLE employee ( eid INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT , ename VARCHAR (20), -- 员工姓名 age INT , -- 员工年龄 sex VARCHAR (6), -- 员工性别 salary DOUBLE , -- 薪水 empdate DATE -- 入职日期 ); # 插入数据 INSERT INTO employee (eid, ename, age, sex, salary, empdate) VALUES(NULL,'李清照',22,'女',4000,'2018-11-12'); INSERT INTO employee (eid, ename, age, sex, salary, empdate) VALUES(NULL,'林黛玉',20,'女',5000,'2019-03-14'); INSERT INTO employee (eid, ename, age, sex, salary, empdate) VALUES(NULL,'杜甫',40,'男',6000,'2020-01-01'); INSERT INTO employee (eid, ename, age, sex, salary, empdate) VALUES(NULL,'李白',25,'男',3000,'2017-10-01');- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
Druid(德鲁伊)是阿里巴巴开发的号称为监控而生的数据库连接池,Druid是目前最好的数据库连接池。在功能、性能、扩展性方面,都超过其他数据库连接池,同时加入了日志监控,可以很好的监控DB池连接和SQL的执行情况。
使用
导入 jar包 配置文件
driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver url=jdbc:mysql:///db1?useSSL=false&useServerPrepStmts=true&characterEncoding=utf-8 username=root password=123456 # 初始化连接数量 initialSize=5 # 最大连接数 maxActive=10 # 最大等待时间 maxWait=3000- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
(二)、 编写Druid工具类🥝
获取数据库连接池对象
通过工厂来来获取 DruidDataSourceFactory类的createDataSource方法createDataSource(Properties p) 方法参数可以是一个属性集对象public class DruidUtils { //1.定义成员变量 public static DataSource dataSource; //2.静态代码块 static{ try { //3.创建属性集对象 Properties p = new Properties(); //4.加载配置文件 Druid 连接池不能够主动加载配置文件 ,需要指定文件 InputStream inputStream = DruidUtils.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("druid.properties"); //5. 使用Properties对象的 load方法 从字节流中读取配置信息 p.load(inputStream); //6. 通过工厂类获取连接池对象 dataSource = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(p); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } //获取连接的方法 public static Connection getConnection(){ try { return dataSource.getConnection(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); return null; } } //释放资源 public static void close(Connection con, Statement statement){ if(con != null && statement != null){ try { statement.close(); //归还连接 con.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } public static void close(Connection con, Statement statement, ResultSet resultSet){ if(con != null && statement != null && resultSet != null){ try { resultSet.close(); statement.close(); //归还连接 con.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
(三)、 测试工具类🥝
需求: 查询薪资在3000 - 5000元之间的员工姓名
// 需求 查询 薪资在3000 到 5000之间的员工的姓名 public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException { //1.获取连接 Connection con = DruidUtils.getConnection(); //2.获取Statement对象 Statement statement = con.createStatement(); //3.执行查询 ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery("select ename from employee where salary between 3000 and 5000"); //4.处理结果集 while(resultSet.next()){ String ename = resultSet.getString("ename"); System.out.println(ename); } //5.释放资源 DruidUtils.close(con,statement,resultSet); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
-
相关阅读:
基于Vivado软件实现电梯控制器仿真设计
steam deck科普、上手教程及模拟器配置指南
《优化接口设计的思路》系列:第五篇—接口发生异常如何统一处理
web系统安全设计原则
ElementPlus-日期选择器实现周选择
PyCharm 2024.1最新变化
如何保护客户数据并降低合规风险
1033 旧键盘打字
超适合练手的一套JavaWeb项目 (保安管理系统)
敏捷项目管理解锁:2023年使用YouTrack的全面指南
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/2301_77444674/article/details/133383955
